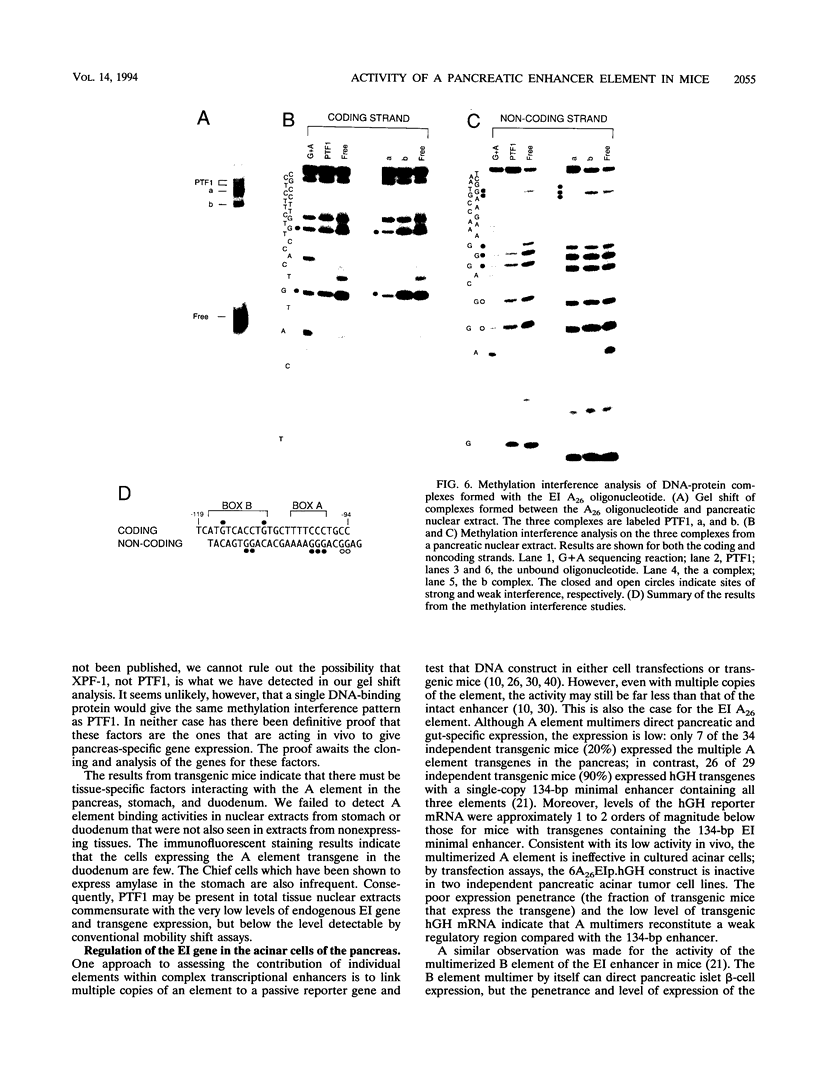
Abstract
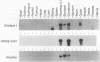
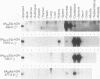
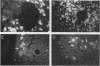
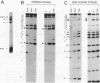
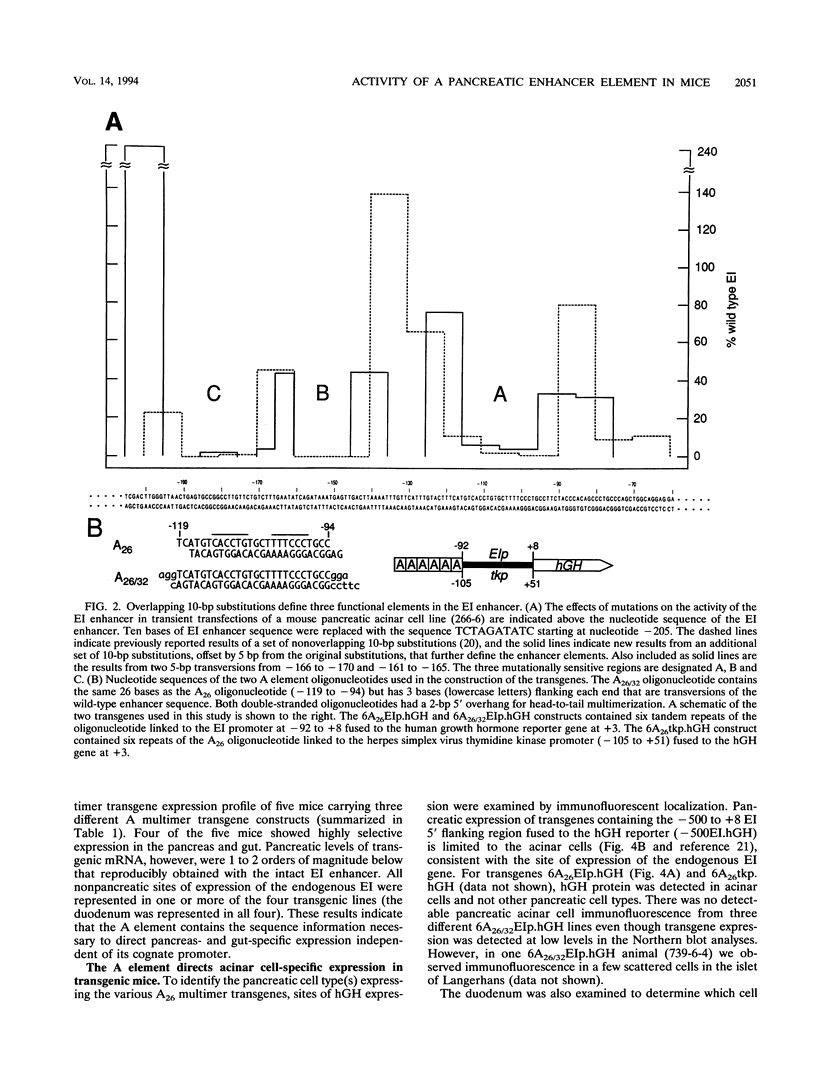
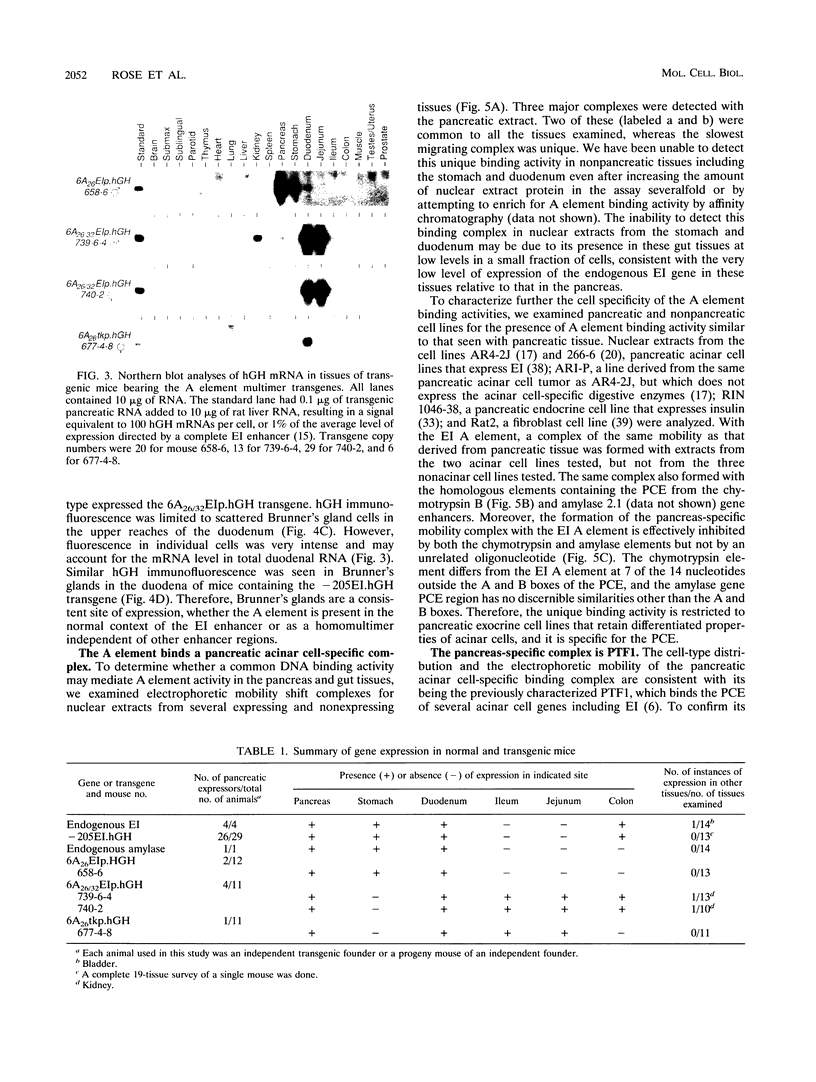
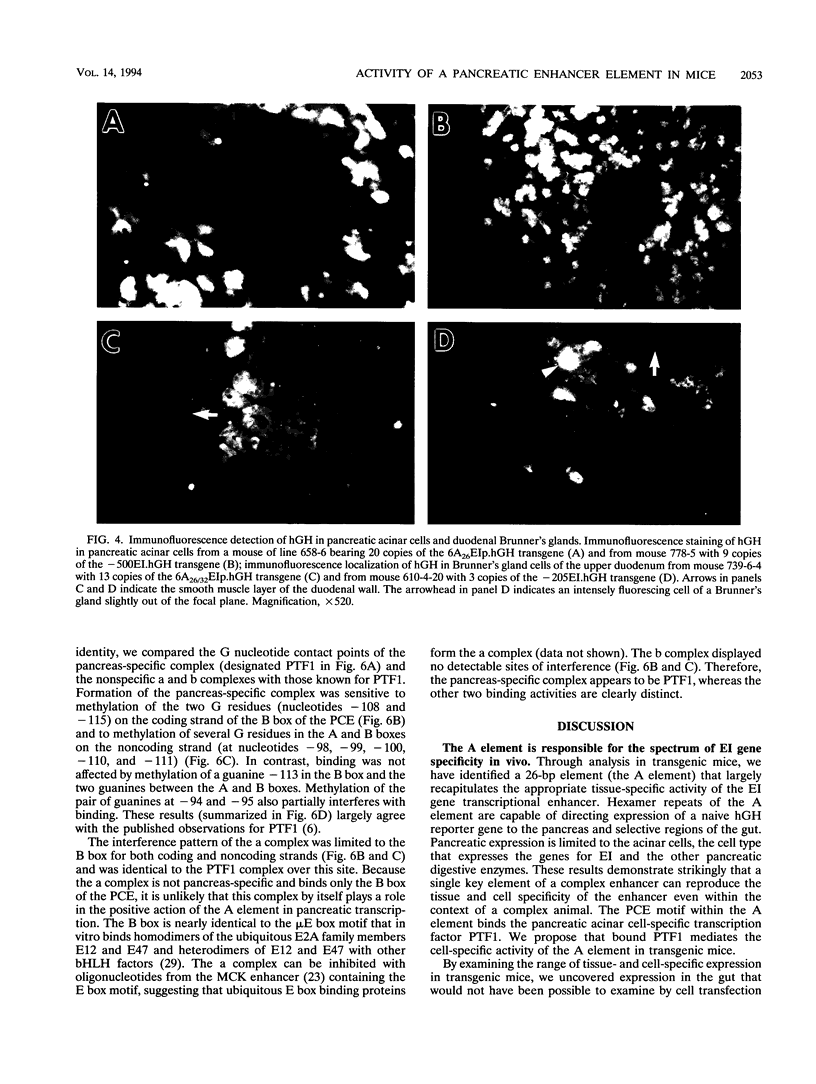
The elastase I (EI) gene is expressed at high levels in the exocrine pancreas and at lower levels in other regions of the gut. The transcriptional enhancer of the EI gene, from nucleotides -205 to -72, recapitulates the expression of the endogenous gene in transgenic mice; it directs not only pancreatic acinar cell expression of a human growth hormone (hGH) transgene but also expression to the stomach, duodenum, and colon. This pattern of selective expression limited to the gastroenteropancreatic organ system is specified by the A element, one of three functional elements in the EI enhancer. When multimerized, the A element directed expression of a hGH reporter gene selectively to the pancreas, stomach, and intestine in transgenic mice. Immunofluorescent localization of hGH indicated that the A element multimer transgenes were expressed in the acinar cells of the pancreas as well as in Brunner's gland cells of the duodenum. The A element binds a pancreatic acinar cell-specific factor, PTF1. Our results show that while the A element is responsible for directing tissue and cell type specificity, other elements of the enhancer must be involved in the regulation of the level of gene expression.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bailey J. M., Davidson N. Methylmercury as a reversible denaturing agent for agarose gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1976 Jan;70(1):75–85. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(76)80049-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulet A. M., Erwin C. R., Rutter W. J. Cell-specific enhancers in the rat exocrine pancreas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3599–3603. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinster R. L., Chen H. Y., Trumbauer M. E., Yagle M. K., Palmiter R. D. Factors affecting the efficiency of introducing foreign DNA into mice by microinjecting eggs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4438–4442. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ceci J. D., Kovatch R. M., Swing D. A., Jones J. M., Snow C. M., Rosenberg M. P., Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G., Meisler M. H. Transgenic mice carrying a murine amylase 2.2/SV40 T antigen fusion gene develop pancreatic acinar cell and stomach carcinomas. Oncogene. 1991 Feb;6(2):323–332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockell M., Stevenson B. J., Strubin M., Hagenbüchle O., Wellauer P. K. Identification of a cell-specific DNA-binding activity that interacts with a transcriptional activator of genes expressed in the acinar pancreas. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;9(6):2464–2476. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.6.2464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis B. P., Hammer R. E., Messing A., MacDonald R. J. Selective expression of trypsin fusion genes in acinar cells of the pancreas and stomach of transgenic mice. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 25;267(36):26070–26077. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durand D. B., Shaw J. P., Bush M. R., Replogle R. E., Belagaje R., Crabtree G. R. Characterization of antigen receptor response elements within the interleukin-2 enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1715–1724. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friend D. S. The fine structure of Brunner's glands in the mouse. J Cell Biol. 1965 Jun;25(3):563–576. doi: 10.1083/jcb.25.3.563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROSSMAN M. L. The glands of Brunner. Physiol Rev. 1958 Oct;38(4):675–690. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1958.38.4.675. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorski K., Carneiro M., Schibler U. Tissue-specific in vitro transcription from the mouse albumin promoter. Cell. 1986 Dec 5;47(5):767–776. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90519-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagenbüchle O., Bovey R., Young R. A. Tissue-specific expression of mouse-alpha-amylase genes: nucleotide sequence of isoenzyme mRNAs from pancreas and salivary gland. Cell. 1980 Aug;21(1):179–187. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90125-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammer R. E., Swift G. H., Ornitz D. M., Quaife C. J., Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L., MacDonald R. J. The rat elastase I regulatory element is an enhancer that directs correct cell specificity and developmental onset of expression in transgenic mice. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2956–2967. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard G., Keller P. R., Johnson T. M., Meisler M. H. Binding of a pancreatic nuclear protein is correlated with amylase enhancer activity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Oct 25;17(20):8185–8195. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.20.8185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kedzierski W., Porter J. C. A novel non-enzymatic procedure for removing DNA template from RNA transcription mixtures. Biotechniques. 1991 Feb;10(2):210–214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiledjian M., Su L. K., Kadesch T. Identification and characterization of two functional domains within the murine heavy-chain enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):145–152. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruse F., Komro C. T., Michnoff C. H., MacDonald R. J. The cell-specific elastase I enhancer comprises two domains. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):893–902. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruse F., Rose S. D., Swift G. H., Hammer R. E., MacDonald R. J. An endocrine-specific element is an integral component of an exocrine-specific pancreatic enhancer. Genes Dev. 1993 May;7(5):774–786. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.5.774. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang I. M., Tansy M. F. Brunner's glands. Int Rev Physiol. 1983;28:85–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassar A. B., Buskin J. N., Lockshon D., Davis R. L., Apone S., Hauschka S. D., Weintraub H. MyoD is a sequence-specific DNA binding protein requiring a region of myc homology to bind to the muscle creatine kinase enhancer. Cell. 1989 Sep 8;58(5):823–831. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90935-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN B. F. Serous cells in Brunner's glands of the rabbit. Nature. 1954 Dec 25;174(4443):1195–1196. doi: 10.1038/1741195b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald R. J., Swift G. H., Przybyla A. E., Chirgwin J. M. Isolation of RNA using guanidinium salts. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:219–227. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52023-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meister A., Weinrich S. L., Nelson C., Rutter W. J. The chymotrypsin enhancer core. Specific factor binding and biological activity. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 5;264(34):20744–20751. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murre C., McCaw P. S., Baltimore D. A new DNA binding and dimerization motif in immunoglobulin enhancer binding, daughterless, MyoD, and myc proteins. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):777–783. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90682-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murre C., McCaw P. S., Vaessin H., Caudy M., Jan L. Y., Jan Y. N., Cabrera C. V., Buskin J. N., Hauschka S. D., Lassar A. B. Interactions between heterologous helix-loop-helix proteins generate complexes that bind specifically to a common DNA sequence. Cell. 1989 Aug 11;58(3):537–544. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90434-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murre C., Voronova A., Baltimore D. B-cell- and myocyte-specific E2-box-binding factors contain E12/E47-like subunits. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;11(2):1156–1160. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.2.1156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ondek B., Shepard A., Herr W. Discrete elements within the SV40 enhancer region display different cell-specific enhancer activities. EMBO J. 1987 Apr;6(4):1017–1025. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04854.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ornitz D. M., Palmiter R. D., Hammer R. E., Brinster R. L., Swift G. H., MacDonald R. J. Specific expression of an elastase-human growth hormone fusion gene in pancreatic acinar cells of transgenic mice. Nature. 1985 Feb 14;313(6003):600–602. doi: 10.1038/313600a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrucco S., Wellauer P. K., Hagenbüchle O. The DNA-binding activity of transcription factor PTF1 parallels the synthesis of pancreas-specific mRNAs during mouse development. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jan;10(1):254–264. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.1.254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philippe J., Chick W. L., Habener J. F. Multipotential phenotypic expression of genes encoding peptide hormones in rat insulinoma cell lines. J Clin Invest. 1987 Feb;79(2):351–358. doi: 10.1172/JCI112819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roux E., Strubin M., Hagenbüchle O., Wellauer P. K. The cell-specific transcription factor PTF1 contains two different subunits that interact with the DNA. Genes Dev. 1989 Oct;3(10):1613–1624. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.10.1613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeburg P. H. The human growth hormone gene family: nucleotide sequences show recent divergence and predict a new polypeptide hormone. DNA. 1982;1(3):239–249. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1982.1.239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swift G. H., Hammer R. E., MacDonald R. J., Brinster R. L. Tissue-specific expression of the rat pancreatic elastase I gene in transgenic mice. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):639–646. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90258-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Topp W. C. Normal rat cell lines deficient in nuclear thymidine kinase. Virology. 1981 Aug;113(1):408–411. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90168-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verweij C. L., Guidos C., Crabtree G. R. Cell type specificity and activation requirements for NFAT-1 (nuclear factor of activated T-cells) transcriptional activity determined by a new method using transgenic mice to assay transcriptional activity of an individual nuclear factor. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 15;265(26):15788–15795. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinrich S. L., Meister A., Rutter W. J. Exocrine pancreas transcription factor 1 binds to a bipartite enhancer element and activates transcription of acinar genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):4985–4997. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.4985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]