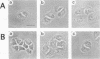
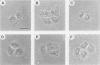
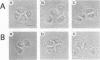
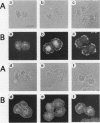
Abstract
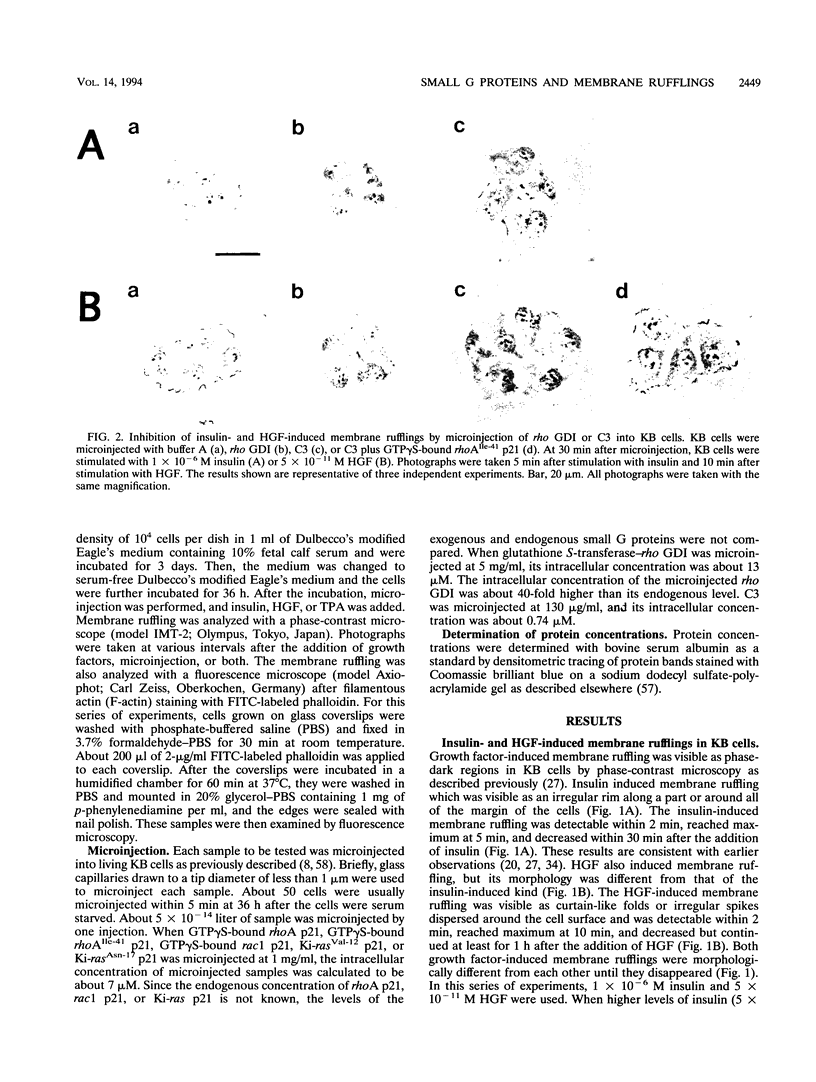
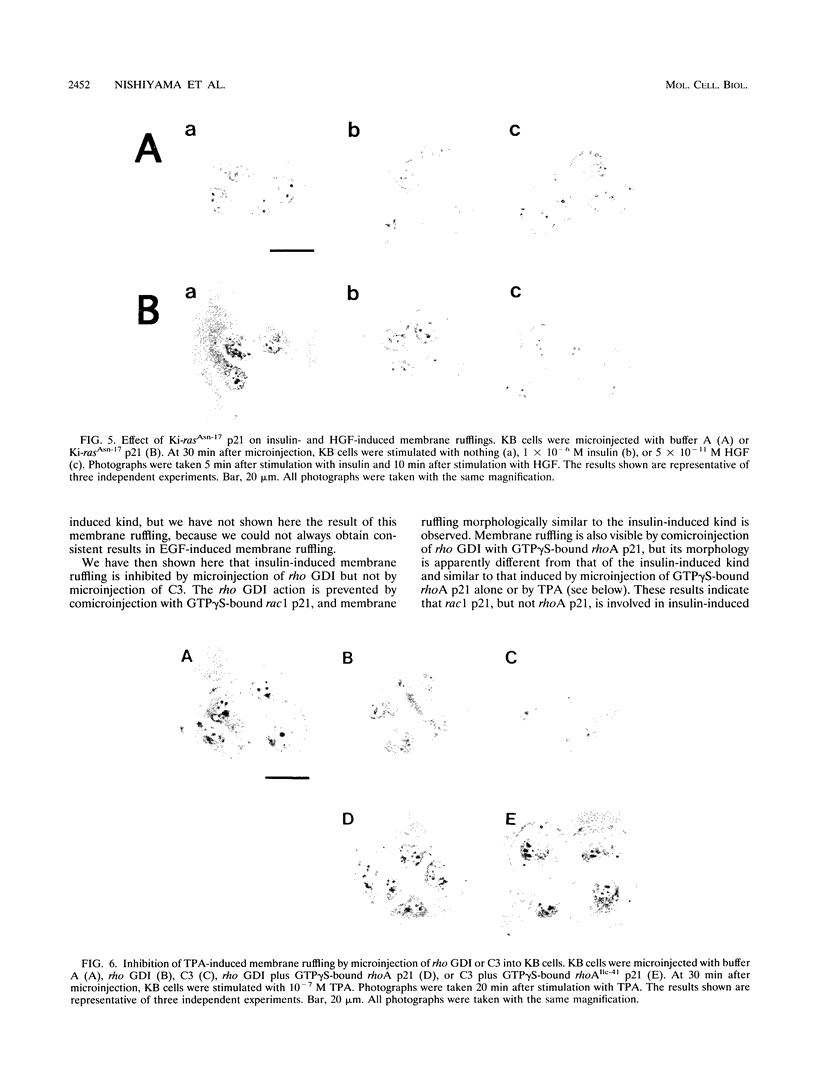
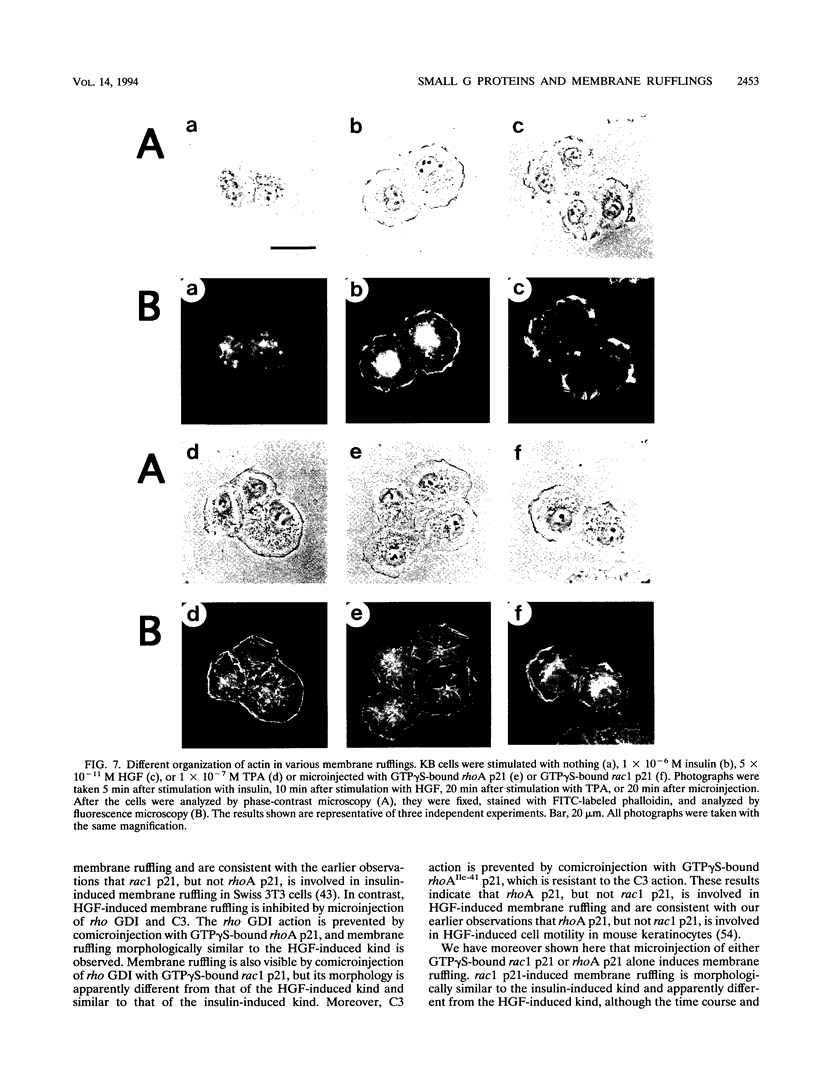
Insulin and hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) induced morphologically different membrane rufflings in KB cells. Insulin-induced membrane ruffling was inhibited by microinjection of rho GDI, an inhibitory GDP/GTP exchange regulator for both rho p21 and rac p21 small GTP-binding proteins, but not inhibited by microinjection of botulinum exoenzyme C3, known to selectively ADP-ribosylate rho p21 and to impair its function. This rho GDI action was prevented by comicroinjection with guanosine 5'-(3-O-thio)triphosphate (GTP gamma S)-bound rac1 p21. In contrast, HGF-induced membrane ruffling was inhibited by microinjection of rho GDI or C3. This rho GDI action was prevented by comicroinjection with GTP gamma S-bound rhoA p21, and this C3 action was prevented by comicroinjection with GTP gamma S-bound rhoAIle-41 p21, which is resistant to C3. Microinjection of either GTP gamma S-bound rac1 p21 or rhoA p21 alone induced membrane ruffling in the absence of the growth factors. The rac1 p21-induced membrane ruffling was morphologically similar to the insulin-induced kind, whereas rhoA p21-induced ruffling was apparently different from both the insulin- and HGF-induced kinds. Membrane ruffling was also induced by 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA), a protein kinase C-activating phorbol ester, but not by Ca2+ ionophore or microinjection of a dominant active Ki-ras p21 mutant (Ki-rasVal-12 p21). The phorbol ester-induced membrane ruffling was morphologically similar to the rhoA p21-induced kind and inhibited by microinjection of rho GDI or C3. These results indicate that rac p21 and rho GDI are involved in insulin-induced membrane ruffling and that rho p21 and rho GDI are involved in HGF- and phorbol ester-induced membrane rufflings.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abercrombie M., Heaysman J. E., Pegrum S. M. The locomotion of fibroblasts in culture. II. "RRuffling". Exp Cell Res. 1970 Jun;60(3):437–444. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(70)90537-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abo A., Pick E., Hall A., Totty N., Teahan C. G., Segal A. W. Activation of the NADPH oxidase involves the small GTP-binding protein p21rac1. Nature. 1991 Oct 17;353(6345):668–670. doi: 10.1038/353668a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed S., Kozma R., Lee J., Monfries C., Harden N., Lim L. The cysteine-rich domain of human proteins, neuronal chimaerin, protein kinase C and diacylglycerol kinase binds zinc. Evidence for the involvement of a zinc-dependent structure in phorbol ester binding. Biochem J. 1991 Nov 15;280(Pt 1):233–241. doi: 10.1042/bj2800233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed S., Kozma R., Monfries C., Hall C., Lim H. H., Smith P., Lim L. Human brain n-chimaerin cDNA encodes a novel phorbol ester receptor. Biochem J. 1990 Dec 15;272(3):767–773. doi: 10.1042/bj2720767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed S., Lee J., Kozma R., Best A., Monfries C., Lim L. A novel functional target for tumor-promoting phorbol esters and lysophosphatidic acid. The p21rac-GTPase activating protein n-chimaerin. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 25;268(15):10709–10712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aktories K., Rösener S., Blaschke U., Chhatwal G. S. Botulinum ADP-ribosyltransferase C3. Purification of the enzyme and characterization of the ADP-ribosylation reaction in platelet membranes. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Mar 1;172(2):445–450. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb13908.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ando S., Kaibuchi K., Sasaki T., Hiraoka K., Nishiyama T., Mizuno T., Asada M., Nunoi H., Matsuda I., Matsuura Y. Post-translational processing of rac p21s is important both for their interaction with the GDP/GTP exchange proteins and for their activation of NADPH oxidase. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 25;267(36):25709–25713. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bar-Sagi D., Feramisco J. R. Induction of membrane ruffling and fluid-phase pinocytosis in quiescent fibroblasts by ras proteins. Science. 1986 Sep 5;233(4768):1061–1068. doi: 10.1126/science.3090687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck T. W., Huleihel M., Gunnell M., Bonner T. I., Rapp U. R. The complete coding sequence of the human A-raf-1 oncogene and transforming activity of a human A-raf carrying retrovirus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jan 26;15(2):595–609. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.2.595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun U., Habermann B., Just I., Aktories K., Vandekerckhove J. Purification of the 22 kDa protein substrate of botulinum ADP-ribosyltransferase C3 from porcine brain cytosol and its characterization as a GTP-binding protein highly homologous to the rho gene product. FEBS Lett. 1989 Jan 16;243(1):70–76. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81220-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgering B. M., Medema R. H., Maassen J. A., van de Wetering M. L., van der Eb A. J., McCormick F., Bos J. L. Insulin stimulation of gene expression mediated by p21ras activation. EMBO J. 1991 May;10(5):1103–1109. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08050.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantley L. C., Auger K. R., Carpenter C., Duckworth B., Graziani A., Kapeller R., Soltoff S. Oncogenes and signal transduction. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):281–302. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90639-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castagna M., Takai Y., Kaibuchi K., Sano K., Kikkawa U., Nishizuka Y. Direct activation of calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase by tumor-promoting phorbol esters. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7847–7851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chardin P., Boquet P., Madaule P., Popoff M. R., Rubin E. J., Gill D. M. The mammalian G protein rhoC is ADP-ribosylated by Clostridium botulinum exoenzyme C3 and affects actin microfilaments in Vero cells. EMBO J. 1989 Apr;8(4):1087–1092. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03477.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Didsbury J., Weber R. F., Bokoch G. M., Evans T., Snyderman R. rac, a novel ras-related family of proteins that are botulinum toxin substrates. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 5;264(28):16378–16382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diekmann D., Brill S., Garrett M. D., Totty N., Hsuan J., Monfries C., Hall C., Lim L., Hall A. Bcr encodes a GTPase-activating protein for p21rac. Nature. 1991 May 30;351(6325):400–402. doi: 10.1038/351400a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dipasquale A. Locomotory activity of epithelial cells in culture. Exp Cell Res. 1975 Aug;94(1):191–215. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(75)90545-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endemann G., Yonezawa K., Roth R. A. Phosphatidylinositol kinase or an associated protein is a substrate for the insulin receptor tyrosine kinase. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 5;265(1):396–400. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukumoto Y., Kaibuchi K., Hori Y., Fujioka H., Araki S., Ueda T., Kikuchi A., Takai Y. Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel type of regulatory protein (GDI) for the rho proteins, ras p21-like small GTP-binding proteins. Oncogene. 1990 Sep;5(9):1321–1328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goshima K., Masuda A., Owaribe K. Insulin-induced formation of ruffling membranes of KB cells and its correlation with enhancement of amino acid transport. J Cell Biol. 1984 Mar;98(3):801–809. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.3.801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graziani A., Gramaglia D., Cantley L. C., Comoglio P. M. The tyrosine-phosphorylated hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor receptor associates with phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 25;266(33):22087–22090. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graziani A., Gramaglia D., dalla Zonca P., Comoglio P. M. Hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor stimulates the Ras-guanine nucleotide exchanger. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 5;268(13):9165–9168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall A. The cellular functions of small GTP-binding proteins. Science. 1990 Aug 10;249(4969):635–640. doi: 10.1126/science.2116664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiraoka K., Kaibuchi K., Ando S., Musha T., Takaishi K., Mizuno T., Asada M., Ménard L., Tomhave E., Didsbury J. Both stimulatory and inhibitory GDP/GTP exchange proteins, smg GDS and rho GDI, are active on multiple small GTP-binding proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Jan 31;182(2):921–930. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91820-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata K., Kikuchi A., Sasaki T., Kuroda S., Kaibuchi K., Matsuura Y., Seki H., Saida K., Takai Y. Involvement of rho p21 in the GTP-enhanced calcium ion sensitivity of smooth muscle contraction. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 5;267(13):8719–8722. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izumi T., Saeki Y., Akanuma Y., Takaku F., Kasuga M. Requirement for receptor-intrinsic tyrosine kinase activities during ligand-induced membrane ruffling of KB cells. Essential sites of src-related growth factor receptor kinases. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 25;263(21):10386–10393. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadowaki T., Koyasu S., Nishida E., Sakai H., Takaku F., Yahara I., Kasuga M. Insulin-like growth factors, insulin, and epidermal growth factor cause rapid cytoskeletal reorganization in KB cells. Clarification of the roles of type I insulin-like growth factor receptors and insulin receptors. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 5;261(34):16141–16147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katzav S., Martin-Zanca D., Barbacid M. vav, a novel human oncogene derived from a locus ubiquitously expressed in hematopoietic cells. EMBO J. 1989 Aug;8(8):2283–2290. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08354.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikuchi A., Yamamoto K., Fujita T., Takai Y. ADP-ribosylation of the bovine brain rho protein by botulinum toxin type C1. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 5;263(31):16303–16308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishi K., Sasaki T., Kuroda S., Itoh T., Takai Y. Regulation of cytoplasmic division of Xenopus embryo by rho p21 and its inhibitory GDP/GTP exchange protein (rho GDI). J Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;120(5):1187–1195. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.5.1187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knaus U. G., Heyworth P. G., Evans T., Curnutte J. T., Bokoch G. M. Regulation of phagocyte oxygen radical production by the GTP-binding protein Rac 2. Science. 1991 Dec 6;254(5037):1512–1515. doi: 10.1126/science.1660188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellström K., Heldin C. H., Westermark B. Induction of circular membrane ruffling on human fibroblasts by platelet-derived growth factor. Exp Cell Res. 1988 Aug;177(2):347–359. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(88)90468-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miura Y., Kikuchi A., Musha T., Kuroda S., Yaku H., Sasaki T., Takai Y. Regulation of morphology by rho p21 and its inhibitory GDP/GTP exchange protein (rho GDI) in Swiss 3T3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 5;268(1):510–515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyata Y., Nishida E., Sakai H. Growth factor- and phorbol ester-induced changes in cell morphology analyzed by digital image processing. Exp Cell Res. 1988 Apr;175(2):286–297. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(88)90193-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuno T., Kaibuchi K., Ando S., Musha T., Hiraoka K., Takaishi K., Asada M., Nunoi H., Matsuda I., Takai Y. Regulation of the superoxide-generating NADPH oxidase by a small GTP-binding protein and its stimulatory and inhibitory GDP/GTP exchange proteins. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 25;267(15):10215–10218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morii N., Teru-uchi T., Tominaga T., Kumagai N., Kozaki S., Ushikubi F., Narumiya S. A rho gene product in human blood platelets. II. Effects of the ADP-ribosylation by botulinum C3 ADP-ribosyltransferase on platelet aggregation. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 15;267(29):20921–20926. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura T., Nishizawa T., Hagiya M., Seki T., Shimonishi M., Sugimura A., Tashiro K., Shimizu S. Molecular cloning and expression of human hepatocyte growth factor. Nature. 1989 Nov 23;342(6248):440–443. doi: 10.1038/342440a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narumiya S., Sekine A., Fujiwara M. Substrate for botulinum ADP-ribosyltransferase, Gb, has an amino acid sequence homologous to a putative rho gene product. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 25;263(33):17255–17257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemoto Y., Namba T., Kozaki S., Narumiya S. Clostridium botulinum C3 ADP-ribosyltransferase gene. Cloning, sequencing, and expression of a functional protein in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 15;266(29):19312–19319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okano Y., Mizuno K., Osada S., Nakamura T., Nozawa Y. Tyrosine phosphorylation of phospholipase C gamma in c-met/HGF receptor-stimulated hepatocytes: comparison with HepG2 hepatocarcinoma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Feb 15;190(3):842–848. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.1125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson H. F., Self A. J., Garrett M. D., Just I., Aktories K., Hall A. Microinjection of recombinant p21rho induces rapid changes in cell morphology. J Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;111(3):1001–1007. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.3.1001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridley A. J., Hall A. The small GTP-binding protein rho regulates the assembly of focal adhesions and actin stress fibers in response to growth factors. Cell. 1992 Aug 7;70(3):389–399. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90163-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridley A. J., Paterson H. F., Johnston C. L., Diekmann D., Hall A. The small GTP-binding protein rac regulates growth factor-induced membrane ruffling. Cell. 1992 Aug 7;70(3):401–410. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90164-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotrosen D., Yeung C. L., Leto T. L., Malech H. L., Kwong C. H. Cytochrome b558: the flavin-binding component of the phagocyte NADPH oxidase. Science. 1992 Jun 5;256(5062):1459–1462. doi: 10.1126/science.1318579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin E. J., Gill D. M., Boquet P., Popoff M. R. Functional modification of a 21-kilodalton G protein when ADP-ribosylated by exoenzyme C3 of Clostridium botulinum. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):418–426. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruderman N. B., Kapeller R., White M. F., Cantley L. C. Activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase by insulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(4):1411–1415. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.4.1411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki T., Kato M., Takai Y. Consequences of weak interaction of rho GDI with the GTP-bound forms of rho p21 and rac p21. J Biol Chem. 1993 Nov 15;268(32):23959–23963. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaap D., de Widt J., van der Wal J., Vandekerckhove J., van Damme J., Gussow D., Ploegh H. L., van Blitterswijk W. J., van der Bend R. L. Purification, cDNA-cloning and expression of human diacylglycerol kinase. FEBS Lett. 1990 Nov 26;275(1-2):151–158. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81461-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekine A., Fujiwara M., Narumiya S. Asparagine residue in the rho gene product is the modification site for botulinum ADP-ribosyltransferase. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):8602–8605. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. B., Johnson K. S. Single-step purification of polypeptides expressed in Escherichia coli as fusions with glutathione S-transferase. Gene. 1988 Jul 15;67(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takai Y., Kaibuchi K., Kikuchi A., Kawata M. Small GTP-binding proteins. Int Rev Cytol. 1992;133:187–230. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61861-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takaishi K., Kikuchi A., Kuroda S., Kotani K., Sasaki T., Takai Y. Involvement of rho p21 and its inhibitory GDP/GTP exchange protein (rho GDI) in cell motility. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;13(1):72–79. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.1.72. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takaishi K., Sasaki T., Kato M., Yamochi W., Kuroda S., Nakamura T., Takeichi M., Takai Y. Involvement of Rho p21 small GTP-binding protein and its regulator in the HGF-induced cell motility. Oncogene. 1994 Jan;9(1):273–279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tominaga T., Sugie K., Hirata M., Morii N., Fukata J., Uchida A., Imura H., Narumiya S. Inhibition of PMA-induced, LFA-1-dependent lymphocyte aggregation by ADP ribosylation of the small molecular weight GTP binding protein, rho. J Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;120(6):1529–1537. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.6.1529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda T., Kikuchi A., Ohga N., Yamamoto J., Takai Y. Purification and characterization from bovine brain cytosol of a novel regulatory protein inhibiting the dissociation of GDP from and the subsequent binding of GTP to rhoB p20, a ras p21-like GTP-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 5;265(16):9373–9380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Pringle J. R., Osborn M. Measurement of molecular weights by electrophoresis on SDS-acrylamide gel. Methods Enzymol. 1972;26:3–27. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(72)26003-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida Y., Kawata M., Miura Y., Musha T., Sasaki T., Kikuchi A., Takai Y. Microinjection of smg/rap1/Krev-1 p21 into Swiss 3T3 cells induces DNA synthesis and morphological changes. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;12(8):3407–3414. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.8.3407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]