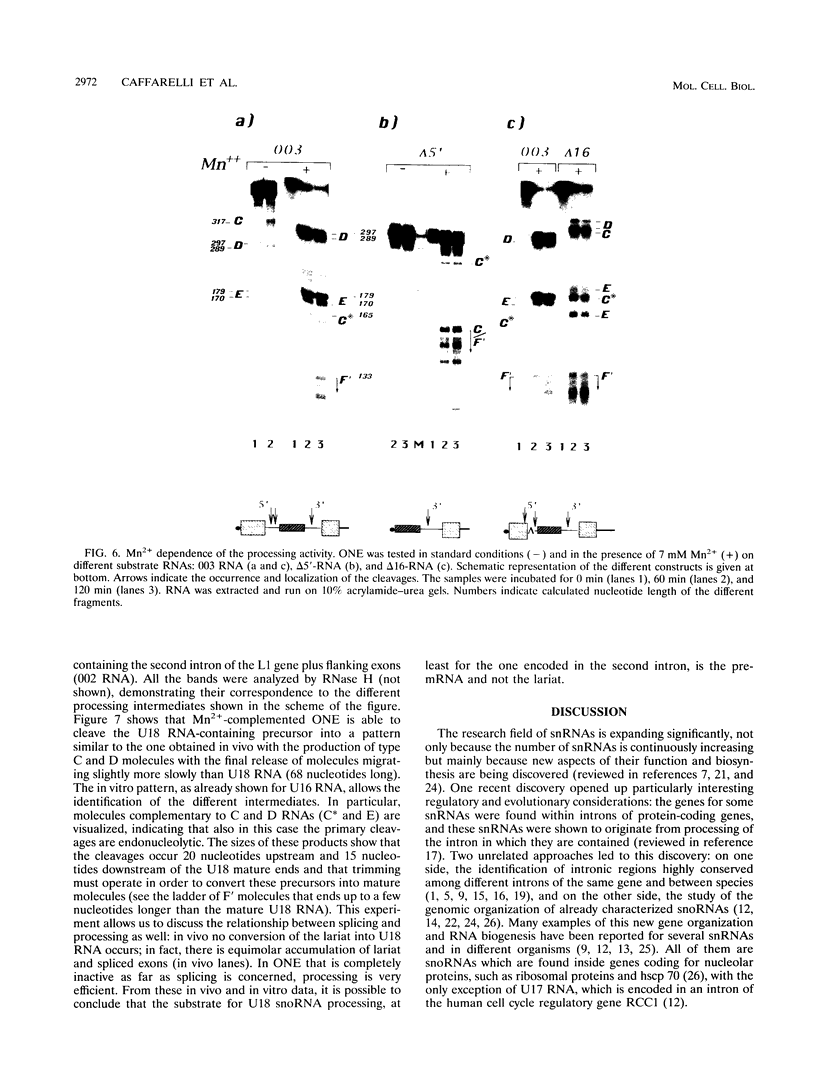
Abstract
It was recently shown that a new class of small nuclear RNAs is encoded in introns of protein-coding genes and that they originate by processing of the pre-mRNA in which they are contained. Little is known about the mechanism and the factors involved in this new type of processing. The L1 ribosomal protein gene of Xenopus laevis is a well-suited system for studying this phenomenon: several different introns encode for two small nucleolar RNAs (snoRNAs; U16 and U18). In this paper, we analyzed the in vitro processing of these snoRNAs and showed that both are released from the pre-mRNA by a common mechanism: endonucleolytic cleavages convert the pre-mRNA into a precursor snoRNA with 5' and 3' trailer sequences. Subsequently, trimming converts the pre-snoRNAs into mature molecules. Oocyte and HeLa nuclear extracts are able to process X. laevis and human substrates in a similar manner, indicating that the processing of this class of snoRNAs relies on a common and evolutionarily conserved mechanism. In addition, we found that the cleavage activity is strongly enhanced in the presence of Mn2+ ions.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bourbon H. M., Amalric F. Nucleolin gene organization in rodents: highly conserved sequences within three of the 13 introns. Gene. 1990 Apr 16;88(2):187–196. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90031-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bozzoni I., Beccari E., Luo Z. X., Amaldi F. Xenopus laevis ribosomal protein genes: isolation of recombinant cDNA clones and study of the genomic organization. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Mar 11;9(5):1069–1086. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.5.1069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caffarelli E., Fragapane P., Bozzoni I. Inefficient in vitro splicing of the regulatory intron of the L1 ribosomal protein gene of X.laevis depends on suboptimal splice site sequences. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Mar 16;183(2):680–687. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)90536-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caffarelli E., Fragapane P., Gehring C., Bozzoni I. The accumulation of mature RNA for the Xenopus laevis ribosomal protein L1 is controlled at the level of splicing and turnover of the precursor RNA. EMBO J. 1987 Nov;6(11):3493–3498. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02674.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cutruzzolá F., Loreni F., Bozzoni I. Complementarity of conserved sequence elements present in 28S ribosomal RNA and in ribosomal protein genes of Xenopus laevis and Xenopus tropicalis. Gene. 1986;49(3):371–376. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90373-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fournier M. J., Maxwell E. S. The nucleolar snRNAs: catching up with the spliceosomal snRNAs. Trends Biochem Sci. 1993 Apr;18(4):131–135. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(93)90020-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fragapane P., Caffarelli E., Lener M., Prislei S., Santoro B., Bozzoni I. Identification of the sequences responsible for the splicing phenotype of the regulatory intron of the L1 ribosomal protein gene of Xenopus laevis. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;12(3):1117–1125. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.3.1117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fragapane P., Prislei S., Michienzi A., Caffarelli E., Bozzoni I. A novel small nucleolar RNA (U16) is encoded inside a ribosomal protein intron and originates by processing of the pre-mRNA. EMBO J. 1993 Jul;12(7):2921–2928. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05954.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gandini-Attardi D., Baldi I. M., Mattoccia E., Tocchini-Valentini G. P. Transfer RNA splicing endonuclease from Xenopus laevis. Methods Enzymol. 1990;181:510–517. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)81148-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurdon J. B., Tiller E., Roberts J., Kato K. A community effect in muscle development. Curr Biol. 1993 Jan;3(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0960-9822(93)90139-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiss T., Filipowicz W. Small nucleolar RNAs encoded by introns of the human cell cycle regulatory gene RCC1. EMBO J. 1993 Jul;12(7):2913–2920. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05953.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leverette R. D., Andrews M. T., Maxwell E. S. Mouse U14 snRNA is a processed intron of the cognate hsc70 heat shock pre-messenger RNA. Cell. 1992 Dec 24;71(7):1215–1221. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(05)80069-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu J., Maxwell E. S. Mouse U14 snRNA is encoded in an intron of the mouse cognate hsc70 heat shock gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Nov 25;18(22):6565–6571. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.22.6565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loreni F., Ruberti I., Bozzoni I., Pierandrei-Amaldi P., Amaldi F. Nucleotide sequence of the L1 ribosomal protein gene of Xenopus laevis: remarkable sequence homology among introns. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 16;4(13A):3483–3488. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04107.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prislei S., Sperandio S., Fragapane P., Caffarelli E., Presutti C., Bozzoni I. The mechanisms controlling ribosomal protein L1 pre-mRNA splicing are maintained in evolution and rely on conserved intron sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Sep 11;20(17):4473–4479. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.17.4473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruff E. A., Rimoldi O. J., Raghu B., Eliceiri G. L. Three small nucleolar RNAs of unique nucleotide sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 15;90(2):635–638. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.2.635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Séraphin B. How many intronic snRNAs? Trends Biochem Sci. 1993 Sep;18(9):330–331. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(93)90067-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tycowski K. T., Shu M. D., Steitz J. A. A small nucleolar RNA is processed from an intron of the human gene encoding ribosomal protein S3. Genes Dev. 1993 Jul;7(7A):1176–1190. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.7a.1176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch W. J., Feramisco J. R. Nuclear and nucleolar localization of the 72,000-dalton heat shock protein in heat-shocked mammalian cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 10;259(7):4501–4513. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]