Abstract
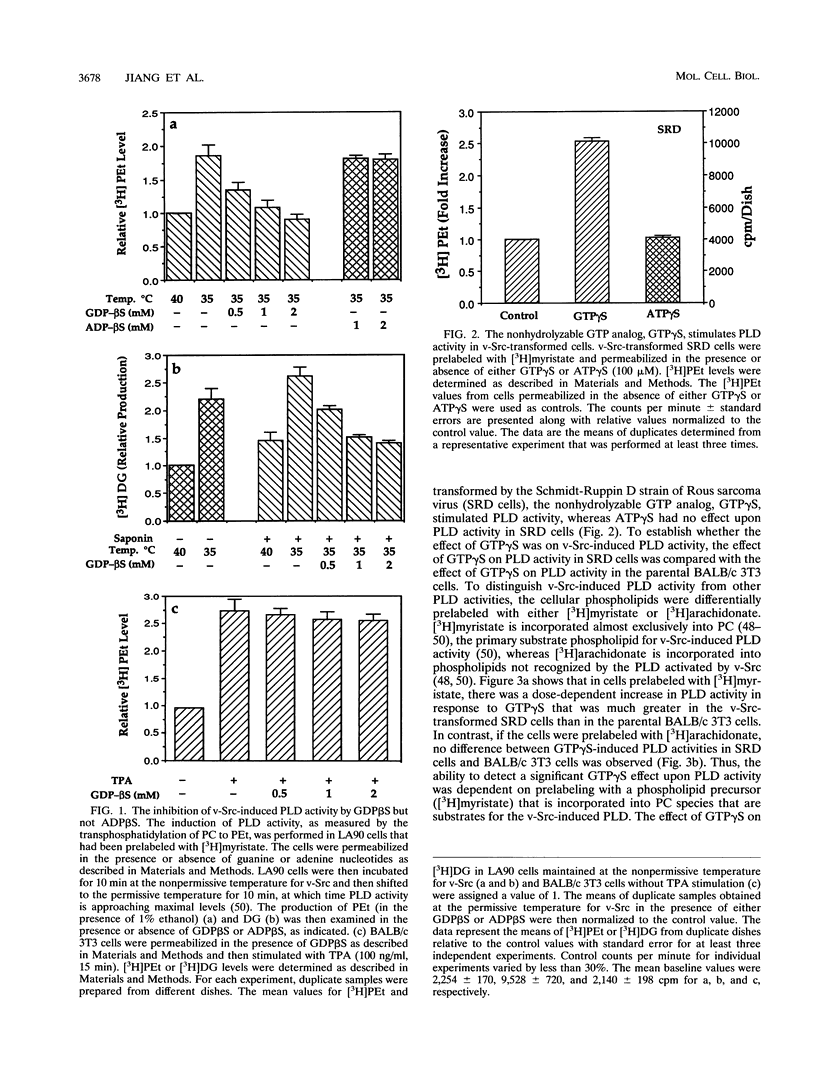
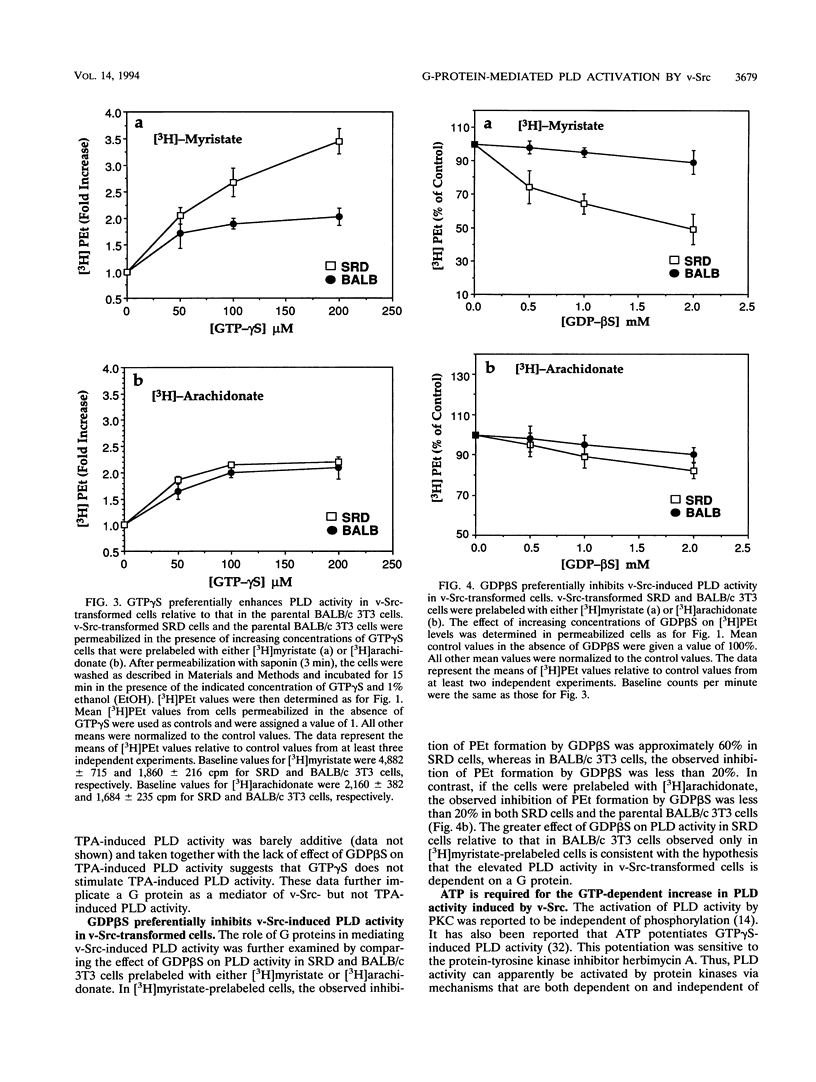
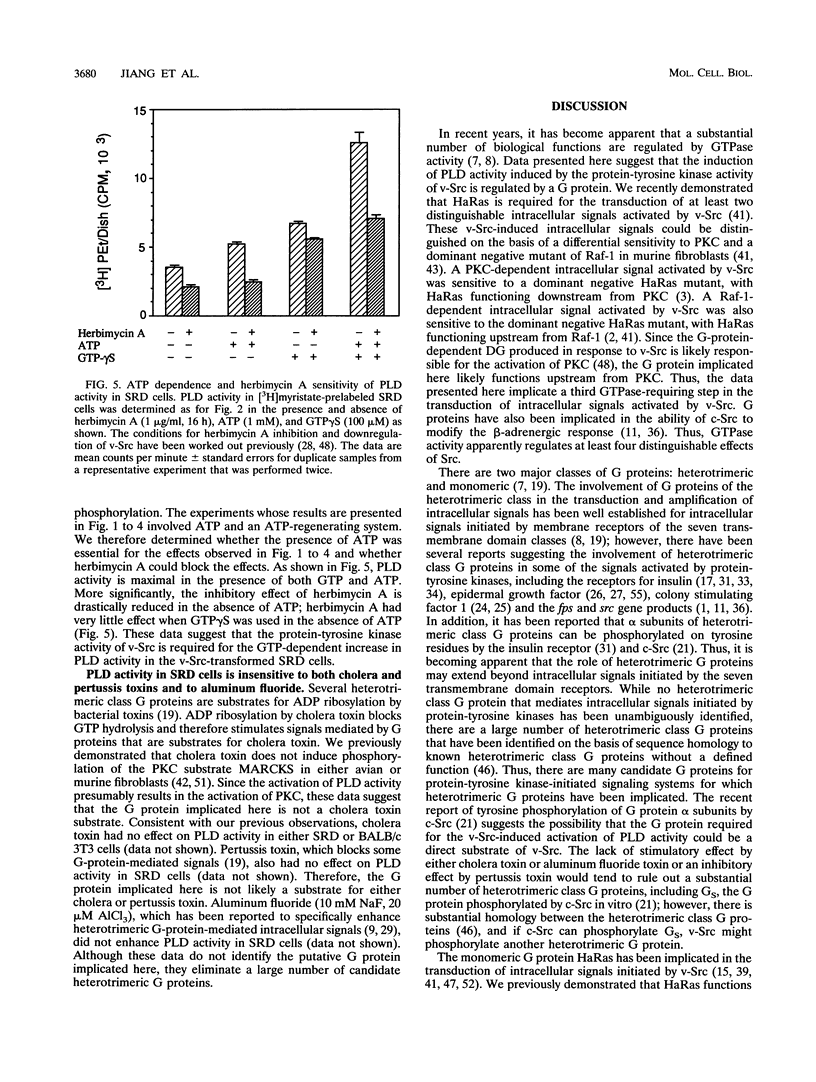
v-Src-induced increases in diglyceride are derived from phosphatidylcholine via a type D phospholipase (PLD) and a phosphatidic acid phosphatase. v-Src-induced PLD activity, as measured by PLD-catalyzed transphosphatidylation of phosphatidylcholine to phosphatidylethanol, is inhibited by GDP beta S, which inhibits G-protein-mediated intracellular signals. Similarly, v-Src-induced increases in diglyceride are also blocked by GDP beta S. In contrast to the PLD activity induced by v-Src, PLD activity induced by the protein kinase C agonist, 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA), was insensitive to GDP beta S. Consistent with the involvement of a G protein in the activation of PLD activity by v-Src, GTP gamma S, a nonhydrolyzable analog of GTP that potentiates G-protein-mediated signals, strongly enhanced PLD activity in v-Src-transformed cells relative to that in parental BALB/c 3T3 cells. The effect of GTP gamma S on PLD activity in v-Src-transformed cells was observed only when cells were prelabeled with [3H]myristate, which is incorporated exclusively into phosphatidylcholine, the substrate for the v-Src-induced PLD. There was no difference in the effect of GTP gamma S-induced PLD activity on v-Src-transformed and BALB/c 3T3 cells when the cells were prelabeled with [3H]arachidonate, which is not incorporated into phospholipids that are substrates for the v-Src-induced PLD. Similarly, GDP beta S inhibited PLD activity in v-Src-transformed cells much more strongly than in BALB/c 3T3 cells when [3H]myristate was used to prelabel the cells. The GTP-dependent activation of PLD by v-Src was dependent upon the presence of ATP but was unaffected by either cholera or pertussis toxin. These data suggest that v-Src induces PLD activity through a phosphorylation event and is mediated by a cholera and pertussis toxin-insensitive G protein.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexandropoulos K., Joseph C. K., Spangler R., Foster D. A. Evidence that a G-protein transduces signals initiated by the protein-tyrosine kinase v-Fps. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 25;266(24):15583–15586. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexandropoulos K., Qureshi S. A., Bruder J. T., Rapp U., Foster D. A. The induction of Egr-1 expression by v-Fps is via a protein kinase C-independent intracellular signal that is sequentially dependent upon HaRas and Raf-1. Cell Growth Differ. 1992 Oct;3(10):731–737. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexandropoulos K., Qureshi S. A., Foster D. A. Ha-Ras functions downstream from protein kinase C in v-Fps-induced gene expression mediated by TPA response elements. Oncogene. 1993 Mar;8(3):803–807. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billah M. M., Eckel S., Mullmann T. J., Egan R. W., Siegel M. I. Phosphatidylcholine hydrolysis by phospholipase D determines phosphatidate and diglyceride levels in chemotactic peptide-stimulated human neutrophils. Involvement of phosphatidate phosphohydrolase in signal transduction. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 15;264(29):17069–17077. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billah M. M., Pai J. K., Mullmann T. J., Egan R. W., Siegel M. I. Regulation of phospholipase D in HL-60 granulocytes. Activation by phorbol esters, diglyceride, and calcium ionophore via protein kinase- independent mechanisms. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):9069–9076. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bocckino S. B., Blackmore P. F., Wilson P. B., Exton J. H. Phosphatidate accumulation in hormone-treated hepatocytes via a phospholipase D mechanism. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 5;262(31):15309–15315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R., Sanders D. A., McCormick F. The GTPase superfamily: a conserved switch for diverse cell functions. Nature. 1990 Nov 8;348(6297):125–132. doi: 10.1038/348125a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R., Sanders D. A., McCormick F. The GTPase superfamily: conserved structure and molecular mechanism. Nature. 1991 Jan 10;349(6305):117–127. doi: 10.1038/349117a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowman E. P., Uhlinger D. J., Lambeth J. D. Neutrophil phospholipase D is activated by a membrane-associated Rho family small molecular weight GTP-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 15;268(29):21509–21512. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown H. A., Gutowski S., Moomaw C. R., Slaughter C., Sternweis P. C. ADP-ribosylation factor, a small GTP-dependent regulatory protein, stimulates phospholipase D activity. Cell. 1993 Dec 17;75(6):1137–1144. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90323-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bushman W. A., Wilson L. K., Luttrell D. K., Moyers J. S., Parsons S. J. Overexpression of c-src enhances beta-adrenergic-induced cAMP accumulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7462–7466. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantley L. C., Auger K. R., Carpenter C., Duckworth B., Graziani A., Kapeller R., Soltoff S. Oncogenes and signal transduction. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):281–302. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90639-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft S., Thomas G. M., Fensome A., Geny B., Cunningham E., Gout I., Hiles I., Totty N. F., Truong O., Hsuan J. J. Phospholipase D: a downstream effector of ARF in granulocytes. Science. 1994 Jan 28;263(5146):523–526. doi: 10.1126/science.8290961. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conricode K. M., Brewer K. A., Exton J. H. Activation of phospholipase D by protein kinase C. Evidence for a phosphorylation-independent mechanism. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 15;267(11):7199–7202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeClue J. E., Zhang K., Redford P., Vass W. C., Lowy D. R. Suppression of src transformation by overexpression of full-length GTPase-activating protein (GAP) or of the GAP C terminus. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2819–2825. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Exton J. H. Signaling through phosphatidylcholine breakdown. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 5;265(1):1–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster D. A. Intracellular signalling mediated by protein-tyrosine kinases: networking through phospholipid metabolism. Cell Signal. 1993 Jul;5(4):389–399. doi: 10.1016/0898-6568(93)90078-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gawler D., Houslay M. D. Insulin stimulates a novel GTPase activity in human platelets. FEBS Lett. 1987 May 25;216(1):94–98. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80763-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins: transducers of receptor-generated signals. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:615–649. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hausdorff W. P., Pitcher J. A., Luttrell D. K., Linder M. E., Kurose H., Parsons S. J., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Tyrosine phosphorylation of G protein alpha subunits by pp60c-src. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 1;89(13):5720–5724. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.13.5720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Cooper J. A. Protein-tyrosine kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:897–930. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.004341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurst K. M., Hughes B. P., Barritt G. J. The roles of phospholipase D and a GTP-binding protein in guanosine 5'-[gamma-thio]triphosphate-stimulated hydrolysis of phosphatidylcholine in rat liver plasma membranes. Biochem J. 1990 Dec 15;272(3):749–753. doi: 10.1042/bj2720749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imamura K., Dianoux A., Nakamura T., Kufe D. Colony-stimulating factor 1 activates protein kinase C in human monocytes. EMBO J. 1990 Aug;9(8):2423-8, 2389. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07418.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imamura K., Kufe D. Colony-stimulating factor 1-induced Na+ influx into human monocytes involves activation of a pertussis toxin-sensitive GTP-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 5;263(28):14093–14098. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. M., Connelly P. A., Sisk R. B., Pobiner B. F., Hewlett E. L., Garrison J. C. Pertussis toxin or phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate can distinguish between epidermal growth factor- and angiotensin-stimulated signals in hepatocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(7):2032–2036. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.7.2032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. M., Garrison J. C. Epidermal growth factor and angiotensin II stimulate formation of inositol 1,4,5- and inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate in hepatocytes. Differential inhibition by pertussis toxin and phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 25;262(36):17285–17293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn R. A. Fluoride is not an activator of the smaller (20-25 kDa) GTP-binding proteins. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 25;266(24):15595–15597. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi M., Kanfer J. N. Phosphatidylethanol formation via transphosphatidylation by rat brain synaptosomal phospholipase D. J Neurochem. 1987 May;48(5):1597–1603. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1987.tb05707.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krupinski J., Rajaram R., Lakonishok M., Benovic J. L., Cerione R. A. Insulin-dependent phosphorylation of GTP-binding proteins in phospholipid vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 5;263(25):12333–12341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusner D. J., Schomisch S. J., Dubyak G. R. ATP-induced potentiation of G-protein-dependent phospholipase D activity in a cell-free system from U937 promonocytic leukocytes. J Biol Chem. 1993 Sep 25;268(27):19973–19982. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luttrell L. M., Hewlett E. L., Romero G., Rogol A. D. Pertussis toxin treatment attenuates some effects of insulin in BC3H-1 murine myocytes. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 5;263(13):6134–6141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luttrell L., Kilgour E., Larner J., Romero G. A pertussis toxin-sensitive G-protein mediates some aspects of insulin action in BC3H-1 murine myocytes. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 5;265(28):16873–16879. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maroney A. C., Qureshi S. A., Foster D. A., Brugge J. S. Cloning and characterization of a thermolabile v-src gene for use in reversible transformation of mammalian cells. Oncogene. 1992 Jun;7(6):1207–1214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moyers J. S., Bouton A. H., Parsons S. J. The sites of phosphorylation by protein kinase C and an intact SH2 domain are required for the enhanced response to beta-adrenergic agonists in cells overexpressing c-src. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;13(4):2391–2400. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.4.2391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. Studies and perspectives of protein kinase C. Science. 1986 Jul 18;233(4761):305–312. doi: 10.1126/science.3014651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nori M., Shawver L. K., Weber M. J. A Swiss 3T3 variant cell line resistant to the effects of tumor promoters cannot be transformed by src. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):4155–4162. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.4155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nori M., Vogel U. S., Gibbs J. B., Weber M. J. Inhibition of v-src-induced transformation by a GTPase-activating protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2812–2818. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2812. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson S. C., Bowman E. P., Lambeth J. D. Phospholipase D activation in a cell-free system from human neutrophils by phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate and guanosine 5'-O-(3-thiotriphosphate). Activation is calcium dependent and requires protein factors in both the plasma membrane and cytosol. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 15;266(26):17236–17242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qureshi S. A., Alexandropoulos K., Joseph C. K., Spangler R., Foster D. A. Cholera toxin induces expression of the immediate-early response gene JE via a cyclic AMP-independent signaling pathway. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;11(1):102–107. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.1.102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qureshi S. A., Alexandropoulos K., Rim M., Joseph C. K., Bruder J. T., Rapp U. R., Foster D. A. Evidence that Ha-Ras mediates two distinguishable intracellular signals activated by v-Src. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 5;267(25):17635–17639. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qureshi S. A., Joseph C. K., Rim M., Maroney A., Foster D. A. v-Src activates both protein kinase C-dependent and independent signaling pathways in murine fibroblasts. Oncogene. 1991 Jun;6(6):995–999. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randall R. W., Bonser R. W., Thompson N. T., Garland L. G. A novel and sensitive assay for phospholipase D in intact cells. FEBS Lett. 1990 May 7;264(1):87–90. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80772-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sagara J., Yamada K. M., Kakunaga T. Induction of an unusual type of shared phosphorylation in human and avian cells by tumor-promoting phorbol esters or transformation. Cancer Res. 1986 Oct;46(10):5291–5296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M. I., Strathmann M. P., Gautam N. Diversity of G proteins in signal transduction. Science. 1991 May 10;252(5007):802–808. doi: 10.1126/science.1902986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. R., DeGudicibus S. J., Stacey D. W. Requirement for c-ras proteins during viral oncogene transformation. Nature. 1986 Apr 10;320(6062):540–543. doi: 10.1038/320540a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song J. G., Pfeffer L. M., Foster D. A. v-Src increases diacylglycerol levels via a type D phospholipase-mediated hydrolysis of phosphatidylcholine. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):4903–4908. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.4903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song J., Jiang Y. W., Foster D. A. Epidermal growth factor induces the production of biologically distinguishable diglyceride species from phosphatidylinositol and phosphatidylcholine via the independent activation of type C and type D phospholipases. Cell Growth Differ. 1994 Jan;5(1):79–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spangler R., Joseph C., Qureshi S. A., Berg K. L., Foster D. A. Evidence that v-src and v-fps gene products use a protein kinase C-mediated pathway to induce expression of a transformation-related gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):7017–7021. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.7017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stacey D. W., Roudebush M., Day R., Mosser S. D., Gibbs J. B., Feig L. A. Dominant inhibitory Ras mutants demonstrate the requirement for Ras activity in the action of tyrosine kinase oncogenes. Oncogene. 1991 Dec;6(12):2297–2304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfman A., Wingrove T. G., Blackshear P. J., Macara I. G. Down-regulation of protein kinase C and of an endogenous 80-kDa substrate in transformed fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 5;262(34):16546–16552. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xie M. S., Dubyak G. R. Guanine-nucleotide- and adenine-nucleotide-dependent regulation of phospholipase D in electropermeabilized HL-60 granulocytes. Biochem J. 1991 Aug 15;278(Pt 1):81–89. doi: 10.1042/bj2780081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang L. J., Baffy G., Rhee S. G., Manning D., Hansen C. A., Williamson J. R. Pertussis toxin-sensitive Gi protein involvement in epidermal growth factor-induced activation of phospholipase C-gamma in rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 25;266(33):22451–22458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



