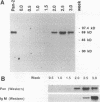
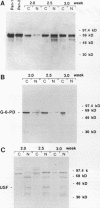
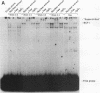
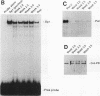
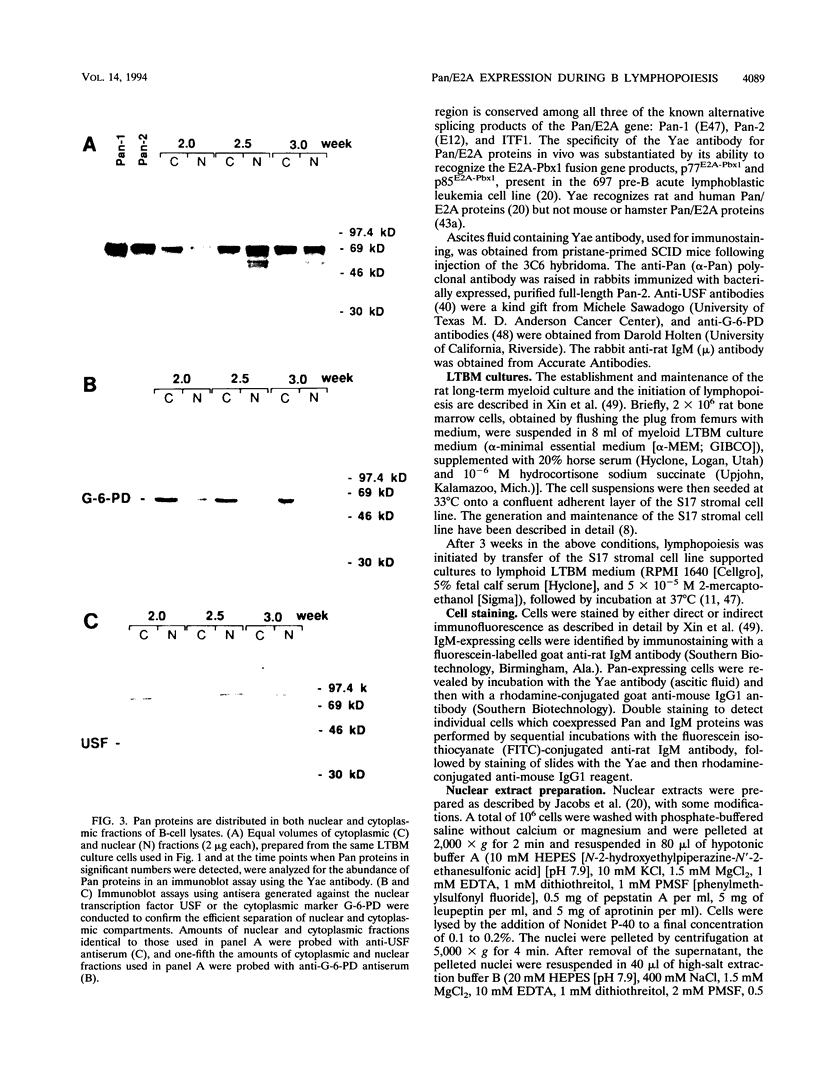
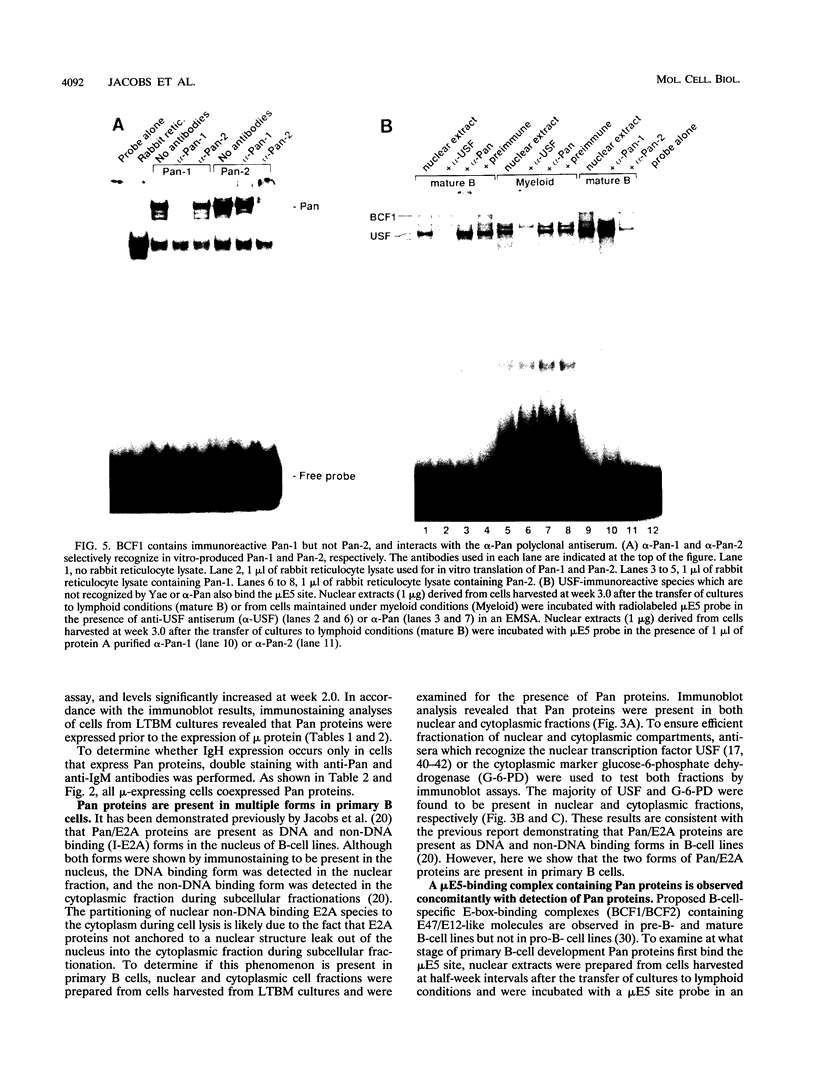
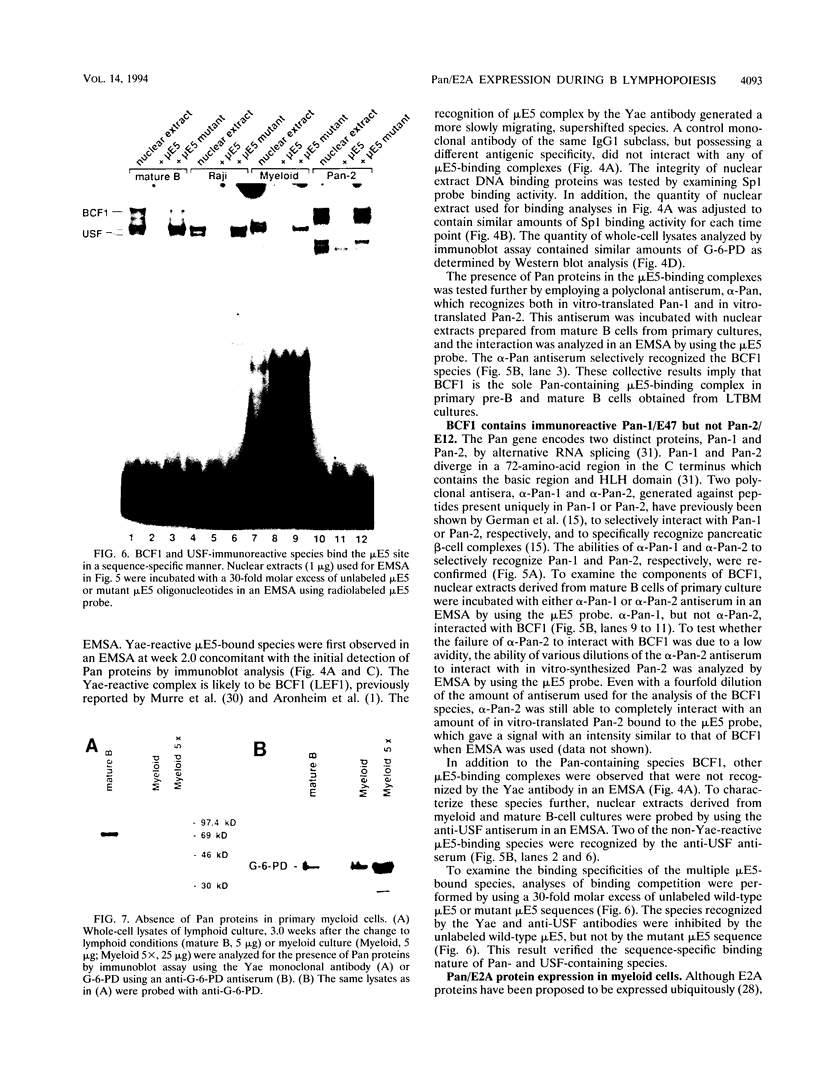
Abstract
A newly developed rat long-term bone marrow culture system was used to study the role of Pan/E2A basic helix-loop-helix transcription factors during B-cell development. In this system, B-lymphocyte progenitors actively differentiate into mature B cells. Monoclonal (Yae) and polyclonal (anti-Pan) antibodies were employed to characterize the expression of Pan proteins by Western blot assay during hematopoiesis and to examine the components of immunoglobulin heavy-chain gene enhancer element-binding species by electrophoretic mobility shift assay. During B-cell development, the appearance of Pan/E2A proteins preceded the expression of immunoglobulin heavy-chain protein. A Pan-containing immunoglobulin heavy-chain enhancer element (mu E5)-binding species (BCF1), composed of immunoreactive Pan-1/E47 but not Pan-2/E12, was observed concomitantly with the detection of Pan/E2A proteins. In addition to BCF1, other mu E5-binding species were detected which were not recognized by the Yae antibody. Two of these species were present in primary B-lymphocyte and myeloid cultures and were recognized by an anti-upstream stimulatory factor antiserum. Although Pan/E2A proteins have been proposed to be ubiquitous, Pan/E2A proteins were not detected in primary myeloid cultures composed mainly of granulocytes and macrophages or in the macrophage cell line J774. The absence of Pan/E2A proteins in differentiated myeloid cells correlated with low steady-state levels of Pan/E2A RNA. However, Pan/E2A proteins were present in a promyeloid cell line, 32DCL3, suggesting that extinction of Pan/E2A expression may play a role in myelopoiesis.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aronheim A., Ohlsson H., Park C. W., Edlund T., Walker M. D. Distribution and characterization of helix-loop-helix enhancer-binding proteins from pancreatic beta cells and lymphocytes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jul 25;19(14):3893–3899. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.14.3893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerji J., Olson L., Schaffner W. A lymphocyte-specific cellular enhancer is located downstream of the joining region in immunoglobulin heavy chain genes. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):729–740. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90015-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckmann H., Su L. K., Kadesch T. TFE3: a helix-loop-helix protein that activates transcription through the immunoglobulin enhancer muE3 motif. Genes Dev. 1990 Feb;4(2):167–179. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.2.167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan T. J., Olson E. N. Myogenin resides in the nucleus and acquires high affinity for a conserved enhancer element on heterodimerization. Genes Dev. 1990 Apr;4(4):582–595. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.4.582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr C. S., Sharp P. A. A helix-loop-helix protein related to the immunoglobulin E box-binding proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):4384–4388. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.4384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Ephrussi A., Gilbert W., Tonegawa S. Cell-type-specific contacts to immunoglobulin enhancers in nuclei. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):798–801. doi: 10.1038/313798a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins L. S., Dorshkind K. A stromal cell line from myeloid long-term bone marrow cultures can support myelopoiesis and B lymphopoiesis. J Immunol. 1987 Feb 15;138(4):1082–1087. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. L., Cheng P. F., Lassar A. B., Weintraub H. The MyoD DNA binding domain contains a recognition code for muscle-specific gene activation. Cell. 1990 Mar 9;60(5):733–746. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90088-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dexter T. M., Allen T. D., Lajtha L. G. Conditions controlling the proliferation of haemopoietic stem cells in vitro. J Cell Physiol. 1977 Jun;91(3):335–344. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040910303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorshkind K. In vitro differentiation of B lymphocytes from primitive hemopoietic precursors present in long-term bone marrow cultures. J Immunol. 1986 Jan;136(2):422–429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorshkind K. Regulation of hemopoiesis by bone marrow stromal cells and their products. Annu Rev Immunol. 1990;8:111–137. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.08.040190.000551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorshkind K., Witte O. N. Long-term murine hemopoietic cultures as model systems for analysis of B lymphocyte differentiation. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1987;135:23–41. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-71851-9_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ephrussi A., Church G. M., Tonegawa S., Gilbert W. B lineage--specific interactions of an immunoglobulin enhancer with cellular factors in vivo. Science. 1985 Jan 11;227(4683):134–140. doi: 10.1126/science.3917574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- German M. S., Blanar M. A., Nelson C., Moss L. G., Rutter W. J. Two related helix-loop-helix proteins participate in separate cell-specific complexes that bind the insulin enhancer. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Feb;5(2):292–299. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-2-292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillies S. D., Morrison S. L., Oi V. T., Tonegawa S. A tissue-specific transcription enhancer element is located in the major intron of a rearranged immunoglobulin heavy chain gene. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):717–728. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90014-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregor P. D., Sawadogo M., Roeder R. G. The adenovirus major late transcription factor USF is a member of the helix-loop-helix group of regulatory proteins and binds to DNA as a dimer. Genes Dev. 1990 Oct;4(10):1730–1740. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.10.1730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henthorn P., Kiledjian M., Kadesch T. Two distinct transcription factors that bind the immunoglobulin enhancer microE5/kappa 2 motif. Science. 1990 Jan 26;247(4941):467–470. doi: 10.1126/science.2105528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu J. S., Olson E. N., Kingston R. E. HEB, a helix-loop-helix protein related to E2A and ITF2 that can modulate the DNA-binding ability of myogenic regulatory factors. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;12(3):1031–1042. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.3.1031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs Y., Vierra C., Nelson C. E2A expression, nuclear localization, and in vivo formation of DNA- and non-DNA-binding species during B-cell development. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Dec;13(12):7321–7333. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.12.7321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiledjian M., Su L. K., Kadesch T. Identification and characterization of two functional domains within the murine heavy-chain enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):145–152. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kincade P. W. Experimental models for understanding B lymphocyte formation. Adv Immunol. 1987;41:181–267. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60032-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein E. S., Simmons D. M., Swanson L. W., Rosenfeld M. G. Tissue-specific RNA splicing generates an ankyrin-like domain that affects the dimerization and DNA-binding properties of a bHLH protein. Genes Dev. 1993 Jan;7(1):55–71. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.1.55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassar A. B., Davis R. L., Wright W. E., Kadesch T., Murre C., Voronova A., Baltimore D., Weintraub H. Functional activity of myogenic HLH proteins requires hetero-oligomerization with E12/E47-like proteins in vivo. Cell. 1991 Jul 26;66(2):305–315. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90620-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitt D., Cooper M. D. Mouse pre-B cells synthesize and secrete mu heavy chains but not light chains. Cell. 1980 Mar;19(3):617–625. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(80)80038-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercola M., Wang X. F., Olsen J., Calame K. Transcriptional enhancer elements in the mouse immunoglobulin heavy chain locus. Science. 1983 Aug 12;221(4611):663–665. doi: 10.1126/science.6306772. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murre C., McCaw P. S., Baltimore D. A new DNA binding and dimerization motif in immunoglobulin enhancer binding, daughterless, MyoD, and myc proteins. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):777–783. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90682-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murre C., McCaw P. S., Vaessin H., Caudy M., Jan L. Y., Jan Y. N., Cabrera C. V., Buskin J. N., Hauschka S. D., Lassar A. B. Interactions between heterologous helix-loop-helix proteins generate complexes that bind specifically to a common DNA sequence. Cell. 1989 Aug 11;58(3):537–544. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90434-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murre C., Voronova A., Baltimore D. B-cell- and myocyte-specific E2-box-binding factors contain E12/E47-like subunits. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;11(2):1156–1160. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.2.1156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson C., Shen L. P., Meister A., Fodor E., Rutter W. J. Pan: a transcriptional regulator that binds chymotrypsin, insulin, and AP-4 enhancer motifs. Genes Dev. 1990 Jun;4(6):1035–1043. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.6.1035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuberger M. S. Expression and regulation of immunoglobulin heavy chain gene transfected into lymphoid cells. EMBO J. 1983;2(8):1373–1378. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01594.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen A. L., Pallisgaard N., Pedersen F. S., Jørgensen P. Murine helix-loop-helix transcriptional activator proteins binding to the E-box motif of the Akv murine leukemia virus enhancer identified by cDNA cloning. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;12(8):3449–3459. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.8.3449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez-Mutul J., Macchi M., Wasylyk B. Mutational analysis of the contribution of sequence motifs within the IgH enhancer to tissue specific transcriptional activation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 11;16(13):6085–6096. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.13.6085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard D., Schaffner W. A lymphocyte-specific enhancer in the mouse immunoglobulin kappa gene. Nature. 1984 Jan 5;307(5946):80–82. doi: 10.1038/307080a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Queen C., Baltimore D. Immunoglobulin gene transcription is activated by downstream sequence elements. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):741–748. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90016-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Queen C., Stafford J. Fine mapping of an immunoglobulin gene activator. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jun;4(6):1042–1049. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.6.1042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raff M. C., Megson M., Owen J. J., Cooper M. D. Early production of intracellular IgM by B-lymphocyte precursors in mouse. Nature. 1976 Jan 22;259(5540):224–226. doi: 10.1038/259224a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawadogo M. Multiple forms of the human gene-specific transcription factor USF. II. DNA binding properties and transcriptional activity of the purified HeLa USF. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 25;263(24):11994–12001. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawadogo M., Roeder R. G. Interaction of a gene-specific transcription factor with the adenovirus major late promoter upstream of the TATA box region. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):165–175. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90021-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawadogo M., Van Dyke M. W., Gregor P. D., Roeder R. G. Multiple forms of the human gene-specific transcription factor USF. I. Complete purification and identification of USF from HeLa cell nuclei. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 25;263(24):11985–11993. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsao B. P., Wang X. F., Peterson C. L., Calame K. In vivo functional analysis of in vitro protein binding sites in the immunoglobulin heavy chain enhancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Apr 25;16(8):3239–3253. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.8.3239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vierra C. A., Jacobs Y., Ly L., Nelson C. Patterns of Pan expression and role of Pan proteins in endocrine cell type-specific complex formation. Mol Endocrinol. 1994 Feb;8(2):197–209. doi: 10.1210/mend.8.2.8170476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Visvader J., Begley C. G., Adams J. M. Differential expression of the LYL, SCL and E2A helix-loop-helix genes within the hemopoietic system. Oncogene. 1991 Feb;6(2):187–194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker M. D., Park C. W., Rosen A., Aronheim A. A cDNA from a mouse pancreatic beta cell encoding a putative transcription factor of the insulin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Mar 11;18(5):1159–1166. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.5.1159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitlock C. A., Witte O. N. Long-term culture of B lymphocytes and their precursors from murine bone marrow. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(11):3608–3612. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.11.3608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winberry L., Holten D. Rat liver glucose-6-p dehydrogenase. Dietary regulation of the rate of synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Nov 10;252(21):7796–7801. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xin X. Q., Nelson C., Collins L., Dorshkind K. Kinetics of E2A basic helix-loop-helix-protein expression during myelopoiesis and primary B cell differentiation. J Immunol. 1993 Nov 15;151(10):5398–5407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y., Babin J., Feldhaus A. L., Singh H., Sharp P. A., Bina M. HTF4: a new human helix-loop-helix protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Aug 25;19(16):4555–4555. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.16.4555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]