Abstract
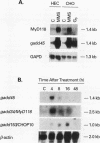
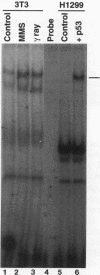
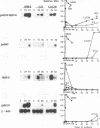
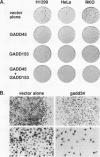
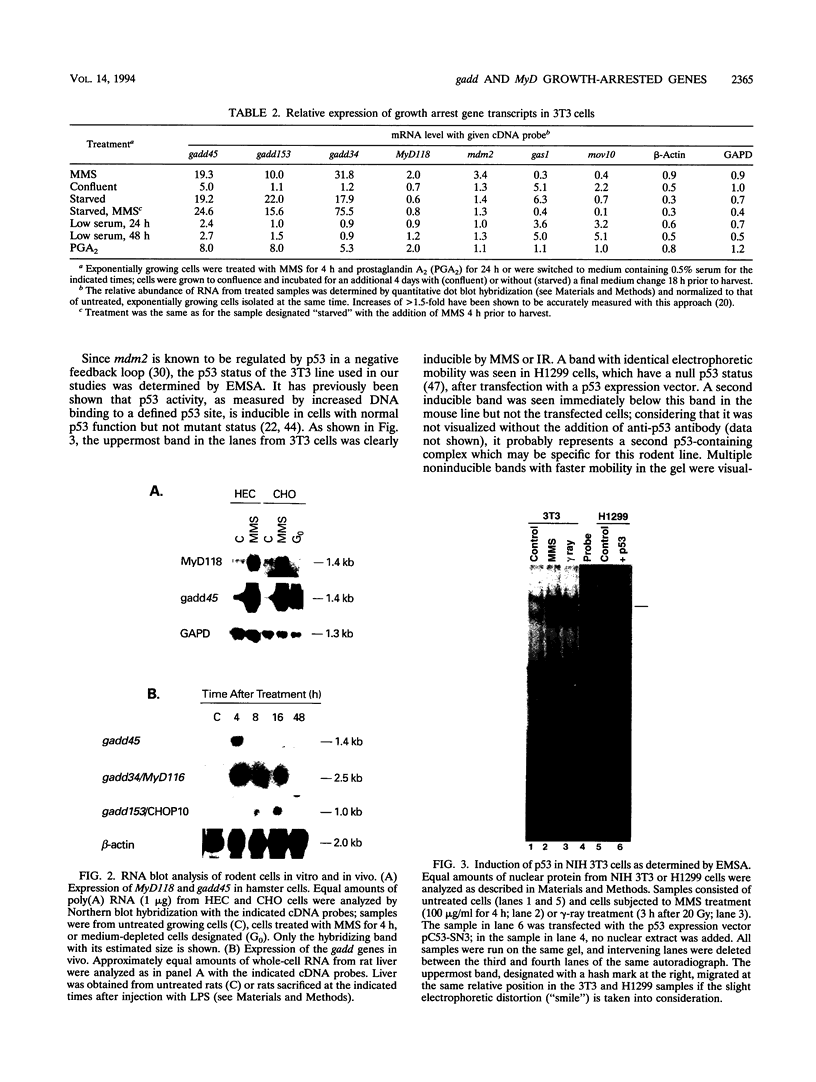
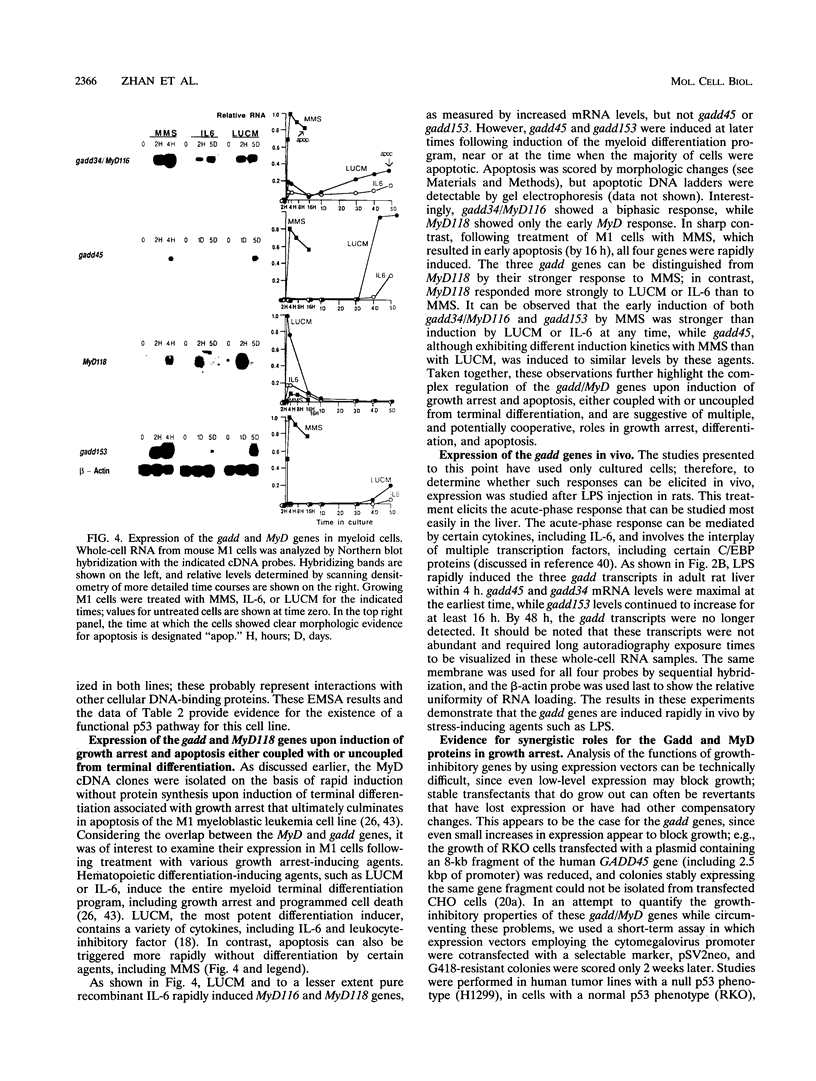
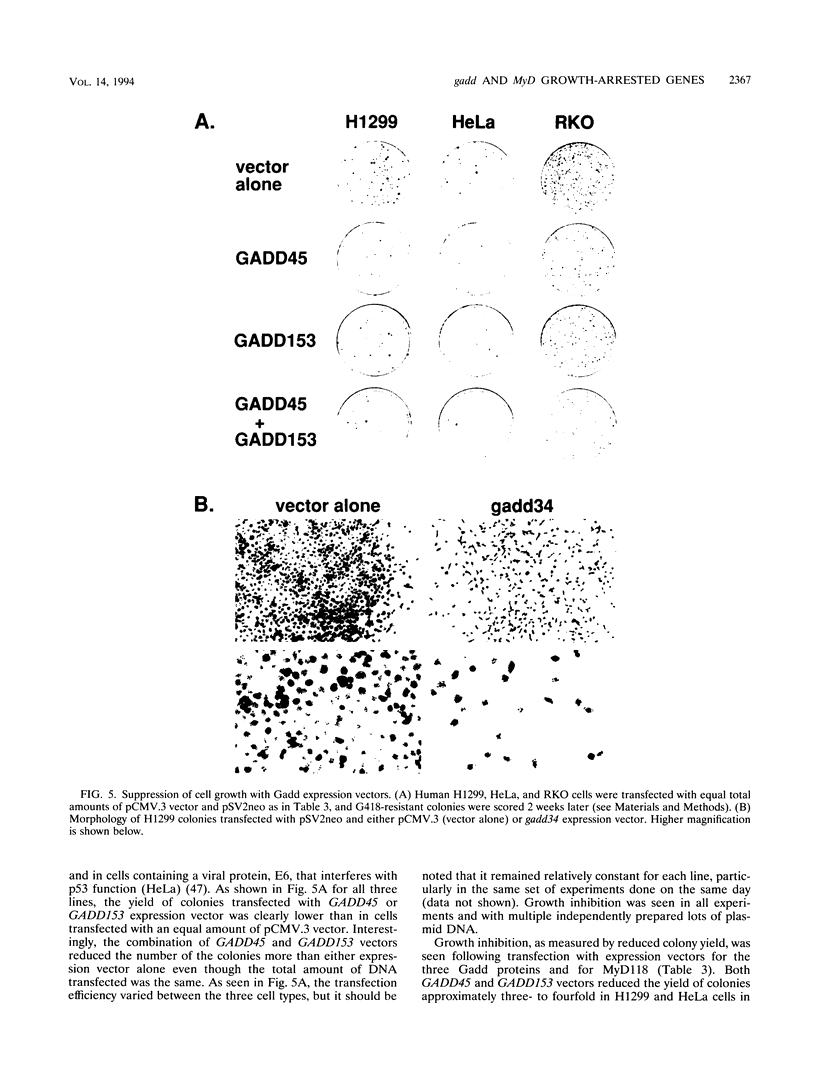
A remarkable overlap was observed between the gadd genes, a group of often coordinately expressed genes that are induced by genotoxic stress and certain other growth arrest signals, and the MyD genes, a set of myeloid differentiation primary response genes. The MyD116 gene was found to be the murine homolog of the hamster gadd34 gene, whereas MyD118 and gadd45 were found to represent two separate but closely related genes. Furthermore, gadd34/MyD116, gadd45, MyD118, and gadd153 encode acidic proteins with very similar and unusual charge characteristics; both this property and a similar pattern of induction are shared with mdm2, whic, like gadd45, has been shown previously to be regulated by the tumor suppressor p53. Expression analysis revealed that they are distinguished from other growth arrest genes in that they are DNA damage inducible and suggest a role for these genes in growth arrest and apoptosis either coupled with or uncoupled from terminal differentiation. Evidence is also presented for coordinate induction in vivo by stress. The use of a short-term transfection assay, in which expression vectors for one or a combination of these gadd/MyD genes were transfected with a selectable marker into several different human tumor cell lines, provided direct evidence for the growth-inhibitory functions of the products of these genes and their ability to synergistically suppress growth. Taken together, these observations indicate that these genes define a novel class of mammalian genes encoding acidic proteins involved in the control of cellular growth.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abdollahi A., Lord K. A., Hoffman-Liebermann B., Liebermann D. A. Sequence and expression of a cDNA encoding MyD118: a novel myeloid differentiation primary response gene induced by multiple cytokines. Oncogene. 1991 Jan;6(1):165–167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adler M. J., Coronel C., Shelton E., Seegmiller J. E., Dewji N. N. Increased gene expression of Alzheimer disease beta-amyloid precursor protein in senescent cultured fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 1;88(1):16–20. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.1.16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brannan C. I., Dees E. C., Ingram R. S., Tilghman S. M. The product of the H19 gene may function as an RNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jan;10(1):28–36. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.1.28. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brockdorff N., Ashworth A., Kay G. F., McCabe V. M., Norris D. P., Cooper P. J., Swift S., Rastan S. The product of the mouse Xist gene is a 15 kb inactive X-specific transcript containing no conserved ORF and located in the nucleus. Cell. 1992 Oct 30;71(3):515–526. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90519-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson S. G., Fawcett T. W., Bartlett J. D., Bernier M., Holbrook N. J. Regulation of the C/EBP-related gene gadd153 by glucose deprivation. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Aug;13(8):4736–4744. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.8.4736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi A. M., Fargnoli J., Carlson S. G., Holbrook N. J. Cell growth inhibition by prostaglandin A2 results in elevated expression of gadd153 mRNA. Exp Cell Res. 1992 Mar;199(1):85–89. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(92)90464-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou J., Roizman B. The gamma 1(34.5) gene of herpes simplex virus 1 precludes neuroblastoma cells from triggering total shutoff of protein synthesis characteristic of programed cell death in neuronal cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 15;89(8):3266–3270. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.8.3266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciccarelli C., Philipson L., Sorrentino V. Regulation of expression of growth arrest-specific genes in mouse fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1525–1529. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crozat A., Aman P., Mandahl N., Ron D. Fusion of CHOP to a novel RNA-binding protein in human myxoid liposarcoma. Nature. 1993 Jun 17;363(6430):640–644. doi: 10.1038/363640a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiPaolo J. A., Nelson R. L., Donovan P. J. Morphological, oncogenic, and karyological characteristics of Syrian hamster embryo cells transformed in vitro by carcinogenic polycyclic hydrocarbons. Cancer Res. 1971 Aug;31(8):1118–1127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fornace A. J., Jr, Alamo I., Jr, Hollander M. C. DNA damage-inducible transcripts in mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8800–8804. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fornace A. J., Jr, Nebert D. W., Hollander M. C., Luethy J. D., Papathanasiou M., Fargnoli J., Holbrook N. J. Mammalian genes coordinately regulated by growth arrest signals and DNA-damaging agents. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;9(10):4196–4203. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.10.4196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fornace A. J., Jr Recombination of parent and daughter strand DNA after UV-irradiation in mammalian cells. Nature. 1983 Aug 11;304(5926):552–554. doi: 10.1038/304552a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman-Liebermann B., Liebermann D. A. Interleukin-6- and leukemia inhibitory factor-induced terminal differentiation of myeloid leukemia cells is blocked at an intermediate stage by constitutive c-myc. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2375–2381. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollander M. C., Alamo I., Jackman J., Wang M. G., McBride O. W., Fornace A. J., Jr Analysis of the mammalian gadd45 gene and its response to DNA damage. J Biol Chem. 1993 Nov 15;268(32):24385–24393. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollander M. C., Fornace A. J., Jr Estimation of relative mRNA content by filter hybridization to a polythymidylate probe. Biotechniques. 1990 Aug;9(2):174–179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlin S., Brendel V. Chance and statistical significance in protein and DNA sequence analysis. Science. 1992 Jul 3;257(5066):39–49. doi: 10.1126/science.1621093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kastan M. B., Zhan Q., el-Deiry W. S., Carrier F., Jacks T., Walsh W. V., Plunkett B. S., Vogelstein B., Fornace A. J., Jr A mammalian cell cycle checkpoint pathway utilizing p53 and GADD45 is defective in ataxia-telangiectasia. Cell. 1992 Nov 13;71(4):587–597. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90593-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuerbitz S. J., Plunkett B. S., Walsh W. V., Kastan M. B. Wild-type p53 is a cell cycle checkpoint determinant following irradiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7491–7495. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee A. S. Mammalian stress response: induction of the glucose-regulated protein family. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;4(2):267–273. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(92)90042-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lord K. A., Abdollahi A., Hoffman-Liebermann B., Liebermann D. A. Dissection of the immediate early response of myeloid leukemia cells to terminal differentiation and growth inhibitory stimuli. Cell Growth Differ. 1990 Dec;1(12):637–645. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lord K. A., Hoffman-Liebermann B., Liebermann D. A. Complexity of the immediate early response of myeloid cells to terminal differentiation and growth arrest includes ICAM-1, Jun-B and histone variants. Oncogene. 1990 Mar;5(3):387–396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lord K. A., Hoffman-Liebermann B., Liebermann D. A. Sequence of MyD116 cDNA: a novel myeloid differentiation primary response gene induced by IL6. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 May 11;18(9):2823–2823. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.9.2823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe S. W., Schmitt E. M., Smith S. W., Osborne B. A., Jacks T. p53 is required for radiation-induced apoptosis in mouse thymocytes. Nature. 1993 Apr 29;362(6423):847–849. doi: 10.1038/362847a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeoch D. J., Barnett B. C. Neurovirulence factor. Nature. 1991 Oct 17;353(6345):609–609. doi: 10.1038/353609b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Momand J., Zambetti G. P., Olson D. C., George D., Levine A. J. The mdm-2 oncogene product forms a complex with the p53 protein and inhibits p53-mediated transactivation. Cell. 1992 Jun 26;69(7):1237–1245. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90644-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mooslehner K., Müller U., Karls U., Hamann L., Harbers K. Structure and expression of a gene encoding a putative GTP-binding protein identified by provirus integration in a transgenic mouse strain. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;11(2):886–893. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.2.886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuell M. J., Stewart D. A., Walker L., Friedman V., Wood C. M., Owens G. A., Smith J. R., Schneider E. L., Dell' Orco R., Lumpkin C. K. Prohibitin, an evolutionarily conserved intracellular protein that blocks DNA synthesis in normal fibroblasts and HeLa cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1372–1381. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliner J. D., Kinzler K. W., Meltzer P. S., George D. L., Vogelstein B. Amplification of a gene encoding a p53-associated protein in human sarcomas. Nature. 1992 Jul 2;358(6381):80–83. doi: 10.1038/358080a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliner J. D., Pietenpol J. A., Thiagalingam S., Gyuris J., Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B. Oncoprotein MDM2 conceals the activation domain of tumour suppressor p53. Nature. 1993 Apr 29;362(6423):857–860. doi: 10.1038/362857a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papathanasiou M. A., Kerr N. C., Robbins J. H., McBride O. W., Alamo I., Jr, Barrett S. F., Hickson I. D., Fornace A. J., Jr Induction by ionizing radiation of the gadd45 gene in cultured human cells: lack of mediation by protein kinase C. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;11(2):1009–1016. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.2.1009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park J. S., Luethy J. D., Wang M. G., Fargnoli J., Fornace A. J., Jr, McBride O. W., Holbrook N. J. Isolation, characterization and chromosomal localization of the human GADD153 gene. Gene. 1992 Jul 15;116(2):259–267. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(92)90523-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price B. D., Calderwood S. K. Gadd45 and Gadd153 messenger RNA levels are increased during hypoxia and after exposure of cells to agents which elevate the levels of the glucose-regulated proteins. Cancer Res. 1992 Jul 1;52(13):3814–3817. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rechsteiner M. Regulation of enzyme levels by proteolysis: the role of pest regions. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1988;27:135–151. doi: 10.1016/0065-2571(88)90014-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ron D., Brasier A. R., Wright K. A., Tate J. E., Habener J. F. An inducible 50-kilodalton NF kappa B-like protein and a constitutive protein both bind the acute-phase response element of the angiotensinogen gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;10(3):1023–1032. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.3.1023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ron D., Habener J. F. CHOP, a novel developmentally regulated nuclear protein that dimerizes with transcription factors C/EBP and LAP and functions as a dominant-negative inhibitor of gene transcription. Genes Dev. 1992 Mar;6(3):439–453. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.3.439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider C., King R. M., Philipson L. Genes specifically expressed at growth arrest of mammalian cells. Cell. 1988 Sep 9;54(6):787–793. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)91065-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selvakumaran M., Liebermann D., Hoffman-Liebermann B. Myeloblastic leukemia cells conditionally blocked by myc-estrogen receptor chimeric transgenes for terminal differentiation coupled to growth arrest and apoptosis. Blood. 1993 May 1;81(9):2257–2262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tishler R. B., Calderwood S. K., Coleman C. N., Price B. D. Increases in sequence specific DNA binding by p53 following treatment with chemotherapeutic and DNA damaging agents. Cancer Res. 1993 May 15;53(10 Suppl):2212–2216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchida S., Sekiguchi T., Nishitani H., Miyauchi K., Ohtsubo M., Nishimoto T. Premature chromosome condensation is induced by a point mutation in the hamster RCC1 gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;10(2):577–584. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.2.577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogelstein B., Kinzler K. W. p53 function and dysfunction. Cell. 1992 Aug 21;70(4):523–526. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90421-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhan Q., Carrier F., Fornace A. J., Jr Induction of cellular p53 activity by DNA-damaging agents and growth arrest. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jul;13(7):4242–4250. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.7.4242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Deiry W. S., Kern S. E., Pietenpol J. A., Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B. Definition of a consensus binding site for p53. Nat Genet. 1992 Apr;1(1):45–49. doi: 10.1038/ng0492-45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]