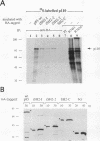
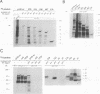
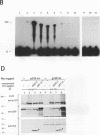
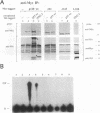
Abstract
Previous studies have suggested that the two subunits of phosphatidylinositol (PI) 3-kinase, p85 and p110, function as localizing and catalytic subunits, respectively. Using recombinant p85 and p110 molecules, we have reconstituted the specific interaction between the two subunits of mouse PI 3-kinase in cells and in vitro. We have previously shown that the region between the two Src homology 2 (SH2) domains of p85 is able to form a functional complex with the 110-kDa subunit in vivo. In this report, we identify the corresponding domain in p110 which directs the binding to p85. We demonstrate that the interactive domains in p85 and p110 are less than 103 and 124 amino acids, respectively, in size. We also show that the association of p85 and p110 mediated by these domains is critical for PI 3-kinase activity. Surprisingly, a complex between a 102-amino-acid segment of p85 and the full-length p110 molecule is catalytically active, whereas p110 alone has no activity. In addition to the catalytic domain in the carboxy-terminal region, 123 amino acids at the amino terminus of p110 were required for catalytic activity and were sufficient for the interaction with p85. These results indicate that the 85-kDa subunit, previously thought to have only a linking role in localizing the p110 catalytic subunit, is an important component of the catalytic complex.
Full text
PDF


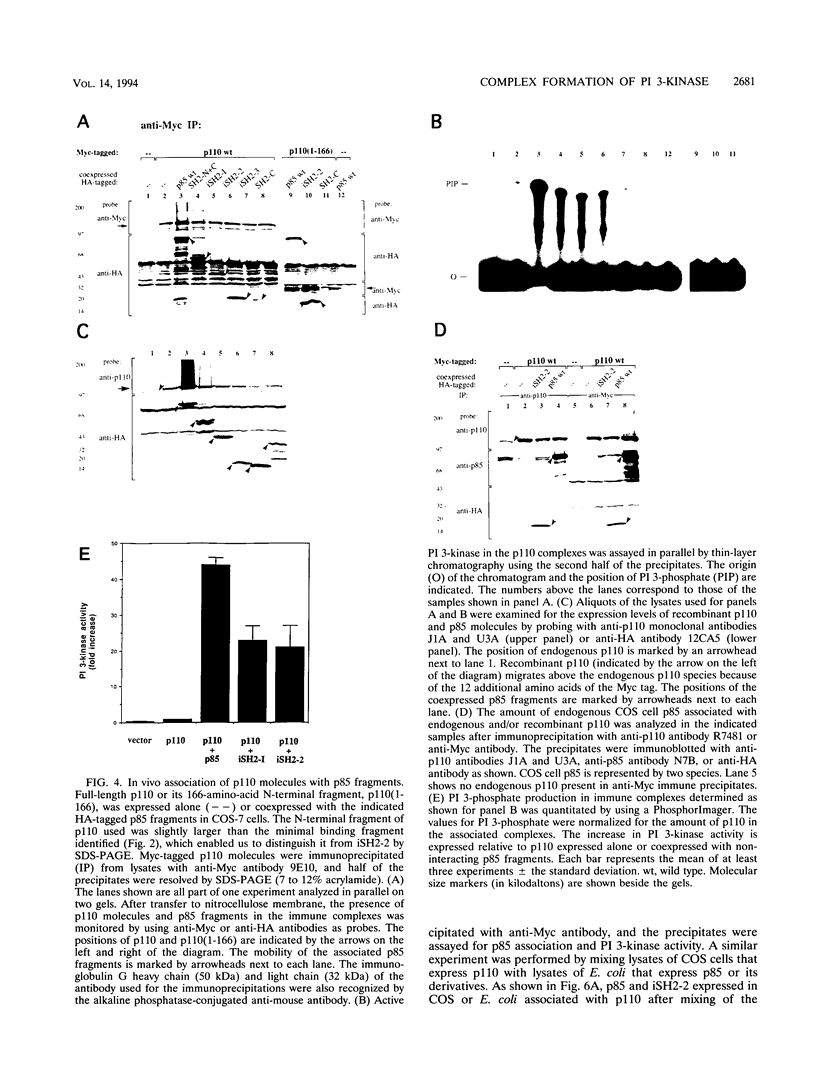
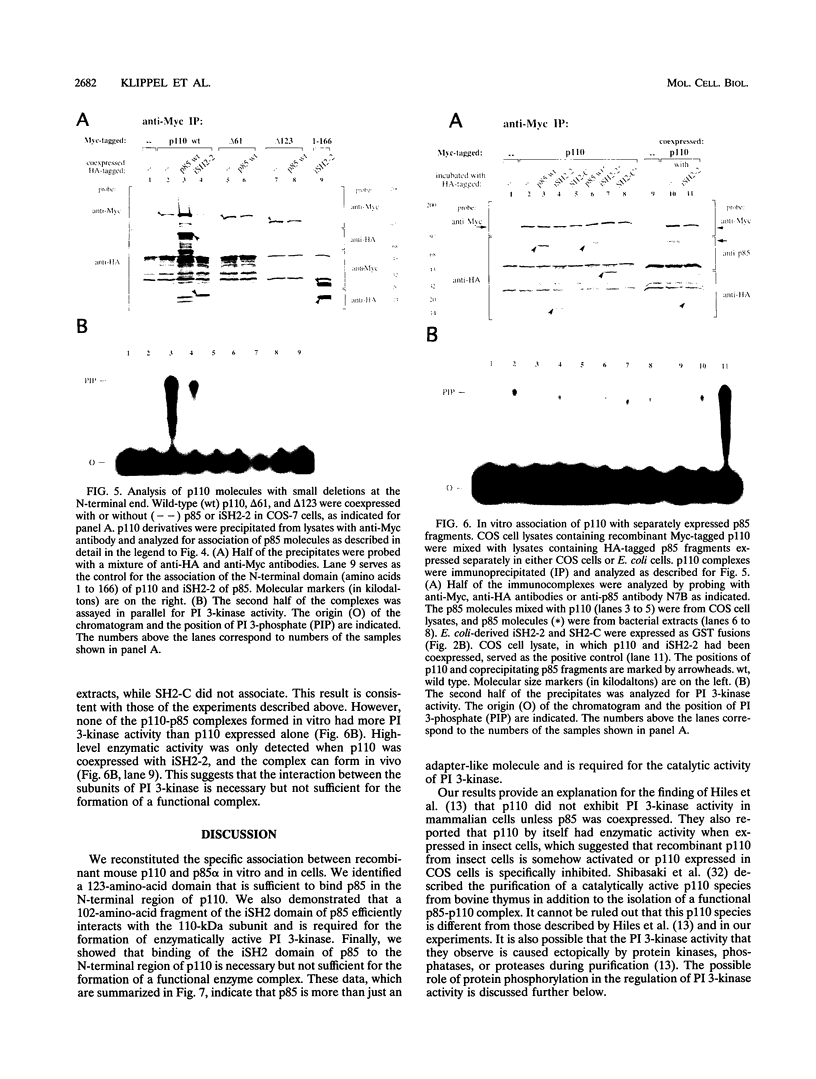



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auger K. R., Serunian L. A., Soltoff S. P., Libby P., Cantley L. C. PDGF-dependent tyrosine phosphorylation stimulates production of novel polyphosphoinositides in intact cells. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):167–175. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90182-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantley L. C., Auger K. R., Carpenter C., Duckworth B., Graziani A., Kapeller R., Soltoff S. Oncogenes and signal transduction. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):281–302. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90639-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter C. L., Auger K. R., Duckworth B. C., Hou W. M., Schaffhausen B., Cantley L. C. A tightly associated serine/threonine protein kinase regulates phosphoinositide 3-kinase activity. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;13(3):1657–1665. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.3.1657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter C. L., Duckworth B. C., Auger K. R., Cohen B., Schaffhausen B. S., Cantley L. C. Purification and characterization of phosphoinositide 3-kinase from rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 15;265(32):19704–19711. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downes C. P., Carter A. N. Phosphoinositide 3-kinase: a new effector in signal transduction? Cell Signal. 1991;3(6):501–513. doi: 10.1016/0898-6568(91)90027-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escobedo J. A., Navankasattusas S., Kavanaugh W. M., Milfay D., Fried V. A., Williams L. T. cDNA cloning of a novel 85 kd protein that has SH2 domains and regulates binding of PI3-kinase to the PDGF beta-receptor. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):75–82. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90409-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escobedo J. A., Williams L. T. A PDGF receptor domain essential for mitogenesis but not for many other responses to PDGF. Nature. 1988 Sep 1;335(6185):85–87. doi: 10.1038/335085a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evan G. I., Lewis G. K., Ramsay G., Bishop J. M. Isolation of monoclonal antibodies specific for human c-myc proto-oncogene product. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;5(12):3610–3616. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.12.3610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fantl W. J., Escobedo J. A., Martin G. A., Turck C. W., del Rosario M., McCormick F., Williams L. T. Distinct phosphotyrosines on a growth factor receptor bind to specific molecules that mediate different signaling pathways. Cell. 1992 May 1;69(3):413–423. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90444-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herman P. K., Stack J. H., Emr S. D. An essential role for a protein and lipid kinase complex in secretory protein sorting. Trends Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;2(12):363–368. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(92)90048-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiles I. D., Otsu M., Volinia S., Fry M. J., Gout I., Dhand R., Panayotou G., Ruiz-Larrea F., Thompson A., Totty N. F. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase: structure and expression of the 110 kd catalytic subunit. Cell. 1992 Aug 7;70(3):419–429. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90166-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu P., Margolis B., Skolnik E. Y., Lammers R., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Interaction of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-associated p85 with epidermal growth factor and platelet-derived growth factor receptors. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;12(3):981–990. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.3.981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapeller R., Chakrabarti R., Cantley L., Fay F., Corvera S. Internalization of activated platelet-derived growth factor receptor-phosphatidylinositol-3' kinase complexes: potential interactions with the microtubule cytoskeleton. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Oct;13(10):6052–6063. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.10.6052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kavanaugh W. M., Klippel A., Escobedo J. A., Williams L. T. Modification of the 85-kilodalton subunit of phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase in platelet-derived growth factor-stimulated cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;12(8):3415–3424. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.8.3415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly K. L., Ruderman N. B. Insulin-stimulated phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. Association with a 185-kDa tyrosine-phosphorylated protein (IRS-1) and localization in a low density membrane vesicle. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 25;268(6):4391–4398. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klippel A., Escobedo J. A., Fantl W. J., Williams L. T. The C-terminal SH2 domain of p85 accounts for the high affinity and specificity of the binding of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase to phosphorylated platelet-derived growth factor beta receptor. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;12(4):1451–1459. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.4.1451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klippel A., Escobedo J. A., Hu Q., Williams L. T. A region of the 85-kilodalton (kDa) subunit of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase binds the 110-kDa catalytic subunit in vivo. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Sep;13(9):5560–5566. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.9.5560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch C. A., Anderson D., Moran M. F., Ellis C., Pawson T. SH2 and SH3 domains: elements that control interactions of cytoplasmic signaling proteins. Science. 1991 May 3;252(5006):668–674. doi: 10.1126/science.1708916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunz J., Henriquez R., Schneider U., Deuter-Reinhard M., Movva N. R., Hall M. N. Target of rapamycin in yeast, TOR2, is an essential phosphatidylinositol kinase homolog required for G1 progression. Cell. 1993 May 7;73(3):585–596. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90144-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthias P., Müller M. M., Schreiber E., Rusconi S., Schaffner W. Eukaryotic expression vectors for the analysis of mutant proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Aug 11;17(15):6418–6418. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.15.6418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGlade C. J., Ellis C., Reedijk M., Anderson D., Mbamalu G., Reith A. D., Panayotou G., End P., Bernstein A., Kazlauskas A. SH2 domains of the p85 alpha subunit of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase regulate binding to growth factor receptors. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;12(3):991–997. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.3.991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan S. J., Smith A. D., Parker P. J. Purification and characterization of bovine brain type I phosphatidylinositol kinase. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Aug 17;191(3):761–767. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19185.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. K., Kaplan D. R., Escobedo J. A., Rapp U. R., Roberts T. M., Williams L. T. Direct activation of the serine/threonine kinase activity of Raf-1 through tyrosine phosphorylation by the PDGF beta-receptor. Cell. 1989 Aug 25;58(4):649–657. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90100-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otsu M., Hiles I., Gout I., Fry M. J., Ruiz-Larrea F., Panayotou G., Thompson A., Dhand R., Hsuan J., Totty N. Characterization of two 85 kd proteins that associate with receptor tyrosine kinases, middle-T/pp60c-src complexes, and PI3-kinase. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):91–104. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90411-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reedijk M., Liu X., van der Geer P., Letwin K., Waterfield M. D., Hunter T., Pawson T. Tyr721 regulates specific binding of the CSF-1 receptor kinase insert to PI 3'-kinase SH2 domains: a model for SH2-mediated receptor-target interactions. EMBO J. 1992 Apr;11(4):1365–1372. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05181.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schu P. V., Takegawa K., Fry M. J., Stack J. H., Waterfield M. D., Emr S. D. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase encoded by yeast VPS34 gene essential for protein sorting. Science. 1993 Apr 2;260(5104):88–91. doi: 10.1126/science.8385367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibasaki F., Homma Y., Takenawa T. Two types of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase from bovine thymus. Monomer and heterodimer form. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 5;266(13):8108–8114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skolnik E. Y., Margolis B., Mohammadi M., Lowenstein E., Fischer R., Drepps A., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Cloning of PI3 kinase-associated p85 utilizing a novel method for expression/cloning of target proteins for receptor tyrosine kinases. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):83–90. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90410-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stack J. H., Herman P. K., Schu P. V., Emr S. D. A membrane-associated complex containing the Vps15 protein kinase and the Vps34 PI 3-kinase is essential for protein sorting to the yeast lysosome-like vacuole. EMBO J. 1993 May;12(5):2195–2204. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05867.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Dubendorff J. W. Use of T7 RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:60–89. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitman M., Downes C. P., Keeler M., Keller T., Cantley L. Type I phosphatidylinositol kinase makes a novel inositol phospholipid, phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate. Nature. 1988 Apr 14;332(6165):644–646. doi: 10.1038/332644a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson I. A., Niman H. L., Houghten R. A., Cherenson A. R., Connolly M. L., Lerner R. A. The structure of an antigenic determinant in a protein. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):767–778. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90412-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoakim M., Hou W., Liu Y., Carpenter C. L., Kapeller R., Schaffhausen B. S. Interactions of polyomavirus middle T with the SH2 domains of the pp85 subunit of phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase. J Virol. 1992 Sep;66(9):5485–5491. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.9.5485-5491.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang J., Fry M. J., Waterfield M. D., Jaken S., Liao L., Fox J. E., Rittenhouse S. E. Activated phosphoinositide 3-kinase associates with membrane skeleton in thrombin-exposed platelets. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 5;267(7):4686–4692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang J., King W. G., Dillon S., Hall A., Feig L., Rittenhouse S. E. Activation of platelet phosphatidylinositide 3-kinase requires the small GTP-binding protein Rho. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 25;268(30):22251–22254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]