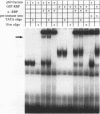
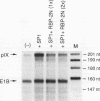
Abstract
We have identified a cellular protein, RBP-2N, a presumed recombinase, as a repressor of transcription. Inhibition of transcription by RBP-2N was dependent on its DNA recognition site and was demonstrated in vitro and in vivo. This repression appears to be general, as transcription mediated by SP1 and Gal4/VP16 was inhibited by RBP-2N. The protein was purified to near homogeneity from human cells on the basis of its binding to a site present in the promoter of the adenovirus pIX gene. The DNA recognition sequence is 5'-TGGGAAAGAA, which is markedly different from the recombination signal sequence originally identified as the target site for this protein. The sequence of the purified protein is 97% identical with that published for the mouse RBP-2N protein. The reported homolog in Drosophila is Suppressor of Hairless. RBP-2N binding sites are present in a number of cellular and viral promoters, so RBP-2N may have a general role in transcriptional repression.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aleström P., Akusjärvi G., Perricaudet M., Mathews M. B., Klessig D. F., Pettersson U. The gene for polypeptide IX of adenovirus type 2 and its unspliced messenger RNA. Cell. 1980 Mar;19(3):671–681. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(80)80044-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashburner M. The genetics of a small autosomal region of Drosophila melanogaster containing the structural gene for alcohol dehydrogenase. III. Hypomorphic and hypermorphic mutations affecting the expression of hairless. Genetics. 1982 Jul-Aug;101(3-4):447–459. doi: 10.1093/genetics/101.3-4.447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babiss L. E., Vales L. D. Promoter of the adenovirus polypeptide IX gene: similarity to E1B and inactivation by substitution of the simian virus 40 TATA element. J Virol. 1991 Feb;65(2):598–605. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.2.598-605.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crossland L. D., Raskas H. J. Identification of adenovirus genes that require template replication for expression. J Virol. 1983 Jun;46(3):737–748. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.3.737-748.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drapkin R., Merino A., Reinberg D. Regulation of RNA polymerase II transcription. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;5(3):469–476. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(93)90013-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores O., Lu H., Reinberg D. Factors involved in specific transcription by mammalian RNA polymerase II. Identification and characterization of factor IIH. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 5;267(4):2786–2793. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furukawa T., Maruyama S., Kawaichi M., Honjo T. The Drosophila homolog of the immunoglobulin recombination signal-binding protein regulates peripheral nervous system development. Cell. 1992 Jun 26;69(7):1191–1197. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90640-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., Smiley J., Russell W. C., Nairn R. Characteristics of a human cell line transformed by DNA from human adenovirus type 5. J Gen Virol. 1977 Jul;36(1):59–74. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-36-1-59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamaguchi Y., Matsunami N., Yamamoto Y., Honjo T. Purification and characterization of a protein that binds to the recombination signal sequence of the immunoglobulin J kappa segment. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Nov 25;17(22):9015–9026. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.22.9015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamaguchi Y., Yamamoto Y., Iwanari H., Maruyama S., Furukawa T., Matsunami N., Honjo T. Biochemical and immunological characterization of the DNA binding protein (RBP-J kappa) to mouse J kappa recombination signal sequence. J Biochem. 1992 Sep;112(3):314–320. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herschbach B. M., Johnson A. D. Transcriptional repression in eukaryotes. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1993;9:479–509. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.09.110193.002403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inostroza J., Flores O., Reinberg D. Factors involved in specific transcription by mammalian RNA polymerase II. Purification and functional analysis of general transcription factor IIE. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 15;266(14):9304–9308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jupp R., Hoffmann S., Depto A., Stenberg R. M., Ghazal P., Nelson J. A. Direct interaction of the human cytomegalovirus IE86 protein with the cis repression signal does not preclude TBP from binding to the TATA box. J Virol. 1993 Sep;67(9):5595–5604. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.9.5595-5604.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadonaga J. T., Tjian R. Affinity purification of sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5889–5893. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawaichi M., Oka C., Shibayama S., Koromilas A. E., Matsunami N., Hamaguchi Y., Honjo T. Genomic organization of mouse J kappa recombination signal binding protein (RBP-J kappa) gene. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 25;267(6):4016–4022. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovesdi I., Reichel R., Nevins J. R. Role of an adenovirus E2 promoter binding factor in E1A-mediated coordinate gene control. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2180–2184. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maldonado E., Ha I., Cortes P., Weis L., Reinberg D. Factors involved in specific transcription by mammalian RNA polymerase II: role of transcription factors IIA, IID, and IIB during formation of a transcription-competent complex. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6335–6347. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsunami N., Hamaguchi Y., Yamamoto Y., Kuze K., Kangawa K., Matsuo H., Kawaichi M., Honjo T. A protein binding to the J kappa recombination sequence of immunoglobulin genes contains a sequence related to the integrase motif. Nature. 1989 Dec 21;342(6252):934–937. doi: 10.1038/342934a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NASH D. THE EXPRESSION OF "HAIRLESS" IN DROSOPHILA AND THE ROLE OF TWO CLOSELY LINKED MODIFIERS OF OPPOSITE EFFECT. Genet Res. 1965 Jul;6:175–189. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300004079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash D. The Mutational Basis for the "Allelic" Modifier Mutants, ENHANCER and SUPPRESSOR OF HAIRLESS, of DROSOPHILA MELANOGASTER. Genetics. 1970 Mar;64(3-4):471–479. doi: 10.1093/genetics/64.3-4.471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsch U., Pine R., Zimmer S. G., Babiss L. E. Induced expression of the endogenous beta interferon gene in adenovirus type 5-transformed rat fibroblasts. J Virol. 1992 Apr;66(4):1884–1890. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.4.1884-1890.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandhu G. S., Eckloff B. W., Kline B. C. Chemiluminescent substrates increase sensitivity of antigen detection in western blots. Biotechniques. 1991 Jul;11(1):14–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweisguth F., Posakony J. W. Suppressor of Hairless, the Drosophila homolog of the mouse recombination signal-binding protein gene, controls sensory organ cell fates. Cell. 1992 Jun 26;69(7):1199–1212. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90641-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tempst P., Link A. J., Riviere L. R., Fleming M., Elicone C. Internal sequence analysis of proteins separated on polyacrylamide gels at the submicrogram level: improved methods, applications and gene cloning strategies. Electrophoresis. 1990 Jul;11(7):537–553. doi: 10.1002/elps.1150110704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tempst P., Riviere L. Examination of automated polypeptide sequencing using standard phenyl isothiocyanate reagent and subpicomole high-performance liquid chromatographic analysis. Anal Biochem. 1989 Dec;183(2):290–300. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(89)90482-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vales L. D., Darnell J. E., Jr Promoter occlusion prevents transcription of adenovirus polypeptide IX mRNA until after DNA replication. Genes Dev. 1989 Jan;3(1):49–59. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.1.49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Pellicer A., Silverstein S., Axel R., Urlaub G., Chasin L. DNA-mediated transfer of the adenine phosphoribosyltransferase locus into mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1373–1376. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J., Jupp R., Stenberg R. M., Nelson J. A., Ghazal P. Site-specific inhibition of RNA polymerase II preinitiation complex assembly by human cytomegalovirus IE86 protein. J Virol. 1993 Dec;67(12):7547–7555. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.12.7547-7555.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu L., Berk A. Constraints on spacing between transcription factor binding sites in a simple adenovirus promoter. Genes Dev. 1988 Apr;2(4):403–411. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.4.403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu L., Rosser D. S., Schmidt M. C., Berk A. A TATA box implicated in E1A transcriptional activation of a simple adenovirus 2 promoter. Nature. 1987 Apr 2;326(6112):512–515. doi: 10.1038/326512a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zawel L., Reinberg D. Initiation of transcription by RNA polymerase II: a multi-step process. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1993;44:67–108. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60217-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]