Abstract
Objectives
The aims of this study were to: (1) determine the validity and reliability of the Nova Biomedical Lactate Plus portable analyzer, and quantify any fixed or proportional bias; (2) determine the effect of any bias on the determination of the lactate threshold and (3) determine the effect that blood sampling methods have on validity and reliability.
Design
In this method comparison study we compared blood lactate concentration measured using the Lactate Plus portable analyzer to lactate concentration measured by a reference analyzer, the YSI 2300.
Setting
University campus in the USA.
Participants
Fifteen active men and women performed a discontinuous graded exercise test to volitional exhaustion on a motorised treadmill. Blood samples were taken via finger prick and collected in microcapillary tubes for analysis by the reference instrument at the end of each stage. Duplicate samples for the portable analyzer were either taken directly from the finger or from the micro capillary tubes.
Primary outcome measurements
Ordinary least products regressions were used to assess validity, reliability and bias in the portable analyzer. Lactate threshold was determined by visual inspection.
Results
Though measurements from both instruments were correlated (r=0.91), the differences between instruments had large variability (SD=1.45 mM/l) when blood was sampled directly from finger. This variability was reduced by ∼95% when both instruments measured blood collected in the capillary tubes. As the proportional and fixed bias between instruments was small, there was no difference in estimates of the lactate threshold between instruments. Reliability for the portable instrument was strong (r=0.99, p<0.05) with no proportional bias (slope=1.02) and small fixed bias (−0.19 mM/l).
Conclusions
The Lactate Plus analyzer provides accurate and reproducible measurements of blood lactate concentration that can be used to estimate workloads corresponding to blood lactate transitions or any absolute lactate concentrations.
Keywords: Accuracy, Lactate Threshold, Bias
Article summary.
Article focus
Determine the validity and reliability of the Lactate Plus analyzer and quantify any systematic bias.
Determine the effect of any bias on the determination of lactate threshold.
Determine the effect that blood sampling methods have on validity and reliability.
Key messages
The Lactate Plus analyzer provides valid and reliable measurements of blood lactate concentration.
The Lactate Plus analyzer demonstrates a small fixed and proportional bias.
Sampling directly from the finger does increase the variability in measurement, likely owing to the milking of the finger rather than the analyzer itself.
Strengths and limitations of this study
This study compares the accuracy and variability in measurements under both laboratory and field sampling conditions.
We used least-product regression analysis to independently quantify fixed and proportional bias rather than Bland-Altman plots or least-squares regression, which lump these biases together or assumes there is no measurement error in the reference method.
We did not compare either instrument to known lactate standards. This may limit our ability to precisely quantify the accuracy of the portable analyzer. However, our reference instrument was calibrated using three known lactate standards across a supraphysiological range. This reduces the likelihood that our reference instrument is inaccurate or non-linear.
Introduction
Not only is blood lactate accumulation a common measure in the physiological assessment of endurance athletes, but is also an important clinical measure.1–4 Portable lactate analyzers have advantages over bench top models including: (1) their ability to rapidly sample blood lactate concentration ([lactate]), in or outside the laboratory; (2) they require a much smaller sample of blood (0.5–0.7 μl) than many bench top analyzers (25–75 μl) and (3) they can be purchased and operated at a lower cost than many bench top models.
Several studies have attempted to evaluate the validity and reliability of these portable analyzers.3–10 While the majority of studies report that the [lactate] measured using portable analyzers is similar to those of various bench top models, the mean difference between the reference and portable analyzers can be as much as 1.0 mM/l. This can represent nearly 10% of the full range of values in some populations.11 This level of disagreement could be explained by the presence of systematic measurement error. Systematic measurement error can result in a proportional bias, where one instrument produces values that are different from those of another instrument by an amount that is proportional to the level of the measured variable, and/or a fixed bias, where one instrument gives values that are different from those of another instrument by a constant amount.12 13 Thus, similar mean values between lactate analyzers could occur while the portable analyzer produces low values at lower [lactate] and high values at higher [lactate] or vice versa. Previous studies have primarily relied on Bland-Altman analysis to determine the presence of any fixed bias. However, this approach does not allow the independent determination of bias, and thus has limited utility in assessing the presence of systematic measurement error. Therefore, while most data appear to show a substantial proportional and/or fixed bias, the presence and degree of bias in portable lactate analyzers remains unresolved.3 4 6–10 Furthermore, because previous studies have not directly examined these biases it is unclear if they are large enough to affect estimates of various lactate parameters, such as pH or lactate threshold (LT).
Blood sampling techniques may also affect measurement accuracy and reliability. Previous studies have either used intravenous blood drawn directly into a syringe,3 7 9 or capillary blood from a finger stick drawn into capillary tubes and then mixed as would be done in the laboratory.6 10 Portable analyzers, however, are designed to sample blood directly from a puncture for ease of use in the field. When using a finger stick to draw blood it is not uncommon to require ‘milking’ of the finger to get an adequate sample. This may dilute the lactate concentration by increasing interstitial fluid in the sample. It would seem important to understand and quantify the effect of differing blood-sampling procedures on the accuracy and reliability of these portable analyzers.
Given the questions that remain regarding the validity and reliability of portable lactate analyzers the specific aims of the present study were: (1) to determine the validity and reliability of the Lactate Plus analyzer (Nova Biomedical), and quantify any fixed and/or proportional bias and (2) determine the effect that blood sampling methods have on validity and reliability.
Methods
Fifteen young (20–36 years; mean=24.5 years) men and women (6 women) participated in the study. All subjects reported at least 90 min of moderate to vigorous physical activity each week. All individuals read and signed an informed consent. The Institutional Review Boards at Wheaton College and the Northern Illinois University approved this study. All procedures conformed to the Declaration of Helsinki.
Instruments
To determine the validity of the Lactate Plus analyzer we used the YSI 2300 Stat Plus Glucose and Lactate analyzer from Yellow Springs Instruments (Yellow Springs, Ohio, USA) as our reference instrument. This bench top laboratory analyzer uses a membrane-bound enzyme electrochemical methodology. l-Lactate oxidase is immobilised in a thin membrane placed over an electrochemical probe. The enzyme catalyses the conversion of l-lactate to pyruvate and hydrogen peroxide, the latter then being oxidised at the platinum anode to measure lactate concentration in whole blood or plasma. A new membrane was used for each data collection session. The analyzer was initially calibrated using 5, 15 and 30 mM/l solutions. In addition, an automated quality control was performed in triplicate every 45 min using a 5 mM/l solution. Blood samples were collected from a finger stick into two heparinised capillary tubes. Blood was then mixed in a micro centrifuge tube. Two 25 μl samples were sequentially aspirated and measured by the analyzer.
The Lactate Plus analyzer uses an electrochemical lactate oxidase biosensor to measure lactate concentration in a 0.7 μl sample. Following the manufacturer's instructions we used low (1.0–1.6 mM/l) and high (4.0–5.4 mM/l) quality control solutions to ensure the lactate analyzer was operating properly at the beginning of each data collection session. For the first nine participants three blood samples were taken directly from the finger between each stage of the graded exercise test (GXT). All samples were taken in this order: (1) portable directly from finger, (2) capillary tubes for the YSI 2300 from the finger and (3) a second sample directly from finger using the portable analyzer. To assess the effect of blood sampling techniques on the accuracy of the portable analyzer blood was drawn from the finger into capillary tubes and allocated to both the YSI 2300 and portable analyzer for the last six participants.
Graded exercise
Participants performed a discontinuous GXT on a motorised treadmill (Quinton TM65). Each stage lasted 2 min with a 1 min blood sampling period between stages. The finger was prepared for sampling just prior to the end of each exercise stage. During the 1 min blood collection period participants straddled the treadmill belt while blood samples were taken from a finger. After 1 min the participants resumed exercise at a higher speed or grade. The initial speed was 1.55 m/s and 0% grade. The speed was increased by either 0.50 or 0.67 m/s for each stage until the participant's heart rate was at least 80% of their age-predicted maximum (220 age). After this point the speed remained constant while grade was increased 2.5% for each stage. Exercise was continued until volitional exhaustion.
Data analysis
Two methods were used to assess validity. First, a Bland-Altman plot was constructed to allow the reader to more directly compare our data with those of previous studies since this is the approach typically used. However, because fixed and proportional biases cannot be determined independently from these plots, ordinary least products regression analysis was used. Validity was determined from the correlation coefficient in combination with the presence and degree of bias. The degree of fixed bias was determined from the y-intercept 95% CIs. If the CI for the intercept includes the value of zero, then there is no fixed bias. Proportional bias was determined from the 95% CI for the slope. If the CI for the slope includes the value of 1.0, then there is no proportional bias. Ordinary least products regression gives different slopes and y-intercepts than does least squares regression because error is assumed in both portable and bench top analyzers.12 13
LT was defined as the point at which blood [lactate] began to increase in a non-linear fashion.14 15 The threshold was estimated by plotting [lactate] against GXT stage. These graphs were visually inspected to determine the lines of best fit by the two evaluators. The following guidelines were used to help guide the evaluators: (1) at least three data points were included in each line, (2) both lines contained unique data points and (3) lines were chosen that produced the highest R2 with the smallest CIs. Once the lines were chosen the equations for each line were set equal to one another and solved for the point of intersection (figure 1). The values from each evaluator were averaged.16 These equations were also used to calculate the stage that corresponded to an absolute blood [lactate] of 2.5 and 4.0 mM/l. A t test for paired data was used to compare means between analyzers. A p value of<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Figure 1.

Determination of the lactate threshold by visual inspection. Shown are data from a representative study participant and the lines of best fit that were determined independently for data from the YSI 2300 lactate analyzer and the Lactate Plus lactate analyzer. Blood samples could not be collected between stages 4 and 5. The Lactate Plus analyzer returned error message between stages 6 and 7.
Reliability was determined using ordinary least products regression to quantify the relationship between sequential measurements for both instruments.
Results
Validity
Lactate values during graded exercise ranged from 1.2 to 16.4 mM/l. When both portable and bench top blood samples are each taken directly from the finger the mean difference between [lactate] measured by the portable and bench top analyzers was small across the full range of lactate values as depicted in figure 2. While the mean difference between the two instruments was near zero, differences between the instruments had a large variability (SD=1.45 mM/l). Even though there can be large differences between values measured by the portable and bench top analyzers, the paired measurements were highly correlated as shown in figure 3A. Least-product regression indicated a small fixed bias (y-intercept=–0.28 mM/l) between [lactate] measured with the portable and bench top analyzers. There was no evidence of a proportional bias (95% CI 0.94 to 1.15). When the same mixed blood sample was used by both analyzers, the fixed bias was reduced to −0.056 mM/l, while a small proportional bias was evident (slope=1.08) as shown in figure 3B.
Figure 2.
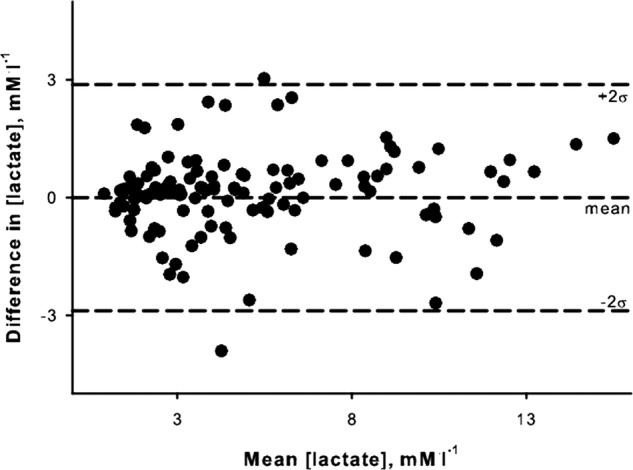
Bland-Altman plot depicting the level of agreement between lactate concentrations determined by Lactate Plus portable analyzer the YSI bench top analyzer.
Figure 3.
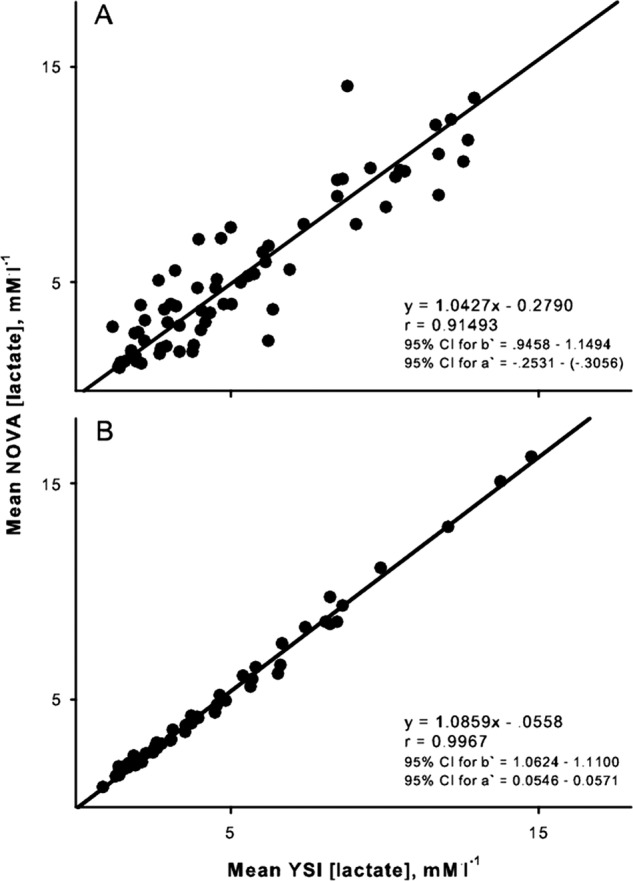
Ordinary least products regression analysis of the relation between lactate concentrations determined by the Lactate Plus portable analyzer and the YSI bench top analyzer. (A) When separate samples for each analyzer were collected directly from finger. (B) When a common sample of blood was used by both analyzers. Regression equations and CIs for slope (B) and y-intercept (A) are presented.
Regardless of a blood sampling approach there was excellent agreement between estimates of the LT based on lactate values from the portable analyzer compared with those from the bench top analyzer (r=0.97). Moreover, there was neither a proportional bias (95% CI for slope: 0.910 to 1.098), nor a fixed bias (95% CI for y-intercept: –0.396 to 0.325) in estimates of the LT from the portable analyzer. Given the lack of bias it is not surprising there was no difference between blood [La] at the LT (2.88NOVA±0.53 vs 3.15YSI±0.46 mM/l; p=0.32). In addition the stages corresponding to absolute blood lactate values of 2.5 mM/l (2.99NOVA vs 2.92YSI) and 4.0 mM/l (4.64NOVA vs 4.61YSI) were not different between portable and bench top values (p=0.86 for both).
Reliability
The relationship between duplicate measurements of [lactate] by the bench top analyzer was very strong (r=0.99, p<0.05). Ordinary least products regression indicated no proportional bias (slope=0.99), and a small fixed bias (0.059 mM/l; figure 4). Ordinary least products regression revealed a small proportional (slope=1.20) and fixed bias (−0.54 mM/l; figure 5A) when the two duplicate blood samples for the portable analyzer were taken directly from the fingers. Thus, the reading from the second sample was typically lower than that from the first. However, when two duplicate measurements were taken from the same mixed blood sample, there was no proportional bias (slope=1.02) and the fixed bias was reduced to −0.19 mM/l).
Figure 4.
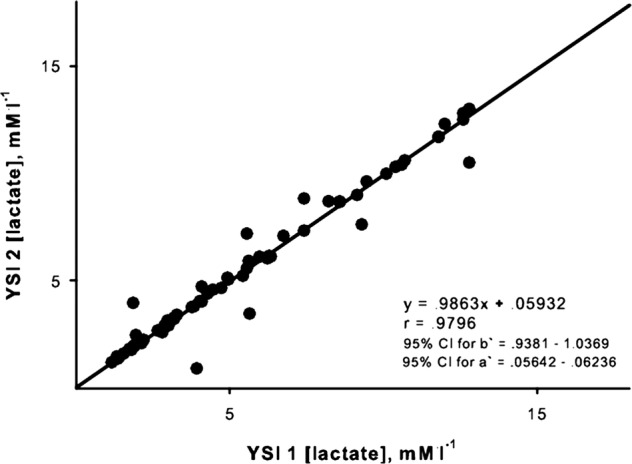
Ordinary least products regression analysis of the relation between sequential estimates of blood lactate concentration by the YSI bench top analyzer. Regression equation and CIs for slope (B) and y-intercept (A) are presented.
Figure 5.
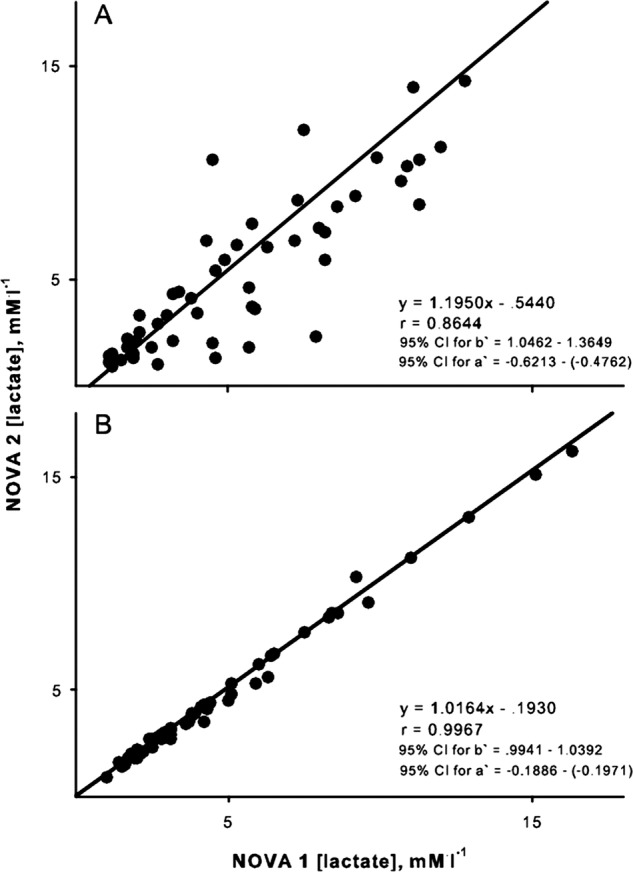
Ordinary least products regression analysis of the relation between sequential estimates of blood lactate concentration by the Lactate Plus portable lactate analyzer. (A) When separate samples for each analyzer were collected directly from finger. (B) When a common sample of blood was used by both analyzers. Regression equation and CIs for slope (B) and y-intercept (A) are presented.
A total of 242 blood samples were taken using the portable analyzer. Twenty-seven of these attempts resulted in error messages (E-4—insufficient sample). Thus, about 1-in-10 measurement attempts resulted in errors.
Discussion
There were three new findings in our study: (1) The very small proportional bias indicates that the Lactate Plus analyzer is a highly linear instrument, (2) multiple blood samples directly from the finger increases measurement error and (3) the small proportional and fixed bias in the portable analyzer does not affect the ability to determine the LT.
We chose to use ordinary least products regression to characterise the relation between the Lactate Plus analyzer and our reference analyzer. Most studies have employed a combination of Bland-Altman plots and least squares regression to determine the degree of agreement between various portable analyzers and a corresponding reference analyzer.3–10 The mean difference between analyzers, as determined through Bland-Altman plots, is determined by the interaction of any fixed and proportional bias. Therefore, the mean difference between methods does not solely reflect the accuracy or fixed bias of the device, but in some cases, the presence of a proportional bias or loss of linearity. The use of least squares regression to characterise the level of proportional bias, as reflected in the slope of the linear relation, is skewed because all error is assigned to the dependent variable, in this case the portable analyzer. The use of least products regression to compare methods avoids both of these issues, allowing independent and more accurate determination of any fixed or proportional bias.12 13 17
Numerous studies have compared blood lactate measured with various portable analyzers to several different bench top analyzers.4 5 7–10 All have reported that these portable analyzers produce similar lactate values compared with their bench top counterparts with average differences ranging from −0.8 to 1.0 mM/l. However, differences of almost 1.0 mM/l can significantly impact the use of absolute [lactate] to characterise training intensity or efficacy. Weltman et al18 reported that women who trained at an intensity corresponding to about 2.5 mM/l showed greater improvement in blood lactate parameters, but less of an improvement in VO2 max than did women training at their LT. If true, then an error in the measurement of blood lactate concentration could lead to suboptimal improvements in either lactate parameters or VO2 max. Of the two studies that have tested the Lactate Plus analyzer, only Tanner et al10 reported the absolute difference between this portable analyzer and a reference analyzer (−0.8 mM/l). Our data show a much smaller difference between the Lactate Plus and the YSI bench top analyzers (fixed bias=−0.056 mM/l). Though not specifically assessed, it does appear that Tanner's reported difference between the hand held and reference analyzer is significantly influenced by a proportional bias (figures 4 and 5 from reference 8). The fact that our data shows little proportional bias (figure 3) may account for the greater agreement between analyzers that we observed. It is possible that if Tanner had been able to independently determine the proportional and fixed biases, their analysis may have revealed a small bias similar to ours. Differences in reference instruments would not likely explain the greater measurement error reported by Tanner, given that their instrument undergoes a three-point and two-point calibrations check every few hours, similar to our reference instrument.
Given that we found a very small proportional bias the estimation of the LT from [lactate] measured by the Lactate Plus analyzer agreed very well with those determined from [lactate] measured by the reference analyzer. Moreover, given the small fixed bias, it was not surprising that the lactate values from the portable analyzer provided similar estimates of the workload corresponding to the 2.5 and the 4.0 mM/l absolute lactate concentrations. These lactate concentrations were chosen because they have both sport and clinical significance.1 2 19 20 The strong correlation coefficient and small biases suggest that the Lactate Plus analyzer can be used to accurately determine exercise intensities based on any blood lactate parameter.
Determination of the LT by visual inspection has come under scrutiny.21 22 To reduce subjectivity our approach to visual inspection is guided by several principles similar to those used by others.16 23 Several methods of assessing the LT have been proposed that purport to be more objective.14 16 24 However, many of these methods are known to be significantly affected by data outliers and/or missing data.25 26 Therefore, the choice of any analytical approach has a subjective component. While our approach likely produces LT values that are different from other approaches, it produced values consistent with other studies that employed similar approaches to LT estimation.18 23 When one considers the strong correlation and small biases in our data, it seems likely the LT estimates would be strongly correlated regardless of the analytical approach chosen.
Duplicate sample readings from the Lactate Plus analyzer were strongly related, however there was a small fixed bias, indicating that the values from the second sample were consistently lower than the values from the first sample. In addition, there was a very small proportional bias. Both of these biases may be explained by using separate samples collected directly from the finger. The milking of the finger to obtain a blood sample can cause the dilution of the blood sample by interstitial fluid. The manufacturer warns the user against vigorous squeezing of the finger to obtain a blood drop. The use of a vasodilating cream may resolve this issue. When we used the same mixed blood sample as the reference analyzer, the proportional bias was eliminated, while the fixed bias was reduced by approximately 65%.
We also found that the portable analyzer was unable to analyse the blood sample 11% of the time, presumably from an insufficient sample volume. This was surprising given that the Lactate Plus lactate analyzer provides an audible signal to indicate when the test strip has a sufficient volume of blood for analysis. Our experience has shown that anticipating the filling of the test strip can result in both the audible signal and an error. However, even when great care is taken, one can still get an audible full signal and the error message.
Ridenour et al4 advocated for a switch from fetal blood sampling to lactate analysis. However, their data showed that the variability in blood [lactate] accounted for only 46% of the variability in pH. This could be owing to the significant proportional bias that is apparent in their data (see ref 1, figures 1 and 3). However, our analysis shows a fixed and proportional bias that are less than half reported by previous studies relying on Bland-Altman plots and simple comparison of means.3 4 This suggests the modest correlation between fetal [lactate] and blood pH is best attributed to the independent regulation of blood lactate and pH rather than unreliable measurement of [lactate].27 28
We did not compare the Lactate Plus lactate analyzer with known standards. This limits the precision with which we can quantify the accuracy of the portable analyzer. However, our reference instrument was calibrated using three known lactate standards across a supraphysiological range. Our analysis assumes measurement error in both the portable and reference instrument. Thus it is likely that by comparing the Lactate Plus lactate analyzer directly to known lactate standards, our fixed bias would be reduced.
While some studies have used blood collected from trained athletes to compare portable lactate analyzers to bench top models,5 6 8 10 several do not.3–5 7 9 This seems quite appropriate given that the importance of accurate lactate measurement extends well beyond the athletic field. Our subjects were healthy and physically active, but not highly trained. This is unlikely to account for any difference between previous studies and ours given that we can find no reason to speculate that either lactate analyzer would more accurately measure [lactate] in one population compared with another.
Similarly, the choice of graded exercise protocol can affect LT determination.29 Thus, our use of a personalised, discontinuous GXT likely produced LT values different from some other protocols. However, this would have no affect on our ability to accomplish the aims of our study, specifically to compare estimates of LT between lactate measurements produced by the portable and reference analyzers.
In summary, the Lactate Plus analyzer is a valid and reliable instrument across a wide range of blood lactate concentrations. Any proportional or fixed bias in blood lactate concentration is nearly indistinguishable from zero. Therefore, the portable analyzer can be used to determine exercise intensities based on absolute or relative blood lactate concentrations. Sampling procedures can have a significant effect on the reliability of the portable analyzer, and the portable analyzer is prone to technical issues in nearly 1 of 10 samples.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
Lactate test strips and quality assurance solutions for the Lactate Plus lactate analyzer were provided by Lactate.com.
Footnotes
Contributors: BEH was the PI and lead writer. AS was a coinvestigator and helped design the study, collect data and revise the manuscript. SH, KD and MA were student investigators who helped conceive of the experimental question, collect and analyse data, and write and revise manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding: This research received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial or not-for-profit sectors.
Competing interests: None.
Ethics approval: Ethics approval was provided by the Institutional Review Boards at Wheaton College and the Northern Illinois University approved this study.
Provenance and peer review: Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
Data sharing statement: No additional data are available.
References
- 1.Callaway DW, Shapiro NI, Donnino MW, et al. Serum lactate and base deficit as predictors of mortality in normotensive elderly blunt trauma patients. J Trauma-Injury Infect Crit Care 2009;66:1040–4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Green JP, Berger T, Garg N, et al. Serum lactate is a better predictor of short-term mortality when stratified by C-reactive protein in adult emergency department patients hospitalized for a suspected infection. Ann Emerg Med 2011;57:291–5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Nordstrom L, Chua S, Roy A, et al. Quality assessment of two lactate test strip methods suitable for obstetric use. J Perinat Med 1998;26:83–8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Ridenour RV, Gada RP, Brost BC, et al. Comparison and validation of point of care lactate meters as a replacement for fetal pH measurement. Clin Biochem 2008;41:1461–5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Baldari C, Bonavolonta V, Emerenziani GP, et al. Accuracy, reliability, linearity of Accutrend and Lactate Pro versus EBIO plus analyzer. Eur J Appl Physiol 2009;107:105–11 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Buckley JD, Bourdon PC, Woolford SM. Effect of measuring blood lactate concentrations using different automated lactate analysers on blood lactate transition thresholds. J Sci Med Sport 2003;6:408–21 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Perez EH, Dawood H, Chetty U, et al. Validation of the Accutrend lactate meter for hyperlactatemia screening during antiretroviral therapy in a resource-poor setting. Int J Infect Dis 2008;12:553–6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Pyne DB, Boston T, Martin DT, et al. Evaluation of the Lactate Pro blood lactate analyser. Eur J Appl Physiol 2000;82:112–16 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Saunders AC, Feldman HA, Correia CE, et al. Clinical evaluation of a portable lactate meter in type I glycogen storage disease. J Inherit Metab Dis 2005;28:695–701 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Tanner RK, Fuller KL, Ross ML. Evaluation of three portable blood lactate analysers: Lactate Pro, Lactate Scout and Lactate Plus. Eur J Appl Physiol 2010;109:551–9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Juel C, Klarskov C, Nielsen JJ, et al. Effect of high-intensity intermittent training on lactate and H+ release from human skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2004;286:E245–51 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Ludbrook J. Comparing methods of measurements. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 1997;24:193–203 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Ludbrook J. Statistical techniques for comparing measurers and methods of measurement: a critical review. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 2002;29:527–36 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Beaver WL, Wasserman K, Whipp BJ. Improved detection of lactate threshold during exercise using a log-log transformation. J Appl Physiol 1985;59:1936–40 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Brooks GA. Anaerobic threshold: review of the concept and directions for future research. Med Sci Sports Exerc 1985;17:22–34 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Gaskill SE, Ruby BC, Walker AJ, et al. Validity and reliability of combining three methods to determine ventilatory threshold. Med Sci Sports Exerc 2001;33:1841–8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Brace RA. Fitting straight lines to experimental data. Am J Physiol 1977;233:R94–9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Weltman A, Seip RL, Snead D, et al. Exercise training at and above the lactate threshold in previously untrained women. Int J Sports Med 1992;13:257–63 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Fernandes RJ, Sousa M, Pinheiro A, et al. Assessment of individual anaerobic threshold and stroking parameters in swimmers aged 10–11 years. Eur J Sport Sci 2010;10:311–17 [Google Scholar]
- 20.Moran P, Prichard JG, Ansley L, et al. The influence of blood lactate sample site on exercise prescription. J Strength Cond Res 2012;26:563–7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Gladden LB, Yates JW, Stremel RW, et al. Gas-exchange and lactate anaerobic thresholds—interevaluator and intraevaluator agreement. J Appl Physiol 1985;58:2082–9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Yeh MP, Gardner RM, Adams TD, et al. Anaerobic threshold—problems of determination and validation. J Appl Physiol 1983;55:1178–86 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.de Oliveira Pires F, Silva AEL, Gagliardi JFL, et al. Characterization of the blood lactate curce and applicability of the Dmax model in a progressive protocol on treadmill. Rev Bras Med Esporte 2006;12:61e–5e [Google Scholar]
- 24.Cheng B, Kuipers H, Snyder AC, et al. A new approach for the determination of ventilatory and lactate thresholds. Int J Sports Med 1992;13:518–22 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Janeba M, Yaeger D, White R, et al. The Dmax method does not produce a valid estimate of the lactate threshold. JEPonline 2010;13:50–7 [Google Scholar]
- 26.Newell J, Higgins D, Madden N, et al. Software for calculating blood lactate endurance markers. J Sports Sci 2007;25:1403–9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Hida K, Suzuki N, Kwee IL, et al. pH-Lactate dissociation in neonatal anoxia: proton and 31P NMR spectroscopic studies in rat pups. Magn Reson Med 1991;22:128–32 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Paschen W, Djuricic B, Mies G, et al. Lactate and pH in the brain: association and dissociation in different pathophysiological states. J Neurochem 1987;48:154–9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Vallier JM, Bigard AX, Carre F, et al. Determination of lactic and ventilatory thresholds. Position of the Societe Francaise de Medecine du Sport (French Sports Medicine Society). Sci Sports 2000;15:133–40 [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.


