Abstract
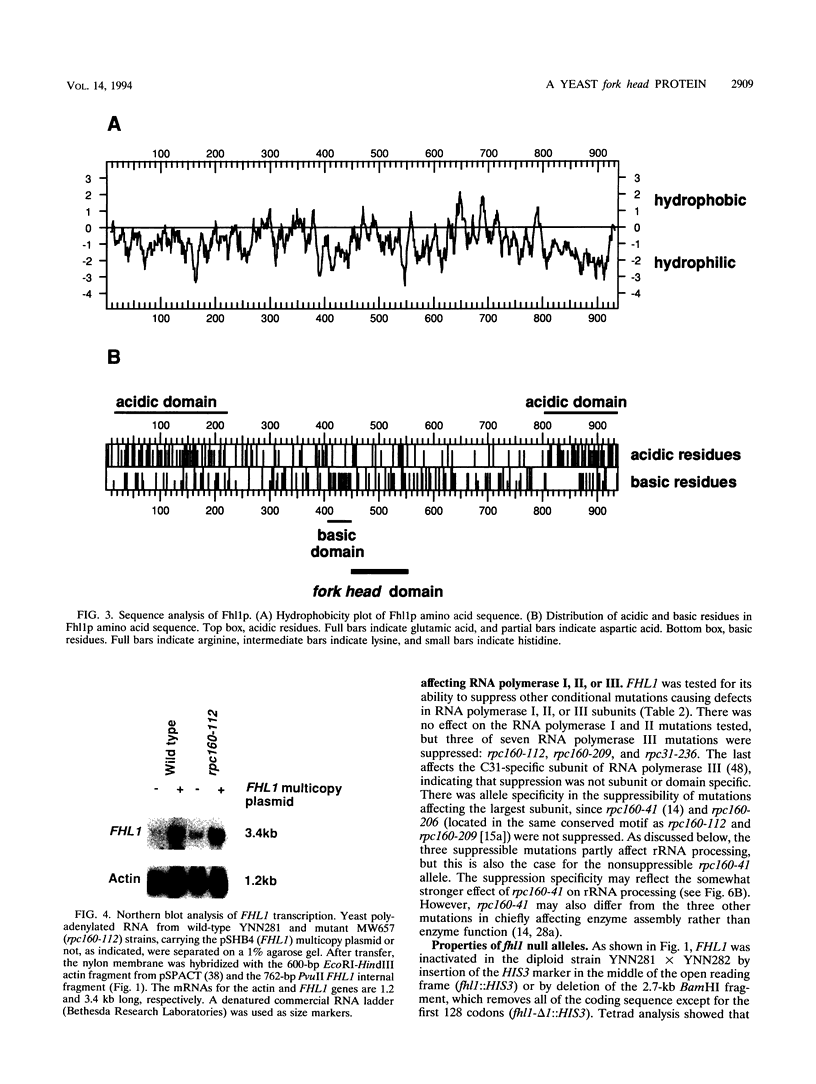
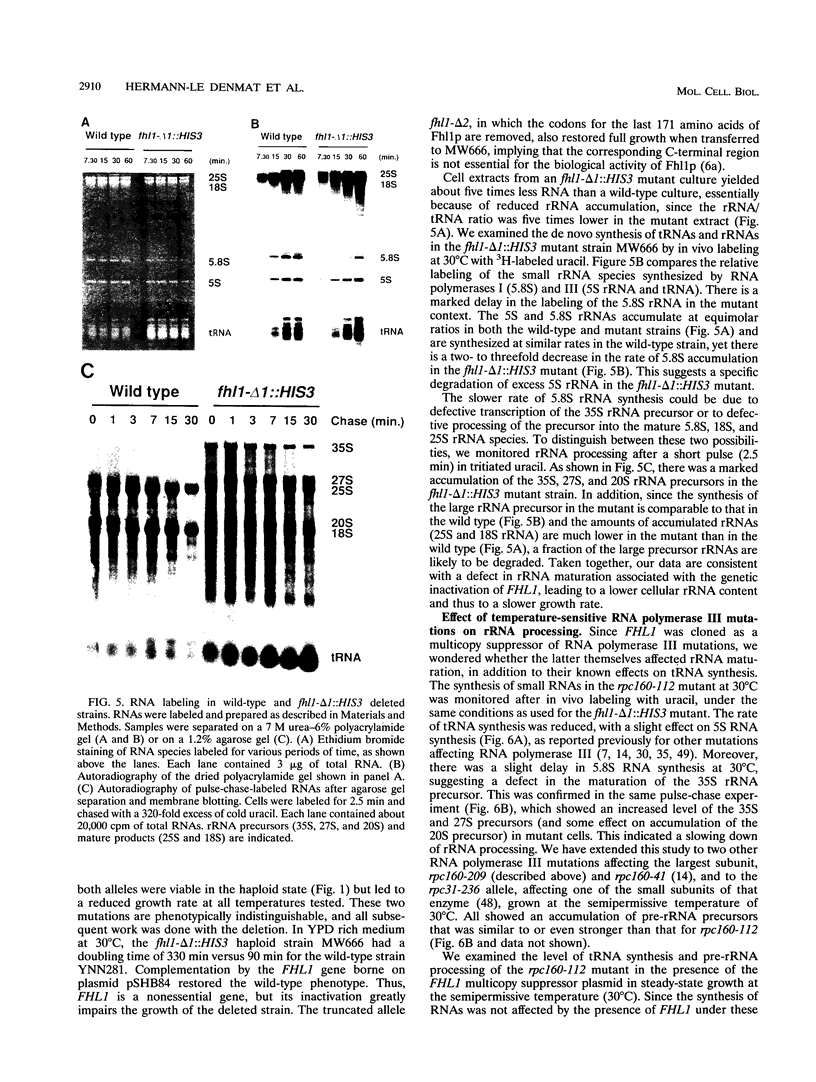
The FHL1 gene was isolated by screening for high-copy-number suppressors of conditional RNA polymerase III mutations. This gene is unique on the yeast genome and was located close to RPC40 and PRE2 on the right arm of chromosome XVI. It codes for a 936-amino-acid protein containing a domain similar to the fork head DNA-binding domain, initially found in the developmental fork head protein of Drosophila melanogaster and in the HNF-3 family of hepatocyte mammalian transcription factors. Null mutations caused a severe reduction in growth rate and a lower rRNA content that resulted from defective rRNA processing. There was no detectable effect on mRNA splicing. Thus, the Fhl1p protein plays a key role in the control of rRNA processing, presumably by acting as a transcriptional regulator of genes specifically involved in that process. Moreover, mutants carrying the RNA polymerase III mutations were slightly defective in rRNA processing. This accounts for the isolation of FHL1 as a dosage-dependent suppressor and suggests that rRNA processing depends on a still-unidentified RNA polymerase III transcript.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allison L. A., Ingles C. J. Mutations in RNA polymerase II enhance or suppress mutations in GAL4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2794–2798. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allison L. A., Moyle M., Shales M., Ingles C. J. Extensive homology among the largest subunits of eukaryotic and prokaryotic RNA polymerases. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):599–610. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90117-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beltrame M., Tollervey D. Identification and functional analysis of two U3 binding sites on yeast pre-ribosomal RNA. EMBO J. 1992 Apr;11(4):1531–1542. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05198.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeke J. D., LaCroute F., Fink G. R. A positive selection for mutants lacking orotidine-5'-phosphate decarboxylase activity in yeast: 5-fluoro-orotic acid resistance. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;197(2):345–346. doi: 10.1007/BF00330984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogenhagen D. F., Brown D. D. Nucleotide sequences in Xenopus 5S DNA required for transcription termination. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):261–270. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90522-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapon C., Legrain P. A novel gene, spp91-1, suppresses the splicing defect and the pre-mRNA nuclear export in the prp9-1 mutant. EMBO J. 1992 Sep;11(9):3279–3288. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05406.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiannilkulchai N., Stalder R., Riva M., Carles C., Werner M., Sentenac A. RPC82 encodes the highly conserved, third-largest subunit of RNA polymerase C (III) from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;12(10):4433–4440. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.10.4433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark K. L., Halay E. D., Lai E., Burley S. K. Co-crystal structure of the HNF-3/fork head DNA-recognition motif resembles histone H5. Nature. 1993 Jul 29;364(6436):412–420. doi: 10.1038/364412a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Della Seta F., Treich I., Buhler J. M., Sentenac A. ABF1 binding sites in yeast RNA polymerase genes. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 5;265(25):15168–15175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dequard-Chablat M., Riva M., Carles C., Sentenac A. RPC19, the gene for a subunit common to yeast RNA polymerases A (I) and C (III). J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 15;266(23):15300–15307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dirksen M. L., Jamrich M. A novel, activin-inducible, blastopore lip-specific gene of Xenopus laevis contains a fork head DNA-binding domain. Genes Dev. 1992 Apr;6(4):599–608. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.4.599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabrielsen O. S., Sentenac A. RNA polymerase III (C) and its transcription factors. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Nov;16(11):412–416. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90166-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiduschek E. P., Tocchini-Valentini G. P. Transcription by RNA polymerase III. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:873–914. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.004301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gudenus R., Mariotte S., Moenne A., Ruet A., Memet S., Buhler J. M., Sentenac A., Thuriaux P. Conditional mutants of RPC160, the gene encoding the largest subunit of RNA polymerase C in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1988 Jul;119(3):517–526. doi: 10.1093/genetics/119.3.517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinemeyer W., Gruhler A., Möhrle V., Mahé Y., Wolf D. H. PRE2, highly homologous to the human major histocompatibility complex-linked RING10 gene, codes for a yeast proteasome subunit necessary for chrymotryptic activity and degradation of ubiquitinated proteins. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 5;268(7):5115–5120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman C. S., Winston F. A ten-minute DNA preparation from yeast efficiently releases autonomous plasmids for transformation of Escherichia coli. Gene. 1987;57(2-3):267–272. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90131-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huet J., Riva M., Sentenac A., Fromageot P. Yeast RNA polymerase C and its subunits. Specific antibodies as structural and functional probes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 5;260(28):15304–15310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes J. M., Konings D. A., Cesareni G. The yeast homologue of U3 snRNA. EMBO J. 1987 Jul;6(7):2145–2155. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02482.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James P., Hall B. D. ret1-1, a yeast mutant affecting transcription termination by RNA polymerase III. Genetics. 1990 Jun;125(2):293–303. doi: 10.1093/genetics/125.2.293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiss T., Marshallsay C., Filipowicz W. 7-2/MRP RNAs in plant and mammalian cells: association with higher order structures in the nucleolus. EMBO J. 1992 Oct;11(10):3737–3746. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05459.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiss T., Marshallsay C., Filipowicz W. Alteration of the RNA polymerase specificity of U3 snRNA genes during evolution and in vitro. Cell. 1991 May 3;65(3):517–526. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90469-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhrer K., Domdey H. Preparation of high molecular weight RNA. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:398–405. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94030-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai E., Prezioso V. R., Smith E., Litvin O., Costa R. H., Darnell J. E., Jr HNF-3A, a hepatocyte-enriched transcription factor of novel structure is regulated transcriptionally. Genes Dev. 1990 Aug;4(8):1427–1436. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.8.1427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai E., Prezioso V. R., Tao W. F., Chen W. S., Darnell J. E., Jr Hepatocyte nuclear factor 3 alpha belongs to a gene family in mammals that is homologous to the Drosophila homeotic gene fork head. Genes Dev. 1991 Mar;5(3):416–427. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.3.416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lalo D., Carles C., Sentenac A., Thuriaux P. Interactions between three common subunits of yeast RNA polymerases I and III. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 15;90(12):5524–5528. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.12.5524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laughon A., Gesteland R. F. Isolation and preliminary characterization of the GAL4 gene, a positive regulator of transcription in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6827–6831. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legrain P., Rosbash M. Some cis- and trans-acting mutants for splicing target pre-mRNA to the cytoplasm. Cell. 1989 May 19;57(4):573–583. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90127-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li C., Lai C. F., Sigman D. S., Gaynor R. B. Cloning of a cellular factor, interleukin binding factor, that binds to NFAT-like motifs in the human immunodeficiency virus long terminal repeat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7739–7743. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann C., Buhler J. M., Treich I., Sentenac A. RPC40, a unique gene for a subunit shared between yeast RNA polymerases A and C. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):627–637. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90241-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann C., Micouin J. Y., Chiannilkulchai N., Treich I., Buhler J. M., Sentenac A. RPC53 encodes a subunit of Saccharomyces cerevisiae RNA polymerase C (III) whose inactivation leads to a predominantly G1 arrest. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;12(10):4314–4326. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.10.4314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marck C. 'DNA Strider': a 'C' program for the fast analysis of DNA and protein sequences on the Apple Macintosh family of computers. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Mar 11;16(5):1829–1836. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.5.1829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller L. M., Gallegos M. E., Morisseau B. A., Kim S. K. lin-31, a Caenorhabditis elegans HNF-3/fork head transcription factor homolog, specifies three alternative cell fates in vulval development. Genes Dev. 1993 Jun;7(6):933–947. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.6.933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moenne A., Camier S., Anderson G., Margottin F., Beggs J., Sentenac A. The U6 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae is transcribed by RNA polymerase C (III) in vivo and in vitro. EMBO J. 1990 Jan;9(1):271–277. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08105.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosrin C., Riva M., Beltrame M., Cassar E., Sentenac A., Thuriaux P. The RPC31 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae encodes a subunit of RNA polymerase C (III) with an acidic tail. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;10(9):4737–4743. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.9.4737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mémet S., Saurin W., Sentenac A. RNA polymerases B and C are more closely related to each other than to RNA polymerase A. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 25;263(21):10048–10051. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nonet M., Scafe C., Sexton J., Young R. Eucaryotic RNA polymerase conditional mutant that rapidly ceases mRNA synthesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1602–1611. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr-Weaver T. L., Szostak J. W., Rothstein R. J. Yeast transformation: a model system for the study of recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6354–6358. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parikh V. S., Conrad-Webb H., Docherty R., Butow R. A. Interaction between the yeast mitochondrial and nuclear genomes influences the abundance of novel transcripts derived from the spacer region of the nuclear ribosomal DNA repeat. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 May;9(5):1897–1907. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.5.1897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Lipman D. J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell I. D., Tollervey D. NOP3 is an essential yeast protein which is required for pre-rRNA processing. J Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;119(4):737–747. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.4.737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs A. B., Davis R. W. Translation initiation and ribosomal biogenesis: involvement of a putative rRNA helicase and RPL46. Science. 1990 Mar 2;247(4946):1077–1079. doi: 10.1126/science.2408148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt M. E., Brown T. A., Trumpower B. L. A rapid and simple method for preparation of RNA from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 May 25;18(10):3091–3092. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.10.3091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt M. E., Clayton D. A. Yeast site-specific ribonucleoprotein endoribonuclease MRP contains an RNA component homologous to mammalian RNase MRP RNA and essential for cell viability. Genes Dev. 1992 Oct;6(10):1975–1985. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.10.1975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman F. Getting started with yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:3–21. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94004-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stettler S., Chiannilkulchai N., Hermann-Le Denmat S., Lalo D., Lacroute F., Sentenac A., Thuriaux P. A general suppressor of RNA polymerase I, II and III mutations in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1993 May;239(1-2):169–176. doi: 10.1007/BF00281615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stettler S., Mariotte S., Riva M., Sentenac A., Thuriaux P. An essential and specific subunit of RNA polymerase III (C) is encoded by gene RPC34 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 25;267(30):21390–21395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tao W., Lai E. Telencephalon-restricted expression of BF-1, a new member of the HNF-3/fork head gene family, in the developing rat brain. Neuron. 1992 May;8(5):957–966. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90210-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tollervey D., Lehtonen H., Carmo-Fonseca M., Hurt E. C. The small nucleolar RNP protein NOP1 (fibrillarin) is required for pre-rRNA processing in yeast. EMBO J. 1991 Mar;10(3):573–583. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07984.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treich I., Carles C., Riva M., Sentenac A. RPC10 encodes a new mini subunit shared by yeast nuclear RNA polymerases. Gene Expr. 1992;2(1):31–37. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner J. R., Udem S. A. Temperature sensitive mutations affecting ribosome synthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Mol Biol. 1972 Mar 28;65(2):243–257. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90280-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigel D., Jäckle H. The fork head domain: a novel DNA binding motif of eukaryotic transcription factors? Cell. 1990 Nov 2;63(3):455–456. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90439-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigel D., Jürgens G., Küttner F., Seifert E., Jäckle H. The homeotic gene fork head encodes a nuclear protein and is expressed in the terminal regions of the Drosophila embryo. Cell. 1989 May 19;57(4):645–658. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90133-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner M., Chaussivert N., Willis I. M., Sentenac A. Interaction between a complex of RNA polymerase III subunits and the 70-kDa component of transcription factor IIIB. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 5;268(28):20721–20724. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner M., Hermann-Le Denmat S., Treich I., Sentenac A., Thuriaux P. Effect of mutations in a zinc-binding domain of yeast RNA polymerase C (III) on enzyme function and subunit association. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;12(3):1087–1095. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.3.1087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittekind M., Dodd J., Vu L., Kolb J. M., Buhler J. M., Sentenac A., Nomura M. Isolation and characterization of temperature-sensitive mutations in RPA190, the gene encoding the largest subunit of RNA polymerase I from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):3997–4008. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.3997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woychik N. A., Liao S. M., Kolodziej P. A., Young R. A. Subunits shared by eukaryotic nuclear RNA polymerases. Genes Dev. 1990 Mar;4(3):313–323. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.3.313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu G., Muller E. G., Amacher S. L., Northrop J. L., Davis T. N. A dosage-dependent suppressor of a temperature-sensitive calmodulin mutant encodes a protein related to the fork head family of DNA-binding proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;13(3):1779–1787. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.3.1779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]