Abstract
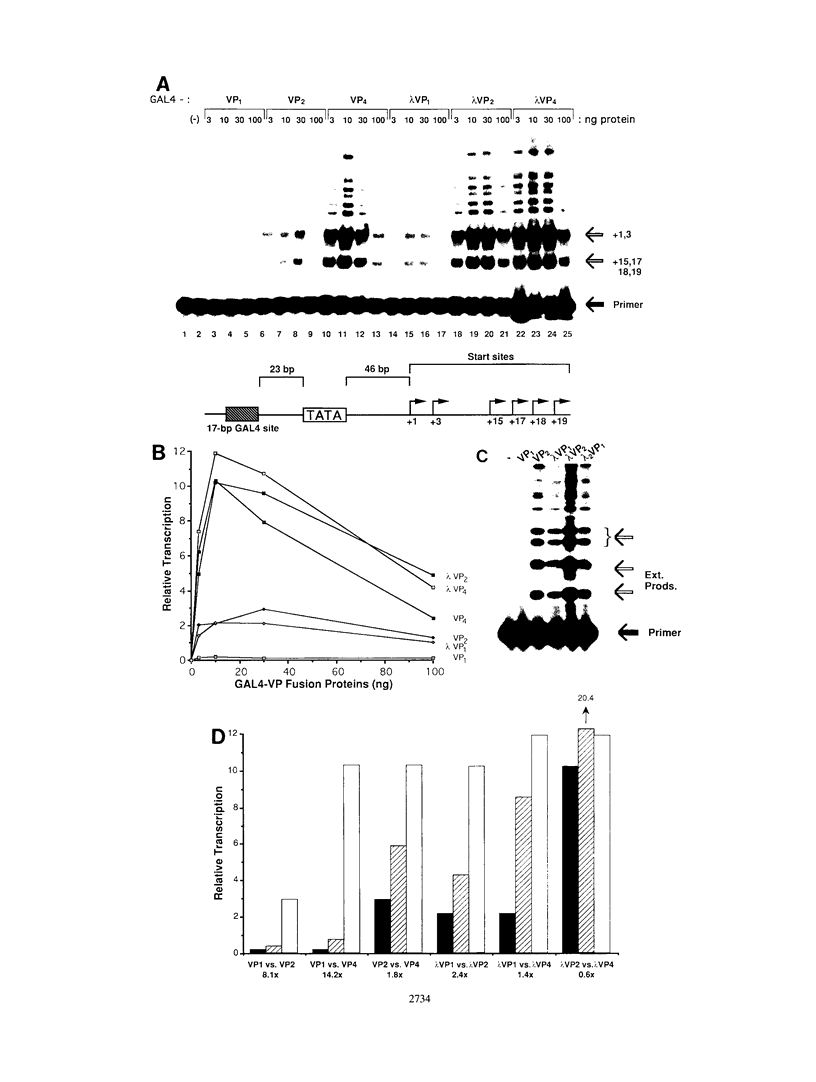
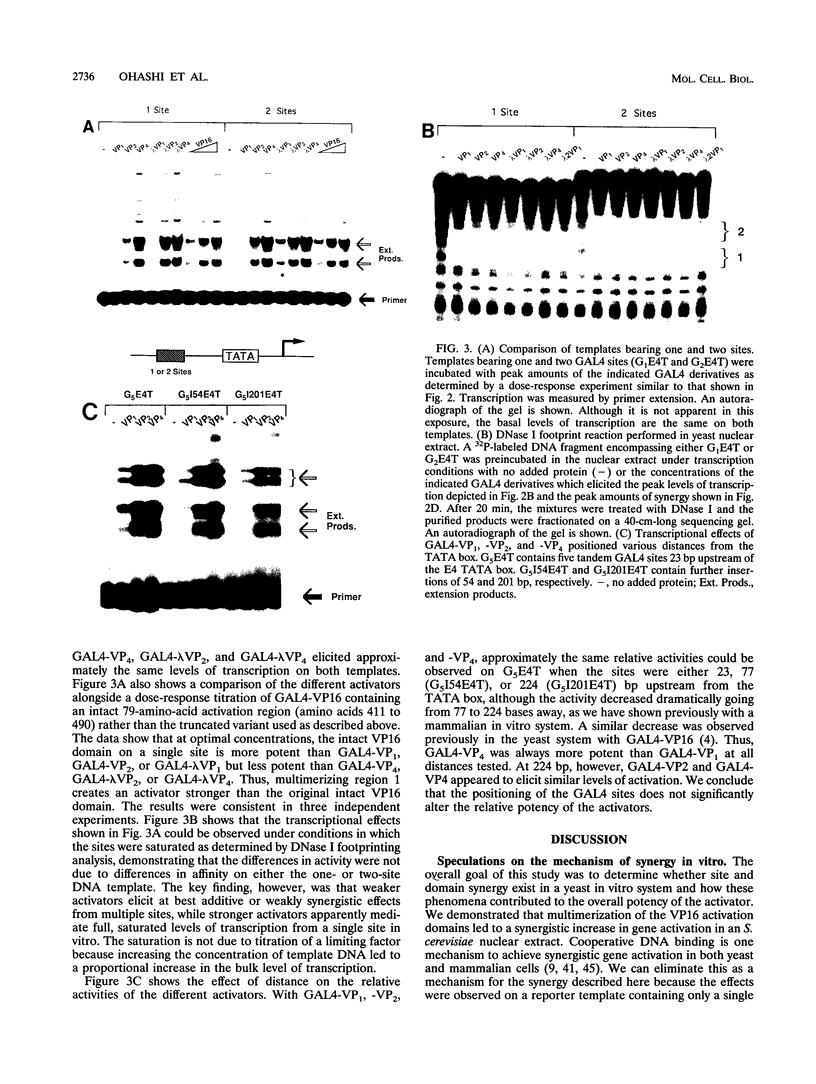
The intrinsic stimulatory potential or potency of a eukaryotic gene activator is controlled by the interaction between the activation domain and the transcriptional machinery. To further understand this interaction, we undertook a biochemical study to identify parameters that could be used to modulate activator potency. We considered how varying the number of activation domains, their flexibility, and the number of promoter sites affects potency in a yeast nuclear extract. The effects of GAL4 derivatives bearing either one, two, or four herpes simplex virus VP16 activation domains (amino acids 413 to 454) were measured on DNA templates containing one or two GAL4 sites in a Saccharomyces cerevisiae nuclear extract. We found that multimerized VP16 activation domains acted synergistically to increase the potency of the activators. The spacing between the activation domains was critical, such that the increased flexibility imparted by a protein linker contributed to increased activator potency. With highly potent activators, the levels of transcription stimulated on a single site were saturating, whereas the stimulatory effect of weaker activators increased with the number of sites. We discuss how these biochemical studies relate to the mechanism of gene activation and synergy in a yeast in vitro system.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berger S. L., Cress W. D., Cress A., Triezenberg S. J., Guarente L. Selective inhibition of activated but not basal transcription by the acidic activation domain of VP16: evidence for transcriptional adaptors. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1199–1208. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90684-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey M., Kolman J., Katz D. A., Gradoville L., Barberis L., Miller G. Transcriptional synergy by the Epstein-Barr virus transactivator ZEBRA. J Virol. 1992 Aug;66(8):4803–4813. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.8.4803-4813.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey M., Lin Y. S., Green M. R., Ptashne M. A mechanism for synergistic activation of a mammalian gene by GAL4 derivatives. Nature. 1990 May 24;345(6273):361–364. doi: 10.1038/345361a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chasman D. I., Leatherwood J., Carey M., Ptashne M., Kornberg R. D. Activation of yeast polymerase II transcription by herpesvirus VP16 and GAL4 derivatives in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):4746–4749. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.4746. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cress W. D., Triezenberg S. J. Critical structural elements of the VP16 transcriptional activation domain. Science. 1991 Jan 4;251(4989):87–90. doi: 10.1126/science.1846049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driever W., Nüsslein-Volhard C. The bicoid protein determines position in the Drosophila embryo in a concentration-dependent manner. Cell. 1988 Jul 1;54(1):95–104. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90183-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emami K. H., Carey M. A synergistic increase in potency of a multimerized VP16 transcriptional activation domain. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(13):5005–5012. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05607.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill G., Ptashne M. Negative effect of the transcriptional activator GAL4. Nature. 1988 Aug 25;334(6184):721–724. doi: 10.1038/334721a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giniger E., Ptashne M. Cooperative DNA binding of the yeast transcriptional activator GAL4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(2):382–386. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.2.382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herschlag D., Johnson F. B. Synergism in transcriptional activation: a kinetic view. Genes Dev. 1993 Feb;7(2):173–179. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.2.173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollenberg S. M., Evans R. M. Multiple and cooperative trans-activation domains of the human glucocorticoid receptor. Cell. 1988 Dec 2;55(5):899–906. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90145-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hope I. A., Mahadevan S., Struhl K. Structural and functional characterization of the short acidic transcriptional activation region of yeast GCN4 protein. Nature. 1988 Jun 16;333(6174):635–640. doi: 10.1038/333635a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelleher R. J., 3rd, Flanagan P. M., Kornberg R. D. A novel mediator between activator proteins and the RNA polymerase II transcription apparatus. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1209–1215. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90685-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin Y. S., Carey M., Ptashne M., Green M. R. How different eukaryotic transcriptional activators can cooperate promiscuously. Nature. 1990 May 24;345(6273):359–361. doi: 10.1038/345359a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin Y. S., Green M. R. Mechanism of action of an acidic transcriptional activator in vitro. Cell. 1991 Mar 8;64(5):971–981. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90321-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lue N. F., Flanagan P. M., Sugimoto K., Kornberg R. D. Initiation by yeast RNA polymerase II at the adenoviral major late promoter in vitro. Science. 1989 Nov 3;246(4930):661–664. doi: 10.1126/science.2510298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lue N. F., Kornberg R. D. Accurate initiation at RNA polymerase II promoters in extracts from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):8839–8843. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.8839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma J., Ptashne M. Deletion analysis of GAL4 defines two transcriptional activating segments. Cell. 1987 Mar 13;48(5):847–853. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90081-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marmorstein R., Carey M., Ptashne M., Harrison S. C. DNA recognition by GAL4: structure of a protein-DNA complex. Nature. 1992 Apr 2;356(6368):408–414. doi: 10.1038/356408a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Tjian R. Transcriptional regulation in mammalian cells by sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):371–378. doi: 10.1126/science.2667136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Immerglück M. M., Schaffner W., Matthias P. Transcription factor Oct-2A contains functionally redundant activating domains and works selectively from a promoter but not from a remote enhancer position in non-lymphoid (HeLa) cells. EMBO J. 1990 May;9(5):1625–1634. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08282.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliviero S., Struhl K. Synergistic transcriptional enhancement does not depend on the number of acidic activation domains bound to the promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 1;88(1):224–228. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.1.224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ondek B., Gloss L., Herr W. The SV40 enhancer contains two distinct levels of organization. Nature. 1988 May 5;333(6168):40–45. doi: 10.1038/333040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabo C. O., Sauer R. T., Sturtevant J. M., Ptashne M. The lambda repressor contains two domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1608–1612. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pascal E., Tjian R. Different activation domains of Sp1 govern formation of multimers and mediate transcriptional synergism. Genes Dev. 1991 Sep;5(9):1646–1656. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.9.1646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson C. L., Herskowitz I. Characterization of the yeast SWI1, SWI2, and SWI3 genes, which encode a global activator of transcription. Cell. 1992 Feb 7;68(3):573–583. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90192-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponticelli A. S., Struhl K. Analysis of Saccharomyces cerevisiae his3 transcription in vitro: biochemical support for multiple mechanisms of transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2832–2839. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M., Gann A. A. Activators and targets. Nature. 1990 Jul 26;346(6282):329–331. doi: 10.1038/346329a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regier J. L., Shen F., Triezenberg S. J. Pattern of aromatic and hydrophobic amino acids critical for one of two subdomains of the VP16 transcriptional activator. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Feb 1;90(3):883–887. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.3.883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell P. R. Evolutionary divergence of the mRNA transcription initiation mechanism in yeast. Nature. 1983 Jan 13;301(5896):167–169. doi: 10.1038/301167a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadowski I., Ma J., Triezenberg S., Ptashne M. GAL4-VP16 is an unusually potent transcriptional activator. Nature. 1988 Oct 6;335(6190):563–564. doi: 10.1038/335563a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saha S., Brickman J. M., Lehming N., Ptashne M. New eukaryotic transcriptional repressors. Nature. 1993 Jun 17;363(6430):648–652. doi: 10.1038/363648a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffner G., Schirm S., Müller-Baden B., Weber F., Schaffner W. Redundancy of information in enhancers as a principle of mammalian transcription control. J Mol Biol. 1988 May 5;201(1):81–90. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90440-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schüle R., Muller M., Kaltschmidt C., Renkawitz R. Many transcription factors interact synergistically with steroid receptors. Science. 1988 Dec 9;242(4884):1418–1420. doi: 10.1126/science.3201230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seipel K., Georgiev O., Schaffner W. Different activation domains stimulate transcription from remote ('enhancer') and proximal ('promoter') positions. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(13):4961–4968. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05603.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland J. A., Cook A., Bannister A. J., Kouzarides T. Conserved motifs in Fos and Jun define a new class of activation domain. Genes Dev. 1992 Sep;6(9):1810–1819. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.9.1810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka M., Herr W. Differential transcriptional activation by Oct-1 and Oct-2: interdependent activation domains induce Oct-2 phosphorylation. Cell. 1990 Feb 9;60(3):375–386. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90589-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor I. C., Workman J. L., Schuetz T. J., Kingston R. E. Facilitated binding of GAL4 and heat shock factor to nucleosomal templates: differential function of DNA-binding domains. Genes Dev. 1991 Jul;5(7):1285–1298. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.7.1285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tora L., White J., Brou C., Tasset D., Webster N., Scheer E., Chambon P. The human estrogen receptor has two independent nonacidic transcriptional activation functions. Cell. 1989 Nov 3;59(3):477–487. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90031-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Triezenberg S. J., Kingsbury R. C., McKnight S. L. Functional dissection of VP16, the trans-activator of herpes simplex virus immediate early gene expression. Genes Dev. 1988 Jun;2(6):718–729. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.6.718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai S. Y., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Cooperative binding of steroid hormone receptors contributes to transcriptional synergism at target enhancer elements. Cell. 1989 May 5;57(3):443–448. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90919-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang W., Carey M., Gralla J. D. Polymerase II promoter activation: closed complex formation and ATP-driven start site opening. Science. 1992 Jan 24;255(5043):450–453. doi: 10.1126/science.1310361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wobbe C. R., Struhl K. Yeast and human TATA-binding proteins have nearly identical DNA sequence requirements for transcription in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):3859–3867. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.3859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiao H., Perisic O., Lis J. T. Cooperative binding of Drosophila heat shock factor to arrays of a conserved 5 bp unit. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):585–593. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90242-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zawel L., Reinberg D. Advances in RNA polymerase II transcription. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;4(3):488–495. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(92)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]