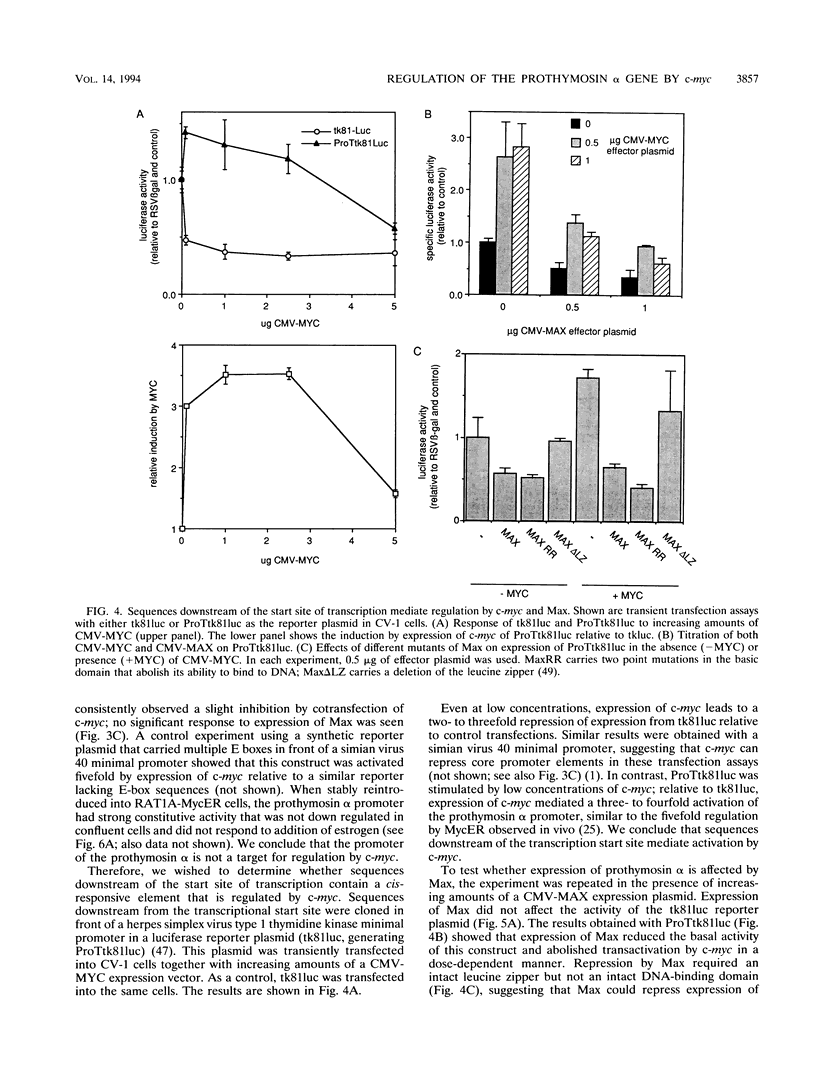
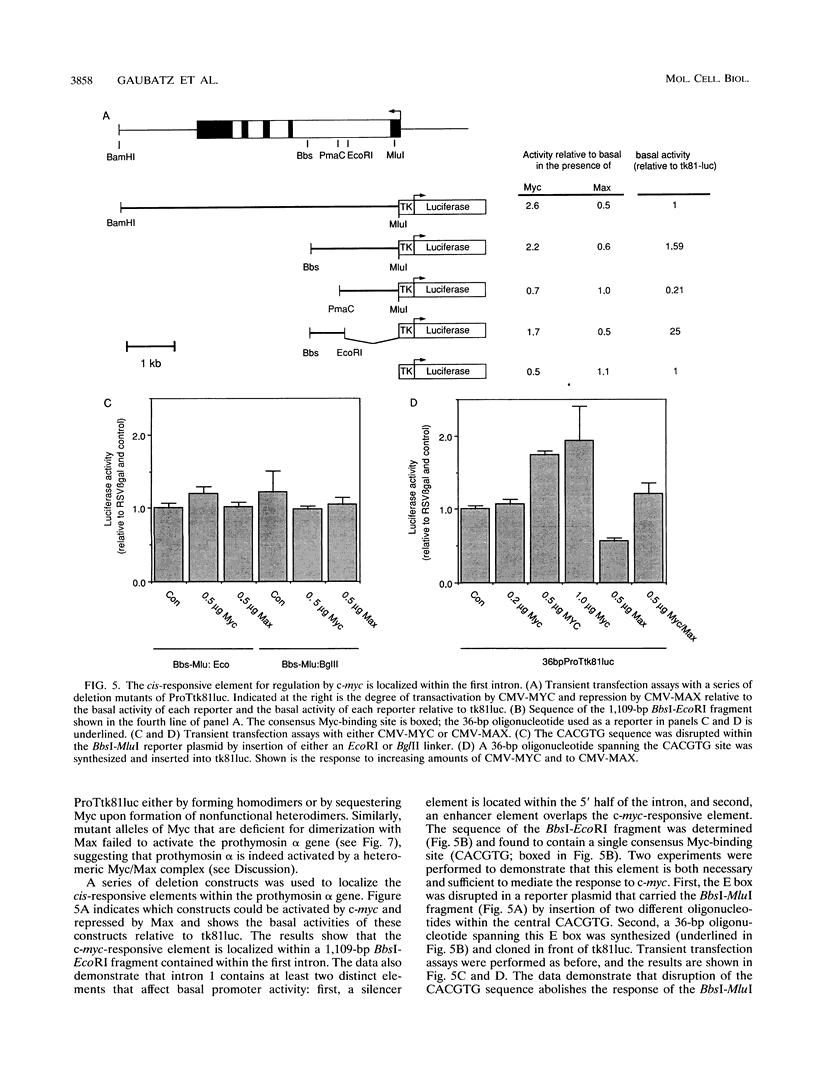
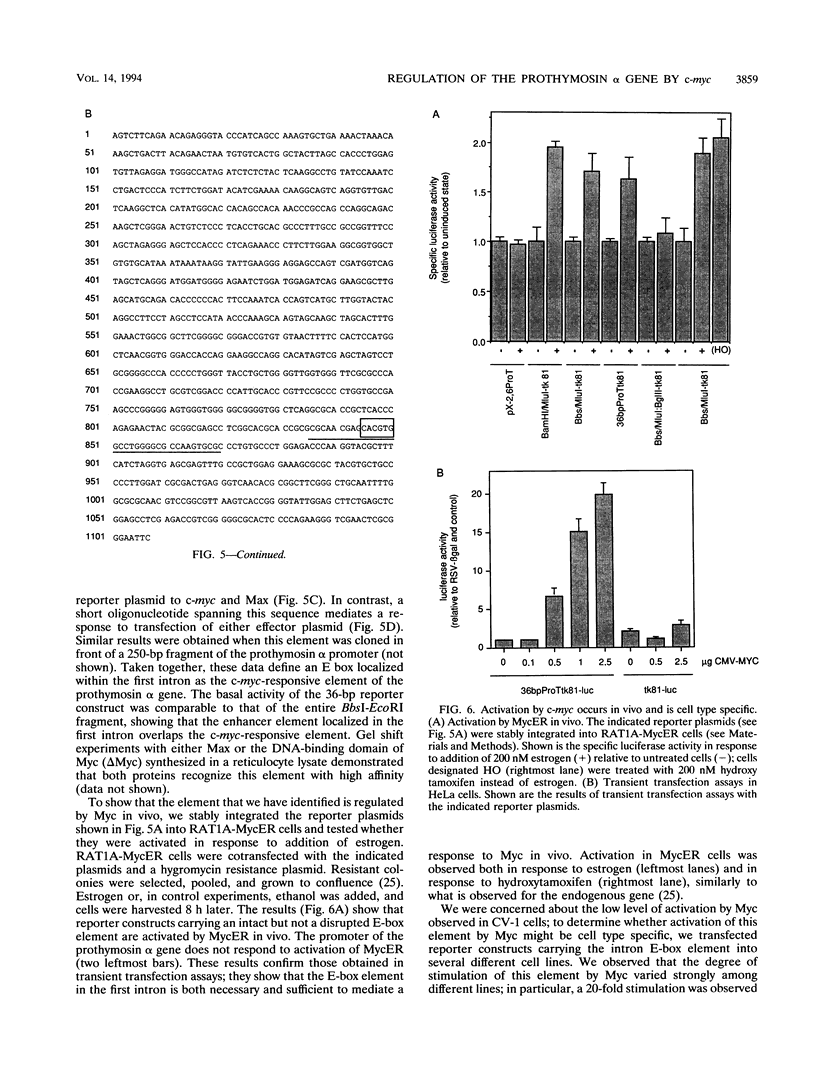
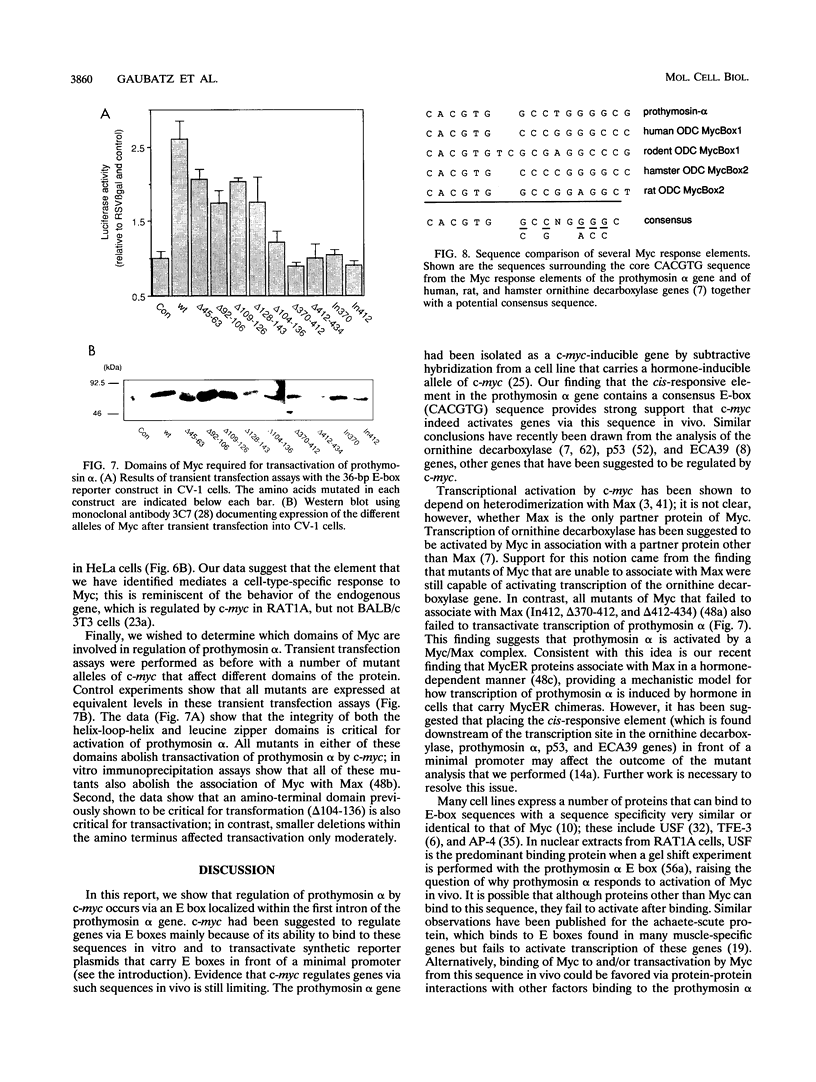
Abstract
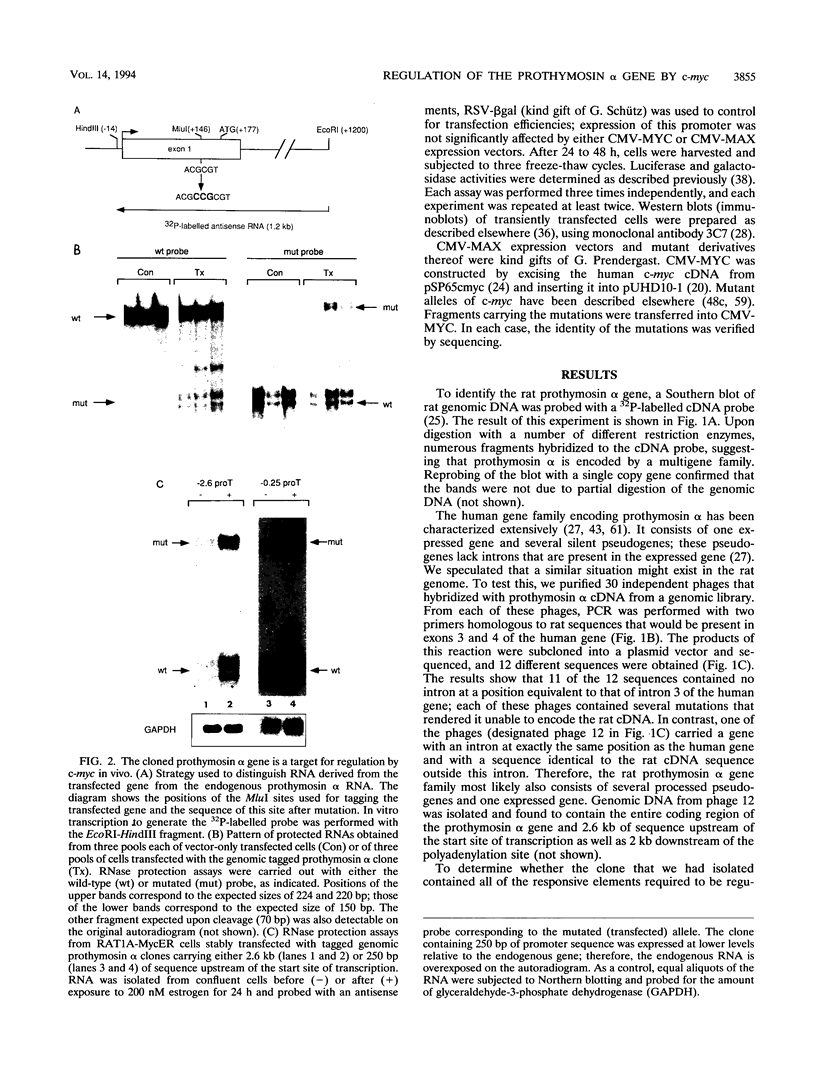
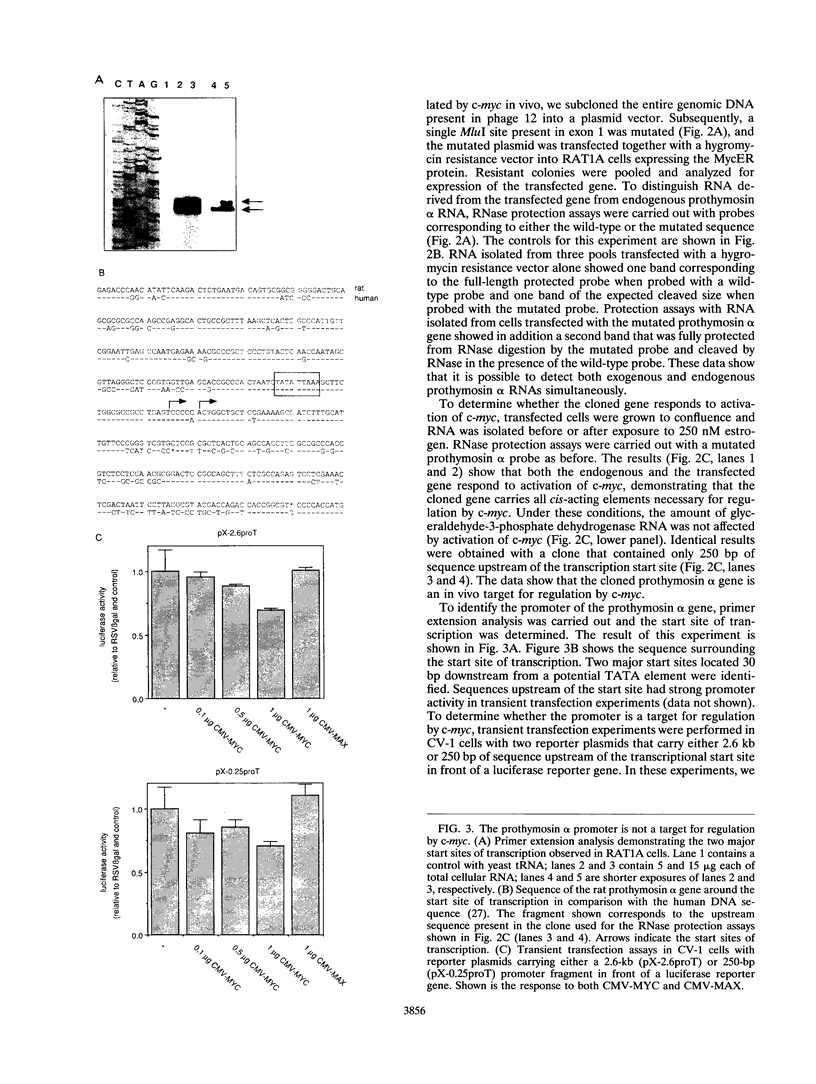
In RAT1A fibroblasts, expression of the prothymosin alpha gene is under the transcriptional control of the c-myc proto-oncogene. We have now cloned the rat gene encoding prothymosin alpha and show that the cloned gene is regulated by c-myc in vivo. We find that regulation by c-myc is mediated by sequences downstream of the transcriptional start site, whereas the promoter is constitutive and not regulated by c-myc. We have identified an enhancer element within the first intron that is sufficient to mediate a response to Myc and Max in transient transfection assays and to activation of estrogen receptor-Myc chimeras in vivo. We find that this element contains a consensus Myc-binding site (CACGTG). Disruption of this site abolishes the response to Myc and Max in both transient and stable assays. Mutants of either Myc or Max that are deficient for heterodimerization fail to regulate the prothymosin alpha gene, suggesting that a heterodimer between Myc and Max activates the prothymosin alpha gene. Our data define the prothymosin alpha gene as a bona fide target gene for c-myc.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abrams H. D., Rohrschneider L. R., Eisenman R. N. Nuclear location of the putative transforming protein of avian myelocytomatosis virus. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):427–439. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90159-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amati B., Brooks M. W., Levy N., Littlewood T. D., Evan G. I., Land H. Oncogenic activity of the c-Myc protein requires dimerization with Max. Cell. 1993 Jan 29;72(2):233–245. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90663-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amati B., Dalton S., Brooks M. W., Littlewood T. D., Evan G. I., Land H. Transcriptional activation by the human c-Myc oncoprotein in yeast requires interaction with Max. Nature. 1992 Oct 1;359(6394):423–426. doi: 10.1038/359423a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amin C., Wagner A. J., Hay N. Sequence-specific transcriptional activation by Myc and repression by Max. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;13(1):383–390. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.1.383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayer D. E., Kretzner L., Eisenman R. N. Mad: a heterodimeric partner for Max that antagonizes Myc transcriptional activity. Cell. 1993 Jan 29;72(2):211–222. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90661-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckmann H., Su L. K., Kadesch T. TFE3: a helix-loop-helix protein that activates transcription through the immunoglobulin enhancer muE3 motif. Genes Dev. 1990 Feb;4(2):167–179. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.2.167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bello-Fernandez C., Packham G., Cleveland J. L. The ornithine decarboxylase gene is a transcriptional target of c-Myc. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Aug 15;90(16):7804–7808. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.16.7804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benvenisty N., Leder A., Kuo A., Leder P. An embryonically expressed gene is a target for c-Myc regulation via the c-Myc-binding sequence. Genes Dev. 1992 Dec;6(12B):2513–2523. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.12b.2513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berberich S., Hyde-DeRuyscher N., Espenshade P., Cole M. max encodes a sequence-specific DNA-binding protein and is not regulated by serum growth factors. Oncogene. 1992 Apr;7(4):775–779. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell T. K., Huang J., Ma A., Kretzner L., Alt F. W., Eisenman R. N., Weintraub H. Binding of myc proteins to canonical and noncanonical DNA sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Sep;13(9):5216–5224. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.9.5216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell T. K., Kretzner L., Blackwood E. M., Eisenman R. N., Weintraub H. Sequence-specific DNA binding by the c-Myc protein. Science. 1990 Nov 23;250(4984):1149–1151. doi: 10.1126/science.2251503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwood E. M., Eisenman R. N. Max: a helix-loop-helix zipper protein that forms a sequence-specific DNA-binding complex with Myc. Science. 1991 Mar 8;251(4998):1211–1217. doi: 10.1126/science.2006410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwood E. M., Lüscher B., Eisenman R. N. Myc and Max associate in vivo. Genes Dev. 1992 Jan;6(1):71–80. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.1.71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bustelo X. R., Otero A., Gómez-Márquez J., Freire M. Expression of the rat prothymosin alpha gene during T-lymphocyte proliferation and liver regeneration. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 25;266(3):1443–1447. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clinton M., Graeve L., el-Dorry H., Rodriguez-Boulan E., Horecker B. L. Evidence for nuclear targeting of prothymosin and parathymosin synthesized in situ. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 1;88(15):6608–6612. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.15.6608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colby W. W., Chen E. Y., Smith D. H., Levinson A. D. Identification and nucleotide sequence of a human locus homologous to the v-myc oncogene of avian myelocytomatosis virus MC29. Nature. 1983 Feb 24;301(5902):722–725. doi: 10.1038/301722a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conteas C. N., Mutchnick M. G., Palmer K. C., Weller F. E., Luk G. D., Naylor P. H., Erdos M. R., Goldstein A. L., Panneerselvam C., Horecker B. L. Cellular levels of thymosin immunoreactive peptides are linked to proliferative events: evidence for a nuclear site of action. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(9):3269–3273. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.9.3269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dang C. V., McGuire M., Buckmire M., Lee W. M. Involvement of the 'leucine zipper' region in the oligomerization and transforming activity of human c-myc protein. Nature. 1989 Feb 16;337(6208):664–666. doi: 10.1038/337664a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. L., Cheng P. F., Lassar A. B., Weintraub H. The MyoD DNA binding domain contains a recognition code for muscle-specific gene activation. Cell. 1990 Mar 9;60(5):733–746. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90088-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deuschle U., Pepperkok R., Wang F. B., Giordano T. J., McAllister W. T., Ansorge W., Bujard H. Regulated expression of foreign genes in mammalian cells under the control of coliphage T3 RNA polymerase and lac repressor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5400–5404. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donner P., Greiser-Wilke I., Moelling K. Nuclear localization and DNA binding of the transforming gene product of avian myelocytomatosis virus. Nature. 1982 Mar 18;296(5854):262–269. doi: 10.1038/296262a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dosil M., Alvarez-Fernández L., Gómez-Márquez J. Differentiation-linked expression of prothymosin alpha gene in human myeloid leukemic cells. Exp Cell Res. 1993 Jan;204(1):94–101. doi: 10.1006/excr.1993.1013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downs K. M., Martin G. R., Bishop J. M. Contrasting patterns of myc and N-myc expression during gastrulation of the mouse embryo. Genes Dev. 1989 Jun;3(6):860–869. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.6.860. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eilers M., Picard D., Yamamoto K. R., Bishop J. M. Chimaeras of myc oncoprotein and steroid receptors cause hormone-dependent transformation of cells. Nature. 1989 Jul 6;340(6228):66–68. doi: 10.1038/340066a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eilers M., Schirm S., Bishop J. M. The MYC protein activates transcription of the alpha-prothymosin gene. EMBO J. 1991 Jan;10(1):133–141. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07929.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eschenfeldt W. H., Berger S. L. The human prothymosin alpha gene is polymorphic and induced upon growth stimulation: evidence using a cloned cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9403–9407. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eschenfeldt W. H., Manrow R. E., Krug M. S., Berger S. L. Isolation and partial sequencing of the human prothymosin alpha gene family. Evidence against export of the gene products. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 5;264(13):7546–7555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evan G. I., Lewis G. K., Ramsay G., Bishop J. M. Isolation of monoclonal antibodies specific for human c-myc proto-oncogene product. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;5(12):3610–3616. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.12.3610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evan G. I., Wyllie A. H., Gilbert C. S., Littlewood T. D., Land H., Brooks M., Waters C. M., Penn L. Z., Hancock D. C. Induction of apoptosis in fibroblasts by c-myc protein. Cell. 1992 Apr 3;69(1):119–128. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90123-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregor P. D., Sawadogo M., Roeder R. G. The adenovirus major late transcription factor USF is a member of the helix-loop-helix group of regulatory proteins and binds to DNA as a dimer. Genes Dev. 1990 Oct;4(10):1730–1740. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.10.1730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gu W., Cechova K., Tassi V., Dalla-Favera R. Opposite regulation of gene transcription and cell proliferation by c-Myc and Max. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 1;90(7):2935–2939. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.7.2935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gómez-Márquez J., Segade F., Dosil M., Pichel J. G., Bustelo X. R., Freire M. The expression of prothymosin alpha gene in T lymphocytes and leukemic lymphoid cells is tied to lymphocyte proliferation. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):8451–8454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gómez-Márquez J., Segade F. Prothymosin alpha is a nuclear protein. FEBS Lett. 1988 Jan 4;226(2):217–219. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)81425-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu Y. F., Lüscher B., Admon A., Mermod N., Tjian R. Transcription factor AP-4 contains multiple dimerization domains that regulate dimer specificity. Genes Dev. 1990 Oct;4(10):1741–1752. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.10.1741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen-Dürr P., Meichle A., Steiner P., Pagano M., Finke K., Botz J., Wessbecher J., Draetta G., Eilers M. Differential modulation of cyclin gene expression by MYC. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3685–3689. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato G. J., Lee W. M., Chen L. L., Dang C. V. Max: functional domains and interaction with c-Myc. Genes Dev. 1992 Jan;6(1):81–92. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.1.81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz S., Kowenz-Leutz E., Müller C., Meese K., Ness S. A., Leutz A. The NF-M transcription factor is related to C/EBP beta and plays a role in signal transduction, differentiation and leukemogenesis of avian myelomonocytic cells. EMBO J. 1993 Apr;12(4):1321–1332. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05777.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keath E. J., Caimi P. G., Cole M. D. Fibroblast lines expressing activated c-myc oncogenes are tumorigenic in nude mice and syngeneic animals. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(2 Pt 1):339–348. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90012-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly K., Cochran B. H., Stiles C. D., Leder P. Cell-specific regulation of the c-myc gene by lymphocyte mitogens and platelet-derived growth factor. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):603–610. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90092-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kretzner L., Blackwood E. M., Eisenman R. N. Myc and Max proteins possess distinct transcriptional activities. Nature. 1992 Oct 1;359(6394):426–429. doi: 10.1038/359426a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landschulz W. H., Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. The leucine zipper: a hypothetical structure common to a new class of DNA binding proteins. Science. 1988 Jun 24;240(4860):1759–1764. doi: 10.1126/science.3289117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manrow R. E., Leone A., Krug M. S., Eschenfeldt W. H., Berger S. L. The human prothymosin alpha gene family contains several processed pseudogenes lacking deleterious lesions. Genomics. 1992 Jun;13(2):319–331. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90248-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manrow R. E., Sburlati A. R., Hanover J. A., Berger S. L. Nuclear targeting of prothymosin alpha. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 25;266(6):3916–3924. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moses H. L., Yang E. Y., Pietenpol J. A. TGF-beta stimulation and inhibition of cell proliferation: new mechanistic insights. Cell. 1990 Oct 19;63(2):245–247. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90155-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murre C., McCaw P. S., Baltimore D. A new DNA binding and dimerization motif in immunoglobulin enhancer binding, daughterless, MyoD, and myc proteins. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):777–783. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90682-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordeen S. K. Luciferase reporter gene vectors for analysis of promoters and enhancers. Biotechniques. 1988 May;6(5):454–458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson H., Leder P. Nuclear localization and DNA binding properties of a protein expressed by human c-myc oncogene. Science. 1984 Aug 17;225(4663):718–721. doi: 10.1126/science.6463648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philipp A., Schneider A., Väsrik I., Finke K., Xiong Y., Beach D., Alitalo K., Eilers M. Repression of cyclin D1: a novel function of MYC. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jun;14(6):4032–4043. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.6.4032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prendergast G. C., Lawe D., Ziff E. B. Association of Myn, the murine homolog of max, with c-Myc stimulates methylation-sensitive DNA binding and ras cotransformation. Cell. 1991 May 3;65(3):395–407. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90457-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prendergast G. C., Ziff E. B. Methylation-sensitive sequence-specific DNA binding by the c-Myc basic region. Science. 1991 Jan 11;251(4990):186–189. doi: 10.1126/science.1987636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy C. D., Dasgupta P., Saikumar P., Dudek H., Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Reddy E. P. Mutational analysis of Max: role of basic, helix-loop-helix/leucine zipper domains in DNA binding, dimerization and regulation of Myc-mediated transcriptional activation. Oncogene. 1992 Oct;7(10):2085–2092. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisman D., Elkind N. B., Roy B., Beamon J., Rotter V. c-Myc trans-activates the p53 promoter through a required downstream CACGTG motif. Cell Growth Differ. 1993 Feb;4(2):57–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy A. L., Carruthers C., Gutjahr T., Roeder R. G. Direct role for Myc in transcription initiation mediated by interactions with TFII-I. Nature. 1993 Sep 23;365(6444):359–361. doi: 10.1038/365359a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy A. L., Meisterernst M., Pognonec P., Roeder R. G. Cooperative interaction of an initiator-binding transcription initiation factor and the helix-loop-helix activator USF. Nature. 1991 Nov 21;354(6350):245–248. doi: 10.1038/354245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sburlati A. R., Manrow R. E., Berger S. L. Prothymosin alpha antisense oligomers inhibit myeloma cell division. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 1;88(1):253–257. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.1.253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shrivastava A., Saleque S., Kalpana G. V., Artandi S., Goff S. P., Calame K. Inhibition of transcriptional regulator Yin-Yang-1 by association with c-Myc. Science. 1993 Dec 17;262(5141):1889–1892. doi: 10.1126/science.8266081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. R., al-Katib A., Mohammad R., Silverman A., Szabo P., Khilnani S., Kohler W., Nath R., Mutchnick M. G. Prothymosin alpha gene expression correlates with proliferation, not differentiation, of HL-60 cells. Blood. 1993 Aug 15;82(4):1127–1132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone J., de Lange T., Ramsay G., Jakobovits E., Bishop J. M., Varmus H., Lee W. Definition of regions in human c-myc that are involved in transformation and nuclear localization. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1697–1709. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szabo P., Ehleiter D., Whittington E., Weksler M. E. Prothymosin alpha expression occurs during G1 in proliferating B or T lymphocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Jun 30;185(3):953–959. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91719-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szabo P., Panneerselvam C., Clinton M., Frangou-Lazaridis M., Weksler D., Whittington E., Macera M. J., Grzeschik K. H., Selvakumar A., Horecker B. L. Prothymosin alpha gene in humans: organization of its promoter region and localization to chromosome 2. Hum Genet. 1993 Feb;90(6):629–634. doi: 10.1007/BF00202480. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner A. J., Meyers C., Laimins L. A., Hay N. c-Myc induces the expression and activity of ornithine decarboxylase. Cell Growth Differ. 1993 Nov;4(11):879–883. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson D. K., Reddy E. P., Duesberg P. H., Papas T. S. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the chicken c-myc gene reveals homologous and unique coding regions by comparison with the transforming gene of avian myelocytomatosis virus MC29, delta gag-myc. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(8):2146–2150. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.8.2146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watts J. D., Cary P. D., Crane-Robinson C. Prothymosin alpha is a nuclear protein. FEBS Lett. 1989 Mar 13;245(1-2):17–20. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80182-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenzel A., Cziepluch C., Hamann U., Schürmann J., Schwab M. The N-Myc oncoprotein is associated in vivo with the phosphoprotein Max(p20/22) in human neuroblastoma cells. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(12):3703–3712. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04938.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westin E. H., Gallo R. C., Arya S. K., Eva A., Souza L. M., Baluda M. A., Aaronson S. A., Wong-Staal F. Differential expression of the amv gene in human hematopoietic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(7):2194–2198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.7.2194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westin E. H., Wong-Staal F., Gelmann E. P., Dalla-Favera R., Papas T. S., Lautenberger J. A., Eva A., Reddy E. P., Tronick S. R., Aaronson S. A. Expression of cellular homologues of retroviral onc genes in human hematopoietic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(8):2490–2494. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.8.2490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zalvide J. B., Cancio E., Alvarez C. V., Regueiro B. J., Dominguez F. Prothymosin alpha mRNA levels are invariant throughout the cell cycle. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 25;267(12):8692–8695. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zervos A. S., Gyuris J., Brent R. Mxi1, a protein that specifically interacts with Max to bind Myc-Max recognition sites. Cell. 1993 Jan 29;72(2):223–232. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90662-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]