Abstract
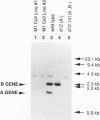
Paramecium tetraurelia contains two types of nuclei, a diploid germinal micronucleus and a large transcriptionally active macronucleus. The macronuclear genome is formed from the micronuclear DNA during sexual reproduction. Previous studies have shown that the processing of the A-type variable surface protein gene during formation of a new macronucleus is dependent on the presence of the A gene in the old macronucleus. It is not clear if this is a general feature that controls the formation of the Paramecium macronuclear genome or a unique feature of the A locus. Using micronuclear transplantation, we have constructed a strain that has a wild-type micronucleus but has macronuclear deletions of the A- and B-type surface protein genes. Neither the A nor the B gene is incorporated into the new macronucleus after sexual reproduction. Macronuclear transformation of this strain with the B gene rescues the B-gene deletion after formation of the next macronucleus but has not effect on the A deletion. Similarly, transformation with the A gene shows gene-specific rescue for A but not B. The effect of the old macronucleus on the processing of the new macronucleus results in a pattern of non-Mendelian inheritance of both macronuclear deletions. Progeny from the wild-type exconjugant are all wild type, and progeny from the A- B- exconjugant are mutant. The features of this A- B- non-Mendelian mutant demonstrate that the regulation of macronuclear DNA processing is gene specific, and our results open the possibility that this type of regulation affects many regions of the Paramecium genome.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Caron F., Meyer E. Molecular basis of surface antigen variation in paramecia. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1989;43:23–42. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.43.100189.000323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein L. M., Forney J. D. Mendelian and non-mendelian mutations affecting surface antigen expression in Paramecium tetraurelia. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;4(8):1583–1590. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.8.1583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forney J. D., Blackburn E. H. Developmentally controlled telomere addition in wild-type and mutant paramecia. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):251–258. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godiska R., Aufderheide K. J., Gilley D., Hendrie P., Fitzwater T., Preer L. B., Polisky B., Preer J. R., Jr Transformation of Paramecium by microinjection of a cloned serotype gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7590–7594. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harumoto T. Induced change in a non-mendelian determinant by transplantation of macronucleoplasm in Paramecium tetraurelia. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;6(10):3498–3501. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.10.3498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jessop-Murray H., Martin L. D., Gilley D., Preer J. R., Jr, Polisky B. Permanent rescue of a non-Mendelian mutation of Paramecium by microinjection of specific DNA sequences. Genetics. 1991 Nov;129(3):727–734. doi: 10.1093/genetics/129.3.727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koizumi S., Kobayashi S. Microinjection of plasmid DNA encoding the A surface antigen of Paramecium tetraurelia restores the ability to regenerate a wild-type macronucleus. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;9(10):4398–4401. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.10.4398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koizumi S. Microinjection and transfer of cytoplasm in Paramecium. Experiments on the transfer of kappa particles into cells at different stages. Exp Cell Res. 1974 Sep;88(1):74–78. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(74)90619-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikami K., Koizumi S. Nuclear transplant studies of the determination of mating type in germ nuclei of Paramecium tetraurelia. Exp Cell Res. 1982 Feb;137(2):397–402. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(82)90041-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preer J. R., Jr, Preer L. B., Rudman B., Barnett A. Molecular biology of the genes for immobilization antigens in Paramecium. J Protozool. 1987 Nov;34(4):418–423. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1987.tb03205.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudman B., Preer L. B., Polisky B., Preer J. R., Jr Mutants affecting processing of DNA in macronuclear development in paramecium. Genetics. 1991 Sep;129(1):47–56. doi: 10.1093/genetics/129.1.47. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J., Leeck C., Forney J. Molecular and genetic analyses of the B type surface protein gene from Paramecium tetraurelia. Genetics. 1993 May;134(1):189–198. doi: 10.1093/genetics/134.1.189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonneborn T. M. Genetics of cellular differentiation: stable nuclear differentiation in eucaryotic unicells. Annu Rev Genet. 1977;11:349–367. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.11.120177.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tondravi M. M., Yao M. C. Transformation of Tetrahymena thermophila by microinjection of ribosomal RNA genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4369–4373. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- You Y., Aufderheide K., Morand J., Rodkey K., Forney J. Macronuclear transformation with specific DNA fragments controls the content of the new macronuclear genome in Paramecium tetraurelia. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;11(2):1133–1137. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.2.1133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]