Abstract
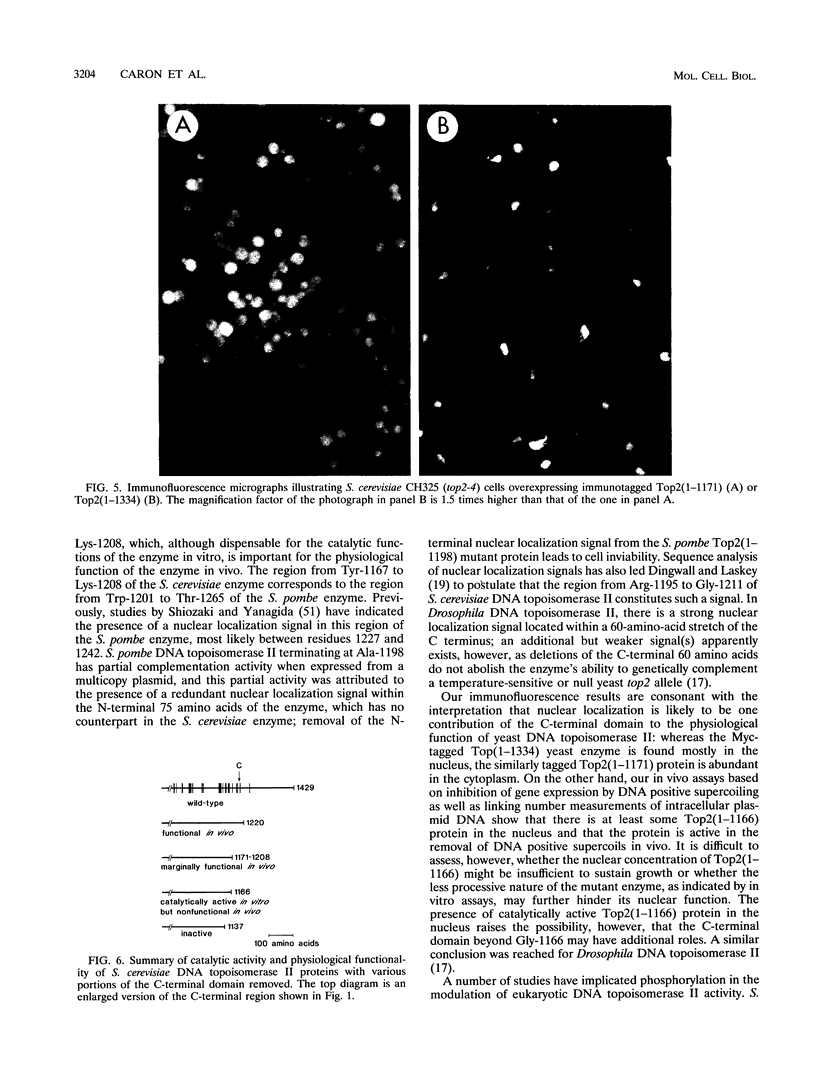
A set of carboxy-terminal deletion mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae DNA topoisomerase II were constructed for studying the functions of the carboxyl domain in vitro and in vivo. The wild-type yeast enzyme is a homodimer with 1,429 amino acid residues in each of the two polypeptides; truncation of the C terminus to Ile-1220 has little effect on the function of the enzyme in vitro or in vivo, whereas truncations extending beyond Gln-1138 yield completely inactive proteins. Several mutant enzymes with C termini in between these two residues were found to be catalytically active but unable to complement a top2-4 temperature-sensitive mutation. Immunomicroscopy results suggest that the removal of a nuclear localization signal in the C-terminal domain is likely to contribute to the physiological dysfunction of these proteins; the ability of these mutant proteins to relax supercoiled DNA in vivo shows, however, that at least some of the mutant proteins are present in the nuclei in a catalytically active form. In contrast to the ability of the catalytically active mutant proteins to relax supercoiled intracellular DNA, all mutants that do not complement the temperature-dependent lethality and high frequency of chromosomal nondisjunction of top2-4 were found to lack decatenation activity in vivo. The plausible roles of the DNA topoisomerase II C-terminal domain, in addition to providing a signal for nuclear localization, are discussed in the light of these results.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackerman P., Glover C. V., Osheroff N. Phosphorylation of DNA topoisomerase II in vivo and in total homogenates of Drosophila Kc cells. The role of casein kinase II. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 5;263(25):12653–12660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adachi Y., Käs E., Laemmli U. K. Preferential, cooperative binding of DNA topoisomerase II to scaffold-associated regions. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 20;8(13):3997–4006. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08582.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams D. E., Shekhtman E. M., Zechiedrich E. L., Schmid M. B., Cozzarelli N. R. The role of topoisomerase IV in partitioning bacterial replicons and the structure of catenated intermediates in DNA replication. Cell. 1992 Oct 16;71(2):277–288. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90356-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berrios M., Osheroff N., Fisher P. A. In situ localization of DNA topoisomerase II, a major polypeptide component of the Drosophila nuclear matrix fraction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4142–4146. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boy de la Tour E., Laemmli U. K. The metaphase scaffold is helically folded: sister chromatids have predominantly opposite helical handedness. Cell. 1988 Dec 23;55(6):937–944. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90239-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brill S. J., DiNardo S., Voelkel-Meiman K., Sternglanz R. Need for DNA topoisomerase activity as a swivel for DNA replication for transcription of ribosomal RNA. 1987 Mar 26-Apr 1Nature. 326(6111):414–416. doi: 10.1038/326414a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchenau P., Saumweber H., Arndt-Jovin D. J. Consequences of topoisomerase II inhibition in early embryogenesis of Drosophila revealed by in vivo confocal laser scanning microscopy. J Cell Sci. 1993 Apr;104(Pt 4):1175–1185. doi: 10.1242/jcs.104.4.1175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burden D. A., Goldsmith L. J., Sullivan D. M. Cell-cycle-dependent phosphorylation and activity of Chinese-hamster ovary topoisomerase II. Biochem J. 1993 Jul 1;293(Pt 1):297–304. doi: 10.1042/bj2930297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cardenas M. E., Dang Q., Glover C. V., Gasser S. M. Casein kinase II phosphorylates the eukaryote-specific C-terminal domain of topoisomerase II in vivo. EMBO J. 1992 May;11(5):1785–1796. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05230.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cardenas M. E., Gasser S. M. Regulation of topoisomerase II by phosphorylation: a role for casein kinase II. J Cell Sci. 1993 Feb;104(Pt 2):219–225. doi: 10.1242/jcs.104.2.219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson M., Botstein D. Two differentially regulated mRNAs with different 5' ends encode secreted with intracellular forms of yeast invertase. Cell. 1982 Jan;28(1):145–154. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90384-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conaway R. C., Bradsher J. N., Conaway J. W. Mechanism of assembly of the RNA polymerase II preinitiation complex. Evidence for a functional interaction between the carboxyl-terminal domain of the largest subunit of RNA polymerase II and a high molecular mass form of the TATA factor. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 25;267(12):8464–8467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crenshaw D. G., Hsieh T. Function of the hydrophilic carboxyl terminus of type II DNA topoisomerase from Drosophila melanogaster. I. In vitro studies. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 5;268(28):21328–21334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crenshaw D. G., Hsieh T. Function of the hydrophilic carboxyl terminus of type II DNA topoisomerase from Drosophila melanogaster. II. In vivo studies. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 5;268(28):21335–21343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiNardo S., Voelkel K., Sternglanz R. DNA topoisomerase II mutant of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: topoisomerase II is required for segregation of daughter molecules at the termination of DNA replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2616–2620. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingwall C., Laskey R. A. Nuclear targeting sequences--a consensus? Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Dec;16(12):478–481. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90184-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dornreiter I., Copeland W. C., Wang T. S. Initiation of simian virus 40 DNA replication requires the interaction of a specific domain of human DNA polymerase alpha with large T antigen. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Feb;13(2):809–820. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.2.809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Earnshaw W. C., Heck M. M. Localization of topoisomerase II in mitotic chromosomes. J Cell Biol. 1985 May;100(5):1716–1725. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.5.1716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gartenberg M. R., Wang J. C. Positive supercoiling of DNA greatly diminishes mRNA synthesis in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 1;89(23):11461–11465. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.23.11461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasser S. M., Laroche T., Falquet J., Boy de la Tour E., Laemmli U. K. Metaphase chromosome structure. Involvement of topoisomerase II. J Mol Biol. 1986 Apr 20;188(4):613–629. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(86)80010-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giaever G. N., Wang J. C. Supercoiling of intracellular DNA can occur in eukaryotic cells. Cell. 1988 Dec 2;55(5):849–856. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90140-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goto T., Wang J. C. Yeast DNA topoisomerase II is encoded by a single-copy, essential gene. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):1073–1080. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90057-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heck M. M., Hittelman W. N., Earnshaw W. C. In vivo phosphorylation of the 170-kDa form of eukaryotic DNA topoisomerase II. Cell cycle analysis. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 15;264(26):15161–15164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hieter P., Mann C., Snyder M., Davis R. W. Mitotic stability of yeast chromosomes: a colony color assay that measures nondisjunction and chromosome loss. Cell. 1985 Feb;40(2):381–392. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90152-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano T., Mitchison T. J. Topoisomerase II does not play a scaffolding role in the organization of mitotic chromosomes assembled in Xenopus egg extracts. J Cell Biol. 1993 Feb;120(3):601–612. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.3.601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holm C., Goto T., Wang J. C., Botstein D. DNA topoisomerase II is required at the time of mitosis in yeast. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):553–563. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80028-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holm C., Stearns T., Botstein D. DNA topoisomerase II must act at mitosis to prevent nondisjunction and chromosome breakage. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jan;9(1):159–168. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.1.159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston L. H., Williamson D. H. An alkaline sucrose gradient analysis of the mechanism of nuclear DNA synthesis in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1978 Aug 17;164(2):217–225. doi: 10.1007/BF00267387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato J., Suzuki H., Ikeda H. Purification and characterization of DNA topoisomerase IV in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 25;267(36):25676–25684. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein F., Laroche T., Cardenas M. E., Hofmann J. F., Schweizer D., Gasser S. M. Localization of RAP1 and topoisomerase II in nuclei and meiotic chromosomes of yeast. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;117(5):935–948. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.5.935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroll D. J., Sullivan D. M., Gutierrez-Hartmann A., Hoeffler J. P. Modification of DNA topoisomerase II activity via direct interactions with the cyclic adenosine-3',5'-monophosphate response element-binding protein and related transcription factors. Mol Endocrinol. 1993 Mar;7(3):305–318. doi: 10.1210/mend.7.3.8387155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Käs E., Laemmli U. K. In vivo topoisomerase II cleavage of the Drosophila histone and satellite III repeats: DNA sequence and structural characteristics. EMBO J. 1992 Feb;11(2):705–716. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05103.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsley J. E., Wang J. C. On the coupling between ATP usage and DNA transport by yeast DNA topoisomerase II. J Biol Chem. 1993 Apr 15;268(11):8096–8104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsley J. E., Wang J. C. Proteolysis patterns of epitopically labeled yeast DNA topoisomerase II suggest an allosteric transition in the enzyme induced by ATP binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10485–10489. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma X., Saitoh N., Curtis P. J. Purification and characterization of a nuclear DNA-binding factor complex containing topoisomerase II and chromosome scaffold protein 2. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 25;268(9):6182–6188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxwell A., Gellert M. Mechanistic aspects of DNA topoisomerases. Adv Protein Chem. 1986;38:69–107. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60526-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moens P. B., Earnshaw W. C. Anti-topoisomerase II recognizes meiotic chromosome cores. Chromosoma. 1989 Nov;98(5):317–322. doi: 10.1007/BF00292383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasheuer H. P., Moore A., Wahl A. F., Wang T. S. Cell cycle-dependent phosphorylation of human DNA polymerase alpha. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 25;266(12):7893–7903. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newport J. Nuclear reconstitution in vitro: stages of assembly around protein-free DNA. Cell. 1987 Jan 30;48(2):205–217. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90424-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philippsen P., Stotz A., Scherf C. DNA of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:169–182. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94014-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prigent C., Lasko D. D., Kodama K., Woodgett J. R., Lindahl T. Activation of mammalian DNA ligase I through phosphorylation by casein kinase II. EMBO J. 1992 Aug;11(8):2925–2933. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05362.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pringle J. R., Adams A. E., Drubin D. G., Haarer B. K. Immunofluorescence methods for yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:565–602. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94043-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reece R. J., Maxwell A. Tryptic fragments of the Escherichia coli DNA gyrase A protein. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 25;264(33):19648–19653. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roca J., Gartenberg M. R., Oshima Y., Wang J. C. A hit-and-run system for targeted genetic manipulations in yeast. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Sep 11;20(17):4671–4672. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.17.4671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saijo M., Ui M., Enomoto T. Growth state and cell cycle dependent phosphorylation of DNA topoisomerase II in Swiss 3T3 cells. Biochemistry. 1992 Jan 21;31(2):359–363. doi: 10.1021/bi00117a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiozaki K., Yanagida M. A functional 125-kDa core polypeptide of fission yeast DNA topoisomerase II. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;11(12):6093–6102. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.12.6093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiozaki K., Yanagida M. Functional dissection of the phosphorylated termini of fission yeast DNA topoisomerase II. J Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;119(5):1023–1036. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.5.1023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sperry A. O., Blasquez V. C., Garrard W. T. Dysfunction of chromosomal loop attachment sites: illegitimate recombination linked to matrix association regions and topoisomerase II. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5497–5501. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stow N. D. Sequences at the C-terminus of the herpes simplex virus type 1 UL30 protein are dispensable for DNA polymerase activity but not for viral origin-dependent DNA replication. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jan 11;21(1):87–92. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.1.87. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stroud R. M., McCarthy M. P., Shuster M. Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor superfamily of ligand-gated ion channels. Biochemistry. 1990 Dec 18;29(50):11009–11023. doi: 10.1021/bi00502a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swedlow J. R., Sedat J. W., Agard D. A. Multiple chromosomal populations of topoisomerase II detected in vivo by time-lapse, three-dimensional wide-field microscopy. Cell. 1993 Apr 9;73(1):97–108. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90163-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas W., Spell R. M., Ming M. E., Holm C. Genetic analysis of the gyrase A-like domain of DNA topoisomerase II of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1991 Aug;128(4):703–716. doi: 10.1093/genetics/128.4.703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uemura T., Ohkura H., Adachi Y., Morino K., Shiozaki K., Yanagida M. DNA topoisomerase II is required for condensation and separation of mitotic chromosomes in S. pombe. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):917–925. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90518-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uemura T., Tanagida M. Mitotic spindle pulls but fails to separate chromosomes in type II DNA topoisomerase mutants: uncoordinated mitosis. EMBO J. 1986 May;5(5):1003–1010. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04315.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uemura T., Yanagida M. Isolation of type I and II DNA topoisomerase mutants from fission yeast: single and double mutants show different phenotypes in cell growth and chromatin organization. EMBO J. 1984 Aug;3(8):1737–1744. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02040.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. C. DNA topoisomerases: why so many? J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 15;266(11):6659–6662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worland S. T., Wang J. C. Inducible overexpression, purification, and active site mapping of DNA topoisomerase II from the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 15;264(8):4412–4416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yocum R. R., Hanley S., West R., Jr, Ptashne M. Use of lacZ fusions to delimit regulatory elements of the inducible divergent GAL1-GAL10 promoter in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Oct;4(10):1985–1998. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.10.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwelling L. A., Perry W. M. Leucine zipper in human DNA topoisomerase II. Mol Endocrinol. 1989 Mar;3(3):603–604. doi: 10.1210/mend-3-3-603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]