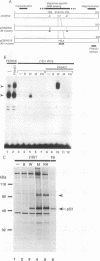
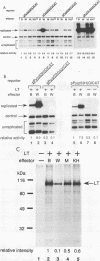
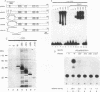
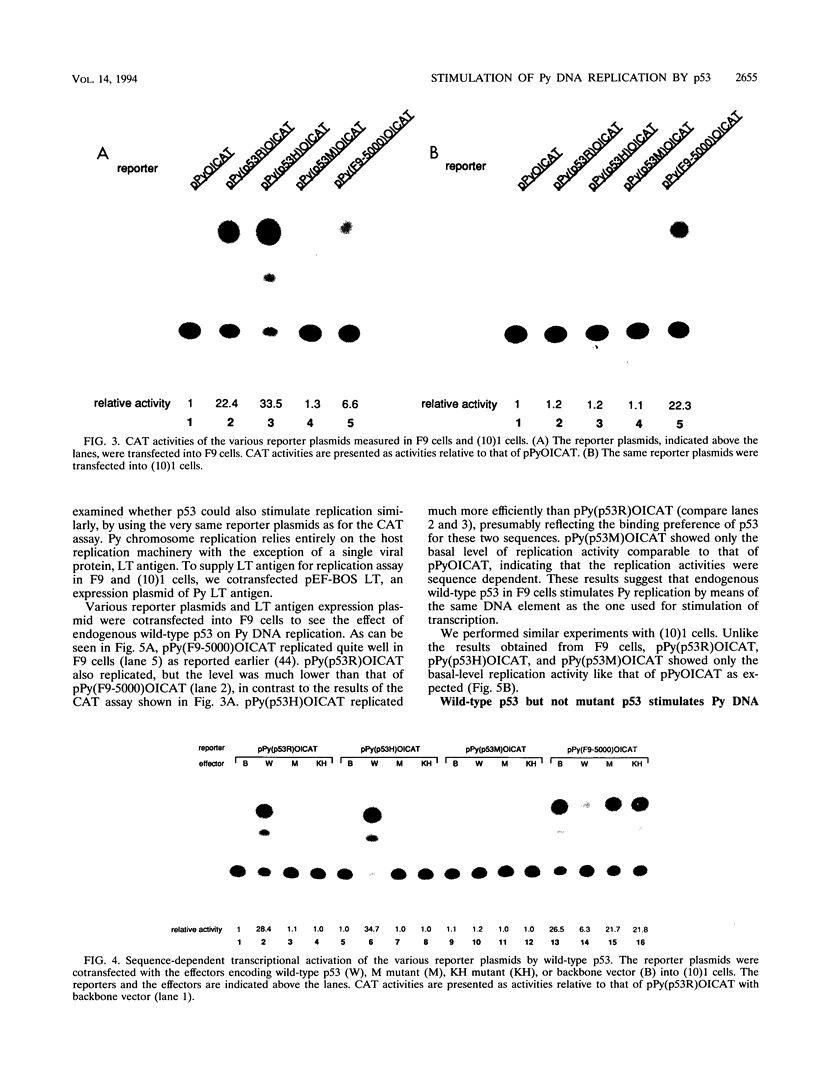
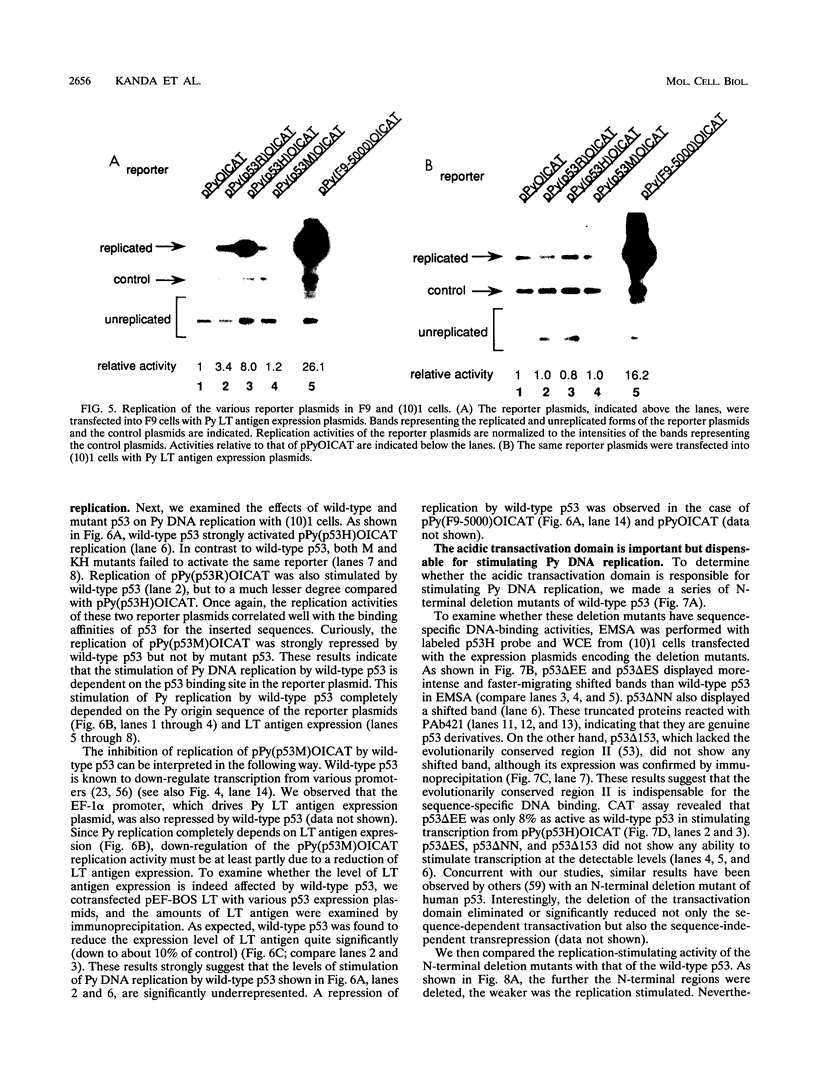
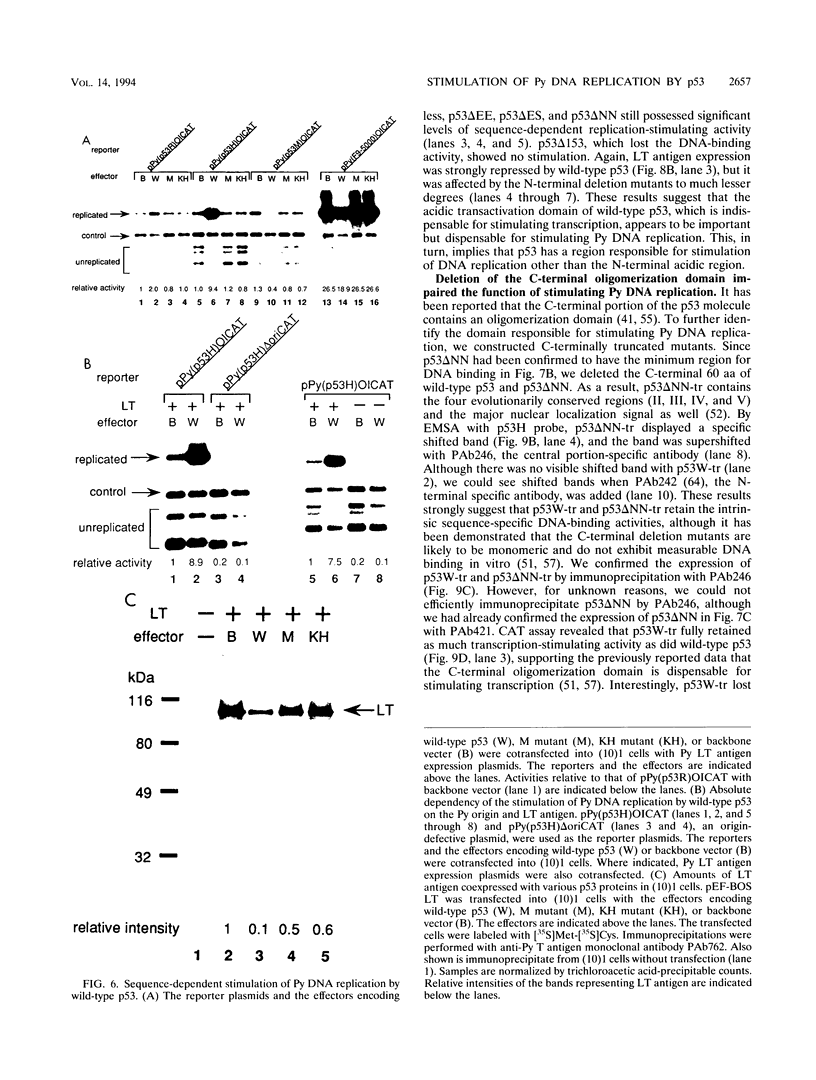
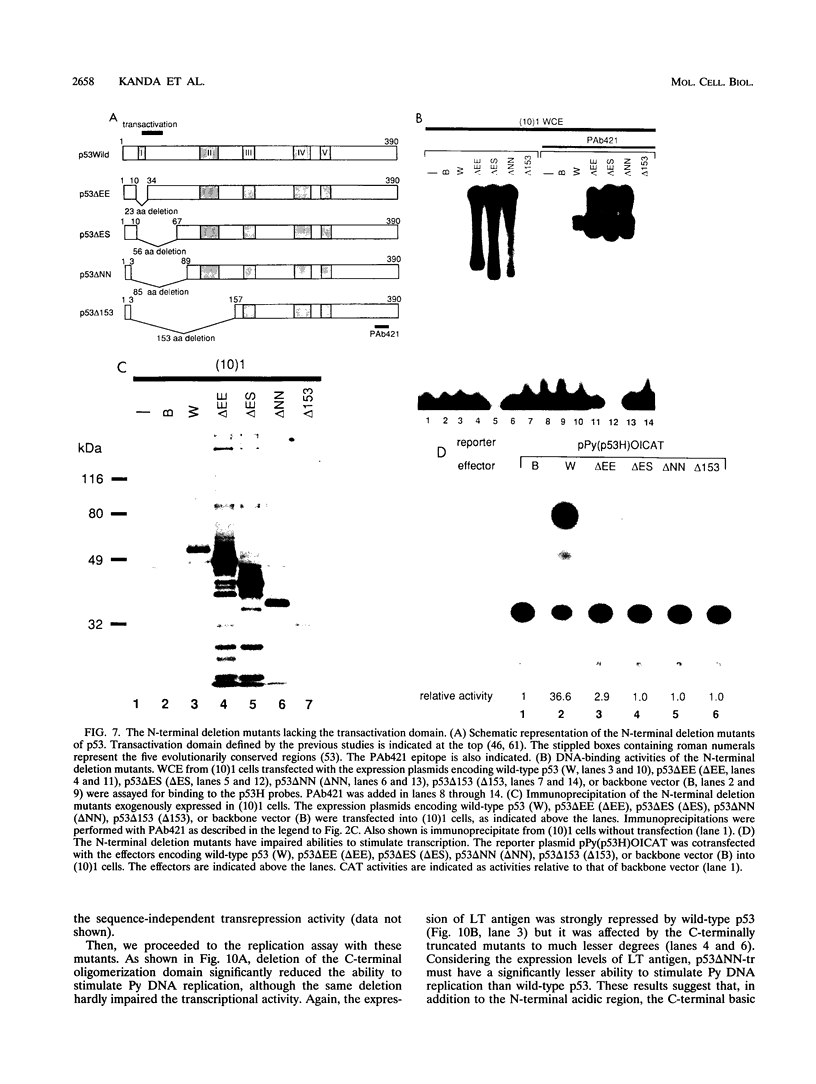
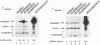Abstract
The tumor suppressor p53 possesses characteristics of a transcription factor; it binds to specific DNA sequences and activates transcription from various promoters. Here we found that murine wild-type p53 stimulated not only transcription but also polyomavirus (Py) DNA replication in a sequence-dependent manner. Oncogenic mutant p53, lacking the DNA-binding activity, showed no stimulation of Py DNA replication. Deletion of the N-terminal acidic transactivation domain of wild-type p53, which completely eliminated the ability to stimulate transcription, only impaired the function to stimulate Py DNA replication. The replication-stimulating activity of wild-type p53 was impaired by the deletion of the C-terminal oligomerization domain as well, without affecting the ability to stimulate transcription. The region responsible for the sequence-specific DNA-binding activity mapped to the central portion of the p53 molecule has a minimal activity. The results indicate that both the N-terminal and the C-terminal regions significantly contribute to the p53-mediated stimulation of Py DNA replication.
Full text
PDF

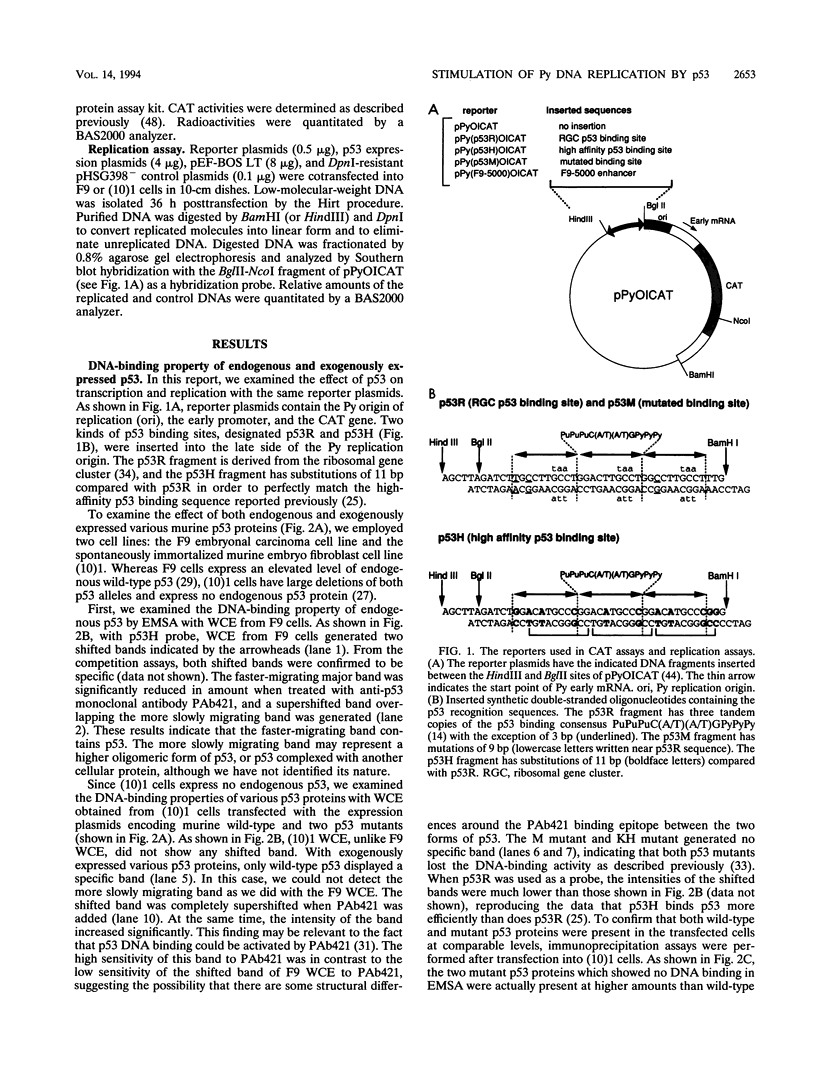
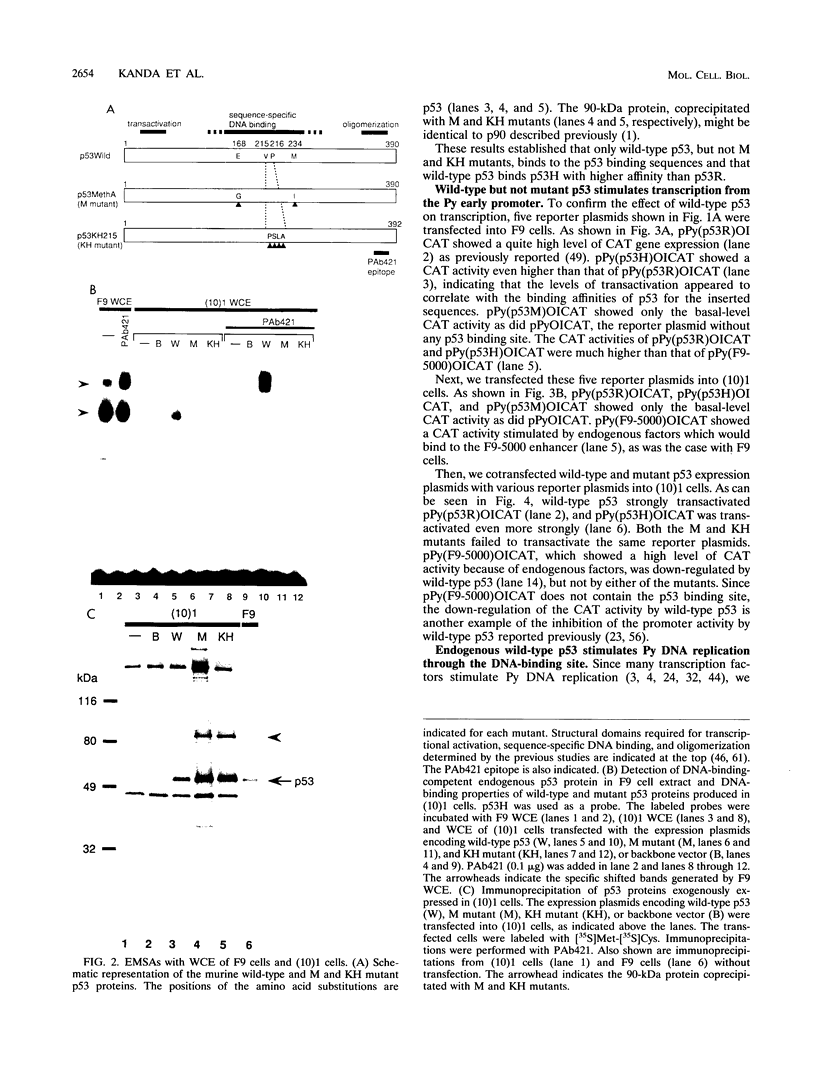




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barak Y., Oren M. Enhanced binding of a 95 kDa protein to p53 in cells undergoing p53-mediated growth arrest. EMBO J. 1992 Jun;11(6):2115–2121. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05270.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bargonetti J., Friedman P. N., Kern S. E., Vogelstein B., Prives C. Wild-type but not mutant p53 immunopurified proteins bind to sequences adjacent to the SV40 origin of replication. Cell. 1991 Jun 14;65(6):1083–1091. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90560-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baru M., Shlissel M., Manor H. The yeast GAL4 protein transactivates the polyomavirus origin of DNA replication in mouse cells. J Virol. 1991 Jul;65(7):3496–3503. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.7.3496-3503.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett-Cook E. R., Hassell J. A. Activation of polyomavirus DNA replication by yeast GAL4 is dependent on its transcriptional activation domains. EMBO J. 1991 Apr;10(4):959–969. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08030.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braithwaite A. W., Sturzbecher H. W., Addison C., Palmer C., Rudge K., Jenkins J. R. Mouse p53 inhibits SV40 origin-dependent DNA replication. Nature. 1987 Oct 1;329(6138):458–460. doi: 10.1038/329458a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C., Okayama H. High-efficiency transformation of mammalian cells by plasmid DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2745–2752. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng L. Z., Workman J. L., Kingston R. E., Kelly T. J. Regulation of DNA replication in vitro by the transcriptional activation domain of GAL4-VP16. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 15;89(2):589–593. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.2.589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng L., Kelly T. J. Transcriptional activator nuclear factor I stimulates the replication of SV40 minichromosomes in vivo and in vitro. Cell. 1989 Nov 3;59(3):541–551. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90037-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DePamphilis M. L. Transcriptional elements as components of eukaryotic origins of DNA replication. Cell. 1988 Mar 11;52(5):635–638. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90398-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diller L., Kassel J., Nelson C. E., Gryka M. A., Litwak G., Gebhardt M., Bressac B., Ozturk M., Baker S. J., Vogelstein B. p53 functions as a cell cycle control protein in osteosarcomas. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;10(11):5772–5781. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.11.5772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dilworth S. M., Brewster C. E., Jones M. D., Lanfrancone L., Pelicci G., Pelicci P. G. Transformation by polyoma virus middle T-antigen involves the binding and tyrosine phosphorylation of Shc. Nature. 1994 Jan 6;367(6458):87–90. doi: 10.1038/367087a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutta A., Ruppert J. M., Aster J. C., Winchester E. Inhibition of DNA replication factor RPA by p53. Nature. 1993 Sep 2;365(6441):79–82. doi: 10.1038/365079a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliyahu D., Goldfinger N., Pinhasi-Kimhi O., Shaulsky G., Skurnik Y., Arai N., Rotter V., Oren M. Meth A fibrosarcoma cells express two transforming mutant p53 species. Oncogene. 1988 Sep;3(3):313–321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliyahu D., Michalovitz D., Eliyahu S., Pinhasi-Kimhi O., Oren M. Wild-type p53 can inhibit oncogene-mediated focus formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8763–8767. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer G., Bargonetti J., Zhu H., Friedman P., Prywes R., Prives C. Wild-type p53 activates transcription in vitro. Nature. 1992 Jul 2;358(6381):83–86. doi: 10.1038/358083a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields S., Jang S. K. Presence of a potent transcription activating sequence in the p53 protein. Science. 1990 Aug 31;249(4972):1046–1049. doi: 10.1126/science.2144363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay C. A., Hinds P. W., Tan T. H., Eliyahu D., Oren M., Levine A. J. Activating mutations for transformation by p53 produce a gene product that forms an hsc70-p53 complex with an altered half-life. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):531–539. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman P. N., Kern S. E., Vogelstein B., Prives C. Wild-type, but not mutant, human p53 proteins inhibit the replication activities of simian virus 40 large tumor antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(23):9275–9279. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.23.9275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funk W. D., Pak D. T., Karas R. H., Wright W. E., Shay J. W. A transcriptionally active DNA-binding site for human p53 protein complexes. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;12(6):2866–2871. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.6.2866. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gannon J. V., Lane D. P. p53 and DNA polymerase alpha compete for binding to SV40 T antigen. Nature. 1987 Oct 1;329(6138):456–458. doi: 10.1038/329456a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsberg D., Mechta F., Yaniv M., Oren M. Wild-type p53 can down-modulate the activity of various promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 15;88(22):9979–9983. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.22.9979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo Z. S., DePamphilis M. L. Specific transcription factors stimulate simian virus 40 and polyomavirus origins of DNA replication. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;12(6):2514–2524. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.6.2514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halazonetis T. D., Davis L. J., Kandil A. N. Wild-type p53 adopts a 'mutant'-like conformation when bound to DNA. EMBO J. 1993 Mar;12(3):1021–1028. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05743.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halazonetis T. D., Kandil A. N. Conformational shifts propagate from the oligomerization domain of p53 to its tetrameric DNA binding domain and restore DNA binding to select p53 mutants. EMBO J. 1993 Dec 15;12(13):5057–5064. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06199.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey D. M., Levine A. J. p53 alteration is a common event in the spontaneous immortalization of primary BALB/c murine embryo fibroblasts. Genes Dev. 1991 Dec;5(12B):2375–2385. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.12b.2375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He Z., Brinton B. T., Greenblatt J., Hassell J. A., Ingles C. J. The transactivator proteins VP16 and GAL4 bind replication factor A. Cell. 1993 Jun 18;73(6):1223–1232. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90650-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinds P., Finlay C., Levine A. J. Mutation is required to activate the p53 gene for cooperation with the ras oncogene and transformation. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):739–746. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.739-746.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollstein M., Sidransky D., Vogelstein B., Harris C. C. p53 mutations in human cancers. Science. 1991 Jul 5;253(5015):49–53. doi: 10.1126/science.1905840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hupp T. R., Meek D. W., Midgley C. A., Lane D. P. Regulation of the specific DNA binding function of p53. Cell. 1992 Nov 27;71(5):875–886. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90562-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa H., Asano M., Kanda T., Kumar S., Gélinas C., Ito Y. Two novel functions associated with the Rel oncoproteins: DNA replication and cell-specific transcriptional activation. Oncogene. 1993 Nov;8(11):2889–2896. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern S. E., Kinzler K. W., Baker S. J., Nigro J. M., Rotter V., Levine A. J., Friedman P., Prives C., Vogelstein B. Mutant p53 proteins bind DNA abnormally in vitro. Oncogene. 1991 Jan;6(1):131–136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern S. E., Kinzler K. W., Bruskin A., Jarosz D., Friedman P., Prives C., Vogelstein B. Identification of p53 as a sequence-specific DNA-binding protein. Science. 1991 Jun 21;252(5013):1708–1711. doi: 10.1126/science.2047879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern S. E., Pietenpol J. A., Thiagalingam S., Seymour A., Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B. Oncogenic forms of p53 inhibit p53-regulated gene expression. Science. 1992 May 8;256(5058):827–830. doi: 10.1126/science.1589764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine A. J., Momand J., Finlay C. A. The p53 tumour suppressor gene. Nature. 1991 Jun 6;351(6326):453–456. doi: 10.1038/351453a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li R., Botchan M. R. The acidic transcriptional activation domains of VP16 and p53 bind the cellular replication protein A and stimulate in vitro BPV-1 DNA replication. Cell. 1993 Jun 18;73(6):1207–1221. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90649-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mack D. H., Vartikar J., Pipas J. M., Laimins L. A. Specific repression of TATA-mediated but not initiator-mediated transcription by wild-type p53. Nature. 1993 May 20;363(6426):281–283. doi: 10.1038/363281a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez J., Georgoff I., Martinez J., Levine A. J. Cellular localization and cell cycle regulation by a temperature-sensitive p53 protein. Genes Dev. 1991 Feb;5(2):151–159. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.2.151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercer W. E., Nelson D., DeLeo A. B., Old L. J., Baserga R. Microinjection of monoclonal antibody to protein p53 inhibits serum-induced DNA synthesis in 3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(20):6309–6312. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.20.6309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner J., Medcalf E. A. Cotranslation of activated mutant p53 with wild type drives the wild-type p53 protein into the mutant conformation. Cell. 1991 May 31;65(5):765–774. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90384-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizushima S., Nagata S. pEF-BOS, a powerful mammalian expression vector. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Sep 11;18(17):5322–5322. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.17.5322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami Y., Asano M., Satake M., Ito Y. A tumor promoting phorbol ester, TPA, enhances polyomavirus DNA replication by activating the function of the viral enhancer. Oncogene. 1990 Jan;5(1):5–13. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami Y., Satake M., Yamaguchi-Iwai Y., Sakai M., Muramatsu M., Ito Y. The nuclear protooncogenes c-jun and c-fos as regulators of DNA replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3947–3951. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagano M., Dürst M., Joswig S., Draetta G., Jansen-Dürr P. Binding of the human E2F transcription factor to the retinoblastoma protein but not to cyclin A is abolished in HPV-16-immortalized cells. Oncogene. 1992 Sep;7(9):1681–1686. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raycroft L., Wu H. Y., Lozano G. Transcriptional activation by wild-type but not transforming mutants of the p53 anti-oncogene. Science. 1990 Aug 31;249(4972):1049–1051. doi: 10.1126/science.2144364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segawa K., Minowa A., Sugasawa K., Takano T., Hanaoka F. Abrogation of p53-mediated transactivation by SV40 large T antigen. Oncogene. 1993 Mar;8(3):543–548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seto E., Usheva A., Zambetti G. P., Momand J., Horikoshi N., Weinmann R., Levine A. J., Shenk T. Wild-type p53 binds to the TATA-binding protein and represses transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 15;89(24):12028–12032. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.24.12028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaulian E., Zauberman A., Milner J., Davies E. A., Oren M. Tight DNA binding and oligomerization are dispensable for the ability of p53 to transactivate target genes and suppress transformation. EMBO J. 1993 Jul;12(7):2789–2797. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05940.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaulsky G., Goldfinger N., Ben-Ze'ev A., Rotter V. Nuclear accumulation of p53 protein is mediated by several nuclear localization signals and plays a role in tumorigenesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6565–6577. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soussi T., Caron de Fromentel C., May P. Structural aspects of the p53 protein in relation to gene evolution. Oncogene. 1990 Jul;5(7):945–952. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stillman B. Initiation of eukaryotic DNA replication in vitro. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1989;5:197–245. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.05.110189.001213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stürzbecher H. W., Brain R., Addison C., Rudge K., Remm M., Grimaldi M., Keenan E., Jenkins J. R. A C-terminal alpha-helix plus basic region motif is the major structural determinant of p53 tetramerization. Oncogene. 1992 Aug;7(8):1513–1523. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subler M. A., Martin D. W., Deb S. Inhibition of viral and cellular promoters by human wild-type p53. J Virol. 1992 Aug;66(8):4757–4762. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.8.4757-4762.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarunina M., Jenkins J. R. Human p53 binds DNA as a protein homodimer but monomeric variants retain full transcription transactivation activity. Oncogene. 1993 Nov;8(11):3165–3173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truant R., Xiao H., Ingles C. J., Greenblatt J. Direct interaction between the transcriptional activation domain of human p53 and the TATA box-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 5;268(4):2284–2287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unger T., Mietz J. A., Scheffner M., Yee C. L., Howley P. M. Functional domains of wild-type and mutant p53 proteins involved in transcriptional regulation, transdominant inhibition, and transformation suppression. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Sep;13(9):5186–5194. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.9.5186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasseur M., Katinka M., Herbomel P., Yaniv M., Blangy D. Physical and biological features of polyoma virus mutants able to infect embryonal carcinoma cell lines. J Virol. 1982 Sep;43(3):800–808. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.3.800-808.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogelstein B., Kinzler K. W. p53 function and dysfunction. Cell. 1992 Aug 21;70(4):523–526. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90421-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang E. H., Friedman P. N., Prives C. The murine p53 protein blocks replication of SV40 DNA in vitro by inhibiting the initiation functions of SV40 large T antigen. Cell. 1989 May 5;57(3):379–392. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90913-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcock D., Lane D. P. Localization of p53, retinoblastoma and host replication proteins at sites of viral replication in herpes-infected cells. Nature. 1991 Jan 31;349(6308):429–431. doi: 10.1038/349429a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yewdell J. W., Gannon J. V., Lane D. P. Monoclonal antibody analysis of p53 expression in normal and transformed cells. J Virol. 1986 Aug;59(2):444–452. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.2.444-452.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zambetti G. P., Bargonetti J., Walker K., Prives C., Levine A. J. Wild-type p53 mediates positive regulation of gene expression through a specific DNA sequence element. Genes Dev. 1992 Jul;6(7):1143–1152. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.7.1143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Villiers J., Schaffner W., Tyndall C., Lupton S., Kamen R. Polyoma virus DNA replication requires an enhancer. Nature. 1984 Nov 15;312(5991):242–246. doi: 10.1038/312242a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Deiry W. S., Kern S. E., Pietenpol J. A., Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B. Definition of a consensus binding site for p53. Nat Genet. 1992 Apr;1(1):45–49. doi: 10.1038/ng0492-45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]