Abstract
In contrast to skeletal muscle, the mechanisms responsible for activation and maintenance of tissue-specific transcription in cardiac muscle remain poorly understood. A family of hormone-encoding genes is expressed in a highly specific manner in cardiac but not skeletal myocytes. This includes the A- and B-type natriuretic peptide (ANP and BNP) genes, which encode peptide hormones with crucial roles in the regulation of blood volume and pressure. Since these genes are markers of cardiac cells, we have used them to probe the mechanisms for cardiac muscle-specific transcription. Cloning and functional analysis of the rat BNP upstream sequences revealed unexpected structural resemblance to erythroid but not to muscle-specific promoters and enhancers, including a requirement for regulatory elements containing GATA motifs. A cDNA clone corresponding to a member of the GATA family of transcription factors was isolated from a cardiomyocyte cDNA library. Transcription of this GATA gene is restricted mostly to the heart and is undetectable in skeletal muscle. Within the heart, GATA transcripts are localized in ANP- and BNP-expressing myocytes, and forced expression of the GATA protein in heterologous cells markedly activates transcription from the natural cardiac muscle-specific ANP and BNP promoters. This GATA-dependent pathway defines the first mechanism for cardiac muscle-specific transcription. Moreover, the present findings reveal striking similarities between the mechanisms controlling gene expression in hematopoietic and cardiac cells and may have important implications for studies of cardiogenesis.
Full text
PDF


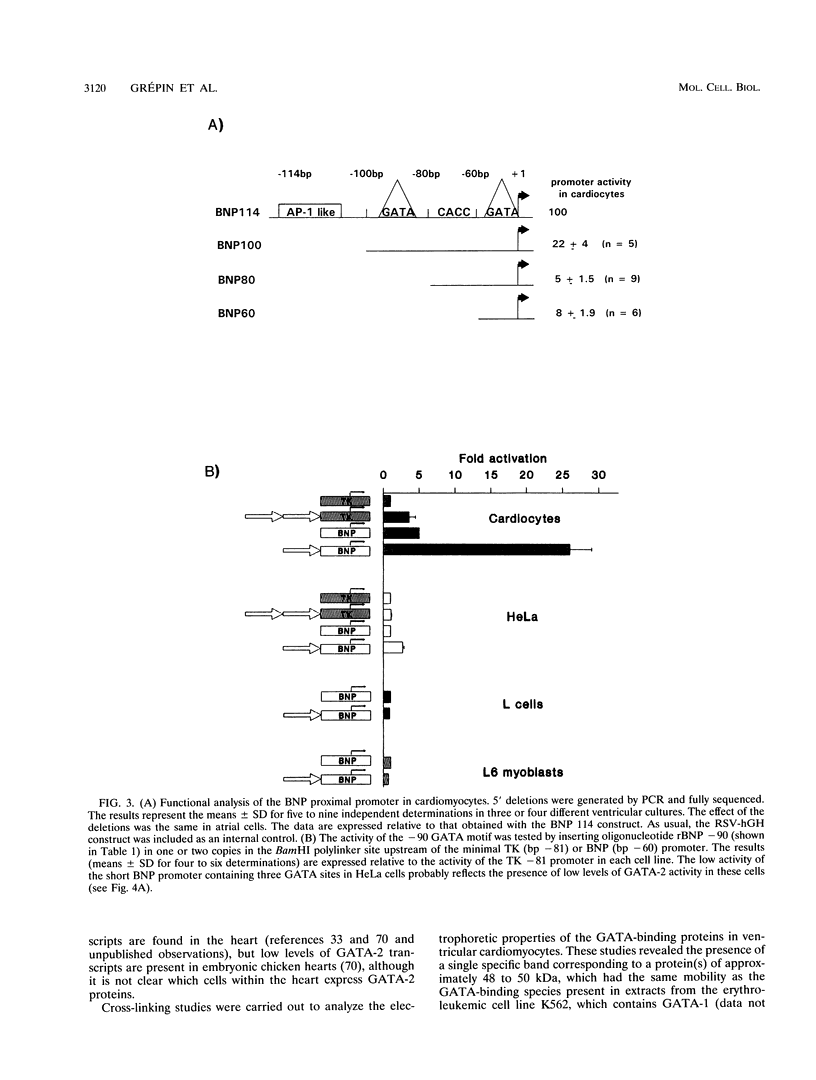
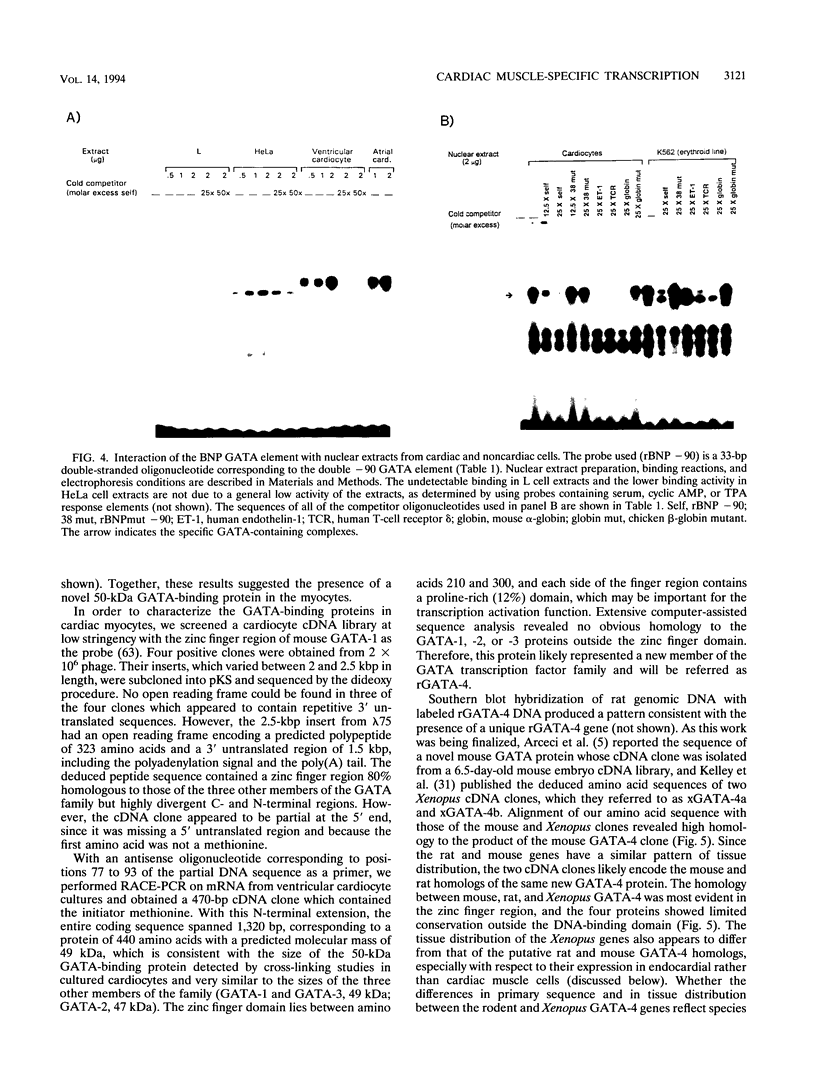
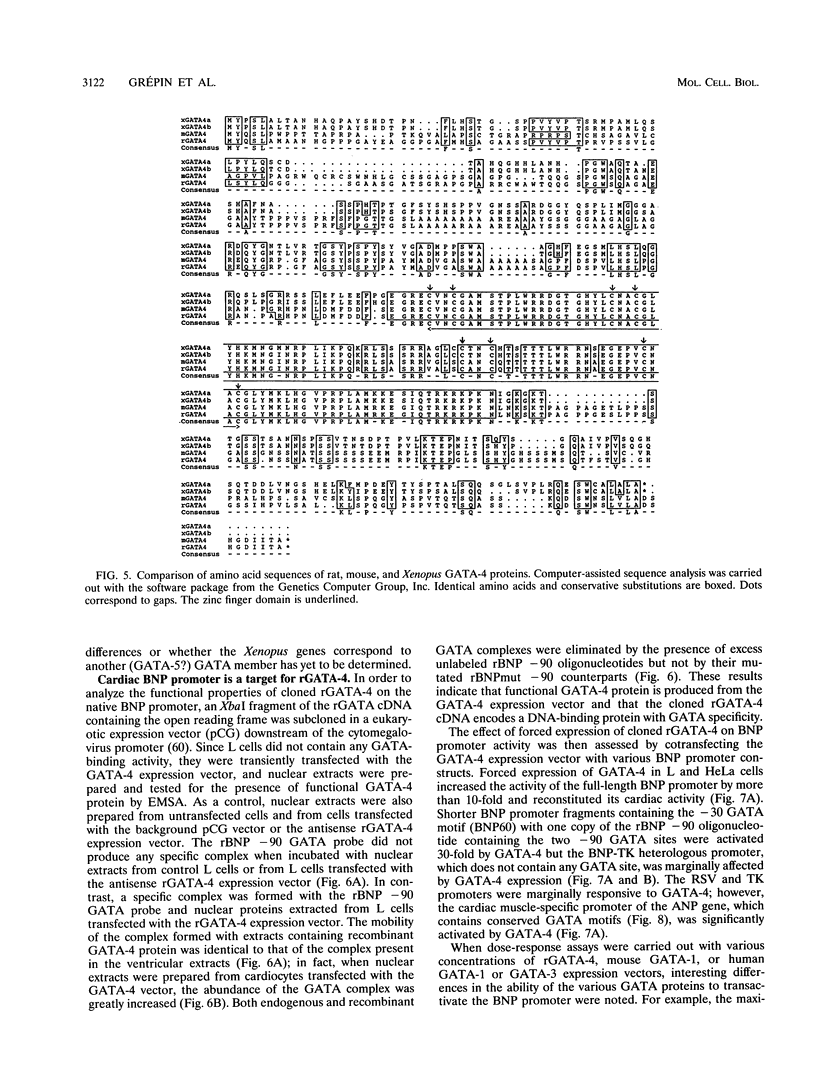

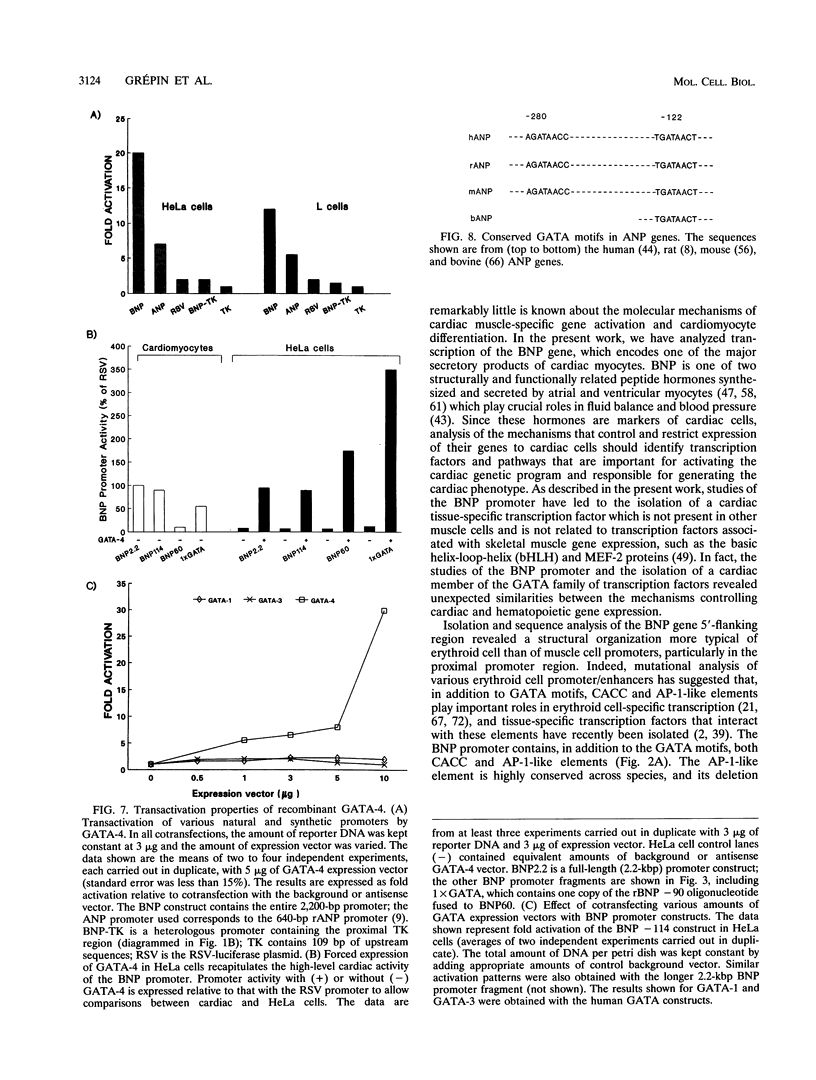
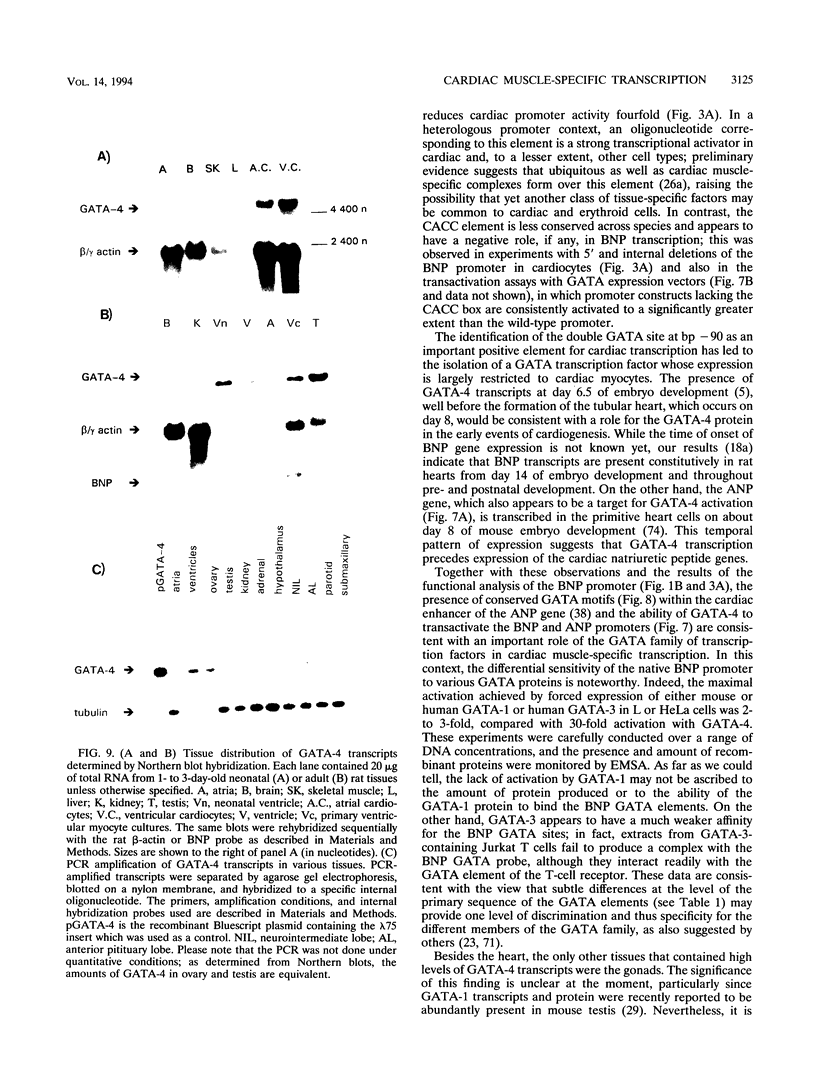
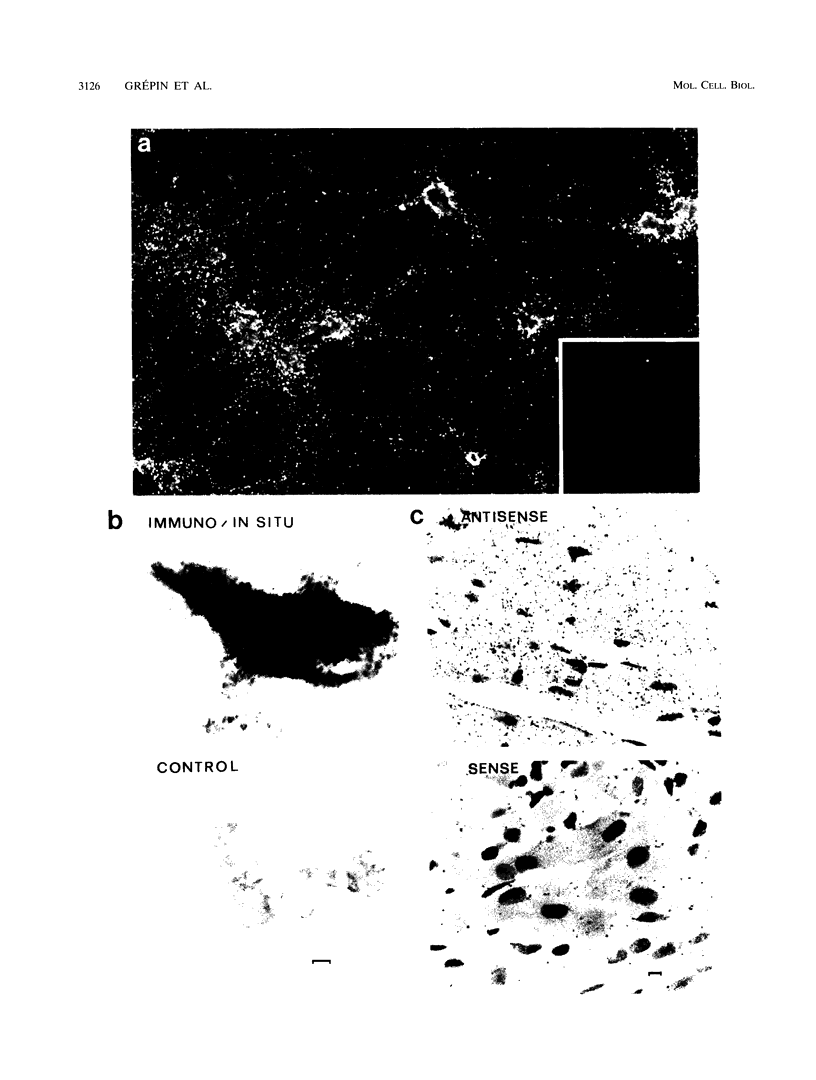



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amacher S. L., Buskin J. N., Hauschka S. D. Multiple regulatory elements contribute differentially to muscle creatine kinase enhancer activity in skeletal and cardiac muscle. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 May;13(5):2753–2764. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.5.2753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews N. C., Erdjument-Bromage H., Davidson M. B., Tempst P., Orkin S. H. Erythroid transcription factor NF-E2 is a haematopoietic-specific basic-leucine zipper protein. Nature. 1993 Apr 22;362(6422):722–728. doi: 10.1038/362722a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antakly T., Sasaki A., Liotta A. S., Palkovits M., Krieger D. T. Induced expression of the glucocorticoid receptor in the rat intermediate pituitary lobe. Science. 1985 Jul 19;229(4710):277–279. doi: 10.1126/science.3892690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antakly T., Thompson E. B., O'Donnell D. Demonstration of the intracellular localization and up-regulation of glucocorticoid receptor by in situ hybridization and immunocytochemistry. Cancer Res. 1989 Apr 15;49(8 Suppl):2230s–2234s. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arceci R. J., King A. A., Simon M. C., Orkin S. H., Wilson D. B. Mouse GATA-4: a retinoic acid-inducible GATA-binding transcription factor expressed in endodermally derived tissues and heart. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;13(4):2235–2246. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.4.2235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ardati A., Nemer M. A nuclear pathway for alpha 1-adrenergic receptor signaling in cardiac cells. EMBO J. 1993 Dec 15;12(13):5131–5139. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06208.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Argentin S., Ardati A., Tremblay S., Lihrmann I., Robitaille L., Drouin J., Nemer M. Developmental stage-specific regulation of atrial natriuretic factor gene transcription in cardiac cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jan;14(1):777–790. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.1.777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Argentin S., Nemer M., Drouin J., Scott G. K., Kennedy B. P., Davies P. L. The gene for rat atrial natriuretic factor. J Biol Chem. 1985 Apr 25;260(8):4568–4571. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Argentin S., Sun Y. L., Lihrmann I., Schmidt T. J., Drouin J., Nemer M. Distal cis-acting promoter sequences mediate glucocorticoid stimulation of cardiac atrial natriuretic factor gene transcription. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 5;266(34):23315–23322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barton P. J., Buckingham M. E. The myosin alkali light chain proteins and their genes. Biochem J. 1985 Oct 15;231(2):249–261. doi: 10.1042/bj2310249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloch K. D., Seidman J. G., Naftilan J. D., Fallon J. T., Seidman C. E. Neonatal atria and ventricles secrete atrial natriuretic factor via tissue-specific secretory pathways. Cell. 1986 Dec 5;47(5):695–702. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90512-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun T., Rudnicki M. A., Arnold H. H., Jaenisch R. Targeted inactivation of the muscle regulatory gene Myf-5 results in abnormal rib development and perinatal death. Cell. 1992 Oct 30;71(3):369–382. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90507-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapeau C., Gutkowska J., Schiller P. W., Milne R. W., Thibault G., Garcia R., Genest J., Cantin M. Localization of immunoreactive synthetic atrial natriuretic factor (ANF) in the heart of various animal species. J Histochem Cytochem. 1985 Jun;33(6):541–550. doi: 10.1177/33.6.3158698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dagnino L., Drouin J., Nemer M. Differential expression of natriuretic peptide genes in cardiac and extracardiac tissues. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Sep;5(9):1292–1300. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-9-1292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dagnino L., Lavigne J. P., Nemer M. Increased transcripts for B-type natriuretic peptide in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Quantitative polymerase chain reaction for atrial and brain natriuretic peptide transcripts. Hypertension. 1992 Nov;20(5):690–700. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.20.5.690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donald J. A., Evans D. H. Immunohistochemical localisation of natriuretic peptides in the heart and brain of the gulf toadfish Opsanus beta. Cell Tissue Res. 1992 Jul;269(1):151–158. doi: 10.1007/BF00384735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerson B. M., Nickol J. M., Fong T. C. Erythroid-specific activation and derepression of the chick beta-globin promoter in vitro. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1189–1200. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90056-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans T., Felsenfeld G. The erythroid-specific transcription factor Eryf1: a new finger protein. Cell. 1989 Sep 8;58(5):877–885. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90940-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans T., Felsenfeld G. trans-Activation of a globin promoter in nonerythroid cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;11(2):843–853. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.2.843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans T., Reitman M., Felsenfeld G. An erythrocyte-specific DNA-binding factor recognizes a regulatory sequence common to all chicken globin genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):5976–5980. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.5976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong T. C., Emerson B. M. The erythroid-specific protein cGATA-1 mediates distal enhancer activity through a specialized beta-globin TATA box. Genes Dev. 1992 Apr;6(4):521–532. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.4.521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gossett L. A., Kelvin D. J., Sternberg E. A., Olson E. N. A new myocyte-specific enhancer-binding factor that recognizes a conserved element associated with multiple muscle-specific genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):5022–5033. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.5022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasty P., Bradley A., Morris J. H., Edmondson D. G., Venuti J. M., Olson E. N., Klein W. H. Muscle deficiency and neonatal death in mice with a targeted mutation in the myogenin gene. Nature. 1993 Aug 5;364(6437):501–506. doi: 10.1038/364501a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho I. C., Vorhees P., Marin N., Oakley B. K., Tsai S. F., Orkin S. H., Leiden J. M. Human GATA-3: a lineage-restricted transcription factor that regulates the expression of the T cell receptor alpha gene. EMBO J. 1991 May;10(5):1187–1192. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08059.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito E., Toki T., Ishihara H., Ohtani H., Gu L., Yokoyama M., Engel J. D., Yamamoto M. Erythroid transcription factor GATA-1 is abundantly transcribed in mouse testis. Nature. 1993 Apr 1;362(6419):466–468. doi: 10.1038/362466a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joulin V., Bories D., Eléouet J. F., Labastie M. C., Chrétien S., Mattéi M. G., Roméo P. H. A T-cell specific TCR delta DNA binding protein is a member of the human GATA family. EMBO J. 1991 Jul;10(7):1809–1816. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07706.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley C., Blumberg H., Zon L. I., Evans T. GATA-4 is a novel transcription factor expressed in endocardium of the developing heart. Development. 1993 Jul;118(3):817–827. doi: 10.1242/dev.118.3.817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keynes R. J., Stern C. D. Mechanisms of vertebrate segmentation. Development. 1988 Jul;103(3):413–429. doi: 10.1242/dev.103.3.413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ko L. J., Yamamoto M., Leonard M. W., George K. M., Ting P., Engel J. D. Murine and human T-lymphocyte GATA-3 factors mediate transcription through a cis-regulatory element within the human T-cell receptor delta gene enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2778–2784. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2778. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. E., Temizer D. H., Clifford J. A., Quertermous T. Cloning of the GATA-binding protein that regulates endothelin-1 gene expression in endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 25;266(24):16188–16192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linask K. K., Lash J. W. Precardiac cell migration: fibronectin localization at mesoderm-endoderm interface during directional movement. Dev Biol. 1986 Mar;114(1):87–101. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(86)90385-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBride K., Robitaille L., Tremblay S., Argentin S., Nemer M. fos/jun repression of cardiac-specific transcription in quiescent and growth-stimulated myocytes is targeted at a tissue-specific cis element. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;13(1):600–612. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.1.600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller I. J., Bieker J. J. A novel, erythroid cell-specific murine transcription factor that binds to the CACCC element and is related to the Krüppel family of nuclear proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 May;13(5):2776–2786. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.5.2776. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minty A., Kedes L. Upstream regions of the human cardiac actin gene that modulate its transcription in muscle cells: presence of an evolutionarily conserved repeated motif. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2125–2136. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakatsuji Y., Hidaka K., Tsujino S., Yamamoto Y., Mukai T., Yanagihara T., Kishimoto T., Sakoda S. A single MEF-2 site is a major positive regulatory element required for transcription of the muscle-specific subunit of the human phosphoglycerate mutase gene in skeletal and cardiac muscle cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;12(10):4384–4390. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.10.4384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navankasattusas S., Zhu H., Garcia A. V., Evans S. M., Chien K. R. A ubiquitous factor (HF-1a) and a distinct muscle factor (HF-1b/MEF-2) form an E-box-independent pathway for cardiac muscle gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;12(4):1469–1479. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.4.1469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Needleman P., Blaine E. H., Greenwald J. E., Michener M. L., Saper C. B., Stockmann P. T., Tolunay H. E. The biochemical pharmacology of atrial peptides. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1989;29:23–54. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.29.040189.000323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemer M., Chamberland M., Sirois D., Argentin S., Drouin J., Dixon R. A., Zivin R. A., Condra J. H. Gene structure of human cardiac hormone precursor, pronatriodilatin. Nature. 1984 Dec 13;312(5995):654–656. doi: 10.1038/312654a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemer M., Lavigne J. P., Drouin J., Thibault G., Gannon M., Antakly T. Expression of atrial natriuretic factor gene in heart ventricular tissue. Peptides. 1986 Nov-Dec;7(6):1147–1152. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(86)90145-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Netchitailo P., Feuilloley M., Pelletier G., Cantin M., De Lean A., Leboulenger F., Vaudry H. Localization and characterization of atrial natriuretic factor (ANF)-like peptide in the frog atrium. Peptides. 1986 Jul-Aug;7(4):573–579. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(86)90029-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa Y., Nakao K., Mukoyama M., Hosoda K., Shirakami G., Arai H., Saito Y., Suga S., Jougasaki M., Imura H. Natriuretic peptides as cardiac hormones in normotensive and spontaneously hypertensive rats. The ventricle is a major site of synthesis and secretion of brain natriuretic peptide. Circ Res. 1991 Aug;69(2):491–500. doi: 10.1161/01.res.69.2.491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson E. N. MyoD family: a paradigm for development? Genes Dev. 1990 Sep;4(9):1454–1461. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.9.1454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pevny L., Simon M. C., Robertson E., Klein W. H., Tsai S. F., D'Agati V., Orkin S. H., Costantini F. Erythroid differentiation in chimaeric mice blocked by a targeted mutation in the gene for transcription factor GATA-1. Nature. 1991 Jan 17;349(6306):257–260. doi: 10.1038/349257a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plumb M., Frampton J., Wainwright H., Walker M., Macleod K., Goodwin G., Harrison P. GATAAG; a cis-control region binding an erythroid-specific nuclear factor with a role in globin and non-globin gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jan 11;17(1):73–92. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.1.73. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollock R., Treisman R. Human SRF-related proteins: DNA-binding properties and potential regulatory targets. Genes Dev. 1991 Dec;5(12A):2327–2341. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.12a.2327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudnicki M. A., Braun T., Hinuma S., Jaenisch R. Inactivation of MyoD in mice leads to up-regulation of the myogenic HLH gene Myf-5 and results in apparently normal muscle development. Cell. 1992 Oct 30;71(3):383–390. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90508-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sassoon D., Lyons G., Wright W. E., Lin V., Lassar A., Weintraub H., Buckingham M. Expression of two myogenic regulatory factors myogenin and MyoD1 during mouse embryogenesis. Nature. 1989 Sep 28;341(6240):303–307. doi: 10.1038/341303a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber E., Matthias P., Müller M. M., Schaffner W. Rapid detection of octamer binding proteins with 'mini-extracts', prepared from a small number of cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Aug 11;17(15):6419–6419. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.15.6419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidman C. E., Bloch K. D., Klein K. A., Smith J. A., Seidman J. G. Nucleotide sequences of the human and mouse atrial natriuretic factor genes. Science. 1984 Dec 7;226(4679):1206–1209. doi: 10.1126/science.6542248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sudoh T., Kangawa K., Minamino N., Matsuo H. A new natriuretic peptide in porcine brain. Nature. 1988 Mar 3;332(6159):78–81. doi: 10.1038/332078a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki E., Hirata Y., Kohmoto O., Sugimoto T., Hayakawa H., Matsuoka H., Sugimoto T., Kojima M., Kangawa K., Minamino N. Cellular mechanisms for synthesis and secretion of atrial natriuretic peptide and brain natriuretic peptide in cultured rat atrial cells. Circ Res. 1992 Nov;71(5):1039–1048. doi: 10.1161/01.res.71.5.1039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takei Y., Takahashi A., Watanabe T. X., Nakajima K., Sakakibara S. Amino acid sequence and relative biological activity of eel atrial natriuretic peptide. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Oct 16;164(1):537–543. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)91752-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka M., Herr W. Differential transcriptional activation by Oct-1 and Oct-2: interdependent activation domains induce Oct-2 phosphorylation. Cell. 1990 Feb 9;60(3):375–386. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90589-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thibault G., Charbonneau C., Bilodeau J., Schiffrin E. L., Garcia R. Rat brain natriuretic peptide is localized in atrial granules and released into the circulation. Am J Physiol. 1992 Aug;263(2 Pt 2):R301–R309. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1992.263.2.R301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toshimori H., Toshimori K., Minamino N., Kangawa K., Oura C., Matsukura S., Matsuo H. Chicken atrial natriuretic peptide (chANP) and its secretion. Cell Tissue Res. 1990 Feb;259(2):293–298. doi: 10.1007/BF00318451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai S. F., Martin D. I., Zon L. I., D'Andrea A. D., Wong G. G., Orkin S. H. Cloning of cDNA for the major DNA-binding protein of the erythroid lineage through expression in mammalian cells. Nature. 1989 Jun 8;339(6224):446–451. doi: 10.1038/339446a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandekerckhove J., Bugaisky G., Buckingham M. Simultaneous expression of skeletal muscle and heart actin proteins in various striated muscle tissues and cells. A quantitative determination of the two actin isoforms. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 5;261(4):1838–1843. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vesely D. L., Giordano A. T. The most primitive heart in the animal kingdom contains the atrial natriuretic peptide hormonal system. Comp Biochem Physiol C. 1992 Feb;101(2):325–329. doi: 10.1016/0742-8413(92)90282-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlasuk G. P., Miller J., Bencen G. H., Lewicki J. A. Structure and analysis of the bovine atrial natriuretic peptide precursor gene. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Apr 14;136(1):396–403. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90924-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walters M., Martin D. I. Functional erythroid promoters created by interaction of the transcription factor GATA-1 with CACCC and AP-1/NFE-2 elements. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 1;89(21):10444–10448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.21.10444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H., Davis R., Tapscott S., Thayer M., Krause M., Benezra R., Blackwell T. K., Turner D., Rupp R., Hollenberg S. The myoD gene family: nodal point during specification of the muscle cell lineage. Science. 1991 Feb 15;251(4995):761–766. doi: 10.1126/science.1846704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. B., Dorfman D. M., Orkin S. H. A nonerythroid GATA-binding protein is required for function of the human preproendothelin-1 promoter in endothelial cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;10(9):4854–4862. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.9.4854. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto M., Ko L. J., Leonard M. W., Beug H., Orkin S. H., Engel J. D. Activity and tissue-specific expression of the transcription factor NF-E1 multigene family. Genes Dev. 1990 Oct;4(10):1650–1662. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.10.1650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang H. Y., Evans T. Distinct roles for the two cGATA-1 finger domains. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;12(10):4562–4570. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.10.4562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu C. Y., Motamed K., Chen J., Bailey A. D., Shen C. K. The CACC box upstream of human embryonic epsilon globin gene binds Sp1 and is a functional promoter element in vitro and in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 15;266(14):8907–8915. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu Y. T., Breitbart R. E., Smoot L. B., Lee Y., Mahdavi V., Nadal-Ginard B. Human myocyte-specific enhancer factor 2 comprises a group of tissue-restricted MADS box transcription factors. Genes Dev. 1992 Sep;6(9):1783–1798. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.9.1783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeller R., Bloch K. D., Williams B. S., Arceci R. J., Seidman C. E. Localized expression of the atrial natriuretic factor gene during cardiac embryogenesis. Genes Dev. 1987 Sep;1(7):693–698. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.7.693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Bold A. J. Atrial natriuretic factor: a hormone produced by the heart. Science. 1985 Nov 15;230(4727):767–770. doi: 10.1126/science.2932797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]