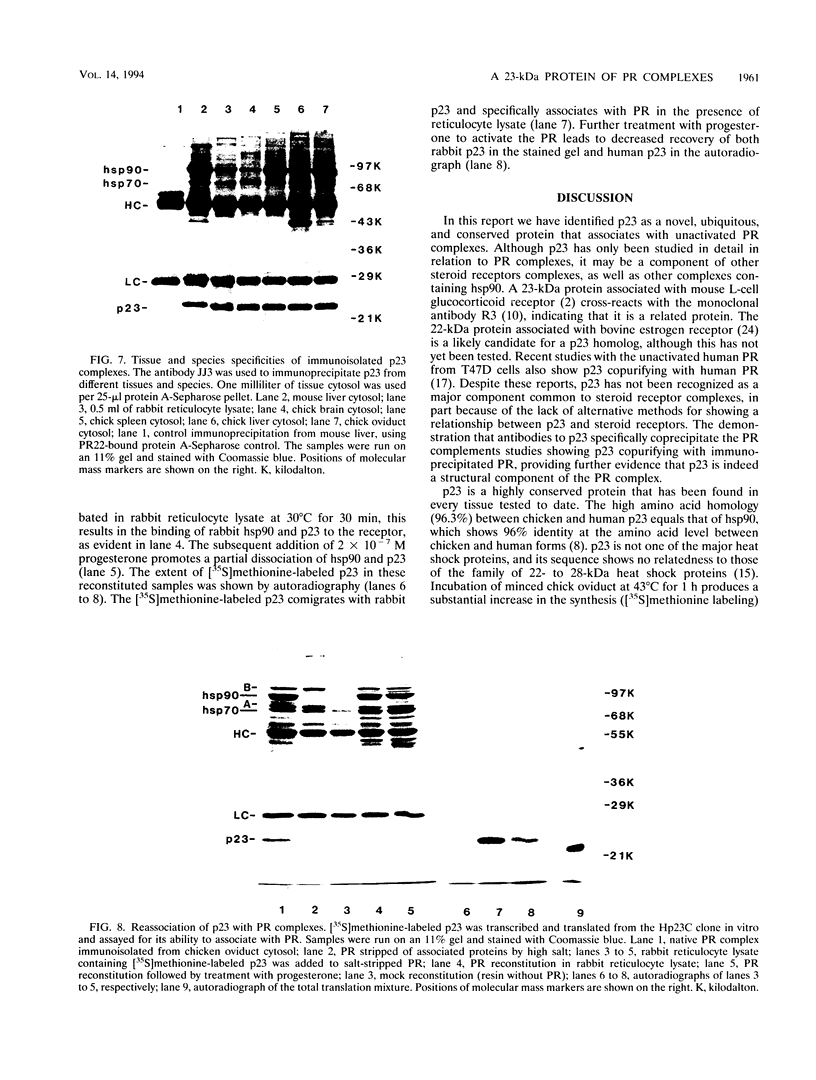
Abstract
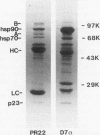
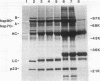
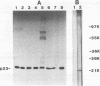
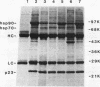
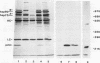
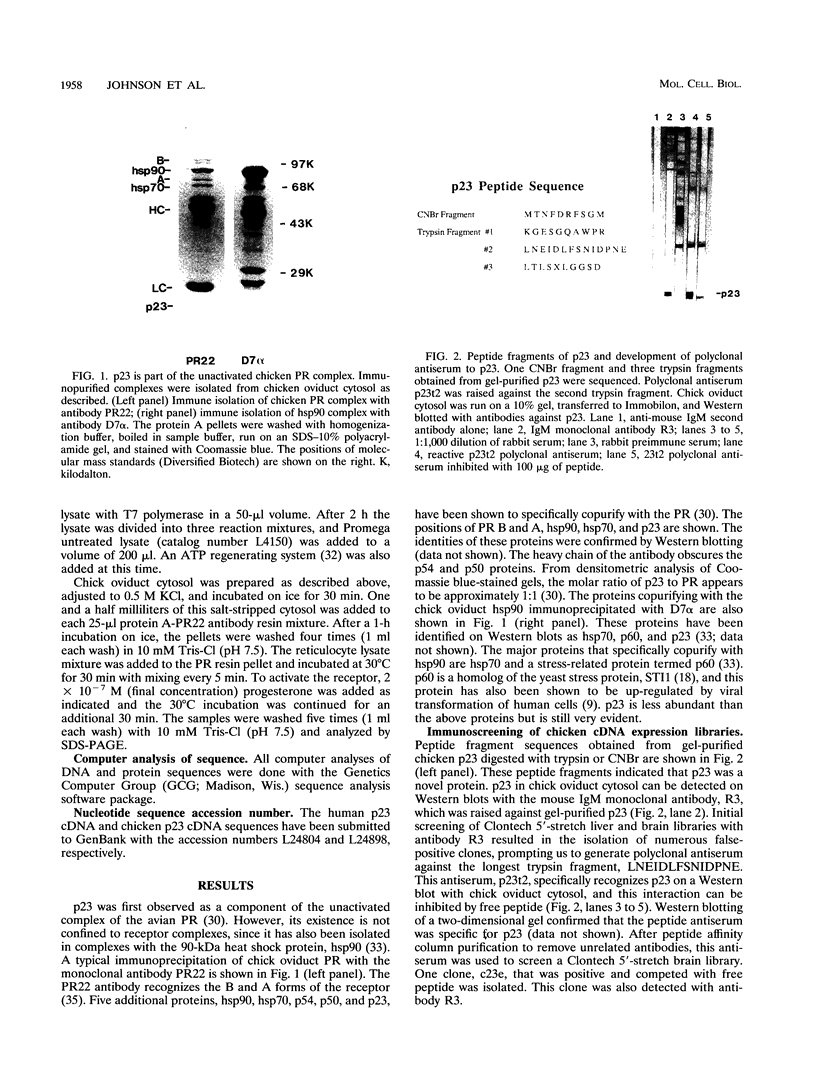
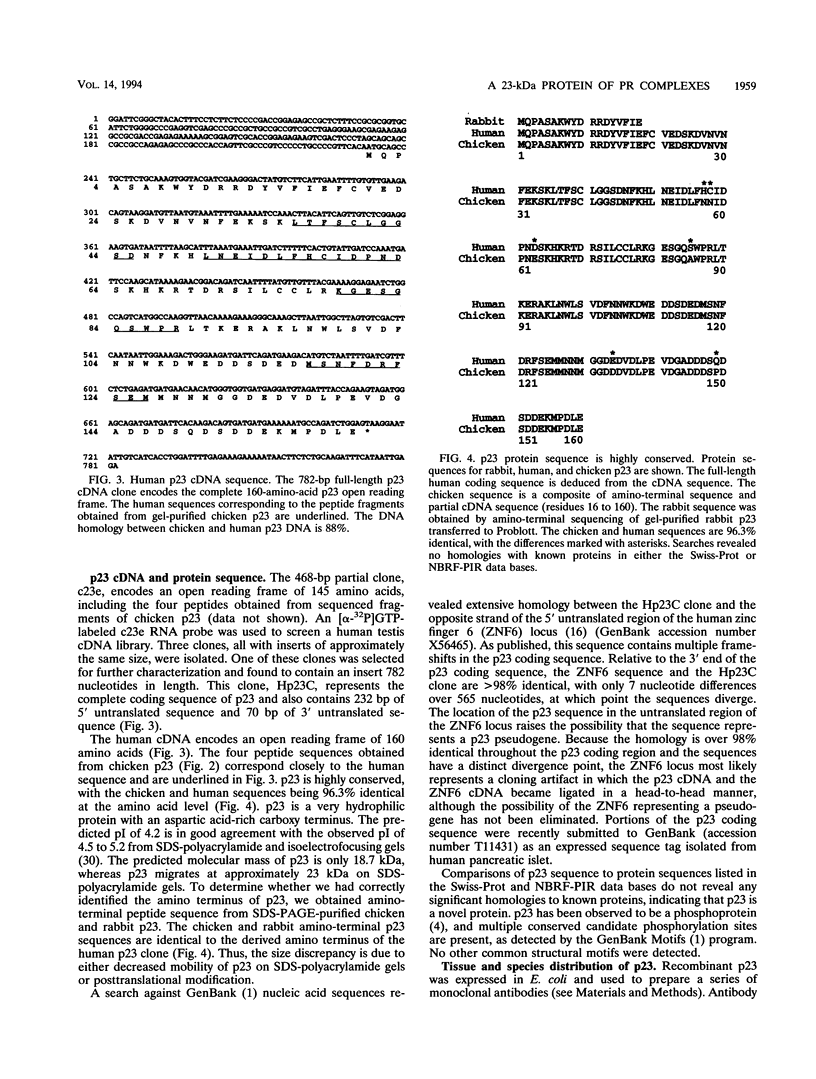
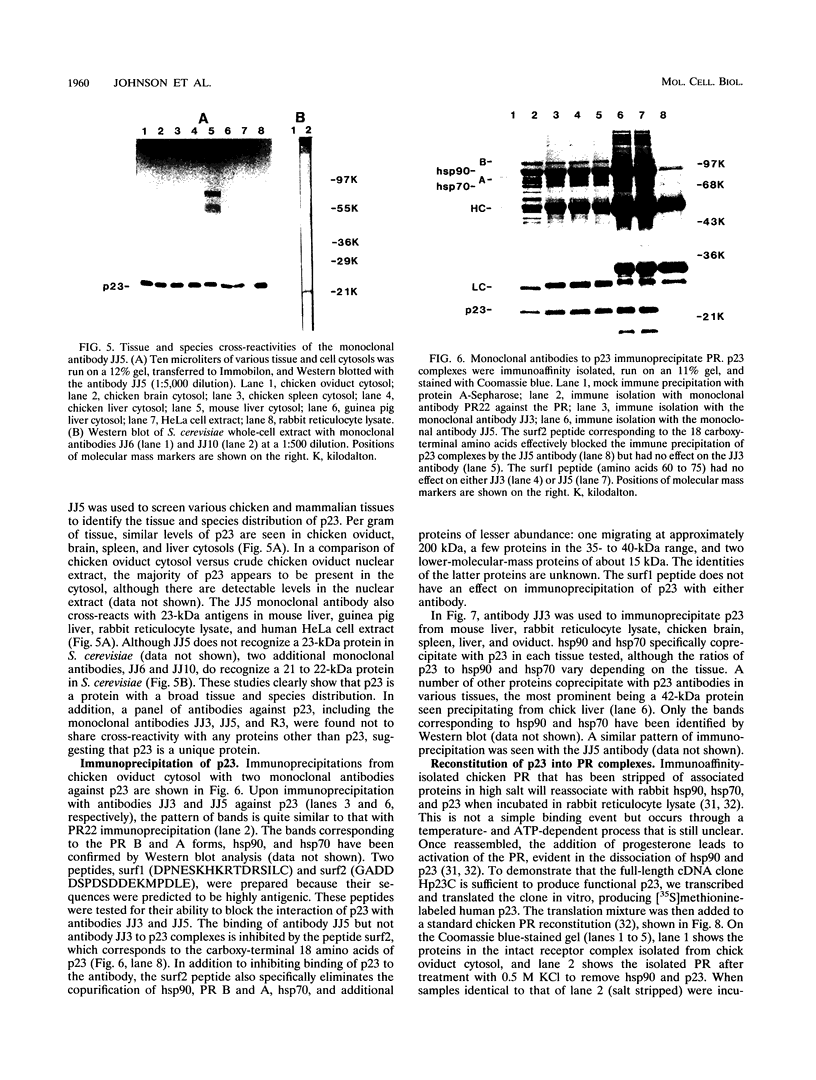
Immunoprecipitation of unactivated avian progesterone receptor results in the copurification of hsp90, hsp70, and three additional proteins, p54, p50, and p23. p23 is also present in immunoaffinity-purified hsp90 complexes along with hsp70 and another protein, p60. Antibody and cDNA probes for p23 were prepared in an effort to elucidate the significance and function of this protein. Antibodies to p23 detect similar levels of p23 in all tissues tested and cross-react with a protein of the same size in mice, rabbits, guinea pigs, humans, and Saccharomyces cerevisiae, indicating that p23 is a conserved protein of broad tissue distribution. These antibodies were used to screen a chicken brain cDNA library, resulting in the isolation of a 468-bp partial cDNA clone encoding a sequence containing four sequences corresponding to peptide fragments isolated from chicken p23. This partial clone was subsequently used to isolate a full-length human cDNA clone. The human cDNA encodes a protein of 160 amino acids that does not show homology to previously identified proteins. The chicken and human cDNAs are 88% identical at the DNA level and 96.3% identical at the protein level. p23 is a highly acidic phosphoprotein with an aspartic acid-rich carboxy-terminal domain. Bacterially overexpressed human p23 was used to raise several monoclonal antibodies to p23. These antibodies specifically immunoprecipitate p23 in complex with hsp90 in all tissues tested and can be used to immunoaffinity isolate progesterone receptor complexes from chicken oviduct cytosol.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bilofsky H. S., Burks C. The GenBank genetic sequence data bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Mar 11;16(5):1861–1863. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.5.1861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bresnick E. H., Dalman F. C., Pratt W. B. Direct stoichiometric evidence that the untransformed Mr 300,000, 9S, glucocorticoid receptor is a core unit derived from a larger heteromeric complex. Biochemistry. 1990 Jan 16;29(2):520–527. doi: 10.1021/bi00454a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brugge J., Yonemoto W., Darrow D. Interaction between the Rous sarcoma virus transforming protein and two cellular phosphoproteins: analysis of the turnover and distribution of this complex. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jan;3(1):9–19. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.1.9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgopoulos C. The emergence of the chaperone machines. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Aug;17(8):295–299. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90439-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrick J. P., Hartl F. U. Molecular chaperone functions of heat-shock proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1993;62:349–384. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.62.070193.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hickey E., Brandon S. E., Smale G., Lloyd D., Weber L. A. Sequence and regulation of a gene encoding a human 89-kilodalton heat shock protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;9(6):2615–2626. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.6.2615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honoré B., Leffers H., Madsen P., Rasmussen H. H., Vandekerckhove J., Celis J. E. Molecular cloning and expression of a transformation-sensitive human protein containing the TPR motif and sharing identity to the stress-inducible yeast protein STI1. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 25;267(12):8485–8491. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kost S. L., Smith D. F., Sullivan W. P., Welch W. J., Toft D. O. Binding of heat shock proteins to the avian progesterone receptor. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;9(9):3829–3838. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.9.3829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebeau M. C., Massol N., Herrick J., Faber L. E., Renoir J. M., Radanyi C., Baulieu E. E. P59, an hsp 90-binding protein. Cloning and sequencing of its cDNA and preparation of a peptide-directed polyclonal antibody. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 5;267(7):4281–4284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindquist S., Craig E. A. The heat-shock proteins. Annu Rev Genet. 1988;22:631–677. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.22.120188.003215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd S. L., Sargent C. A., Chalmers J., Lim E., Habeebu S. S., Affara N. A. An X-linked zinc finger gene mapping to Xq21.1-q21.3 closely related to ZFX and ZFY: possible origins from a common ancestral gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Sep 25;19(18):4835–4841. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.18.4835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolet C. M., Craig E. A. Isolation and characterization of STI1, a stress-inducible gene from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;9(9):3638–3646. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.9.3638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson B. O., Larsson A. Intrasplenic immunization with minute amounts of antigen. Immunol Today. 1990 Jan;11(1):10–12. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(90)90004-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oñate S. A., Estes P. A., Welch W. J., Nordeen S. K., Edwards D. P. Evidence that heat shock protein-70 associated with progesterone receptors is not involved in receptor-DNA binding. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Dec;5(12):1993–2004. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-12-1993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peattie D. A., Harding M. W., Fleming M. A., DeCenzo M. T., Lippke J. A., Livingston D. J., Benasutti M. Expression and characterization of human FKBP52, an immunophilin that associates with the 90-kDa heat shock protein and is a component of steroid receptor complexes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 15;89(22):10974–10978. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.22.10974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pratt W. B. Control of steroid receptor function and cytoplasmic-nuclear transport by heat shock proteins. Bioessays. 1992 Dec;14(12):841–848. doi: 10.1002/bies.950141209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratajczak T., Carrello A., Mark P. J., Warner B. J., Simpson R. J., Moritz R. L., House A. K. The cyclophilin component of the unactivated estrogen receptor contains a tetratricopeptide repeat domain and shares identity with p59 (FKBP59). J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 25;268(18):13187–13192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratajczak T., Hlaing J., Brockway M. J., Hähnel R. Isolation of untransformed bovine estrogen receptor without molybdate stabilization. J Steroid Biochem. 1990 Apr;35(5):543–553. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(90)90197-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez E. R., Hirst M., Scherrer L. C., Tang H. Y., Welsh M. J., Harmon J. M., Simons S. S., Jr, Ringold G. M., Pratt W. B. Hormone-free mouse glucocorticoid receptors overexpressed in Chinese hamster ovary cells are localized to the nucleus and are associated with both hsp70 and hsp90. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 25;265(33):20123–20130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez E. R. Hsp56: a novel heat shock protein associated with untransformed steroid receptor complexes. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 25;265(36):22067–22070. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schowalter D. B., Sullivan W. P., Maihle N. J., Dobson A. D., Conneely O. M., O'Malley B. W., Toft D. O. Characterization of progesterone receptor binding to the 90- and 70-kDa heat shock proteins. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 5;266(31):21165–21173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. F., Baggenstoss B. A., Marion T. N., Rimerman R. A. Two FKBP-related proteins are associated with progesterone receptor complexes. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 25;268(24):18365–18371. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. F., Faber L. E., Toft D. O. Purification of unactivated progesterone receptor and identification of novel receptor-associated proteins. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 5;265(7):3996–4003. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. F., Schowalter D. B., Kost S. L., Toft D. O. Reconstitution of progesterone receptor with heat shock proteins. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Nov;4(11):1704–1711. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-11-1704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. F., Stensgard B. A., Welch W. J., Toft D. O. Assembly of progesterone receptor with heat shock proteins and receptor activation are ATP mediated events. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 15;267(2):1350–1356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. F., Sullivan W. P., Marion T. N., Zaitsu K., Madden B., McCormick D. J., Toft D. O. Identification of a 60-kilodalton stress-related protein, p60, which interacts with hsp90 and hsp70. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Feb;13(2):869–876. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.2.869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. F., Toft D. O. Steroid receptors and their associated proteins. Mol Endocrinol. 1993 Jan;7(1):4–11. doi: 10.1210/mend.7.1.8446107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan W. P., Beito T. G., Proper J., Krco C. J., Toft D. O. Preparation of monoclonal antibodies to the avian progesterone receptor. Endocrinology. 1986 Oct;119(4):1549–1557. doi: 10.1210/endo-119-4-1549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tai P. K., Albers M. W., Chang H., Faber L. E., Schreiber S. L. Association of a 59-kilodalton immunophilin with the glucocorticoid receptor complex. Science. 1992 May 29;256(5061):1315–1318. doi: 10.1126/science.1376003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tai P. K., Maeda Y., Nakao K., Wakim N. G., Duhring J. L., Faber L. E. A 59-kilodalton protein associated with progestin, estrogen, androgen, and glucocorticoid receptors. Biochemistry. 1986 Sep 9;25(18):5269–5275. doi: 10.1021/bi00366a043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessel D., Flügge U. I. A method for the quantitative recovery of protein in dilute solution in the presence of detergents and lipids. Anal Biochem. 1984 Apr;138(1):141–143. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90782-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yem A. W., Tomasselli A. G., Heinrikson R. L., Zurcher-Neely H., Ruff V. A., Johnson R. A., Deibel M. R., Jr The Hsp56 component of steroid receptor complexes binds to immobilized FK506 and shows homology to FKBP-12 and FKBP-13. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 15;267(5):2868–2871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]