Abstract
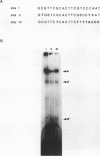
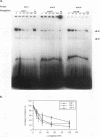
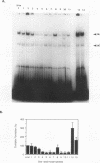
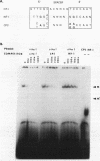
The herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) origin of DNA replication, oriS, contains an AT-rich region and three highly homologous sequences, sites I, II, and III, identified as binding sites for the HSV-1 origin-binding protein (OBP). In the present study, interactions between specific oriS DNA sequences and proteins in uninfected cell extracts were characterized. The formation of one predominant protein-DNA complex, M, was demonstrated in gel shift assays following incubation of uninfected cell extracts with site I DNA. The cellular protein(s) that comprises complex M has been designated origin factor I (OF-I). The OF-I binding site was shown to partially overlap the OBP binding site within site I. Complexes with mobilities indistinguishable from that of complex M also formed with site II and III DNAs in gel shift assays. oriS-containing plasmid DNA mutated in the OF-I binding site exhibited reduced replication efficiency in transient assays, demonstrating a role for this site in oriS function. The OF-I binding site is highly homologous to binding sites for the cellular CCAAT DNA-binding proteins. The binding site for the CCAAT protein CP2 was found to compete for OF-I binding to site I DNA. These studies support a model involving the participation of cellular proteins in the initiation of HSV-1 DNA synthesis at oriS.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barinaga M. Dimers direct development. Science. 1991 Mar 8;251(4998):1176–1177. doi: 10.1126/science.1848724. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann R. P., Yalamanchili V. R., O'Callaghan D. J. Functional mapping and DNA sequence of an equine herpesvirus 1 origin of replication. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1275–1283. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1275-1283.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camp H. S., Coussens P. M., Silva R. F. Cloning, sequencing, and functional analysis of a Marek's disease virus origin of DNA replication. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):6320–6324. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.6320-6324.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakraborty T., Brennan T. J., Li L., Edmondson D., Olson E. N. Inefficient homooligomerization contributes to the dependence of myogenin on E2A products for efficient DNA binding. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;11(7):3633–3641. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.7.3633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Challberg M. D., Kelly T. J. Animal virus DNA replication. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:671–717. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.003323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chodosh L. A., Baldwin A. S., Carthew R. W., Sharp P. A. Human CCAAT-binding proteins have heterologous subunits. Cell. 1988 Apr 8;53(1):11–24. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90483-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dabrowski C. E., Schaffer P. A. Herpes simplex virus type 1 origin-specific binding protein: oriS-binding properties and effects of cellular proteins. J Virol. 1991 Jun;65(6):3140–3150. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.6.3140-3150.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLuca N. A., Schaffer P. A. Activation of immediate-early, early, and late promoters by temperature-sensitive and wild-type forms of herpes simplex virus type 1 protein ICP4. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):1997–2008. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deb S., Deb S. P. A 269-amino-acid segment with a pseudo-leucine zipper and a helix-turn-helix motif codes for the sequence-specific DNA-binding domain of herpes simplex virus type 1 origin-binding protein. J Virol. 1991 Jun;65(6):2829–2838. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.6.2829-2838.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deb S., Deb S. P. Analysis of Ori-S sequence of HSV-1: identification of one functional DNA binding domain. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Apr 11;17(7):2733–2752. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.7.2733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deb S., Doelberg M. A 67-base-pair segment from the Ori-S region of herpes simplex virus type 1 encodes origin function. J Virol. 1988 Jul;62(7):2516–2519. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.7.2516-2519.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodson M. S., Lehman I. R. The herpes simplex virus type I origin binding protein. DNA-dependent nucleoside triphosphatase activity. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 15;268(2):1213–1219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elias P., Gustafsson C. M., Hammarsten O., Stow N. D. Structural elements required for the cooperative binding of the herpes simplex virus origin binding protein to oriS reside in the N-terminal part of the protein. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 25;267(24):17424–17429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elias P., Gustafsson C. M., Hammarsten O. The origin binding protein of herpes simplex virus 1 binds cooperatively to the viral origin of replication oris. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 5;265(28):17167–17173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elias P., Lehman I. R. Interaction of origin binding protein with an origin of replication of herpes simplex virus 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):2959–2963. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.2959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elias P., O'Donnell M. E., Mocarski E. S., Lehman I. R. A DNA binding protein specific for an origin of replication of herpes simplex virus type 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6322–6326. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez T. R., Dutch R. E., Lehman I. R., Gustafsson C., Elias P. Mutations in a herpes simplex virus type 1 origin that inhibit interaction with origin-binding protein also inhibit DNA replication. J Virol. 1991 Mar;65(3):1649–1652. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.3.1649-1652.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang H. C., Sundseth R., Hansen U. Transcription factor LSF binds two variant bipartite sites within the SV40 late promoter. Genes Dev. 1990 Feb;4(2):287–298. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.2.287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. Eukaryotic transcriptional regulatory proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:799–839. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.004055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Kadonaga J. T., Rosenfeld P. J., Kelly T. J., Tjian R. A cellular DNA-binding protein that activates eukaryotic transcription and DNA replication. Cell. 1987 Jan 16;48(1):79–89. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90358-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones N. Transcriptional regulation by dimerization: two sides to an incestuous relationship. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):9–11. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90207-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koff A., Schwedes J. F., Tegtmeyer P. Herpes simplex virus origin-binding protein (UL9) loops and distorts the viral replication origin. J Virol. 1991 Jun;65(6):3284–3292. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.6.3284-3292.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koff A., Tegtmeyer P. Characterization of major recognition sequences for a herpes simplex virus type 1 origin-binding protein. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4096–4103. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4096-4103.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockshon D., Galloway D. A. Cloning and characterization of oriL2, a large palindromic DNA replication origin of herpes simplex virus type 2. J Virol. 1986 May;58(2):513–521. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.2.513-521.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin D. W., Deb S. P., Klauer J. S., Deb S. Analysis of the herpes simplex virus type 1 OriS sequence: mapping of functional domains. J Virol. 1991 Aug;65(8):4359–4369. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.8.4359-4369.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeoch D. J., Dalrymple M. A., Davison A. J., Dolan A., Frame M. C., McNab D., Perry L. J., Scott J. E., Taylor P. The complete DNA sequence of the long unique region in the genome of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Gen Virol. 1988 Jul;69(Pt 7):1531–1574. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-7-1531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeoch D. J., Dalrymple M. A., Dolan A., McNab D., Perry L. J., Taylor P., Challberg M. D. Structures of herpes simplex virus type 1 genes required for replication of virus DNA. J Virol. 1988 Feb;62(2):444–453. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.2.444-453.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalf J. B., Bates R. C., Lederman M. Interaction of virally coded protein and a cell cycle-regulated cellular protein with the bovine parvovirus left terminus ori. J Virol. 1990 Nov;64(11):5485–5490. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.11.5485-5490.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller W. J., Dufort D., Hassell J. A. Multiple subelements within the polyomavirus enhancer function synergistically to activate DNA replication. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;8(11):5000–5015. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.11.5000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murre C., McCaw P. S., Vaessin H., Caudy M., Jan L. Y., Jan Y. N., Cabrera C. V., Buskin J. N., Hauschka S. D., Lassar A. B. Interactions between heterologous helix-loop-helix proteins generate complexes that bind specifically to a common DNA sequence. Cell. 1989 Aug 11;58(3):537–544. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90434-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagata K., Guggenheimer R. A., Hurwitz J. Specific binding of a cellular DNA replication protein to the origin of replication of adenovirus DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(20):6177–6181. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.20.6177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oh S. J., Chittenden T., Levine A. J. Identification of cellular factors that bind specifically to the Epstein-Barr virus origin of DNA replication. J Virol. 1991 Jan;65(1):514–519. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.1.514-519.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olivo P. D., Nelson N. J., Challberg M. D. Herpes simplex virus DNA replication: the UL9 gene encodes an origin-binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5414–5418. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olivo P. D., Nelson N. J., Challberg M. D. Herpes simplex virus type 1 gene products required for DNA replication: identification and overexpression. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):196–204. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.196-204.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabkin S. D., Hanlon B. Nucleoprotein complex formed between herpes simplex virus UL9 protein and the origin of DNA replication: inter- and intramolecular interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10946–10950. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sock E., Wegner M., Grummt F. DNA replication of human polyomavirus JC is stimulated by NF-I in vivo. Virology. 1991 May;182(1):298–308. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90673-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spaete R. R., Frenkel N. The herpes simplex virus amplicon: analyses of cis-acting replication functions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):694–698. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stow N. D., Davison A. J. Identification of a varicella-zoster virus origin of DNA replication and its activation by herpes simplex virus type 1 gene products. J Gen Virol. 1986 Aug;67(Pt 8):1613–1623. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-8-1613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stow N. D., McMonagle E. C. Characterization of the TRS/IRS origin of DNA replication of herpes simplex virus type 1. Virology. 1983 Oct 30;130(2):427–438. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90097-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stow N. D., Weir H. M., Stow E. C. Analysis of the binding sites for the varicella-zoster virus gene 51 product within the viral origin of DNA replication. Virology. 1990 Aug;177(2):570–577. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90522-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thömmes P., Hübscher U. Eukaryotic DNA replication. Enzymes and proteins acting at the fork. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Dec 27;194(3):699–712. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19460.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traut W., Fanning E. Sequence-specific interactions between a cellular DNA-binding protein and the simian virus 40 origin of DNA replication. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):903–911. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travers A. A. DNA conformation and protein binding. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:427–452. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.002235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weir H. M., Calder J. M., Stow N. D. Binding of the herpes simplex virus type 1 UL9 gene product to an origin of viral DNA replication. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Feb 25;17(4):1409–1425. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.4.1409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weir H. M., Stow N. D. Two binding sites for the herpes simplex virus type 1 UL9 protein are required for efficient activity of the oriS replication origin. J Gen Virol. 1990 Jun;71(Pt 6):1379–1385. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-6-1379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller S. K., Lee K. J., Sabourin D. J., Schaffer P. A. Genetic analysis of temperature-sensitive mutants which define the gene for the major herpes simplex virus type 1 DNA-binding protein. J Virol. 1983 Jan;45(1):354–366. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.1.354-366.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller S. K., Spadaro A., Schaffer J. E., Murray A. W., Maxam A. M., Schaffer P. A. Cloning, sequencing, and functional analysis of oriL, a herpes simplex virus type 1 origin of DNA synthesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 May;5(5):930–942. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.5.930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. A., Nelson N. J., McGeoch D. J., Challberg M. D. Identification of herpes simplex virus type 1 genes required for origin-dependent DNA synthesis. J Virol. 1988 Feb;62(2):435–443. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.2.435-443.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]