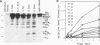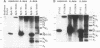Abstract
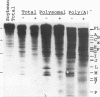
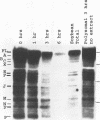
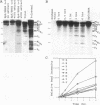
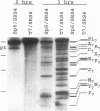
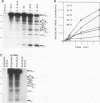
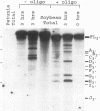
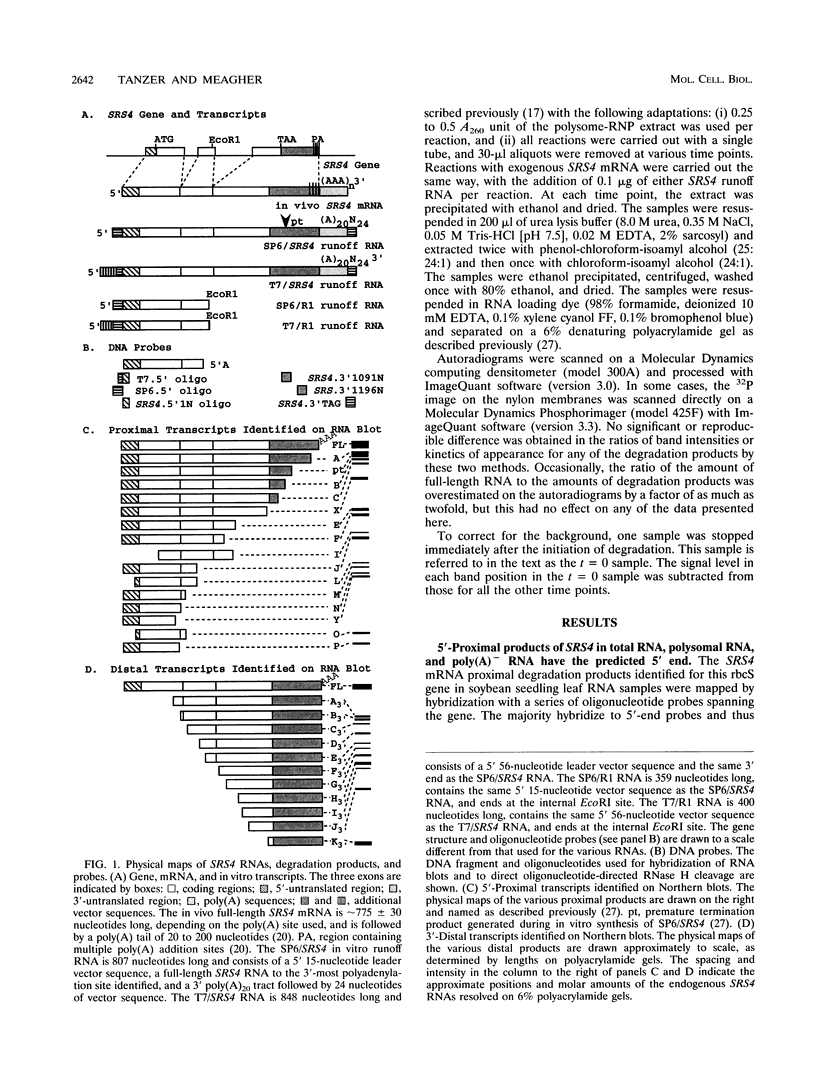
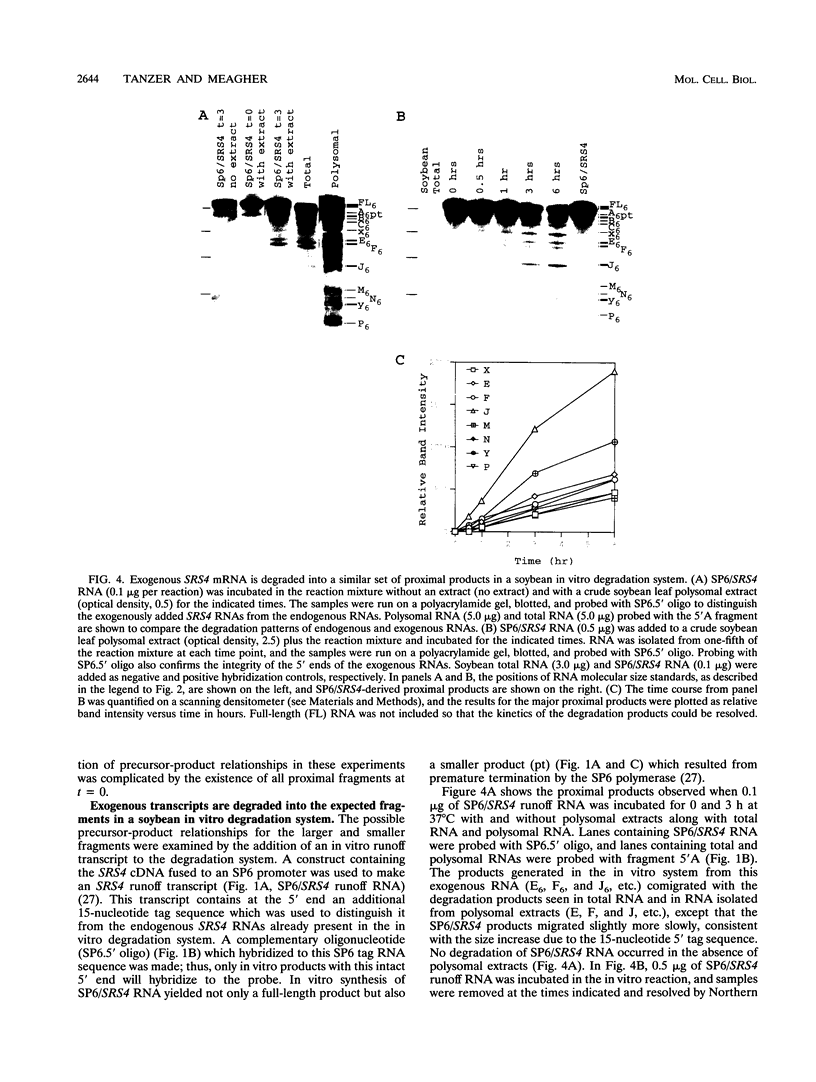
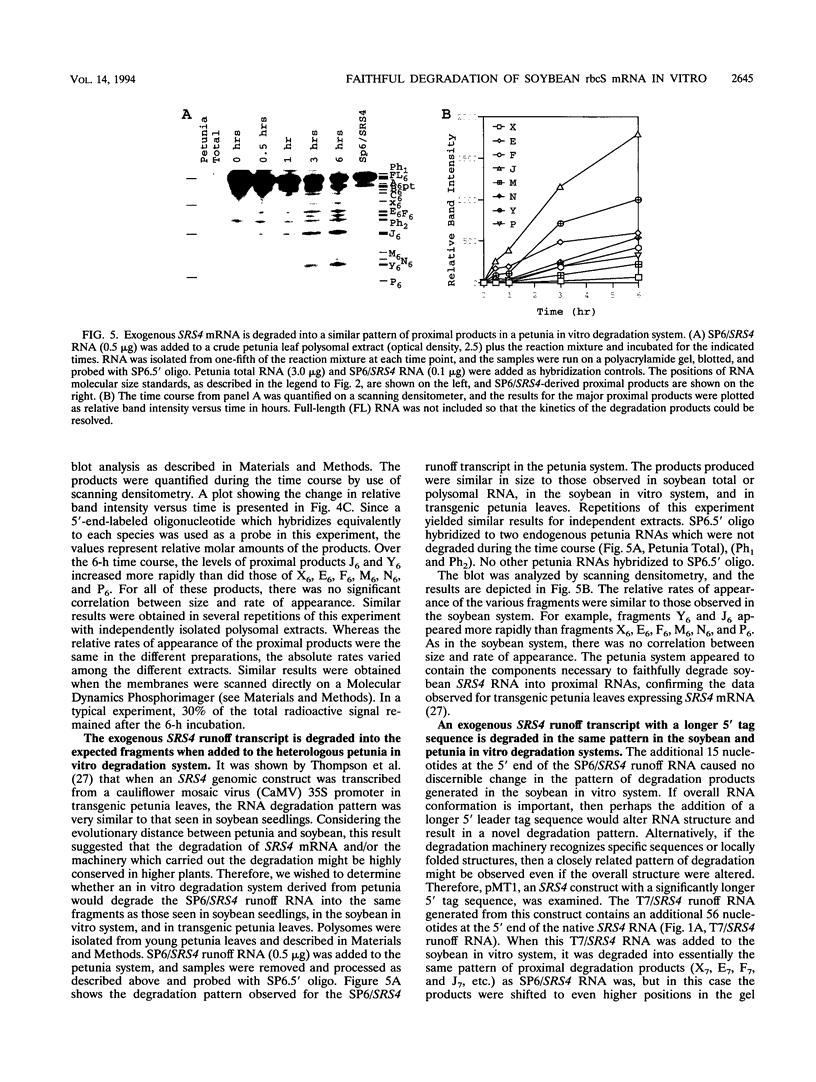
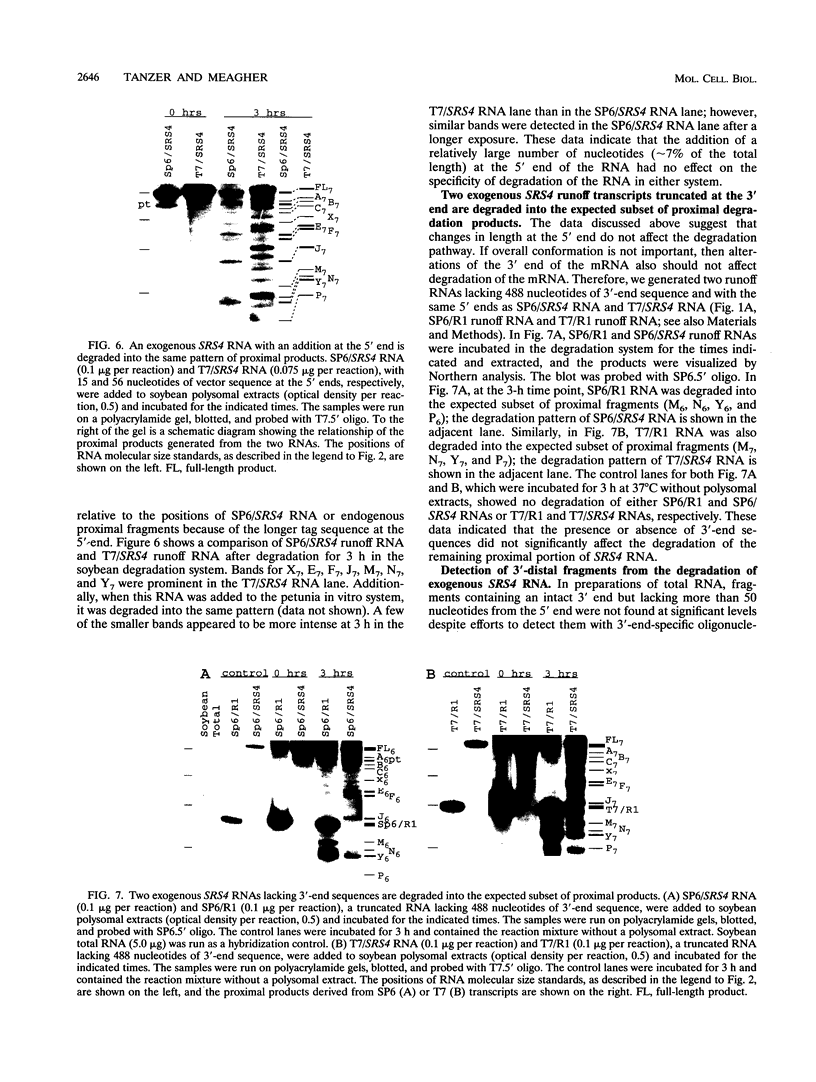
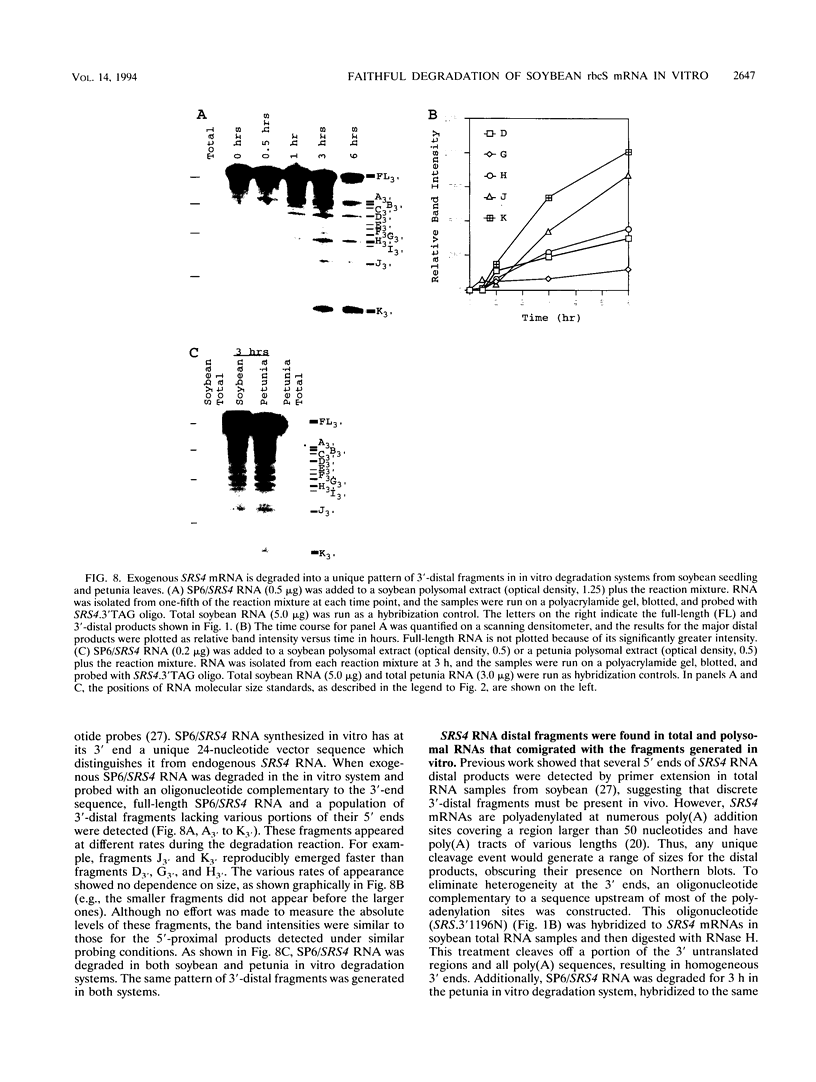
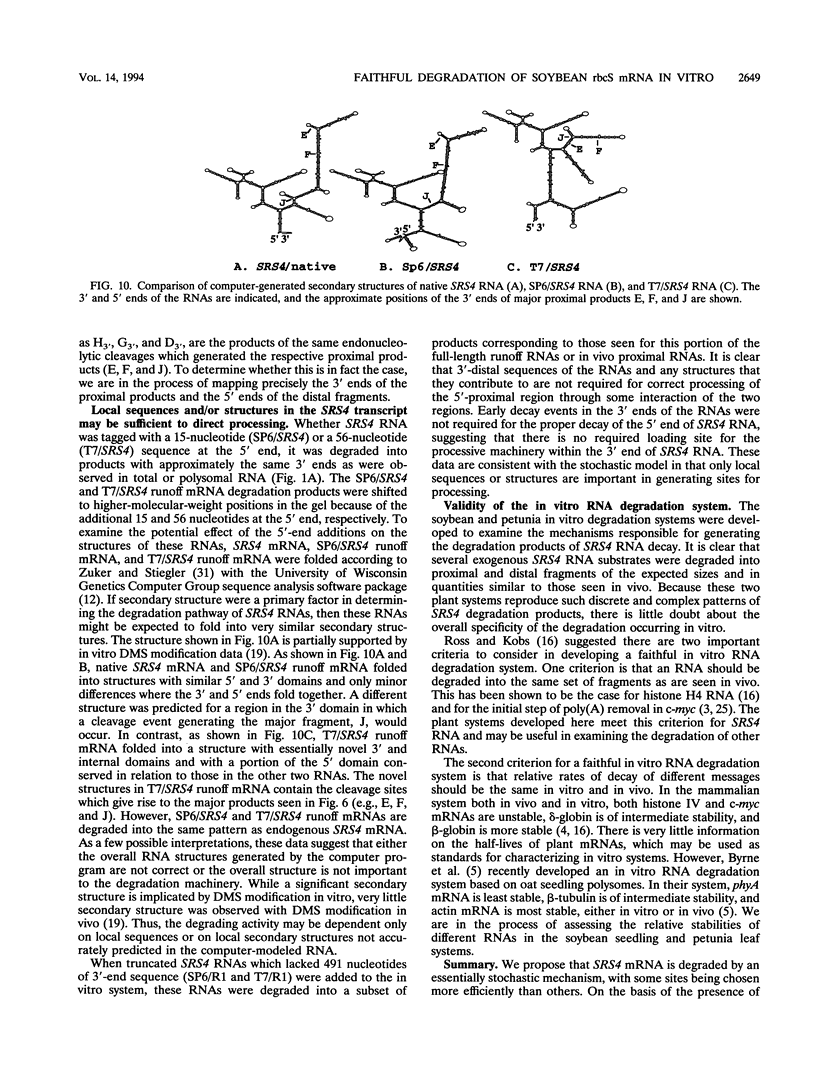
The mRNA encoding the soybean rbcS gene, SRS4, is degraded into a set of discrete lower-molecular-weight products in light-grown soybean seedlings and in transgenic petunia leaves. The 5'-proximal products have intact 5' ends, lack poly(A) tails, lack various amounts of 3'-end sequences, and are found at higher concentrations in the polysomal fraction. To study the mechanisms of SRS4 mRNA decay more closely, we developed a cell-free RNA degradation system based on a polysomal fraction isolated from soybean seedlings or mature petunia leaves. In the soybean in vitro degradation system, endogenous SRS4 mRNA and proximal product levels decreased over a 6-h time course. When full-length in vitro-synthesized SRS4 RNAs were added to either in vitro degradation system, the RNAs were degraded into the expected set of proximal products, such as those observed for total endogenous RNA samples. When exogenously added SRS4 RNAs already truncated at their 3' ends were added to either system, they too were degraded into the expected subset of proximal products. A set of distal fragments containing intact 3' ends and lacking various portions of 5'-end sequences were identified in vivo when the heterogeneous 3' ends of the SRS4 RNAs were removed by oligonucleotide-directed RNase H cleavage. Significant amounts of distal fragments which comigrated with the in vivo products were also observed when exogenous SRS4 RNAs were degraded in either in vitro system. These proximal and distal products lacking various portions of their 3' and 5' sequences, respectively, were generated in essentially a random order, a result supporting a nonprocessive mechanism. Tagging of the in vitro-synthesized RNAs on their 5' and 3' ends with plasmid vector sequences or truncation of the 3' end had no apparent effect on the degradation pattern. Therefore, RNA sequences and/or structures in the immediate vicinity of each 3' end point may be important in the degradation machinery. Together, these data suggest that SRS4 mRNA is degraded by a stochastic mechanism and that endonucleolytic cleavage may be the initial event. These plant in vitro systems should be useful in identifying the cis- and trans-acting factors involved in the degradation of mRNAs.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Belasco J. G., Higgins C. F. Mechanisms of mRNA decay in bacteria: a perspective. Gene. 1988 Dec 10;72(1-2):15–23. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90123-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein P. L., Herrick D. J., Prokipcak R. D., Ross J. Control of c-myc mRNA half-life in vitro by a protein capable of binding to a coding region stability determinant. Genes Dev. 1992 Apr;6(4):642–654. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.4.642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer G., Ross J. Messenger RNA turnover in cell-free extracts. Methods Enzymol. 1990;181:202–209. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)81122-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer G., Ross J. Poly(A) shortening and degradation of the 3' A+U-rich sequences of human c-myc mRNA in a cell-free system. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1697–1708. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrazana E. J., Pasieka K. B., Majzoub J. A. The vasopressin mRNA poly(A) tract is unusually long and increases during stimulation of vasopressin gene expression in vivo. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jun;8(6):2267–2274. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.6.2267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claverie-Martin F., Diaz-Torres M. R., Yancey S. D., Kushner S. R. Analysis of the altered mRNA stability (ams) gene from Escherichia coli. Nucleotide sequence, transcriptional analysis, and homology of its product to MRP3, a mitochondrial ribosomal protein from Neurospora crassa. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 15;266(5):2843–2851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies E., Fillingham B. D., Oto Y., Abe S. Evidence for the existence of cytoskeleton-bound polysomes in plants. Cell Biol Int Rep. 1991 Oct;15(10):973–981. doi: 10.1016/0309-1651(91)90147-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larkins B. A., Davies E. Polyribosomes from Peas: V. An Attempt to Characterize the Total Free and Membrane-bound Polysomal Population. Plant Physiol. 1975 Apr;55(4):749–756. doi: 10.1104/pp.55.4.749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pei R., Calame K. Differential stability of c-myc mRNAS in a cell-free system. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jul;8(7):2860–2868. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.7.2860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross J., Kobs G., Brewer G., Peltz S. W. Properties of the exonuclease activity that degrades H4 histone mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 5;262(19):9374–9381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross J., Kobs G. H4 histone messenger RNA decay in cell-free extracts initiates at or near the 3' terminus and proceeds 3' to 5'. J Mol Biol. 1986 Apr 20;188(4):579–593. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(86)80008-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowland L. J., Strommer J. N. Anaerobic treatment of maize roots affects transcription of Adh1 and transcript stability. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;6(10):3368–3372. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.10.3368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senecoff J. F., Meagher R. B. In vivo analysis of plant RNA structure: soybean 18S ribosomal and ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase small subunit RNAs. Plant Mol Biol. 1992 Jan;18(2):219–234. doi: 10.1007/BF00034951. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirley B. W., Ham D. P., Senecoff J. F., Berry-Lowe S. L., Zurfluh L. L., Shah D. M., Meagher R. B. Comparison of the expression of two highly homologous members of the soybean ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase small subunit gene family. Plant Mol Biol. 1990 Jun;14(6):909–925. doi: 10.1007/BF00019389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirley B. W., Meagher R. B. A potential role for RNA turnover in the light regulation of plant gene expression: ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase small subunit in soybean. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jun 11;18(11):3377–3385. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.11.3377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shure M., Wessler S., Fedoroff N. Molecular identification and isolation of the Waxy locus in maize. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):225–233. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90225-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stolle C. A., Payne M. S., Benz E. J., Jr Equal stabilities of normal beta globin and nontranslatable beta0 -39 thalassemic transcripts in cell-free extracts. Blood. 1987 Jul;70(1):293–300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sunitha I., Slobin L. I. An in vitro system derived from Friend erythroleukemia cells to study messenger RNA stability. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Apr 29;144(2):560–568. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(87)80003-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swartwout S. G., Kinniburgh A. J. c-myc RNA degradation in growing and differentiating cells: possible alternate pathways. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jan;9(1):288–295. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.1.288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson D. M., Meagher R. B. Transcriptional and post-transcriptional processes regulate expression of RNA encoding the small subunit of ribulose-1,5-biphosphate carboxylase differently in petunia and in soybean. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jun 25;18(12):3621–3629. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.12.3621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson D. M., Tanzer M. M., Meagher R. B. Degradation products of the mRNA encoding the small subunit of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase in soybean and transgenic petunia. Plant Cell. 1992 Jan;4(1):47–58. doi: 10.1105/tpc.4.1.47. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vreken P., Buddelmeijer N., Raué H. A. A cell-free extract from yeast cells for studying mRNA turnover. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 May 25;20(10):2503–2510. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.10.2503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walling L., Drews G. N., Goldberg R. B. Transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation of soybean seed protein mRNA levels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(7):2123–2127. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.7.2123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wanner L. A., Gruissem W. Expression dynamics of the tomato rbcS gene family during development. Plant Cell. 1991 Dec;3(12):1289–1303. doi: 10.1105/tpc.3.12.1289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuker M., Stiegler P. Optimal computer folding of large RNA sequences using thermodynamics and auxiliary information. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 10;9(1):133–148. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.1.133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]