Abstract
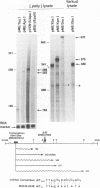
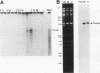
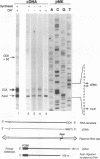
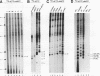
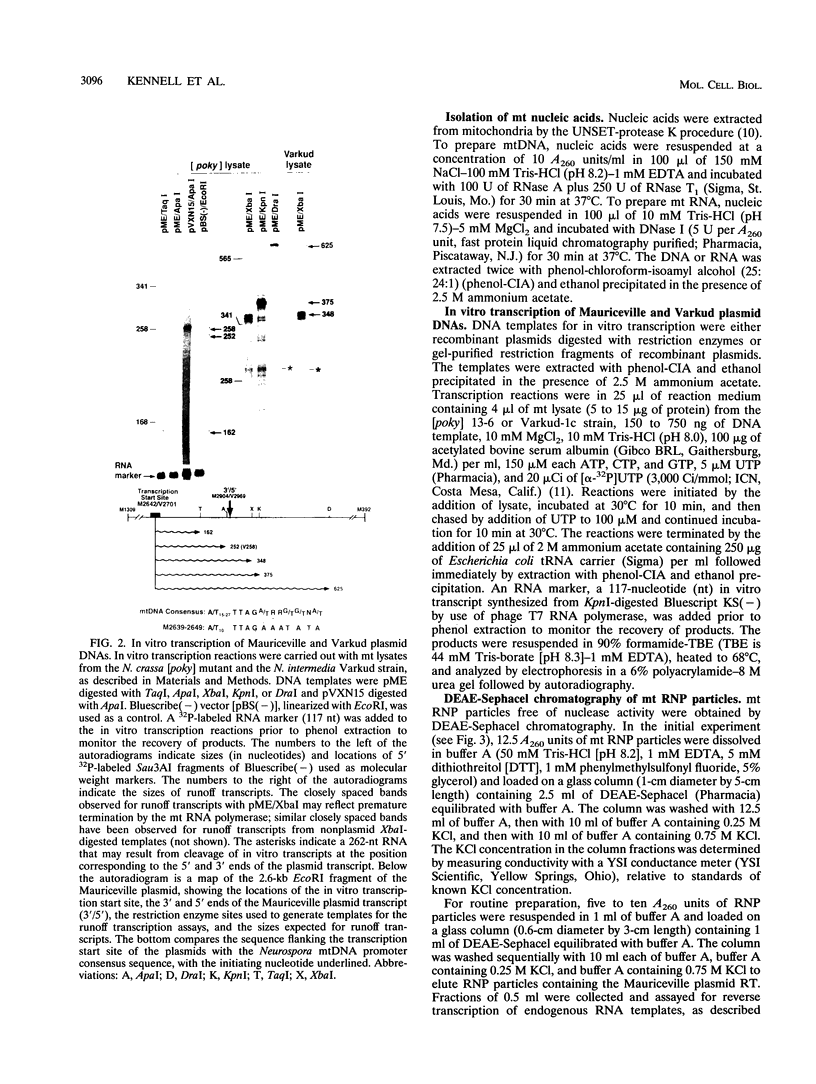
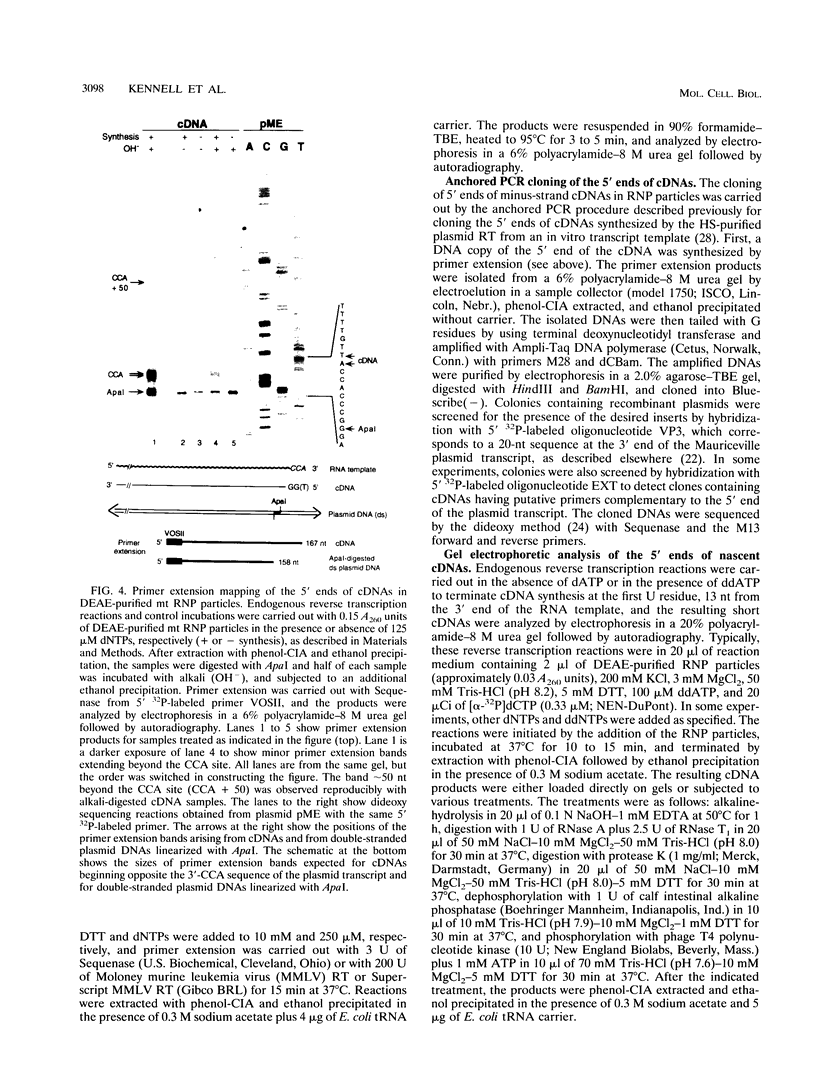
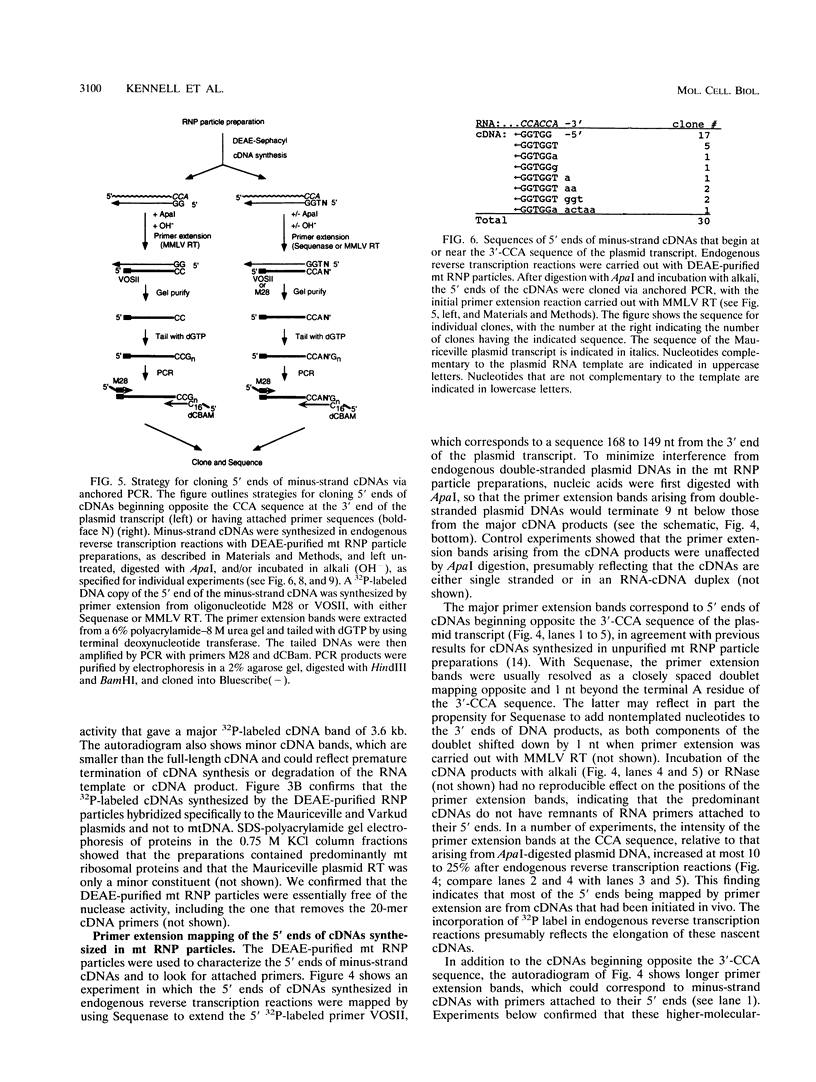
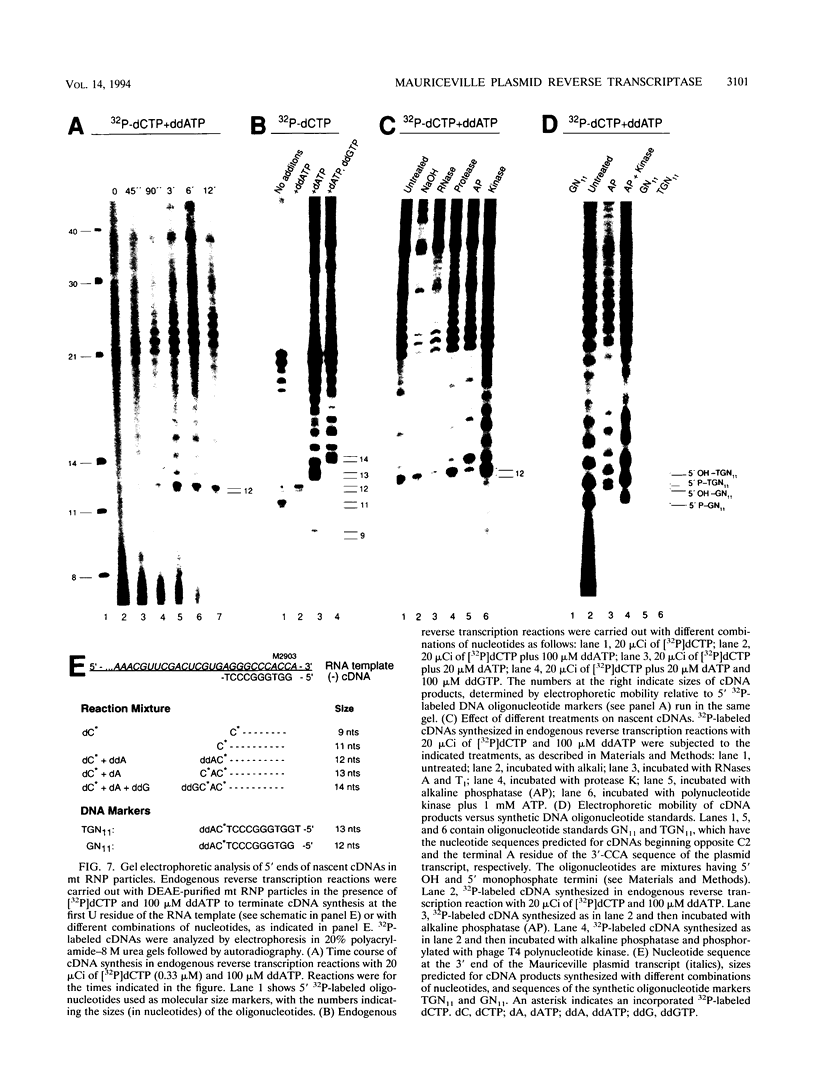
The Mauriceville plasmid and the closely related Varkud plasmid of Neurospora spp. are retroelements that propagate in mitochondria. Replication appears to occur by a novel mechanism in which a monomer-length plasmid transcript having a 3' tRNA-like structure ending in CCA is reverse transcribed to give a full-length minus-strand cDNA beginning at or near the 3' end of the RNA. Here, we show that the plasmids are transcribed in vitro by the Neurospora mitochondrial RNA polymerase, with the major in vitro transcription start site approximately 260 bp upstream of the 5' end of the plasmid transcript. The location of the transcription start site suggests that the monomer-length transcripts are generated by transcription around the plasmid combined with a site-specific RNA cleavage after the 3'-CCA sequence. The 5' ends of minus-strand cDNAs in ribonucleoprotein particles were analyzed to obtain insight into the mechanism of initiation of reverse transcription in vivo. A major class of minus-strand cDNAs begins opposite C2 of the 3'-CCA sequence, the same site used for de novo initiation of cDNA synthesis by the plasmid reverse transcriptase in vitro. A second class of minus-strand cDNAs begins with putative primer sequences that correspond to cDNA copies of the plasmid or mitochondrial transcripts. These findings are consistent with the possibility that the plasmid reverse transcriptase initiates minus-strand cDNA synthesis in vivo both by de novo initiation and by a novel template-switching mechanism in which the 3' OH of a previously synthesized cDNA is used to prime the synthesis of a new minus-strand cDNA directly at the 3' end of the plasmid transcript.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akins R. A., Grant D. M., Stohl L. L., Bottorff D. A., Nargang F. E., Lambowitz A. M. Nucleotide sequence of the Varkud mitochondrial plasmid of Neurospora and synthesis of a hybrid transcript with a 5' leader derived from mitochondrial RNA. J Mol Biol. 1988 Nov 5;204(1):1–25. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90594-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akins R. A., Kelley R. L., Lambowitz A. M. Characterization of mutant mitochondrial plasmids of Neurospora spp. that have incorporated tRNAs by reverse transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):678–691. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akins R. A., Kelley R. L., Lambowitz A. M. Mitochondrial plasmids of Neurospora: integration into mitochondrial DNA and evidence for reverse transcription in mitochondria. Cell. 1986 Nov 21;47(4):505–516. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90615-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barath Z., Küntzel H. Induction of mitochondrial RNA polymerase in Neurospora crassa. Nat New Biol. 1972 Dec 13;240(102):195–197. doi: 10.1038/newbio240195a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins R. A., Stohl L. L., Cole M. D., Lambowitz A. M. Characterization of a novel plasmid DNA found in mitochondria of N. crassa. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):443–452. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90335-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denhardt D. T. A membrane-filter technique for the detection of complementary DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Jun 13;23(5):641–646. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90447-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganem D., Varmus H. E. The molecular biology of the hepatitis B viruses. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:651–693. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garriga G., Lambowitz A. M. RNA splicing in neurospora mitochondria: self-splicing of a mitochondrial intron in vitro. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):631–641. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90470-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennell J. C., Lambowitz A. M. Development of an in vitro transcription system for Neurospora crassa mitochondrial DNA and identification of transcription initiation sites. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;9(9):3603–3613. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.9.3603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubelik A. R., Kennell J. C., Akins R. A., Lambowitz A. M. Identification of Neurospora mitochondrial promoters and analysis of synthesis of the mitochondrial small rRNA in wild-type and the promoter mutant [poky]. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 15;265(8):4515–4526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuiper M. T., Lambowitz A. M. A novel reverse transcriptase activity associated with mitochondrial plasmids of Neurospora. Cell. 1988 Nov 18;55(4):693–704. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90228-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuiper M. T., Sabourin J. R., Lambowitz A. M. Identification of the reverse transcriptase encoded by the Mauriceville and Varkud mitochondrial plasmids of Neurospora. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 25;265(12):6936–6943. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambowitz A. M. Preparation and analysis of mitochondrial ribosomes. Methods Enzymol. 1979;59:421–433. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)59103-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maleszka R. Electrophoretic profiles of mitochondrial plasmids in Neurospora suggest they replicate by a rolling circle mechanism. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Aug 14;186(3):1669–1673. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)81600-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel F., Lang B. F. Mitochondrial class II introns encode proteins related to the reverse transcriptases of retroviruses. Nature. 1985 Aug 15;316(6029):641–643. doi: 10.1038/316641a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller W. A., Bujarski J. J., Dreher T. W., Hall T. C. Minus-strand initiation by brome mosaic virus replicase within the 3' tRNA-like structure of native and modified RNA templates. J Mol Biol. 1986 Feb 20;187(4):537–546. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90332-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nargang F. E., Bell J. B., Stohl L. L., Lambowitz A. M. The DNA sequence and genetic organization of a Neurospora mitochondrial plasmid suggest a relationship to introns and mobile elements. Cell. 1984 Sep;38(2):441–453. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90499-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao A. L., Dreher T. W., Marsh L. E., Hall T. C. Telomeric function of the tRNA-like structure of brome mosaic virus RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5335–5339. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanfaçon H., Hohn T. Proximity to the promoter inhibits recognition of cauliflower mosaic virus polyadenylation signal. Nature. 1990 Jul 5;346(6279):81–84. doi: 10.1038/346081a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saville B. J., Collins R. A. A site-specific self-cleavage reaction performed by a novel RNA in Neurospora mitochondria. Cell. 1990 May 18;61(4):685–696. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90480-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang H., Kennell J. C., Kuiper M. T., Sabourin J. R., Saldanha R., Lambowitz A. M. The Mauriceville plasmid of Neurospora crassa: characterization of a novel reverse transcriptase that begins cDNA synthesis at the 3' end of template RNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;12(11):5131–5144. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.11.5131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang H., Lambowitz A. M. Reverse transcription of the Mauriceville plasmid of Neurospora. Lack of ribonuclease H activity associated with the reverse transcriptase and possible use of mitochondrial ribonuclease H. J Biol Chem. 1993 Sep 5;268(25):18951–18959. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang H., Lambowitz A. M. The Mauriceville plasmid reverse transcriptase can initiate cDNA synthesis de novo and may be related to reverse transcriptase and DNA polymerase progenitor. Cell. 1993 Dec 17;75(6):1071–1081. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90317-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiong Y., Eickbush T. H. Origin and evolution of retroelements based upon their reverse transcriptase sequences. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3353–3362. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07536.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]