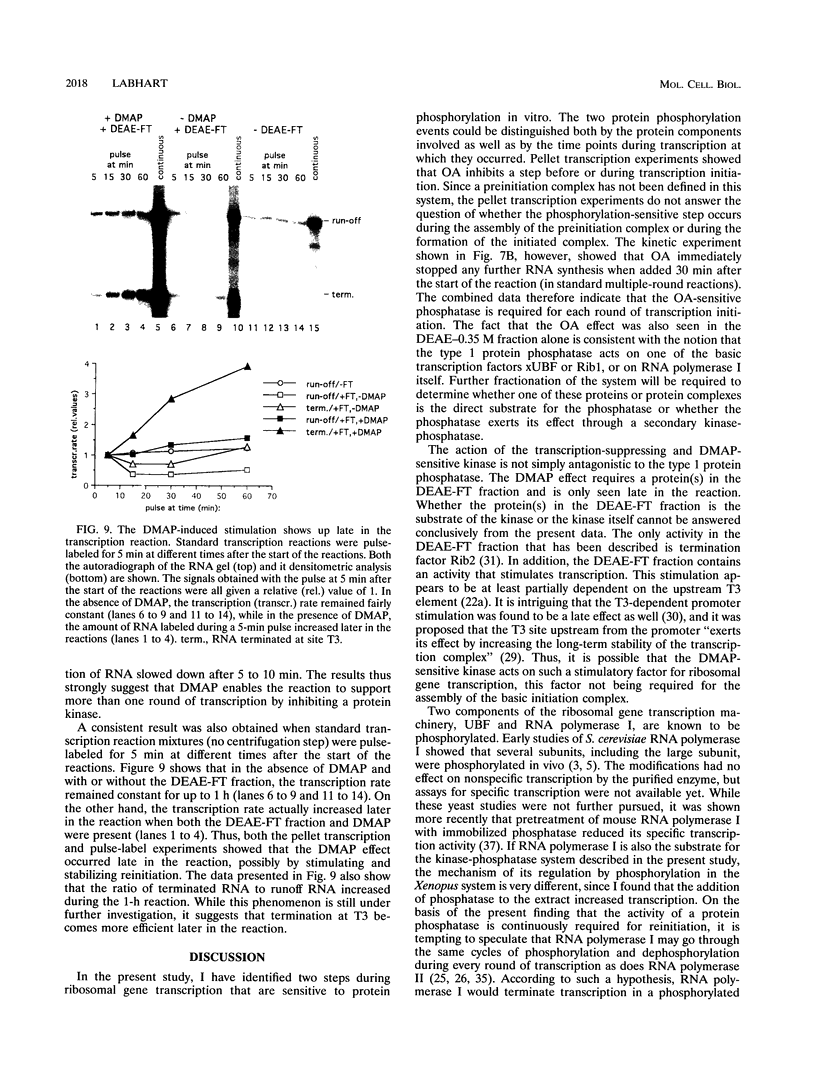
Abstract
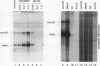
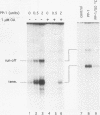
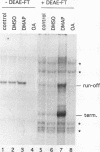
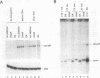
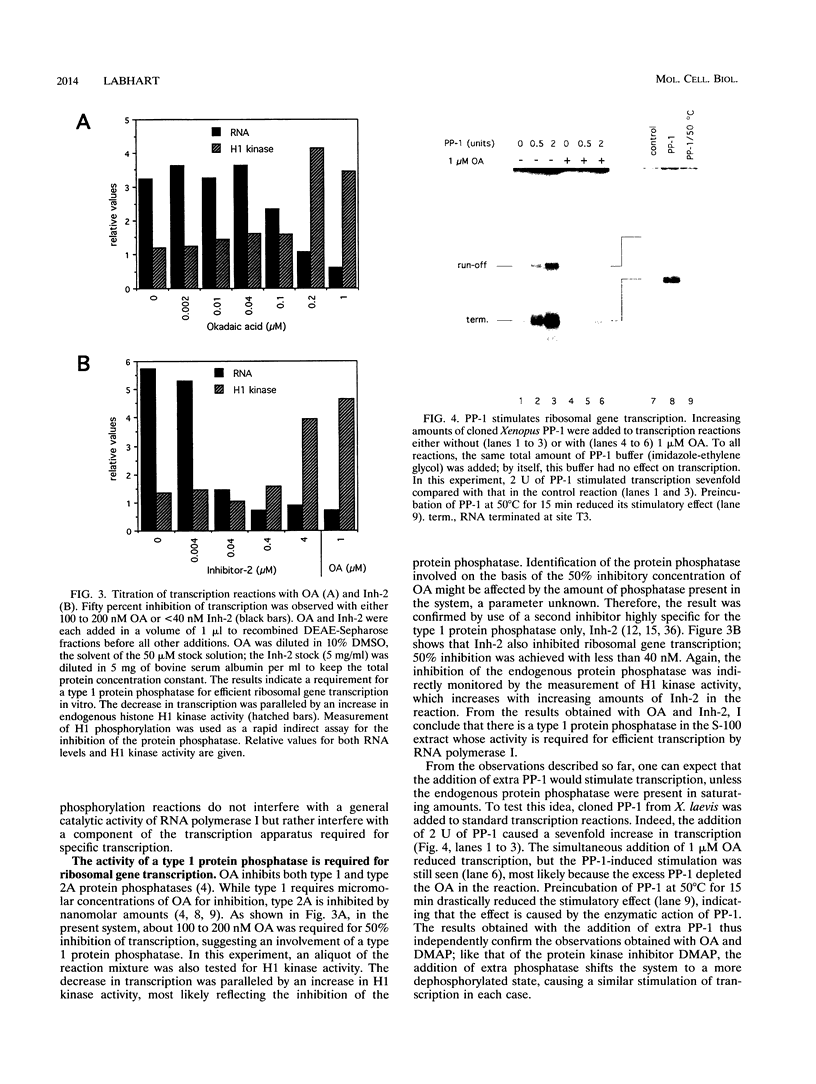
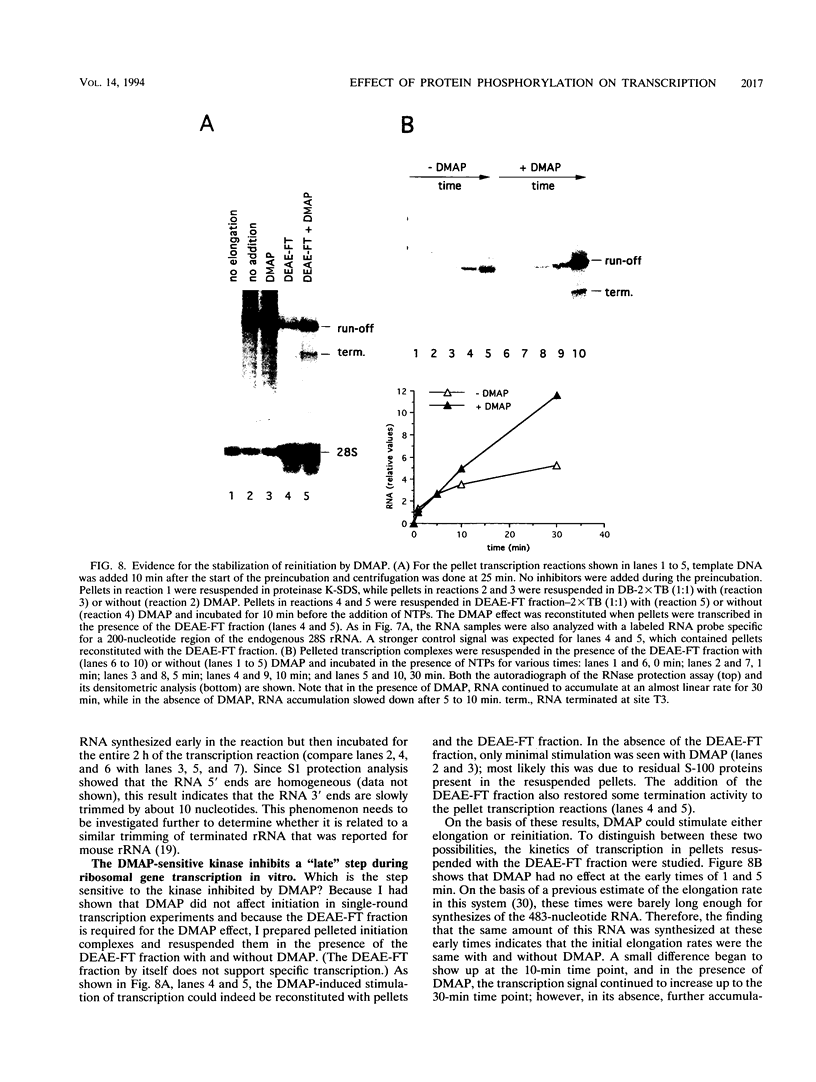
Protein kinase(s) and protein phosphatase(s) present in a Xenopus S-100 transcription extract strongly influence promoter-dependent transcription by RNA polymerase I. The protein kinase inhibitor 6-dimethyl-aminopurine causes transcription to increase, while the protein phosphatase inhibitor okadaic acid causes transcription to decrease. Repression is also observed with inhibitor 2, and the addition of extra protein phosphatase 1 stimulates transcription, indicating that the endogenous phosphatase is a type 1 enzyme. Partial fractionation of the system, single-round transcription reactions, and kinetic experiments show that two different steps during ribosomal gene transcription are sensitive to protein phosphorylation: okadaic acid affects a step before or during transcription initiation, while 6-dimethylaminopurine stimulates a process "late" in the reaction, possibly reinitiation. The present results are a clear demonstration that transcription by RNA polymerase I can be regulated by protein phosphorylation.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachvarov D., Moss T. The RNA polymerase I transcription factor xUBF contains 5 tandemly repeated HMG homology boxes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 May 11;19(9):2331–2335. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.9.2331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bateman E., Paule M. R. Regulation of eukaryotic ribosomal RNA transcription by RNA polymerase modification. Cell. 1986 Nov 7;47(3):445–450. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90601-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell G. I., Valenzuela P., Rutter W. J. Phosphorylation of yeast DNA-dependent RNA polymerases in vivo and in vitro. Isolation of enzymes and identification of phosphorylated subunits. J Biol Chem. 1977 May 10;252(9):3082–3091. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bialojan C., Takai A. Inhibitory effect of a marine-sponge toxin, okadaic acid, on protein phosphatases. Specificity and kinetics. Biochem J. 1988 Nov 15;256(1):283–290. doi: 10.1042/bj2560283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buhler J. M., Iborra F., Sentenac A., Fromageot P. The presence of phosphorylated subunits in yeast RNA polymerases A and B. FEBS Lett. 1976 Nov 15;72(1):37–41. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80893-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavanaugh A. H., Thompson E. A., Jr Hormonal regulation of transcription of rDNA. Initiation of transcription by RNA polymerase I in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 25;261(27):12738–12744. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chao Y., Pellegrini M. In vitro transcription of Drosophila rRNA genes shows stimulation by a phorbol ester and serum. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Feb;13(2):934–941. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.2.934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P., Cohen P. T. Protein phosphatases come of age. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 25;264(36):21435–21438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P., Schelling D. L., Stark M. J. Remarkable similarities between yeast and mammalian protein phosphatases. FEBS Lett. 1989 Jul 3;250(2):601–606. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80804-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Culotta V. C., Wides R. J., Sollner-Webb B. Eucaryotic transcription complexes are specifically associated in large sedimentable structures: rapid isolation of polymerase I, II, and III transcription factors. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jul;5(7):1582–1590. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.7.1582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunphy W. G., Newport J. W. Fission yeast p13 blocks mitotic activation and tyrosine dephosphorylation of the Xenopus cdc2 protein kinase. Cell. 1989 Jul 14;58(1):181–191. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90414-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foulkes J. G., Cohen P. The regulation of glycogen metabolism. Purification and properties of protein phosphatase inhibitor-2 from rabbit skeletal muscle. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Mar;105(1):195–203. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04489.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gokal P. K., Mahajan P. B., Thompson E. A. Hormonal regulation of transcription of rDNA. Formation of initiated complexes by RNA polymerase I in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 25;265(27):16234–16243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartl P., Gottesfeld J., Forbes D. J. Mitotic repression of transcription in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1993 Feb;120(3):613–624. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.3.613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes C. F., Campbell D. G., Caudwell F. B., Aitken A., Cohen P. The protein phosphatases involved in cellular regulation. Primary structure of inhibitor-2 from rabbit skeletal muscle. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Feb 17;155(1):173–182. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09473.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Karin M. The regulation of transcription by phosphorylation. Cell. 1992 Aug 7;70(3):375–387. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90162-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson S. P. Regulating transcription factor activity by phosphorylation. Trends Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;2(4):104–108. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(92)90014-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jantzen H. M., Admon A., Bell S. P., Tjian R. Nucleolar transcription factor hUBF contains a DNA-binding motif with homology to HMG proteins. Nature. 1990 Apr 26;344(6269):830–836. doi: 10.1038/344830a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn A., Grummt I. 3'-end formation of mouse pre-rRNA involves both transcription termination and a specific processing reaction. Genes Dev. 1989 Feb;3(2):224–231. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.2.224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn A., Grummt I. Dual role of the nucleolar transcription factor UBF: trans-activator and antirepressor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7340–7344. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn A., Stefanovsky V., Grummt I. The nucleolar transcription activator UBF relieves Ku antigen-mediated repression of mouse ribosomal gene transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 May 11;21(9):2057–2063. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.9.2057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labhart P. Characterization of two types of ribosomal gene transcription in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Gene Expr. 1992;2(4):409–423. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labhart P., Reeder R. H. A point mutation uncouples RNA 3'-end formation and termination during ribosomal gene transcription in Xenopus laevis. Genes Dev. 1990 Feb;4(2):269–276. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.2.269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lofquist A. K., Li H., Imboden M. A., Paule M. R. Promoter opening (melting) and transcription initiation by RNA polymerase I requires neither nucleotide beta,gamma hydrolysis nor protein phosphorylation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jul 11;21(14):3233–3238. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.14.3233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu H., Flores O., Weinmann R., Reinberg D. The nonphosphorylated form of RNA polymerase II preferentially associates with the preinitiation complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 15;88(22):10004–10008. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.22.10004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu H., Zawel L., Fisher L., Egly J. M., Reinberg D. Human general transcription factor IIH phosphorylates the C-terminal domain of RNA polymerase II. Nature. 1992 Aug 20;358(6388):641–645. doi: 10.1038/358641a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahajan P. B., Thompson E. A. Hormonal regulation of transcription of rDNA. Purification and characterization of the hormone-regulated transcription factor IC. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 25;265(27):16225–16233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McStay B., Hu C. H., Pikaard C. S., Reeder R. H. xUBF and Rib 1 are both required for formation of a stable polymerase I promoter complex in X. laevis. EMBO J. 1991 Aug;10(8):2297–2303. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07766.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McStay B., Reeder R. H. A DNA-binding protein is required for termination of transcription by RNA polymerase I in Xenopus laevis. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2793–2800. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McStay B., Reeder R. H. A termination site for Xenopus RNA polymerase I also acts as an element of an adjacent promoter. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):913–920. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90806-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McStay B., Reeder R. H. An RNA polymerase I termination site can stimulate the adjacent ribosomal gene promoter by two distinct mechanisms in Xenopus laevis. Genes Dev. 1990 Jul;4(7):1240–1251. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.7.1240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neant I., Guerrier P. 6-Dimethylaminopurine blocks starfish oocyte maturation by inhibiting a relevant protein kinase activity. Exp Cell Res. 1988 May;176(1):68–79. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(88)90121-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Mahony D. J., Xie W. Q., Smith S. D., Singer H. A., Rothblum L. I. Differential phosphorylation and localization of the transcription factor UBF in vivo in response to serum deprivation. In vitro dephosphorylation of UBF reduces its transactivation properties. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 5;267(1):35–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paule M. R. Polymerase I transcription, termination, and processing. Gene Expr. 1993;3(1):1–9. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne J. M., Laybourn P. J., Dahmus M. E. The transition of RNA polymerase II from initiation to elongation is associated with phosphorylation of the carboxyl-terminal domain of subunit IIa. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 25;264(33):19621–19629. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picking W. D., Kudlicki W., Kramer G., Hardesty B., Vandenheede J. R., Merlevede W., Park I. K., DePaoli-Roach A. Fluorescence studies on the interaction of inhibitor 2 and okadaic acid with the catalytic subunit of type 1 phosphoprotein phosphatases. Biochemistry. 1991 Oct 22;30(42):10280–10287. doi: 10.1021/bi00106a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnapp A., Pfleiderer C., Rosenbauer H., Grummt I. A growth-dependent transcription initiation factor (TIF-IA) interacting with RNA polymerase I regulates mouse ribosomal RNA synthesis. EMBO J. 1990 Sep;9(9):2857–2863. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07475.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnapp A., Rosenbauer H., Grummt I. Trans-acting factors involved in species-specificity and control of mouse ribosomal gene transcription. 1991 May 29-Jun 12Mol Cell Biochem. 104(1-2):137–147. doi: 10.1007/BF00229813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tower J., Sollner-Webb B. Transcription of mouse rDNA is regulated by an activated subform of RNA polymerase I. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):873–883. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90514-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallett S. M., Brudnak M., Pellegrini M., Weber H. W. In vivo regulation of rRNA transcription occurs rapidly in nondividing and dividing Drosophila cells in response to a phorbol ester and serum. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Feb;13(2):928–933. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.2.928. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voit R., Schnapp A., Kuhn A., Rosenbauer H., Hirschmann P., Stunnenberg H. G., Grummt I. The nucleolar transcription factor mUBF is phosphorylated by casein kinase II in the C-terminal hyperacidic tail which is essential for transactivation. EMBO J. 1992 Jun;11(6):2211–2218. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05280.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson J. A., Miller K. G., Sollner-Webb B. Dinucleotide primers facilitate convenient identification of the mouse ribosomal DNA transcription initiation site. A general method for analysis of transcription by RNA polymerases I and III. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 25;258(22):13919–13928. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zandomeni R., Zandomeni M. C., Shugar D., Weinmann R. Casein kinase type II is involved in the inhibition by 5,6-dichloro-1-beta-D-ribofuranosylbenzimidazole of specific RNA polymerase II transcription. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 5;261(7):3414–3419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]