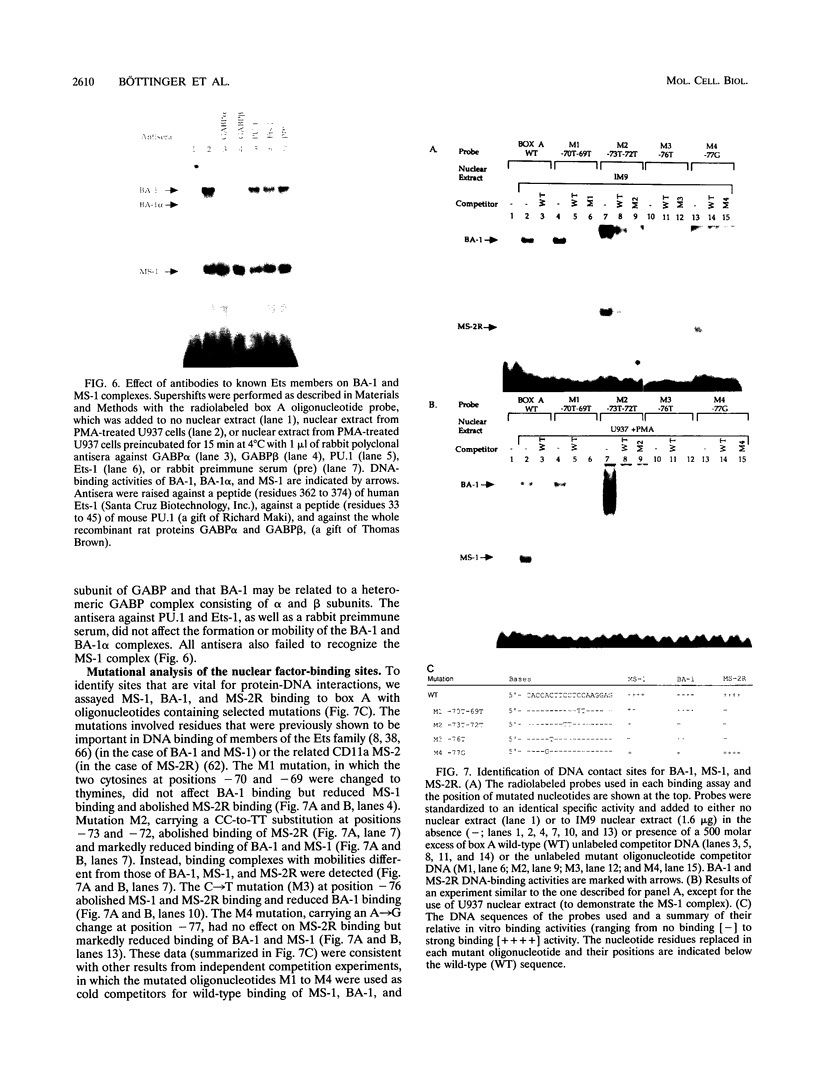
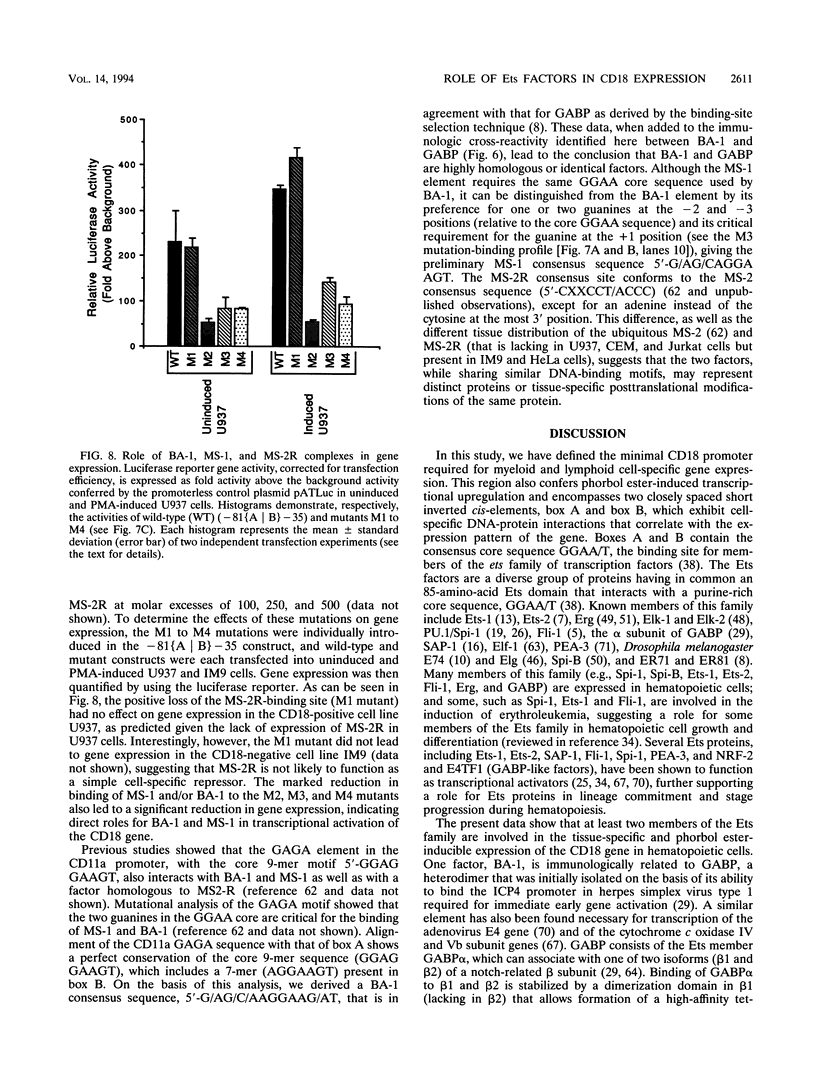
Abstract
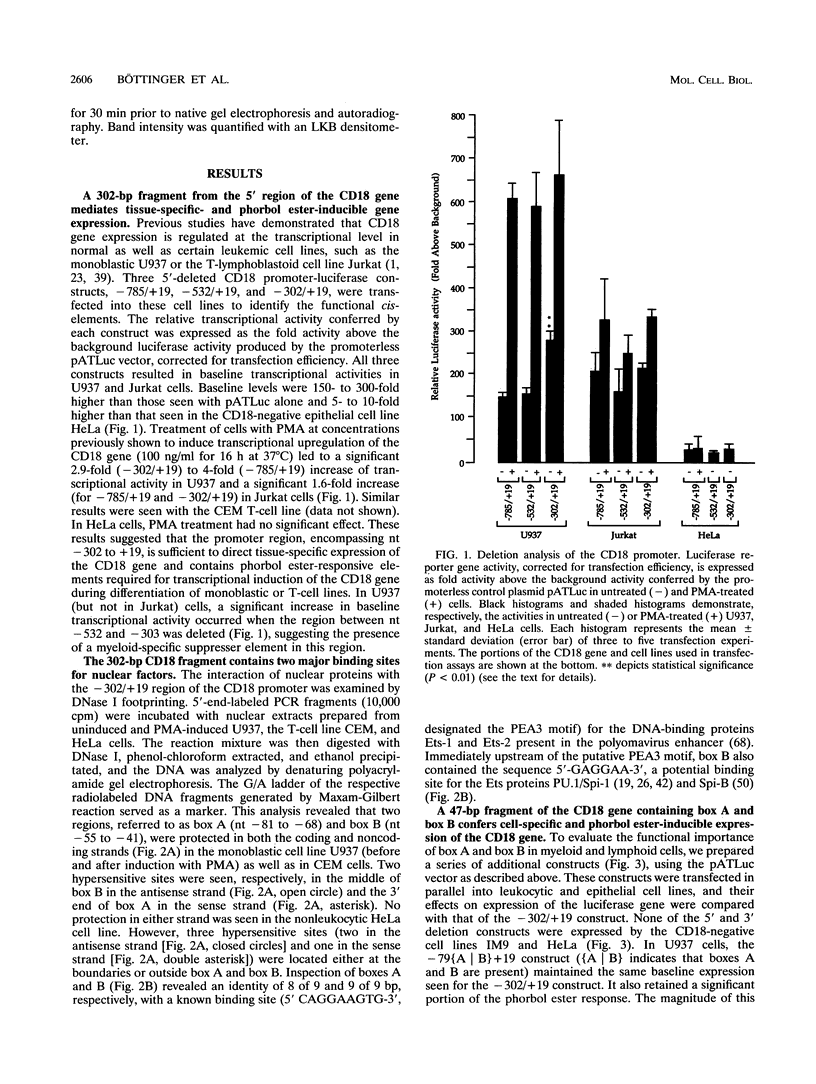
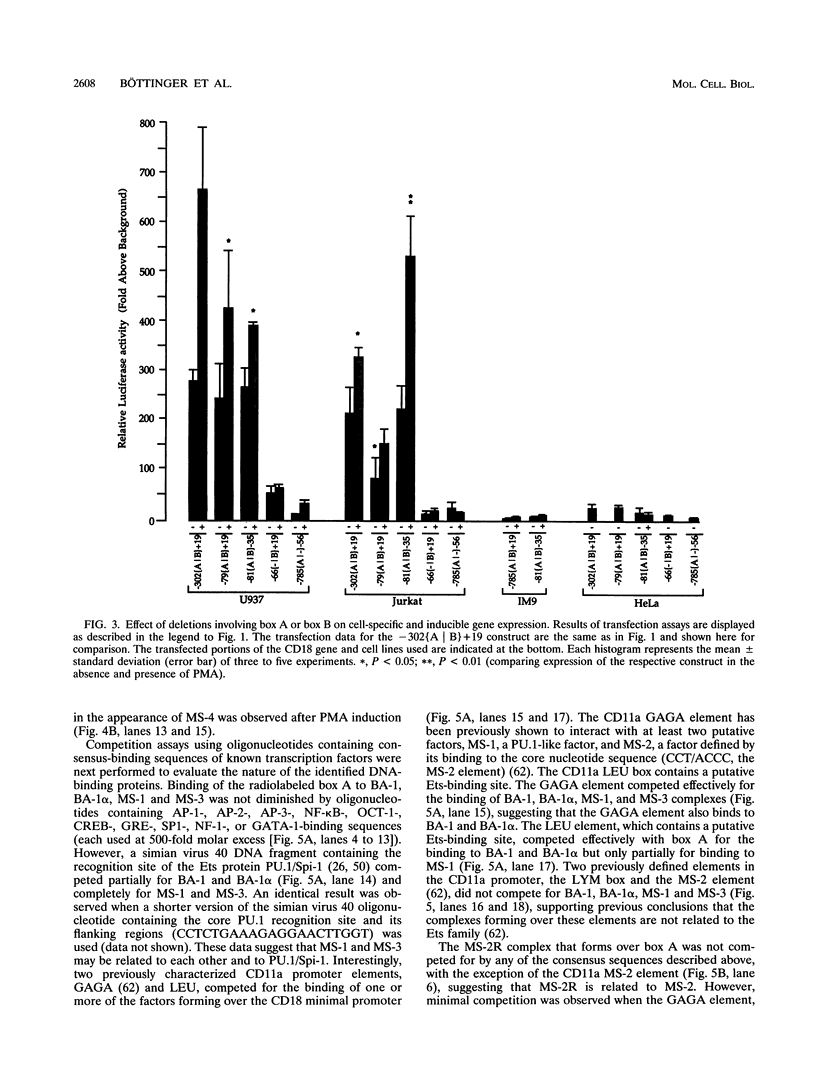
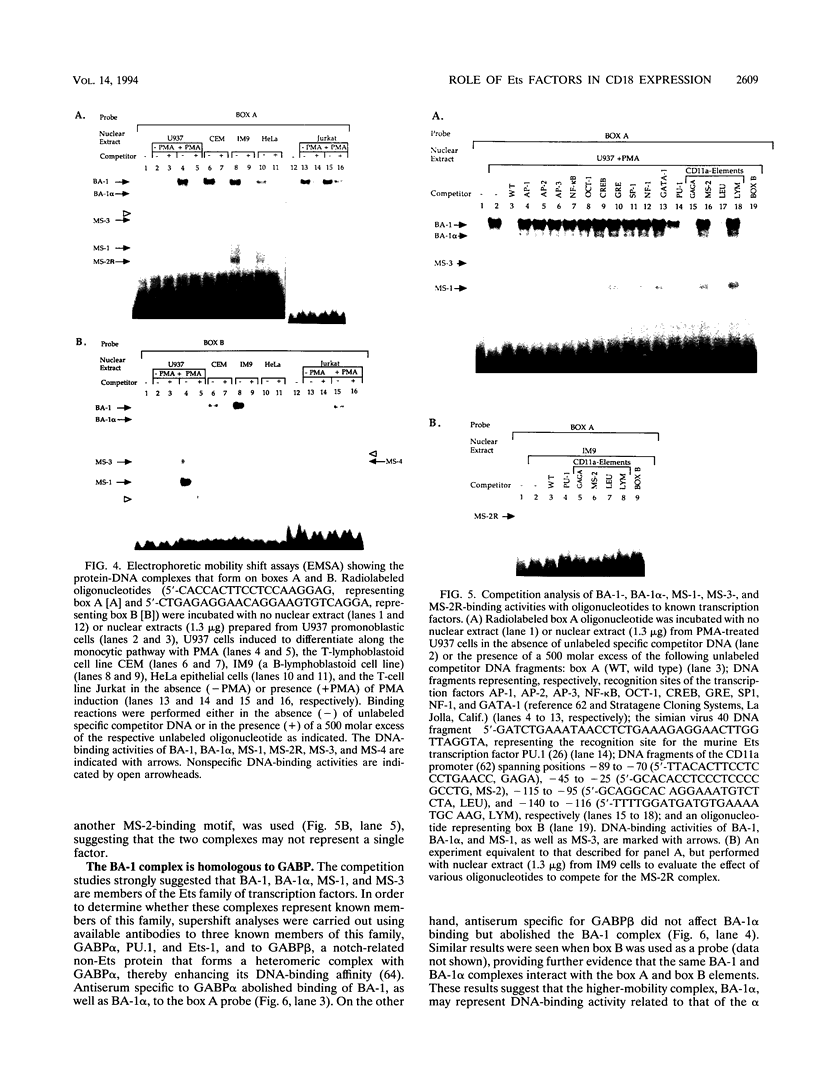
To define the minimal promoter responsible for expression of CD18 in myeloid and lymphoid cells, we generated 5' and 3' deletion constructs of a segment extending 785 bp upstream and 19 bp downstream of a major transcription start site and determined their effects on driving expression of the luciferase reporter gene in transfected hematopoietic cell lines. A region extending from nucleotides (nt) -302 to +19 was sufficient for cell-restricted and phorbol ester-inducible expression. DNase I footprinting of this region revealed two adjacent protected segments extending from nt -81 to -68 (box A) and -55 to -41 (box B). When a construct of 47 nt in length containing box A and box B and lacking other 3' or 5' elements was cloned into a promoterless vector, it conferred tissue-specific and phorbol ester-inducible expression. Gel retardation revealed that the protein components of two major protein-DNA complexes that form on both box A and box B and are required for transcriptional activation are members of the Ets oncoprotein family; one is related to the GA-binding protein (GABP), and the other is related to PU.1/Spi-1. The minimal CD18 promoter, lacking TATA, CAAT, and initiator elements and consisting primarily of Ets repeats, may exemplify an emerging class of promoters with which the concerted binding of Ets factors is necessary and sufficient to mediate transcriptional activation through direct recruitment of the basal transcription machinery.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agura E. D., Howard M., Collins S. J. Identification and sequence analysis of the promoter for the leukocyte integrin beta-subunit (CD18): a retinoic acid-inducible gene. Blood. 1992 Feb 1;79(3):602–609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnaout M. A. Leukocyte adhesion molecules deficiency: its structural basis, pathophysiology and implications for modulating the inflammatory response. Immunol Rev. 1990 Apr;114:145–180. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1990.tb00564.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnaout M. A., Remold-O'Donnell E., Pierce M. W., Harris P., Tenen D. G. Molecular cloning of the alpha subunit of human and guinea pig leukocyte adhesion glycoprotein Mo1: chromosomal localization and homology to the alpha subunits of integrins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2776–2780. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2776. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnaout M. A. Structure and function of the leukocyte adhesion molecules CD11/CD18. Blood. 1990 Mar 1;75(5):1037–1050. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-David Y., Giddens E. B., Letwin K., Bernstein A. Erythroleukemia induction by Friend murine leukemia virus: insertional activation of a new member of the ets gene family, Fli-1, closely linked to c-ets-1. Genes Dev. 1991 Jun;5(6):908–918. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.6.908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birkenmeier T. M., McQuillan J. J., Boedeker E. D., Argraves W. S., Ruoslahti E., Dean D. C. The alpha 5 beta 1 fibronectin receptor. Characterization of the alpha 5 gene promoter. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 25;266(30):20544–20549. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulukos K. E., Pognonec P., Begue A., Galibert F., Gesquière J. C., Stéhelin D., Ghysdael J. Identification in chickens of an evolutionarily conserved cellular ets-2 gene (c-ets-2) encoding nuclear proteins related to the products of the c-ets proto-oncogene. EMBO J. 1988 Mar;7(3):697–705. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02865.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown T. A., McKnight S. L. Specificities of protein-protein and protein-DNA interaction of GABP alpha and two newly defined ets-related proteins. Genes Dev. 1992 Dec;6(12B):2502–2512. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.12b.2502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burmeister M., Kim S., Price E. R., de Lange T., Tantravahi U., Myers R. M., Cox D. R. A map of the distal region of the long arm of human chromosome 21 constructed by radiation hybrid mapping and pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. Genomics. 1991 Jan;9(1):19–30. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90216-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burtis K. C., Thummel C. S., Jones C. W., Karim F. D., Hogness D. S. The Drosophila 74EF early puff contains E74, a complex ecdysone-inducible gene that encodes two ets-related proteins. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):85–99. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90217-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cervella P., Silengo L., Pastore C., Altruda F. Human beta 1-integrin gene expression is regulated by two promoter regions. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 5;268(7):5148–5155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen H. M., Pahl H. L., Scheibe R. J., Zhang D. E., Tenen D. G. The Sp1 transcription factor binds the CD11b promoter specifically in myeloid cells in vivo and is essential for myeloid-specific promoter activity. J Biol Chem. 1993 Apr 15;268(11):8230–8239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J. H. The proto-oncogene c-ets is preferentially expressed in lymphoid cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;5(11):2993–3000. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.11.2993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbi A. L., Larson R. S., Kishimoto T. K., Springer T. A., Morton C. C. Chromosomal location of the genes encoding the leukocyte adhesion receptors LFA-1, Mac-1 and p150,95. Identification of a gene cluster involved in cell adhesion. J Exp Med. 1988 May 1;167(5):1597–1607. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.5.1597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornwell R. D., Gollahon K. A., Hickstein D. D. Description of the leukocyte function-associated antigen 1 (LFA-1 or CD11a) promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 1;90(9):4221–4225. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.9.4221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalton S., Treisman R. Characterization of SAP-1, a protein recruited by serum response factor to the c-fos serum response element. Cell. 1992 Feb 7;68(3):597–612. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90194-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gille H., Sharrocks A. D., Shaw P. E. Phosphorylation of transcription factor p62TCF by MAP kinase stimulates ternary complex formation at c-fos promoter. Nature. 1992 Jul 30;358(6385):414–417. doi: 10.1038/358414a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goebl M. K. The PU.1 transcription factor is the product of the putative oncogene Spi-1. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1165–1166. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90676-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagemeier C., Bannister A. J., Cook A., Kouzarides T. The activation domain of transcription factor PU.1 binds the retinoblastoma (RB) protein and the transcription factor TFIID in vitro: RB shows sequence similarity to TFIID and TFIIB. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Feb 15;90(4):1580–1584. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.4.1580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanvey J. C., Peffer N. J., Bisi J. E., Thomson S. A., Cadilla R., Josey J. A., Ricca D. J., Hassman C. F., Bonham M. A., Au K. G. Antisense and antigene properties of peptide nucleic acids. Science. 1992 Nov 27;258(5087):1481–1485. doi: 10.1126/science.1279811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogge D. E., Misawa S., Parsa N. Z., Pollak A., Testa J. R. Abnormalities of chromosome 16 in association with acute myelomonocytic leukemia and dysplastic bone marrow eosinophils. J Clin Oncol. 1984 Jun;2(6):550–557. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1984.2.6.550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemsz M. J., Maki R. A., Papayannopoulou T., Moore J., Hromas R. Characterization of the ets oncogene family member, fli-1. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 15;268(8):5769–5773. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemsz M. J., McKercher S. R., Celada A., Van Beveren C., Maki R. A. The macrophage and B cell-specific transcription factor PU.1 is related to the ets oncogene. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):113–124. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90219-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kudo A., Sakaguchi N., Melchers F. Organization of the murine Ig-related lambda 5 gene transcribed selectively in pre-B lymphocytes. EMBO J. 1987 Jan;6(1):103–107. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04725.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar V., Chambon P. The estrogen receptor binds tightly to its responsive element as a ligand-induced homodimer. Cell. 1988 Oct 7;55(1):145–156. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90017-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaMarco K., Thompson C. C., Byers B. P., Walton E. M., McKnight S. L. Identification of Ets- and notch-related subunits in GA binding protein. Science. 1991 Aug 16;253(5021):789–792. doi: 10.1126/science.1876836. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Beau M. M., Larson R. A., Bitter M. A., Vardiman J. W., Golomb H. M., Rowley J. D. Association of an inversion of chromosome 16 with abnormal marrow eosinophils in acute myelomonocytic leukemia. A unique cytogenetic-clinicopathological association. N Engl J Med. 1983 Sep 15;309(11):630–636. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198309153091103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemarchandel V., Ghysdael J., Mignotte V., Rahuel C., Roméo P. H. GATA and Ets cis-acting sequences mediate megakaryocyte-specific expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;13(1):668–676. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.1.668. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung S., McCracken S., Ghysdael J., Miyamoto N. G. Requirement of an ETS-binding element for transcription of the human lck type I promoter. Oncogene. 1993 Apr;8(4):989–997. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- López-Cabrera M., Nueda A., Vara A., García-Aguilar J., Tugores A., Corbí A. L. Characterization of the p150,95 leukocyte integrin alpha subunit (CD11c) gene promoter. Identification of cis-acting elements. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 15;268(2):1187–1193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macleod K., Leprince D., Stehelin D. The ets gene family. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Jul;17(7):251–256. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90404-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller L. J., Schwarting R., Springer T. A. Regulated expression of the Mac-1, LFA-1, p150,95 glycoprotein family during leukocyte differentiation. J Immunol. 1986 Nov 1;137(9):2891–2900. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelsen B., Tian G., Erman B., Gregoire J., Maki R., Graves B., Sen R. Regulation of lymphoid-specific immunoglobulin mu heavy chain gene enhancer by ETS-domain proteins. Science. 1993 Jul 2;261(5117):82–86. doi: 10.1126/science.8316859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson C., Rabb H., Arnaout M. A. Genetic cause of leukocyte adhesion molecule deficiency. Abnormal splicing and a missense mutation in a conserved region of CD18 impair cell surface expression of beta 2 integrins. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 15;267(5):3351–3357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nye J. A., Petersen J. M., Gunther C. V., Jonsen M. D., Graves B. J. Interaction of murine ets-1 with GGA-binding sites establishes the ETS domain as a new DNA-binding motif. Genes Dev. 1992 Jun;6(6):975–990. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.6.975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pahl H. L., Rosmarin A. G., Tenen D. G. Characterization of the myeloid-specific CD11b promoter. Blood. 1992 Feb 15;79(4):865–870. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pahl H. L., Scheibe R. J., Zhang D. E., Chen H. M., Galson D. L., Maki R. A., Tenen D. G. The proto-oncogene PU.1 regulates expression of the myeloid-specific CD11b promoter. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 5;268(7):5014–5020. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pongubala J. M., Nagulapalli S., Klemsz M. J., McKercher S. R., Maki R. A., Atchison M. L. PU.1 recruits a second nuclear factor to a site important for immunoglobulin kappa 3' enhancer activity. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;12(1):368–378. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.1.368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pongubala J. M., Van Beveren C., Nagulapalli S., Klemsz M. J., McKercher S. R., Maki R. A., Atchison M. L. Effect of PU.1 phosphorylation on interaction with NF-EM5 and transcriptional activation. Science. 1993 Mar 12;259(5101):1622–1625. doi: 10.1126/science.8456286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter H., Weir L., Leder P. Enhancer-dependent expression of human kappa immunoglobulin genes introduced into mouse pre-B lymphocytes by electroporation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):7161–7165. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.7161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prandini M. H., Denarier E., Frachet P., Uzan G., Marguerie G. Isolation of the human platelet glycoprotein IIb gene and characterization of the 5' flanking region. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Oct 14;156(1):595–601. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80884-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pribyl L. J., Watson D. K., Schulz R. A., Papas T. S. D-elg, a member of the Drosophila ets gene family: sequence, expression and evolutionary comparison. Oncogene. 1991 Jul;6(7):1175–1183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prosser H. M., Wotton D., Gegonne A., Ghysdael J., Wang S., Speck N. A., Owen M. J. A phorbol ester response element within the human T-cell receptor beta-chain enhancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 15;89(20):9934–9938. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.20.9934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao V. N., Huebner K., Isobe M., ar-Rushdi A., Croce C. M., Reddy E. S. elk, tissue-specific ets-related genes on chromosomes X and 14 near translocation breakpoints. Science. 1989 Apr 7;244(4900):66–70. doi: 10.1126/science.2539641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao V. N., Papas T. S., Reddy E. S. erg, a human ets-related gene on chromosome 21: alternative splicing, polyadenylation, and translation. Science. 1987 Aug 7;237(4815):635–639. doi: 10.1126/science.3299708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray D., Bosselut R., Ghysdael J., Mattei M. G., Tavitian A., Moreau-Gachelin F. Characterization of Spi-B, a transcription factor related to the putative oncoprotein Spi-1/PU.1. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;12(10):4297–4304. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.10.4297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy E. S., Rao V. N. erg, an ets-related gene, codes for sequence-specific transcriptional activators. Oncogene. 1991 Dec;6(12):2285–2289. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts R., Gallagher J., Spooncer E., Allen T. D., Bloomfield F., Dexter T. M. Heparan sulphate bound growth factors: a mechanism for stromal cell mediated haemopoiesis. Nature. 1988 Mar 24;332(6162):376–378. doi: 10.1038/332376a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roesler W. J., Vandenbark G. R., Hanson R. W. Cyclic AMP and the induction of eukaryotic gene transcription. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 5;263(19):9063–9066. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal P., Rimm I. J., Umiel T., Griffin J. D., Osathanondh R., Schlossman S. F., Nadler L. M. Ontogeny of human hematopoietic cells: analysis utilizing monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol. 1983 Jul;131(1):232–237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosmarin A. G., Levy R., Tenen D. G. Cloning and analysis of the CD18 promoter. Blood. 1992 May 15;79(10):2598–2604. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosmarin A. G., Weil S. C., Rosner G. L., Griffin J. D., Arnaout M. A., Tenen D. G. Differential expression of CD11b/CD18 (Mo1) and myeloperoxidase genes during myeloid differentiation. Blood. 1989 Jan;73(1):131–136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin C. M., Larson R. A., Bitter M. A., Carrino J. J., Le Beau M. M., Diaz M. O., Rowley J. D. Association of a chromosomal 3;21 translocation with the blast phase of chronic myelogenous leukemia. Blood. 1987 Nov;70(5):1338–1342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryseck R. P., Bravo R. c-JUN, JUN B, and JUN D differ in their binding affinities to AP-1 and CRE consensus sequences: effect of FOS proteins. Oncogene. 1991 Apr;6(4):533–542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacchi N., Nalbantoglu J., Sergovich F. R., Papas T. S. Human ETS2 gene on chromosome 21 is not rearranged in Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(20):7675–7679. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.20.7675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelley C. S., Arnaout M. A. The promoter of the CD11b gene directs myeloid-specific and developmentally regulated expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10525–10529. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelley C. S., Farokhzad O. C., Arnaout M. A. Identification of cell-specific and developmentally regulated nuclear factors that direct myeloid and lymphoid expression of the CD11a gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 1;90(11):5364–5368. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.11.5364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson C. B., Wang C. Y., Ho I. C., Bohjanen P. R., Petryniak B., June C. H., Miesfeldt S., Zhang L., Nabel G. J., Karpinski B. cis-acting sequences required for inducible interleukin-2 enhancer function bind a novel Ets-related protein, Elf-1. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;12(3):1043–1053. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.3.1043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson C. C., Brown T. A., McKnight S. L. Convergence of Ets- and notch-related structural motifs in a heteromeric DNA binding complex. Science. 1991 Aug 16;253(5021):762–768. doi: 10.1126/science.1876833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travis A., Hagman J., Grosschedl R. Heterogeneously initiated transcription from the pre-B- and B-cell-specific mb-1 promoter: analysis of the requirement for upstream factor-binding sites and initiation site sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;11(11):5756–5766. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.11.5756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urness L. D., Thummel C. S. Molecular interactions within the ecdysone regulatory hierarchy: DNA binding properties of the Drosophila ecdysone-inducible E74A protein. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):47–61. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90287-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virbasius J. V., Virbasius C. A., Scarpulla R. C. Identity of GABP with NRF-2, a multisubunit activator of cytochrome oxidase expression, reveals a cellular role for an ETS domain activator of viral promoters. Genes Dev. 1993 Mar;7(3):380–392. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.3.380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk B., Wasylyk C., Flores P., Begue A., Leprince D., Stehelin D. The c-ets proto-oncogenes encode transcription factors that cooperate with c-Fos and c-Jun for transcriptional activation. Nature. 1990 Jul 12;346(6280):191–193. doi: 10.1038/346191a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk C., Gutman A., Nicholson R., Wasylyk B. The c-Ets oncoprotein activates the stromelysin promoter through the same elements as several non-nuclear oncoproteins. EMBO J. 1991 May;10(5):1127–1134. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08053.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe H., Sawada J., Yano K., Yamaguchi K., Goto M., Handa H. cDNA cloning of transcription factor E4TF1 subunits with Ets and notch motifs. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;13(3):1385–1391. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.3.1385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xin J. H., Cowie A., Lachance P., Hassell J. A. Molecular cloning and characterization of PEA3, a new member of the Ets oncogene family that is differentially expressed in mouse embryonic cells. Genes Dev. 1992 Mar;6(3):481–496. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.3.481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y., Rom W. N. Regulation of the interleukin-1 beta (IL-1 beta) gene by mycobacterial components and lipopolysaccharide is mediated by two nuclear factor-IL6 motifs. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;13(6):3831–3837. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.6.3831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]