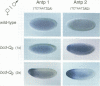
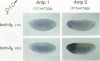
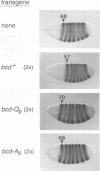
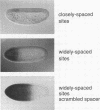
Abstract
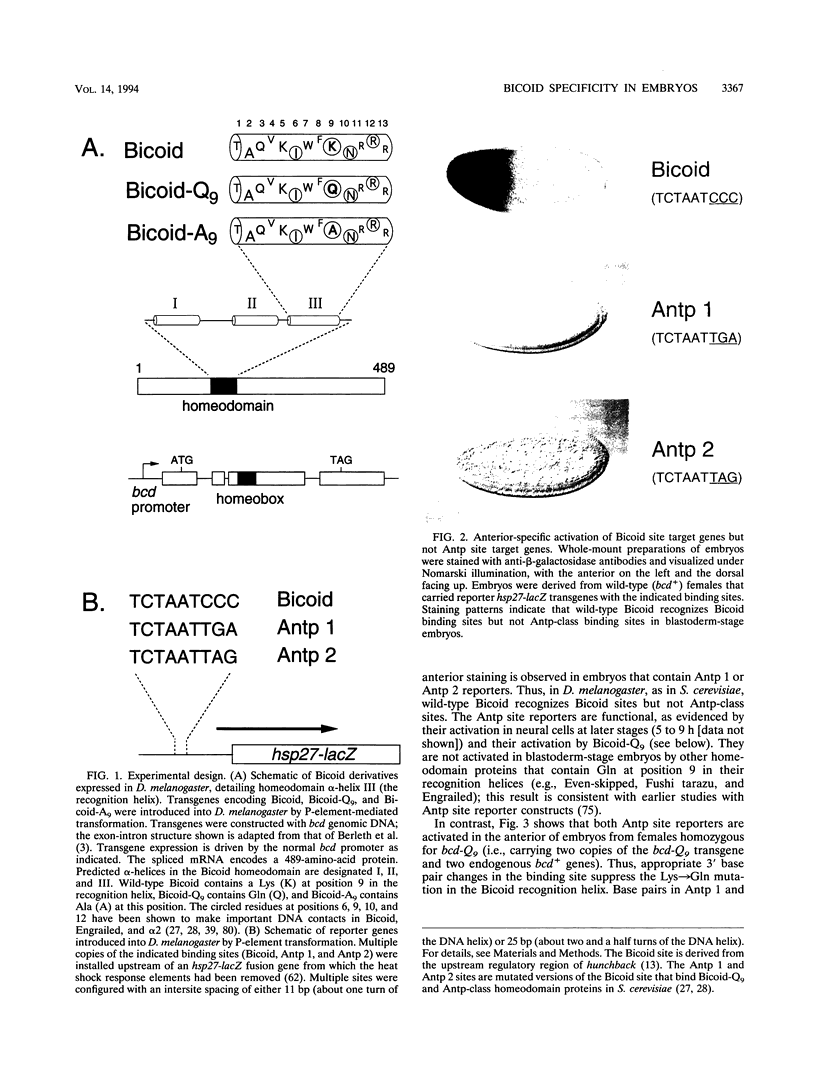
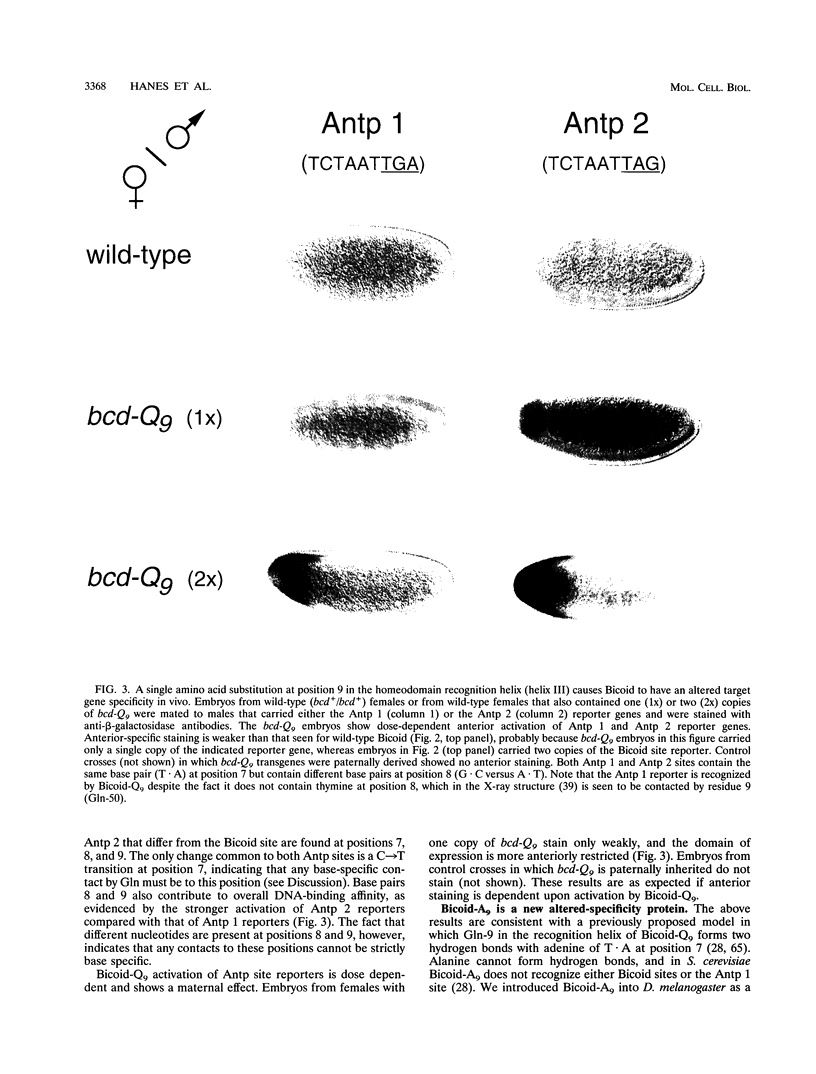
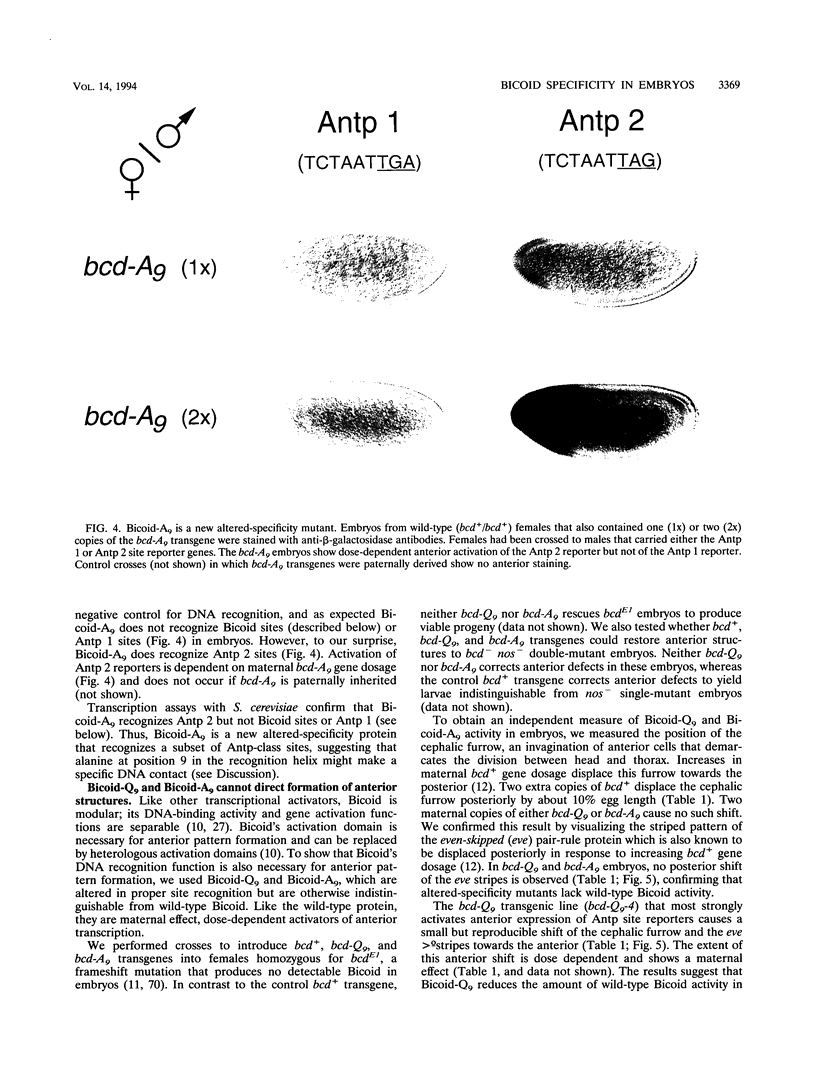
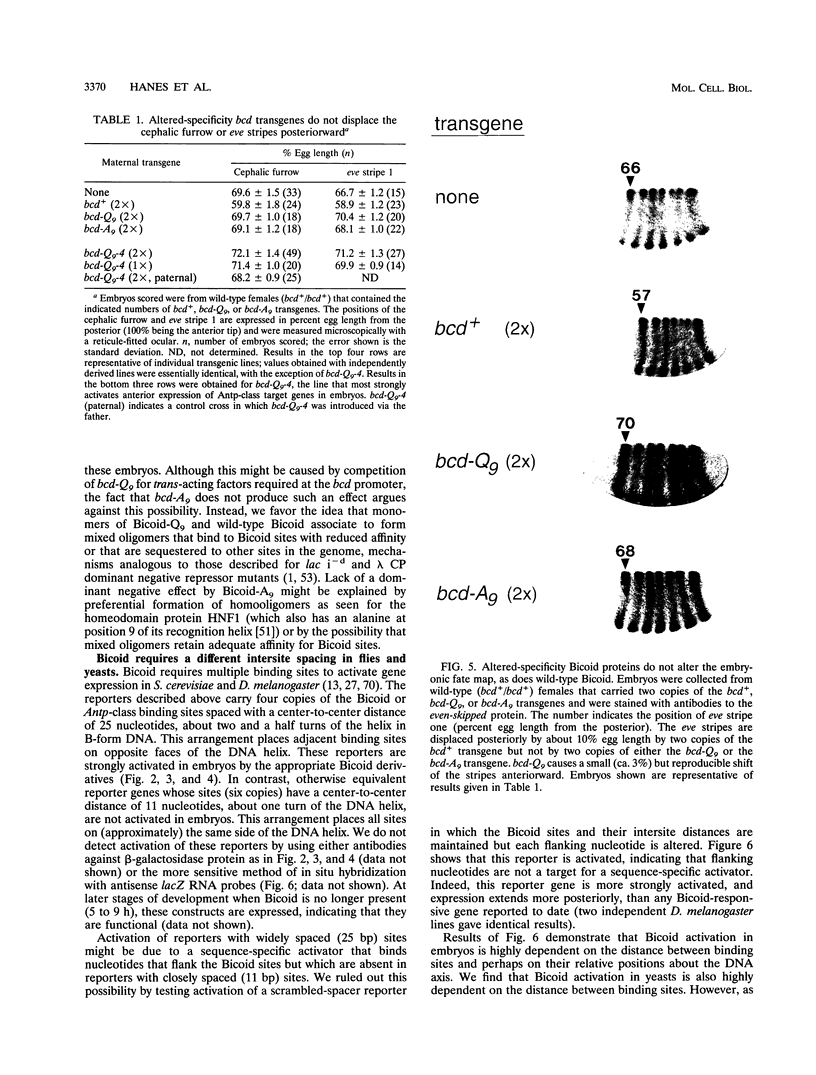
We examined DNA site recognition by Bicoid and its importance for pattern formation in developing Drosophila embryos. Using altered DNA specificity Bicoid mutants and appropriate reporter genes, we show that Bicoid distinguishes among related DNA-binding sites in vivo by a specific contact between amino acid 9 of its recognition alpha-helix (lysine 50 of the homeodomain) and bp 7 of the site. This result is consistent with our earlier results using Saccharomyces cerevisiae but differs from that predicted by crystallographic analysis of another homeodomain-DNA interaction. Our results also demonstrate that Bicoid binds directly to those genes whose transcription it regulates and that the amino acid 9 contact is necessary for Bicoid to direct anterior pattern formation. In both Drosophila embryos and yeast cells, Bicoid requires multiple binding sites to activate transcription of target genes. We find that the distance between binding sites is critical for Bicoid activation but that, unexpectedly, this critical distance differs between Drosophila and S. cerevisiae. This result suggests that Bicoid activation in Drosophila might require an ancillary protein(s) not present in S. cerevisiae.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler K., Beyreuther K., Fanning E., Geisler N., Gronenborn B., Klemm A., Müller-Hill B., Pfahl M., Schmitz A. How lac repressor binds to DNA. Nature. 1972 Jun 9;237(5354):322–327. doi: 10.1038/237322a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Affolter M., Percival-Smith A., Müller M., Leupin W., Gehring W. J. DNA binding properties of the purified Antennapedia homeodomain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(11):4093–4097. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.11.4093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berleth T., Burri M., Thoma G., Bopp D., Richstein S., Frigerio G., Noll M., Nüsslein-Volhard C. The role of localization of bicoid RNA in organizing the anterior pattern of the Drosophila embryo. EMBO J. 1988 Jun;7(6):1749–1756. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03004.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey M., Lin Y. S., Green M. R., Ptashne M. A mechanism for synergistic activation of a mammalian gene by GAL4 derivatives. Nature. 1990 May 24;345(6273):361–364. doi: 10.1038/345361a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalfie M. Homeobox genes in Caenorhabditis elegans. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1993 Apr;3(2):275–277. doi: 10.1016/0959-437x(93)90034-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. M., Jürgens G. Mediation of Drosophila head development by gap-like segmentation genes. Nature. 1990 Aug 2;346(6283):482–485. doi: 10.1038/346482a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Robertis E. M., Morita E. A., Cho K. W. Gradient fields and homeobox genes. Development. 1991 Jul;112(3):669–678. doi: 10.1242/dev.112.3.669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desplan C., Theis J., O'Farrell P. H. The sequence specificity of homeodomain-DNA interaction. Cell. 1988 Sep 23;54(7):1081–1090. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90123-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driever W., Ma J., Nüsslein-Volhard C., Ptashne M. Rescue of bicoid mutant Drosophila embryos by bicoid fusion proteins containing heterologous activating sequences. Nature. 1989 Nov 9;342(6246):149–154. doi: 10.1038/342149a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driever W., Nüsslein-Volhard C. A gradient of bicoid protein in Drosophila embryos. Cell. 1988 Jul 1;54(1):83–93. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90182-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driever W., Nüsslein-Volhard C. The bicoid protein determines position in the Drosophila embryo in a concentration-dependent manner. Cell. 1988 Jul 1;54(1):95–104. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90183-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driever W., Nüsslein-Volhard C. The bicoid protein is a positive regulator of hunchback transcription in the early Drosophila embryo. Nature. 1989 Jan 12;337(6203):138–143. doi: 10.1038/337138a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driever W., Thoma G., Nüsslein-Volhard C. Determination of spatial domains of zygotic gene expression in the Drosophila embryo by the affinity of binding sites for the bicoid morphogen. Nature. 1989 Aug 3;340(6232):363–367. doi: 10.1038/340363a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn T. M., Hahn S., Ogden S., Schleif R. F. An operator at -280 base pairs that is required for repression of araBAD operon promoter: addition of DNA helical turns between the operator and promoter cyclically hinders repression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(16):5017–5020. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.16.5017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekker S. C., von Kessler D. P., Beachy P. A. Differential DNA sequence recognition is a determinant of specificity in homeotic gene action. EMBO J. 1992 Nov;11(11):4059–4072. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05499.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein R., Perrimon N. The orthodenticle gene is regulated by bicoid and torso and specifies Drosophila head development. Nature. 1990 Aug 2;346(6283):485–488. doi: 10.1038/346485a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Florence B., Handrow R., Laughon A. DNA-binding specificity of the fushi tarazu homeodomain. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;11(7):3613–3623. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.7.3613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frigerio G., Burri M., Bopp D., Baumgartner S., Noll M. Structure of the segmentation gene paired and the Drosophila PRD gene set as part of a gene network. Cell. 1986 Dec 5;47(5):735–746. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90516-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gehring W. J. Homeo boxes in the study of development. Science. 1987 Jun 5;236(4806):1245–1252. doi: 10.1126/science.2884726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gehring W. J. Homeotic genes, the homeo box, and the genetic control of development. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1985;50:243–251. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1985.050.01.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gehring W. J., Müller M., Affolter M., Percival-Smith A., Billeter M., Qian Y. Q., Otting G., Wüthrich K. The structure of the homeodomain and its functional implications. Trends Genet. 1990 Oct;6(10):323–329. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90253-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goutte C., Johnson A. D. a1 protein alters the DNA binding specificity of alpha 2 repressor. Cell. 1988 Mar 25;52(6):875–882. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90429-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyuris J., Golemis E., Chertkov H., Brent R. Cdi1, a human G1 and S phase protein phosphatase that associates with Cdk2. Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):791–803. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90498-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanes S. D., Brent R. A genetic model for interaction of the homeodomain recognition helix with DNA. Science. 1991 Jan 25;251(4992):426–430. doi: 10.1126/science.1671176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanes S. D., Brent R. DNA specificity of the bicoid activator protein is determined by homeodomain recognition helix residue 9. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1275–1283. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90063-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison S. C. A structural taxonomy of DNA-binding domains. Nature. 1991 Oct 24;353(6346):715–719. doi: 10.1038/353715a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartman P. E., Roth J. R. Mechanisms of suppression. Adv Genet. 1973;17:1–105. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2660(08)60170-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi S., Scott M. P. What determines the specificity of action of Drosophila homeodomain proteins? Cell. 1990 Nov 30;63(5):883–894. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90492-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoch M., Seifert E., Jäckle H. Gene expression mediated by cis-acting sequences of the Krüppel gene in response to the Drosophila morphogens bicoid and hunchback. EMBO J. 1991 Aug;10(8):2267–2278. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07763.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochschild A., Ptashne M. Cooperative binding of lambda repressors to sites separated by integral turns of the DNA helix. Cell. 1986 Mar 14;44(5):681–687. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90833-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hülskamp M., Pfeifle C., Tautz D. A morphogenetic gradient of hunchback protein organizes the expression of the gap genes Krüppel and knirps in the early Drosophila embryo. Nature. 1990 Aug 9;346(6284):577–580. doi: 10.1038/346577a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingham P. W. Genetic control of the spatial pattern of selector gene expression in Drosophila. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1985;50:201–208. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1985.050.01.026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karess R. E., Rubin G. M. Analysis of P transposable element functions in Drosophila. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):135–146. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90534-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keleher C. A., Goutte C., Johnson A. D. The yeast cell-type-specific repressor alpha 2 acts cooperatively with a non-cell-type-specific protein. Cell. 1988 Jun 17;53(6):927–936. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)90449-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai J. S., Cleary M. A., Herr W. A single amino acid exchange transfers VP16-induced positive control from the Oct-1 to the Oct-2 homeo domain. Genes Dev. 1992 Nov;6(11):2058–2065. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.11.2058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laughon A. DNA binding specificity of homeodomains. Biochemistry. 1991 Dec 3;30(48):11357–11367. doi: 10.1021/bi00112a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laughon A., Scott M. P. Sequence of a Drosophila segmentation gene: protein structure homology with DNA-binding proteins. Nature. 1984 Jul 5;310(5972):25–31. doi: 10.1038/310025a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurent B. C., Carlson M. Yeast SNF2/SWI2, SNF5, and SNF6 proteins function coordinately with the gene-specific transcriptional activators GAL4 and Bicoid. Genes Dev. 1992 Sep;6(9):1707–1715. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.9.1707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurent B. C., Treitel M. A., Carlson M. Functional interdependence of the yeast SNF2, SNF5, and SNF6 proteins in transcriptional activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 1;88(7):2687–2691. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.7.2687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M., Hoey T. Homeobox proteins as sequence-specific transcription factors. Cell. 1988 Nov 18;55(4):537–540. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90209-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luo Y., Fujii H., Gerster T., Roeder R. G. A novel B cell-derived coactivator potentiates the activation of immunoglobulin promoters by octamer-binding transcription factors. Cell. 1992 Oct 16;71(2):231–241. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90352-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macdonald P. M., Ingham P., Struhl G. Isolation, structure, and expression of even-skipped: a second pair-rule gene of Drosophila containing a homeo box. Cell. 1986 Dec 5;47(5):721–734. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90515-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macdonald P. M., Struhl G. cis-acting sequences responsible for anterior localization of bicoid mRNA in Drosophila embryos. Nature. 1988 Dec 8;336(6199):595–598. doi: 10.1038/336595a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGinnis W., Krumlauf R. Homeobox genes and axial patterning. Cell. 1992 Jan 24;68(2):283–302. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90471-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendel D. B., Crabtree G. R. HNF-1, a member of a novel class of dimerizing homeodomain proteins. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 15;266(2):677–680. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nüsslein-Volhard C., Frohnhöfer H. G., Lehmann R. Determination of anteroposterior polarity in Drosophila. Science. 1987 Dec 18;238(4834):1675–1681. doi: 10.1126/science.3686007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheim A. B., Noff D. Deletion mapping of trans dominant mutations in the lambda repressor gene. Virology. 1975 Apr;64(2):553–556. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90132-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otting G., Qian Y. Q., Billeter M., Müller M., Affolter M., Gehring W. J., Wüthrich K. Protein--DNA contacts in the structure of a homeodomain--DNA complex determined by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy in solution. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3085–3092. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07505.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otting G., Qian Y. Q., Müller M., Affolter M., Gehring W., Wüthrich K. Secondary structure determination for the Antennapedia homeodomain by nuclear magnetic resonance and evidence for a helix-turn-helix motif. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4305–4309. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03329.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabo C. O., Sauer R. T. Protein-DNA recognition. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:293–321. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.001453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabo C. O., Sauer R. T. Transcription factors: structural families and principles of DNA recognition. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:1053–1095. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.005201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Percival-Smith A., Müller M., Affolter M., Gehring W. J. The interaction with DNA of wild-type and mutant fushi tarazu homeodomains. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(12):3967–3974. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07617.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson C. L., Herskowitz I. Characterization of the yeast SWI1, SWI2, and SWI3 genes, which encode a global activator of transcription. Cell. 1992 Feb 7;68(3):573–583. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90192-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pomerantz J. L., Kristie T. M., Sharp P. A. Recognition of the surface of a homeo domain protein. Genes Dev. 1992 Nov;6(11):2047–2057. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.11.2047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qian Y. Q., Billeter M., Otting G., Müller M., Gehring W. J., Wüthrich K. The structure of the Antennapedia homeodomain determined by NMR spectroscopy in solution: comparison with prokaryotic repressors. Cell. 1989 Nov 3;59(3):573–580. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90040-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riddihough G., Ish-Horowicz D. Individual stripe regulatory elements in the Drosophila hairy promoter respond to maternal, gap, and pair-rule genes. Genes Dev. 1991 May;5(5):840–854. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.5.840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schier A. F., Gehring W. J. Direct homeodomain-DNA interaction in the autoregulation of the fushi tarazu gene. Nature. 1992 Apr 30;356(6372):804–807. doi: 10.1038/356804a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott M. P., Tamkun J. W., Hartzell G. W., 3rd The structure and function of the homeodomain. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Jul 28;989(1):25–48. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(89)90033-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeman N. C., Rosenberg J. M., Rich A. Sequence-specific recognition of double helical nucleic acids by proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Mar;73(3):804–808. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.3.804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small S., Kraut R., Hoey T., Warrior R., Levine M. Transcriptional regulation of a pair-rule stripe in Drosophila. Genes Dev. 1991 May;5(5):827–839. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.5.827. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. L., Johnson A. D. A molecular mechanism for combinatorial control in yeast: MCM1 protein sets the spacing and orientation of the homeodomains of an alpha 2 dimer. Cell. 1992 Jan 10;68(1):133–142. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90212-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steller H., Pirrotta V. A transposable P vector that confers selectable G418 resistance to Drosophila larvae. EMBO J. 1985 Jan;4(1):167–171. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb02332.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern S., Tanaka M., Herr W. The Oct-1 homoeodomain directs formation of a multiprotein-DNA complex with the HSV transactivator VP16. Nature. 1989 Oct 19;341(6243):624–630. doi: 10.1038/341624a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl G., Struhl K., Macdonald P. M. The gradient morphogen bicoid is a concentration-dependent transcriptional activator. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1259–1273. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90062-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamkun J. W., Deuring R., Scott M. P., Kissinger M., Pattatucci A. M., Kaufman T. C., Kennison J. A. brahma: a regulator of Drosophila homeotic genes structurally related to the yeast transcriptional activator SNF2/SWI2. Cell. 1992 Feb 7;68(3):561–572. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90191-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tautz D., Pfeifle C. A non-radioactive in situ hybridization method for the localization of specific RNAs in Drosophila embryos reveals translational control of the segmentation gene hunchback. Chromosoma. 1989 Aug;98(2):81–85. doi: 10.1007/BF00291041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman J., Harris E., Wilson D., Desplan C. The homeodomain: a new face for the helix-turn-helix? Bioessays. 1992 Mar;14(3):145–150. doi: 10.1002/bies.950140302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent J. P., Kassis J. A., O'Farrell P. H. A synthetic homeodomain binding site acts as a cell type specific, promoter specific enhancer in Drosophila embryos. EMBO J. 1990 Aug;9(8):2573–2578. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07438.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West R. W., Jr, Yocum R. R., Ptashne M. Saccharomyces cerevisiae GAL1-GAL10 divergent promoter region: location and function of the upstream activating sequence UASG. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;4(11):2467–2478. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.11.2467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wharton R. P., Ptashne M. A new-specificity mutant of 434 repressor that defines an amino acid-base pair contact. 1987 Apr 30-May 6Nature. 326(6116):888–891. doi: 10.1038/326888a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winston F., Carlson M. Yeast SNF/SWI transcriptional activators and the SPT/SIN chromatin connection. Trends Genet. 1992 Nov;8(11):387–391. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(92)90300-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolberger C., Vershon A. K., Liu B., Johnson A. D., Pabo C. O. Crystal structure of a MAT alpha 2 homeodomain-operator complex suggests a general model for homeodomain-DNA interactions. Cell. 1991 Nov 1;67(3):517–528. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90526-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshinaga S. K., Peterson C. L., Herskowitz I., Yamamoto K. R. Roles of SWI1, SWI2, and SWI3 proteins for transcriptional enhancement by steroid receptors. Science. 1992 Dec 4;258(5088):1598–1604. doi: 10.1126/science.1360703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]