Abstract
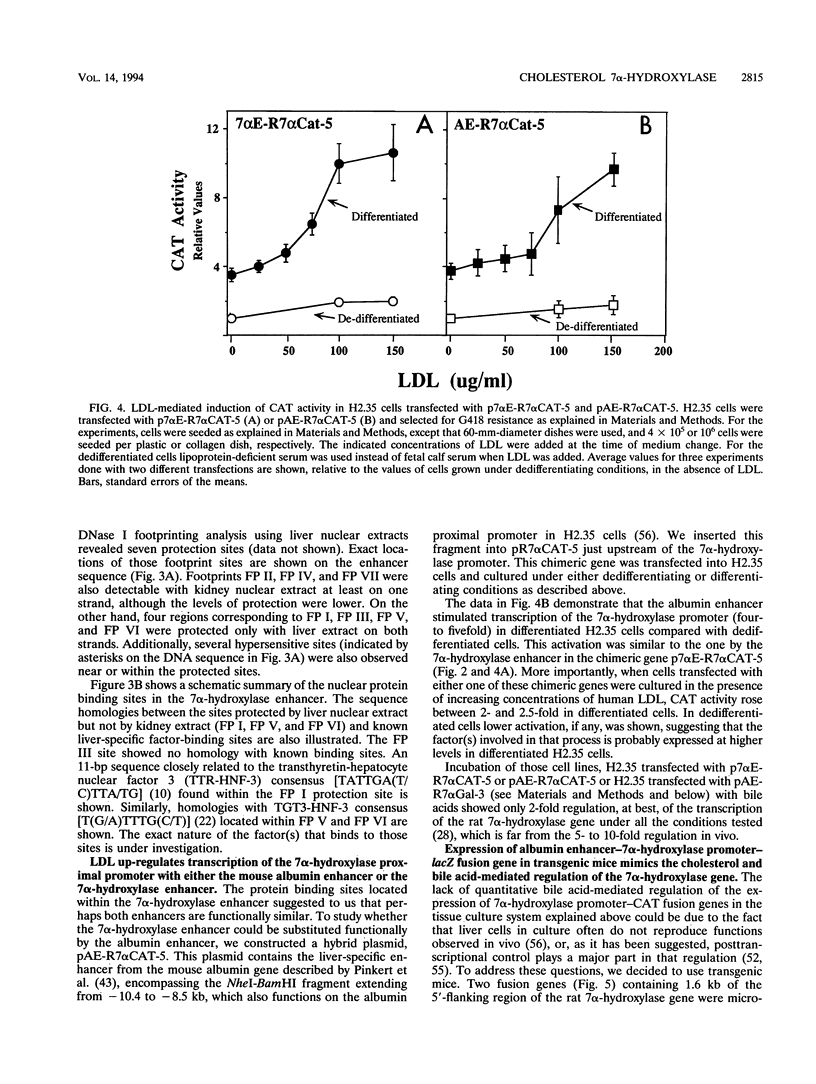
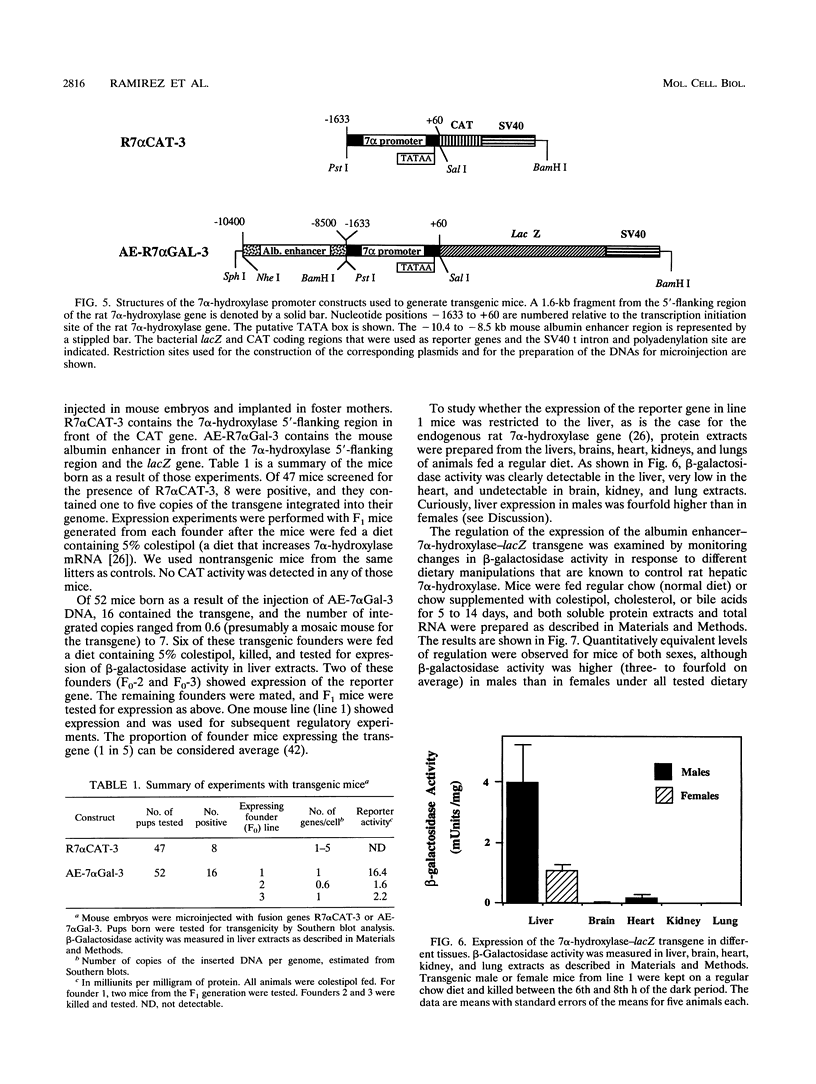
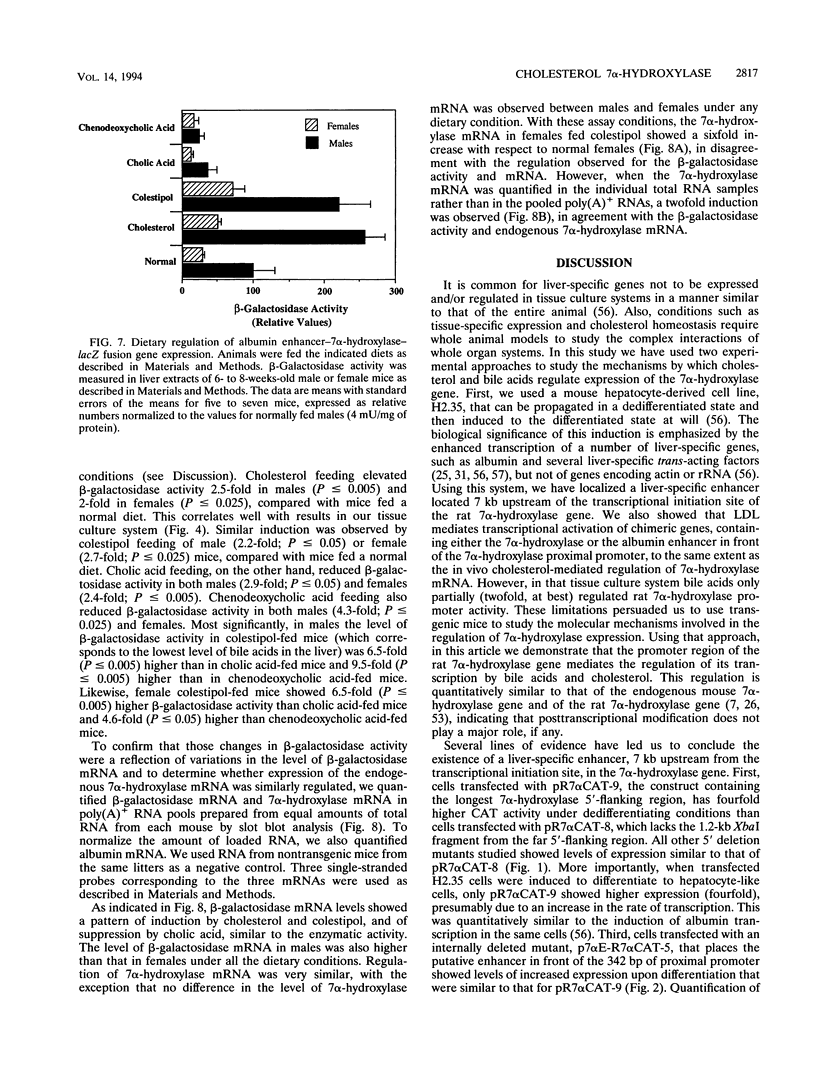
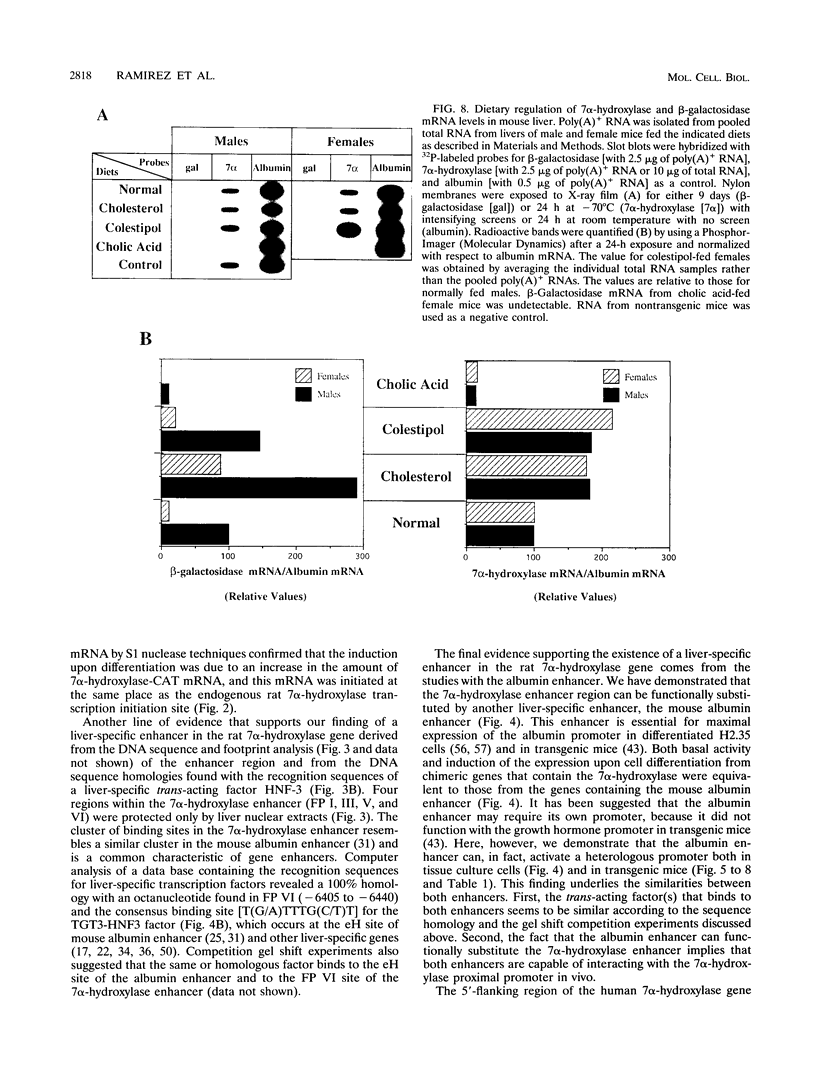
Cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase (7 alpha-hydroxylase) is the rate-limiting enzyme in bile acid biosynthesis. It is subject to a feedback control, whereby high levels of bile acids suppress its activity, and cholesterol exerts a positive control. It has been suggested that posttranscriptional control plays a major part in that regulation. We have studied the mechanisms by which cholesterol and bile acids regulate expression of the 7 alpha-hydroxylase gene and found it to be solely at the transcriptional level by using two different approaches. First, using a tissue culture system, we localized a liver-specific enhancer located 7 kb upstream of the transcriptional initiation site. We also showed that low-density lipoprotein mediates transcriptional activation of chimeric genes, containing either the 7 alpha-hydroxylase or the albumin enhancer in front of the 7 alpha-hydroxylase proximal promoter, to the same extent as the in vivo cholesterol-mediated regulation of 7 alpha-hydroxylase mRNA. In a second approach, using transgenic mice, we have found that expression of an albumin enhancer-7 alpha-hydroxylase-lacZ fusion gene is restricted to the liver and is regulated by cholesterol and bile acids in a manner quantitatively similar to that of the endogenous gene. We also found, that a liver-specific enhancer is necessary for expression of the rat 7 alpha-hydroxylase gene, in agreement with the tissue culture experiments. Together, these results demonstrate that cholesterol and bile acids regulate the expression of the 7 alpha-hydroxylase gene solely at the transcriptional level.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beck E., Ludwig G., Auerswald E. A., Reiss B., Schaller H. Nucleotide sequence and exact localization of the neomycin phosphotransferase gene from transposon Tn5. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):327–336. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90023-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briggs M. R., Yokoyama C., Wang X., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Nuclear protein that binds sterol regulatory element of low density lipoprotein receptor promoter. I. Identification of the protein and delineation of its target nucleotide sequence. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 5;268(19):14490–14496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Suppression of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase activity and inhibition of growth of human fibroblasts by 7-ketocholesterol. J Biol Chem. 1974 Nov 25;249(22):7306–7314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. A., Okayama H. Calcium phosphate-mediated gene transfer: a highly efficient transfection system for stably transforming cells with plasmid DNA. Biotechniques. 1988 Jul-Aug;6(7):632–638. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiang J. Y., Miller W. F., Lin G. M. Regulation of cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase in the liver. Purification of cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase and the immunochemical evidence for the induction of cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase by cholestyramine and circadian rhythm. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 5;265(7):3889–3897. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa R. H., Grayson D. R., Darnell J. E., Jr Multiple hepatocyte-enriched nuclear factors function in the regulation of transthyretin and alpha 1-antitrypsin genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1415–1425. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danielsson H., Sjövall J. Bile acid metabolism. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:233–253. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.001313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deininger P. L. Approaches to rapid DNA sequence analysis. Anal Biochem. 1983 Dec;135(2):247–263. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90680-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietschy J. M. Regulation of cholesterol metabolism in man and in other species. Klin Wochenschr. 1984 Apr 16;62(8):338–345. doi: 10.1007/BF01716251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engler P., Haasch D., Pinkert C. A., Doglio L., Glymour M., Brinster R., Storb U. A strain-specific modifier on mouse chromosome 4 controls the methylation of independent transgene loci. Cell. 1991 Jun 14;65(6):939–947. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90546-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gil G., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Cytoplasmic 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A synthase from the hamster. II. Isolation of the gene and characterization of the 5' flanking region. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 15;261(8):3717–3724. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gil G., Esser V. Cholesterol-mediated suppression of alpha 1-inhibitor III, a plasma alpha-macroglobulin family protein. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 25;266(30):20512–20518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godbout R., Ingram R., Tilghman S. M. Multiple regulatory elements in the intergenic region between the alpha-fetoprotein and albumin genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;6(2):477–487. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.2.477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Basu S. K., Brown M. S. Receptor-mediated endocytosis of low-density lipoprotein in cultured cells. Methods Enzymol. 1983;98:241–260. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)98152-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. Regulation of the mevalonate pathway. Nature. 1990 Feb 1;343(6257):425–430. doi: 10.1038/343425a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. The low-density lipoprotein pathway and its relation to atherosclerosis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:897–930. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.004341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grange T., Roux J., Rigaud G., Pictet R. Cell-type specific activity of two glucocorticoid responsive units of rat tyrosine aminotransferase gene is associated with multiple binding sites for C/EBP and a novel liver-specific nuclear factor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jan 11;19(1):131–139. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.1.131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hylemon P. B., Gurley E. C., Stravitz R. T., Litz J. S., Pandak W. M., Chiang J. Y., Vlahcevic Z. R. Hormonal regulation of cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase mRNA levels and transcriptional activity in primary rat hepatocyte cultures. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 25;267(24):16866–16871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson D. A., Rowader K. E., Stevens K., Jiang C., Milos P., Zaret K. S. Modulation of liver-specific transcription by interactions between hepatocyte nuclear factor 3 and nuclear factor 1 binding DNA in close apposition. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;13(4):2401–2410. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.4.2401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelinek D. F., Russell D. W. Structure of the rat gene encoding cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase. Biochemistry. 1990 Aug 28;29(34):7781–7785. doi: 10.1021/bi00486a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y. C., Wang D. P., Chiang J. Y. Regulation of cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase in the liver. Cloning, sequencing, and regulation of cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 15;265(20):12012–12019. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu J. K., DiPersio C. M., Zaret K. S. Extracellular signals that regulate liver transcription factors during hepatic differentiation in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;11(2):773–784. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.2.773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitropoulos K. A., Balasubramaniam S. The role of glucocorticoids in the regulation of the diurnal rhythm of hepatic beta-hydroxy-beta-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase and cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase. Biochem J. 1976 Oct 15;160(1):49–55. doi: 10.1042/bj1600049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molowa D. T., Chen W. S., Cimis G. M., Tan C. P. Transcriptional regulation of the human cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase gene. Biochemistry. 1992 Mar 10;31(9):2539–2544. doi: 10.1021/bi00124a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaci P., Nicosia A., Cortese R. Two different liver-specific factors stimulate in vitro transcription from the human alpha 1-antitrypsin promoter. EMBO J. 1988 Jul;7(7):2075–2087. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03047.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myant N. B., Mitropoulos K. A. Cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase. J Lipid Res. 1977 Mar;18(2):135–153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nitsch D., Boshart M., Schütz G. Activation of the tyrosine aminotransferase gene is dependent on synergy between liver-specific and hormone-responsive elements. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 15;90(12):5479–5483. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.12.5479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noshiro M., Nishimoto M., Morohashi K., Okuda K. Molecular cloning of cDNA for cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase from rat liver microsomes. Nucleotide sequence and expression. FEBS Lett. 1989 Oct 23;257(1):97–100. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81795-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noshiro M., Nishimoto M., Okuda K. Rat liver cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase. Pretranslational regulation for circadian rhythm. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 15;265(17):10036–10041. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noshiro M., Okuda K. Molecular cloning and sequence analysis of cDNA encoding human cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase. FEBS Lett. 1990 Jul 30;268(1):137–140. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80992-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborne T. F. Single nucleotide resolution of sterol regulatory region in promoter for 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 25;266(21):13947–13951. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L. Germ-line transformation of mice. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:465–499. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.002341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L. Transgenic mice. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):343–345. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80004-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinkert C. A., Ornitz D. M., Brinster R. L., Palmiter R. D. An albumin enhancer located 10 kb upstream functions along with its promoter to direct efficient, liver-specific expression in transgenic mice. Genes Dev. 1987 May;1(3):268–276. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.3.268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pondel M. D., Proudfoot N. J., Whitelaw C., Whitelaw E. The developmental regulation of the human zeta-globin gene in transgenic mice employing beta-galactosidase as a reporter gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Nov 11;20(21):5655–5660. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.21.5655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal N. Identification of regulatory elements of cloned genes with functional assays. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:704–720. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52075-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell D. W., Setchell K. D. Bile acid biosynthesis. Biochemistry. 1992 May 26;31(20):4737–4749. doi: 10.1021/bi00135a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaul Y., Ben-Levy R. Multiple nuclear proteins in liver cells are bound to hepatitis B virus enhancer element and its upstream sequences. EMBO J. 1987 Jul;6(7):1913–1920. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02451.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. R., Osborne T. F., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L., Gil G. Multiple sterol regulatory elements in promoter for hamster 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A synthase. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 5;263(34):18480–18487. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stravitz R. T., Hylemon P. B., Heuman D. M., Hagey L. R., Schteingart C. D., Ton-Nu H. T., Hofmann A. F., Vlahcevic Z. R. Transcriptional regulation of cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase mRNA by conjugated bile acids in primary cultures of rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 5;268(19):13987–13993. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundseth S. S., Waxman D. J. Hepatic P-450 cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase. Regulation in vivo at the protein and mRNA level in response to mevalonate, diurnal rhythm, and bile acid feedback. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 5;265(25):15090–15095. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swain J. L., Stewart T. A., Leder P. Parental legacy determines methylation and expression of an autosomal transgene: a molecular mechanism for parental imprinting. Cell. 1987 Aug 28;50(5):719–727. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90330-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twisk J., Lehmann E. M., Princen H. M. Differential feedback regulation of cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase mRNA and transcriptional activity by rat bile acids in primary monolayer cultures of rat hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1993 Mar 15;290(Pt 3):685–691. doi: 10.1042/bj2900685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaret K. S., DiPersio C. M., Jackson D. A., Montigny W. J., Weinstat D. L. Conditional enhancement of liver-specific gene transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):9076–9080. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.9076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaret K. S., Liu J. K., DiPersio C. M. Site-directed mutagenesis reveals a liver transcription factor essential for the albumin transcriptional enhancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(14):5469–5473. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.14.5469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]