Abstract
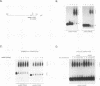
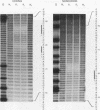
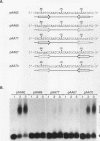
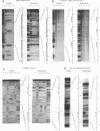
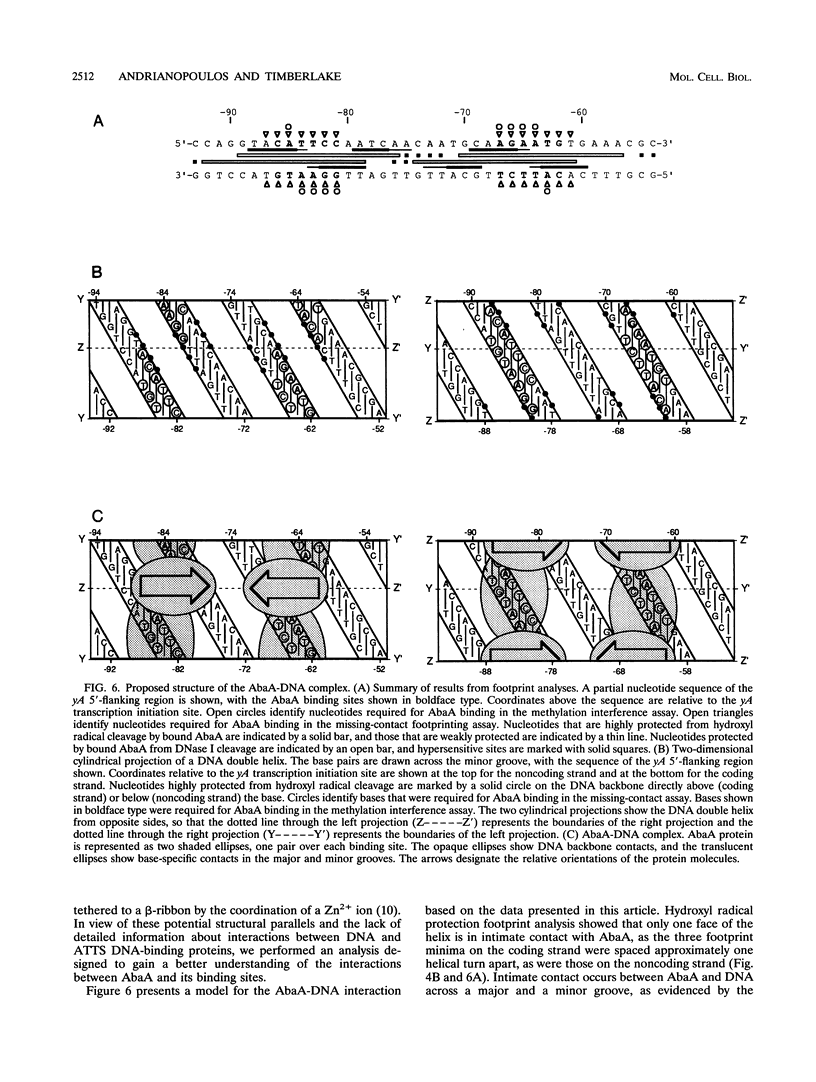
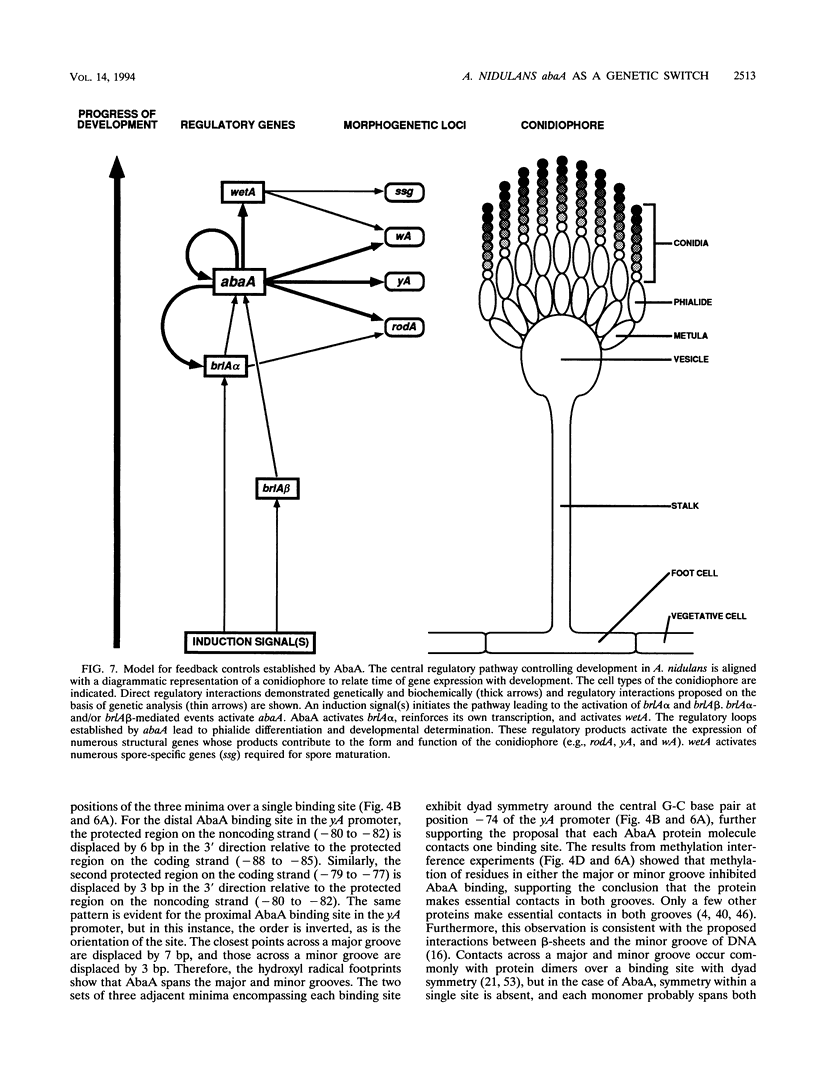
The Aspergillus nidulans abaA gene encodes a protein containing an ATTS DNA-binding motif and is required for the terminal stages of conidiophore development. Results from gel mobility shift and protection, missing-contact, and interference footprint assays showed that AbaA binds to the sequence 5'-CATTCY-3', where Y is a pyrimidine, making both major- and minor-groove contacts. Multiple AbaA binding sites are present in the cis-acting regulatory regions of several developmentally controlled structural genes as well as those of the upstream regulatory gene brlA, the downstream regulatory gene wetA, and abaA itself. These cis-acting regulatory regions confer AbaA-dependent transcriptional activation in a heterologous Saccharomyces cerevisiae gene expression system. From these observations, we propose that the AbaA transcription factor establishes a novel set of feedback regulatory loops responsible for determination of conidiophore development.
Full text
PDF
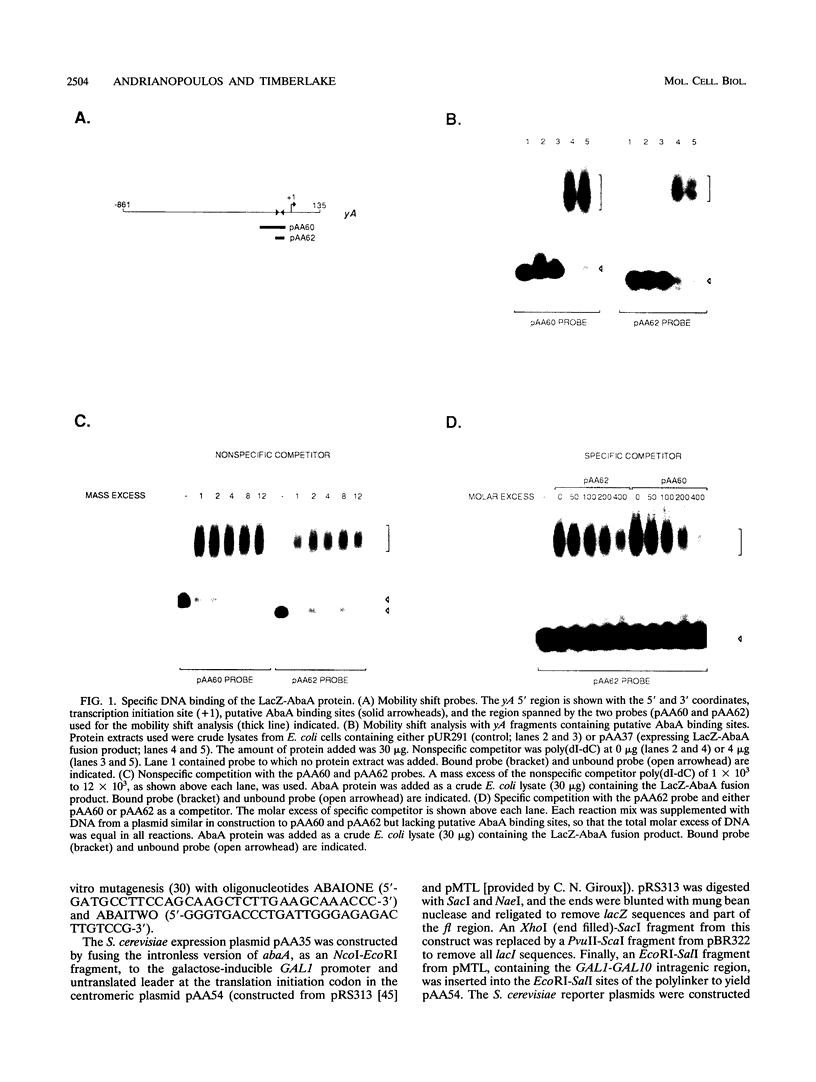
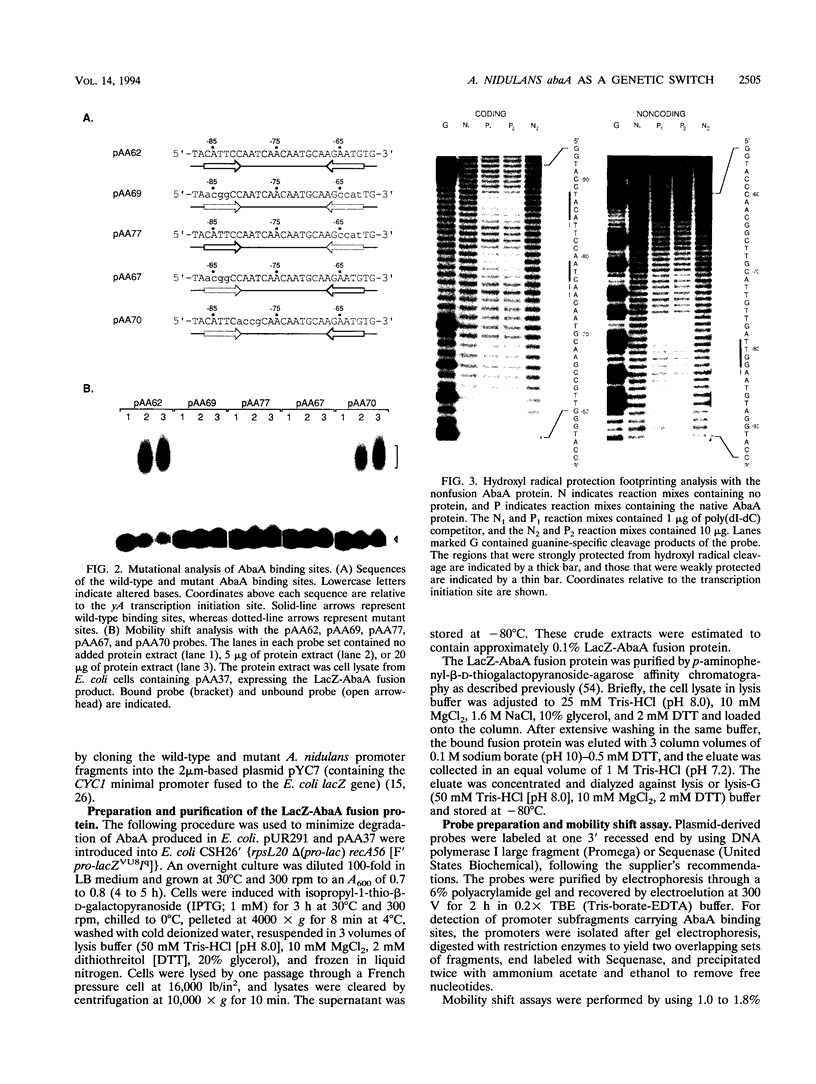
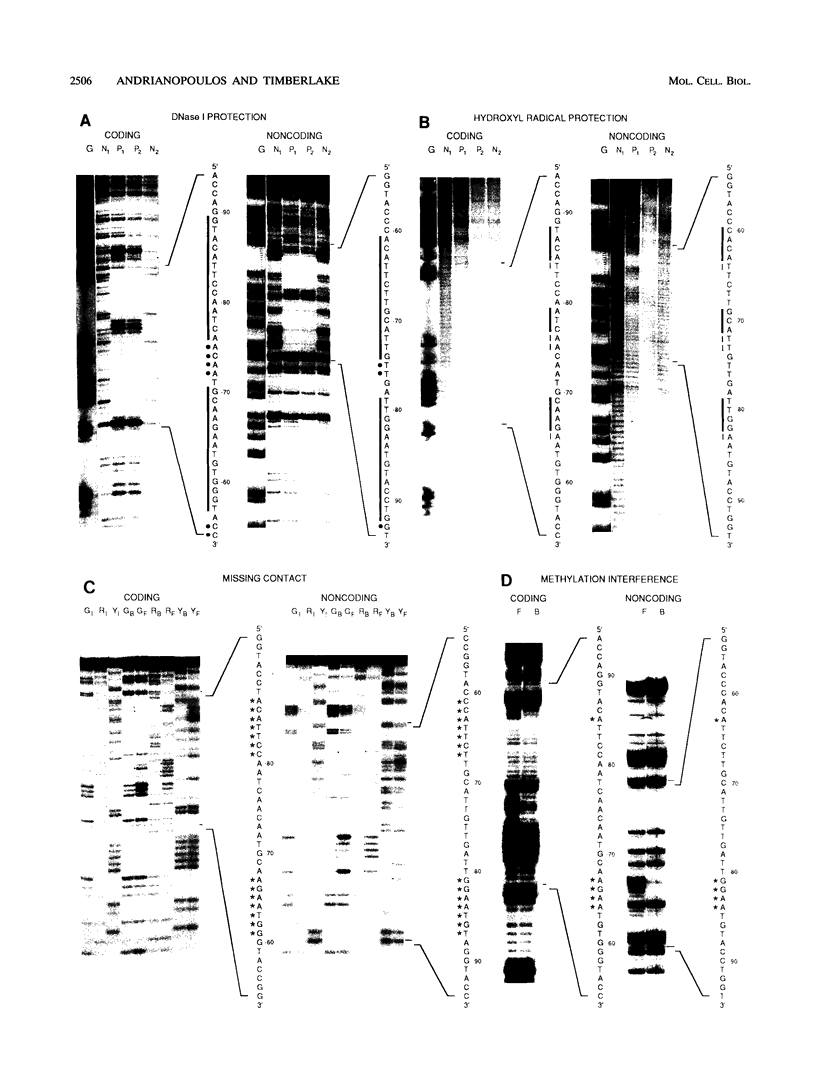



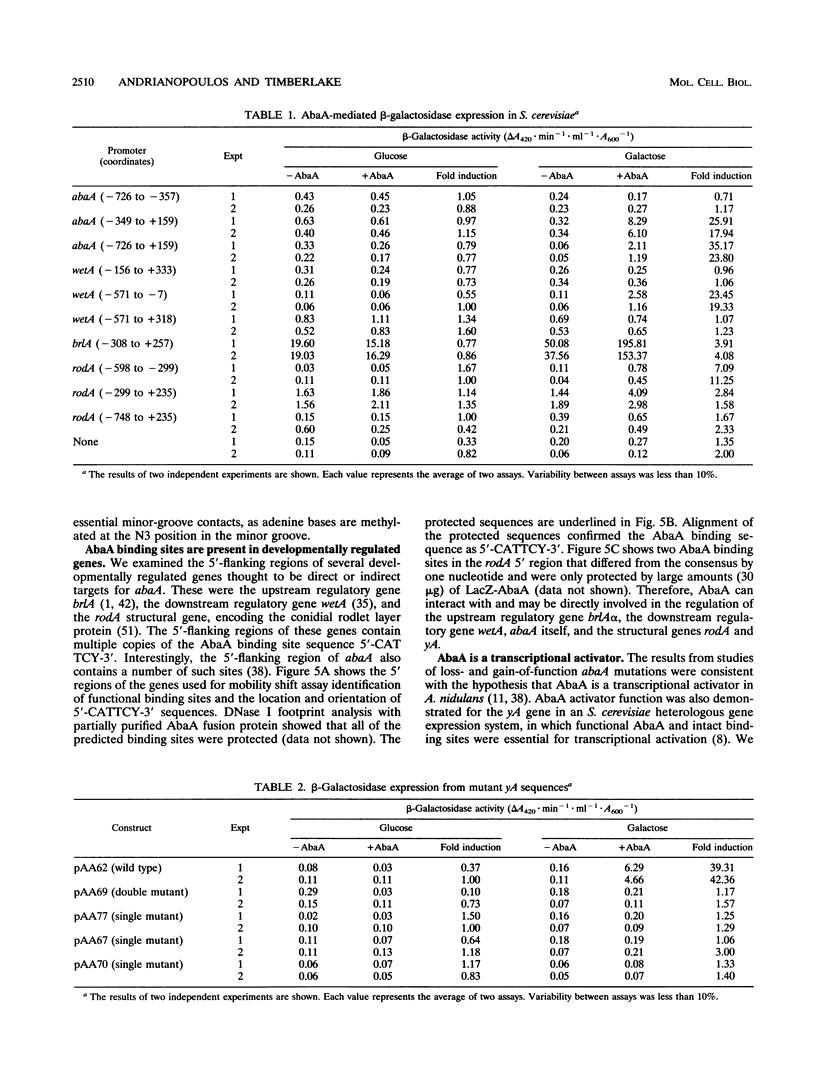



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams T. H., Boylan M. T., Timberlake W. E. brlA is necessary and sufficient to direct conidiophore development in Aspergillus nidulans. Cell. 1988 Jul 29;54(3):353–362. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90198-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams T. H., Timberlake W. E. Upstream elements repress premature expression of an Aspergillus developmental regulatory gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;10(9):4912–4919. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.9.4912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson J. E., Ptashne M., Harrison S. C. Structure of the repressor-operator complex of bacteriophage 434. 1987 Apr 30-May 6Nature. 326(6116):846–852. doi: 10.1038/326846a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrianopoulos A., Timberlake W. E. ATTS, a new and conserved DNA binding domain. Plant Cell. 1991 Aug;3(8):747–748. doi: 10.1105/tpc.3.8.747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aramayo R., Timberlake W. E. Sequence and molecular structure of the Aspergillus nidulans yA (laccase I) gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jun 11;18(11):3415–3415. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.11.3415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aramayo R., Timberlake W. E. The Aspergillus nidulans yA gene is regulated by abaA. EMBO J. 1993 May;12(5):2039–2048. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05853.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg J. M. Proposed structure for the zinc-binding domains from transcription factor IIIA and related proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(1):99–102. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.1.99. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boylan M. T., Mirabito P. M., Willett C. E., Zimmerman C. R., Timberlake W. E. Isolation and physical characterization of three essential conidiation genes from Aspergillus nidulans. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;7(9):3113–3118. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.9.3113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunelle A., Schleif R. F. Missing contact probing of DNA-protein interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6673–6676. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bürglin T. R. The TEA domain: a novel, highly conserved DNA-binding motif. Cell. 1991 Jul 12;66(1):11–12. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90132-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell S., Inamdar M., Rodrigues V., Raghavan V., Palazzolo M., Chovnick A. The scalloped gene encodes a novel, evolutionarily conserved transcription factor required for sensory organ differentiation in Drosophila. Genes Dev. 1992 Mar;6(3):367–379. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.3.367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang Y. C., Timberlake W. E. Identification of Aspergillus brlA response elements (BREs) by genetic selection in yeast. Genetics. 1993 Jan;133(1):29–38. doi: 10.1093/genetics/133.1.29. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Sussman J. L., Kim S. H. Secondary structural complementarity between DNA and proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Apr;74(4):1458–1462. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.4.1458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clutterbuck A. J. A mutational analysis of conidial development in Aspergillus nidulans. Genetics. 1969 Oct;63(2):317–327. doi: 10.1093/genetics/63.2.317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Company M., Errede B. A Ty1 cell-type-specific regulatory sequence is a recognition element for a constitutive binding factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;8(12):5299–5309. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.12.5299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson I., Xiao J. H., Rosales R., Staub A., Chambon P. The HeLa cell protein TEF-1 binds specifically and cooperatively to two SV40 enhancer motifs of unrelated sequence. Cell. 1988 Sep 23;54(7):931–942. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90108-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon W. J., Hayes J. J., Levin J. R., Weidner M. F., Dombroski B. A., Tullius T. D. Hydroxyl radical footprinting. Methods Enzymol. 1991;208:380–413. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)08021-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Errede B., Company M., Hutchison C. A., 3rd Ty1 sequence with enhancer and mating-type-dependent regulatory activities. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):258–265. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrance I. K., Mar J. H., Ordahl C. P. M-CAT binding factor is related to the SV40 enhancer binding factor, TEF-1. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 25;267(24):17234–17240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fromental C., Kanno M., Nomiyama H., Chambon P. Cooperativity and hierarchical levels of functional organization in the SV40 enhancer. Cell. 1988 Sep 23;54(7):943–953. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90109-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gietz D., St Jean A., Woods R. A., Schiestl R. H. Improved method for high efficiency transformation of intact yeast cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Mar 25;20(6):1425–1425. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.6.1425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarente L., Mason T. Heme regulates transcription of the CYC1 gene of S. cerevisiae via an upstream activation site. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1279–1286. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90309-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamer J. E., Timberlake W. E. Functional organization of the Aspergillus nidulans trpC promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;7(7):2352–2359. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.7.2352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han S., Navarro J., Greve R. A., Adams T. H. Translational repression of brlA expression prevents premature development in Aspergillus. EMBO J. 1993 Jun;12(6):2449–2457. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05899.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laloux I., Dubois E., Dewerchin M., Jacobs E. TEC1, a gene involved in the activation of Ty1 and Ty1-mediated gene expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: cloning and molecular analysis. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;10(7):3541–3550. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.7.3541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee D. K., Horikoshi M., Roeder R. G. Interaction of TFIID in the minor groove of the TATA element. Cell. 1991 Dec 20;67(6):1241–1250. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90300-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mar J. H., Ordahl C. P. A conserved CATTCCT motif is required for skeletal muscle-specific activity of the cardiac troponin T gene promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6404–6408. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mar J. H., Ordahl C. P. M-CAT binding factor, a novel trans-acting factor governing muscle-specific transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):4271–4283. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.4271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall M. A., Timberlake W. E. Aspergillus nidulans wetA activates spore-specific gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;11(1):55–62. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.1.55. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirabito P. M., Adams T. H., Timberlake W. E. Interactions of three sequentially expressed genes control temporal and spatial specificity in Aspergillus development. Cell. 1989 Jun 2;57(5):859–868. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90800-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikolov D. B., Hu S. H., Lin J., Gasch A., Hoffmann A., Horikoshi M., Chua N. H., Roeder R. G., Burley S. K. Crystal structure of TFIID TATA-box binding protein. Nature. 1992 Nov 5;360(6399):40–46. doi: 10.1038/360040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otting G., Qian Y. Q., Billeter M., Müller M., Affolter M., Gehring W. J., Wüthrich K. Protein--DNA contacts in the structure of a homeodomain--DNA complex determined by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy in solution. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3085–3092. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07505.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prade R. A., Timberlake W. E. The Aspergillus nidulans brlA regulatory locus consists of overlapping transcription units that are individually required for conidiophore development. EMBO J. 1993 Jun;12(6):2439–2447. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05898.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rüther U., Müller-Hill B. Easy identification of cDNA clones. EMBO J. 1983;2(10):1791–1794. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01659.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sewall T. C., Mims C. W., Timberlake W. E. abaA controls phialide differentiation in Aspergillus nidulans. Plant Cell. 1990 Aug;2(8):731–739. doi: 10.1105/tpc.2.8.731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikorski R. S., Hieter P. A system of shuttle vectors and yeast host strains designed for efficient manipulation of DNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1989 May;122(1):19–27. doi: 10.1093/genetics/122.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sluka J. P., Horvath S. J., Glasgow A. C., Simon M. I., Dervan P. B. Importance of minor-groove contacts for recognition of DNA by the binding domain of Hin recombinase. Biochemistry. 1990 Jul 17;29(28):6551–6561. doi: 10.1021/bi00480a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smale S. T., Baltimore D. The "initiator" as a transcription control element. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):103–113. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90176-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somers W. S., Phillips S. E. Crystal structure of the met repressor-operator complex at 2.8 A resolution reveals DNA recognition by beta-strands. Nature. 1992 Oct 1;359(6394):387–393. doi: 10.1038/359387a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Johnston D., Nüsslein-Volhard C. The origin of pattern and polarity in the Drosophila embryo. Cell. 1992 Jan 24;68(2):201–219. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90466-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starr D. B., Hawley D. K. TFIID binds in the minor groove of the TATA box. Cell. 1991 Dec 20;67(6):1231–1240. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90299-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stringer M. A., Dean R. A., Sewall T. C., Timberlake W. E. Rodletless, a new Aspergillus developmental mutant induced by directed gene inactivation. Genes Dev. 1991 Jul;5(7):1161–1171. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.7.1161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takanami M. RNA polymerase nascent product analysis. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):497–499. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65058-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timberlake W. E. Molecular genetics of Aspergillus development. Annu Rev Genet. 1990;24:5–36. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.24.120190.000253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tullius T. D., Dombroski B. A. Hydroxyl radical "footprinting": high-resolution information about DNA-protein contacts and application to lambda repressor and Cro protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(15):5469–5473. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.15.5469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullmann A. One-step purification of hybrid proteins which have beta-galactosidase activity. Gene. 1984 Jul-Aug;29(1-2):27–31. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90162-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White S. W., Appelt K., Wilson K. S., Tanaka I. A protein structural motif that bends DNA. Proteins. 1989;5(4):281–288. doi: 10.1002/prot.340050405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiao J. H., Davidson I., Matthes H., Garnier J. M., Chambon P. Cloning, expression, and transcriptional properties of the human enhancer factor TEF-1. Cell. 1991 May 17;65(4):551–568. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90088-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang C. C., Nash H. A. The interaction of E. coli IHF protein with its specific binding sites. Cell. 1989 Jun 2;57(5):869–880. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90801-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]