Abstract
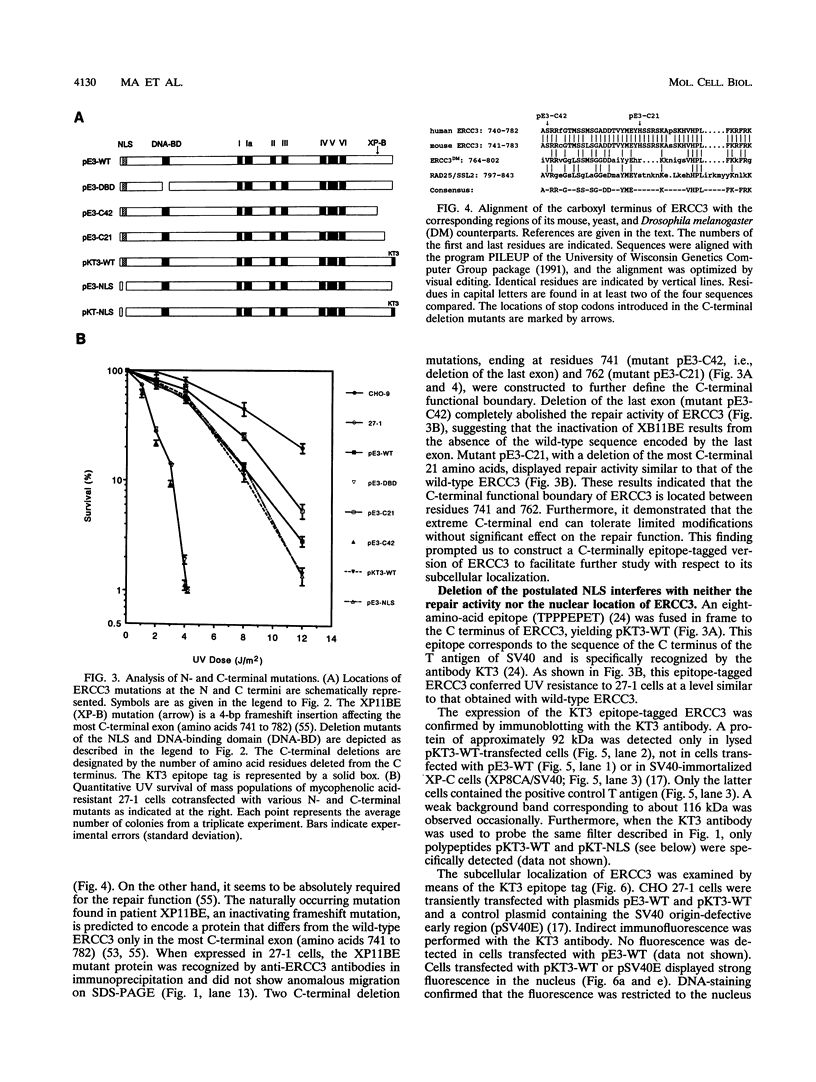
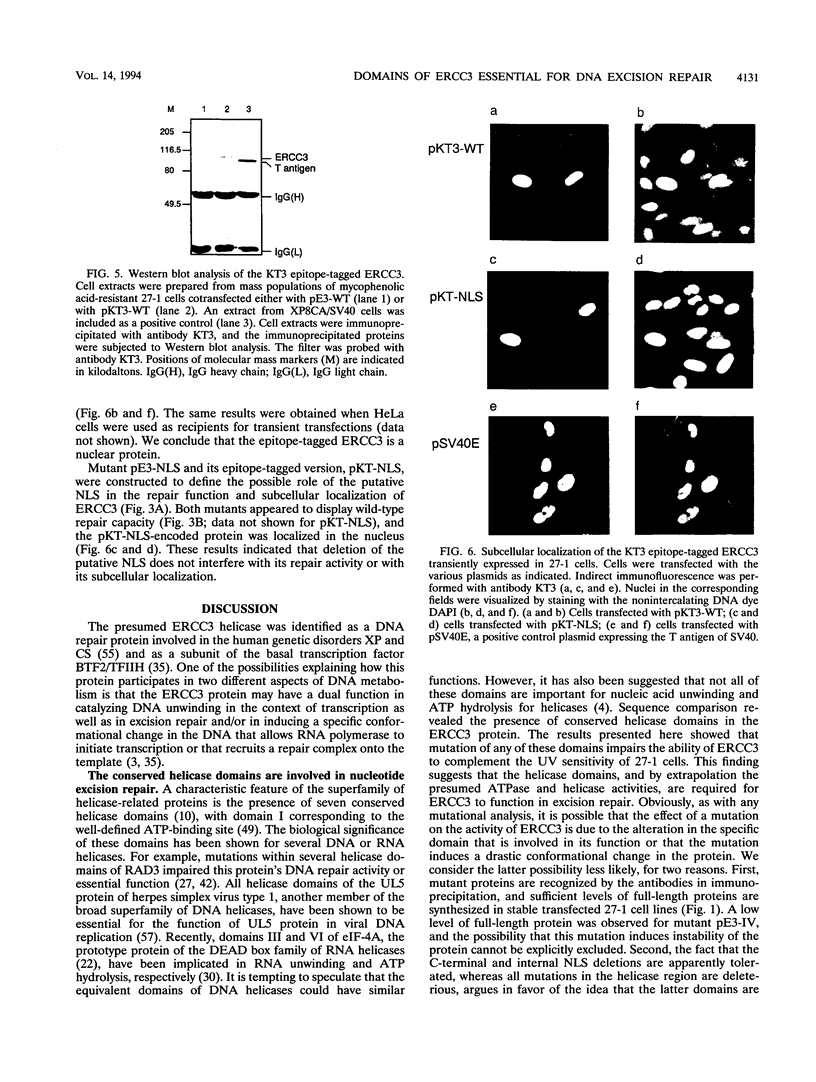
The human ERCC3 gene, which corrects specifically the nucleotide excision repair defect in human xeroderma pigmentosum group B and cross-complements the repair deficiency in rodent UV-sensitive mutants of group 3, encodes a presumed DNA helicase that is identical to the p89 subunit of the general transcription factor TFIIH/BTF2. To examine the significance of the postulated functional domains in ERCC3, we have introduced mutations in the ERCC3 cDNA by means of site-specific mutagenesis and have determined the repair capacity of each mutant to complement the UV-sensitive phenotype of rodent group 3 cells. A conservative substitution of arginine for the invariant lysine residue in the ATPase motif (helicase domain I), six deletion mutations in the other helicase domains, and a deletion in the potential helix-turn-helix DNA-binding motif fail to complement the ERCC3 excision repair defect of rodent group 3 mutants, which implies that the helicase domains as well as the potential DNA-binding motif are required for the repair function of ERCC3. Analysis of carboxy-terminal deletions suggests that the carboxy-terminal exon may comprise a distinct determinant for the DNA repair function. In addition, we show that a functional epitope-tagged version of ERCC3 accumulates in the nucleus. Deletion of the putative nuclear location signal impairs neither the nuclear location nor the repair function, indicating that other sequences may (also) be involved in translocation of ERCC3 to the nucleus.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Azzaria M., Schurr E., Gros P. Discrete mutations introduced in the predicted nucleotide-binding sites of the mdr1 gene abolish its ability to confer multidrug resistance. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;9(12):5289–5297. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.12.5289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailly V., Sung P., Prakash L., Prakash S. DNA.RNA helicase activity of RAD3 protein of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9712–9716. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bootsma D., Hoeijmakers J. H. DNA repair. Engagement with transcription. Nature. 1993 May 13;363(6425):114–115. doi: 10.1038/363114a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chao K., Lohman T. M. DNA and nucleotide-induced conformational changes in the Escherichia coli Rep and helicase II (UvrD) proteins. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 15;265(2):1067–1076. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feaver W. J., Svejstrup J. Q., Bardwell L., Bardwell A. J., Buratowski S., Gulyas K. D., Donahue T. F., Friedberg E. C., Kornberg R. D. Dual roles of a multiprotein complex from S. cerevisiae in transcription and DNA repair. Cell. 1993 Dec 31;75(7):1379–1387. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90624-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer L., Gerard M., Chalut C., Lutz Y., Humbert S., Kanno M., Chambon P., Egly J. M. Cloning of the 62-kilodalton component of basic transcription factor BTF2. Science. 1992 Sep 4;257(5075):1392–1395. doi: 10.1126/science.1529339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flejter W. L., McDaniel L. D., Johns D., Friedberg E. C., Schultz R. A. Correction of xeroderma pigmentosum complementation group D mutant cell phenotypes by chromosome and gene transfer: involvement of the human ERCC2 DNA repair gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 1;89(1):261–265. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.1.261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fry D. C., Kuby S. A., Mildvan A. S. ATP-binding site of adenylate kinase: mechanistic implications of its homology with ras-encoded p21, F1-ATPase, and other nucleotide-binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(4):907–911. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.4.907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorbalenya A. E., Koonin E. V., Donchenko A. P., Blinov V. M. Two related superfamilies of putative helicases involved in replication, recombination, repair and expression of DNA and RNA genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jun 26;17(12):4713–4730. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.12.4713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman L., Thiagalingam S. Nucleotide excision repair, a tracking mechanism in search of damage. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 15;268(23):16871–16874. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gulyas K. D., Donahue T. F. SSL2, a suppressor of a stem-loop mutation in the HIS4 leader encodes the yeast homolog of human ERCC-3. Cell. 1992 Jun 12;69(6):1031–1042. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90621-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guzder S. N., Qiu H., Sommers C. H., Sung P., Prakash L., Prakash S. DNA repair gene RAD3 of S. cerevisiae is essential for transcription by RNA polymerase II. Nature. 1994 Jan 6;367(6458):91–94. doi: 10.1038/367091a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoeijmakers J. H. Nucleotide excision repair I: from E. coli to yeast. Trends Genet. 1993 May;9(5):173–177. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(93)90164-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoeijmakers J. H. Nucleotide excision repair. II: From yeast to mammals. Trends Genet. 1993 Jun;9(6):211–217. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(93)90121-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp B. E., Pearson R. B. Protein kinase recognition sequence motifs. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Sep;15(9):342–346. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90073-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein B., Pastink A., Odijk H., Westerveld A., van der Eb A. J. Transformation and immortalization of diploid xeroderma pigmentosum fibroblasts. Exp Cell Res. 1990 Dec;191(2):256–262. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(90)90012-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koken M. H., Vreeken C., Bol S. A., Cheng N. C., Jaspers-Dekker I., Hoeijmakers J. H., Eeken J. C., Weeda G., Pastink A. Cloning and characterization of the Drosophila homolog of the xeroderma pigmentosum complementation-group B correcting gene, ERCC3. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Nov 11;20(21):5541–5548. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.21.5541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legerski R., Peterson C. Expression cloning of a human DNA repair gene involved in xeroderma pigmentosum group C. Nature. 1992 Sep 3;359(6390):70–73. doi: 10.1038/359070a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin J. J., Sancar A. (A)BC excinuclease: the Escherichia coli nucleotide excision repair enzyme. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Aug;6(16):2219–2224. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01398.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linder P., Lasko P. F., Ashburner M., Leroy P., Nielsen P. J., Nishi K., Schnier J., Slonimski P. P. Birth of the D-E-A-D box. Nature. 1989 Jan 12;337(6203):121–122. doi: 10.1038/337121a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu H., Zawel L., Fisher L., Egly J. M., Reinberg D. Human general transcription factor IIH phosphorylates the C-terminal domain of RNA polymerase II. Nature. 1992 Aug 20;358(6388):641–645. doi: 10.1038/358641a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacArthur H., Walter G. Monoclonal antibodies specific for the carboxy terminus of simian virus 40 large T antigen. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):483–491. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.483-491.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mounkes L. C., Jones R. S., Liang B. C., Gelbart W., Fuller M. T. A Drosophila model for xeroderma pigmentosum and Cockayne's syndrome: haywire encodes the fly homolog of ERCC3, a human excision repair gene. Cell. 1992 Dec 11;71(6):925–937. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90389-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nance M. A., Berry S. A. Cockayne syndrome: review of 140 cases. Am J Med Genet. 1992 Jan 1;42(1):68–84. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320420115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naumovski L., Friedberg E. C. Analysis of the essential and excision repair functions of the RAD3 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae by mutagenesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;6(4):1218–1227. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.4.1218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donovan A., Wood R. D. Identical defects in DNA repair in xeroderma pigmentosum group G and rodent ERCC group 5. Nature. 1993 May 13;363(6425):185–188. doi: 10.1038/363185a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park E., Guzder S. N., Koken M. H., Jaspers-Dekker I., Weeda G., Hoeijmakers J. H., Prakash S., Prakash L. RAD25 (SSL2), the yeast homolog of the human xeroderma pigmentosum group B DNA repair gene, is essential for viability. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 1;89(23):11416–11420. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.23.11416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pause A., Sonenberg N. Mutational analysis of a DEAD box RNA helicase: the mammalian translation initiation factor eIF-4A. EMBO J. 1992 Jul;11(7):2643–2654. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05330.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson M. G., Tjian R. Transcription. The tell-tail trigger. Nature. 1992 Aug 20;358(6388):620–621. doi: 10.1038/358620a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qiu H., Park E., Prakash L., Prakash S. The Saccharomyces cerevisiae DNA repair gene RAD25 is required for transcription by RNA polymerase II. Genes Dev. 1993 Nov;7(11):2161–2171. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.11.2161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinstein J., Schlichting I., Wittinghofer A. Structurally and catalytically important residues in the phosphate binding loop of adenylate kinase of Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1990 Aug 14;29(32):7451–7459. doi: 10.1021/bi00484a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saraste M., Sibbald P. R., Wittinghofer A. The P-loop--a common motif in ATP- and GTP-binding proteins. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Nov;15(11):430–434. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90281-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaeffer L., Roy R., Humbert S., Moncollin V., Vermeulen W., Hoeijmakers J. H., Chambon P., Egly J. M. DNA repair helicase: a component of BTF2 (TFIIH) basic transcription factor. Science. 1993 Apr 2;260(5104):58–63. doi: 10.1126/science.8465201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherly D., Nouspikel T., Corlet J., Ucla C., Bairoch A., Clarkson S. G. Complementation of the DNA repair defect in xeroderma pigmentosum group G cells by a human cDNA related to yeast RAD2. Nature. 1993 May 13;363(6425):182–185. doi: 10.1038/363182a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeley T. W., Grossman L. Mutations in the Escherichia coli UvrB ATPase motif compromise excision repair capacity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6577–6581. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selby C. P., Sancar A. Molecular mechanism of transcription-repair coupling. Science. 1993 Apr 2;260(5104):53–58. doi: 10.1126/science.8465200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. B., Johnson K. S. Single-step purification of polypeptides expressed in Escherichia coli as fusions with glutathione S-transferase. Gene. 1988 Jul 15;67(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Story R. M., Steitz T. A. Structure of the recA protein-ADP complex. Nature. 1992 Jan 23;355(6358):374–376. doi: 10.1038/355374a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sung P., Bailly V., Weber C., Thompson L. H., Prakash L., Prakash S. Human xeroderma pigmentosum group D gene encodes a DNA helicase. Nature. 1993 Oct 28;365(6449):852–855. doi: 10.1038/365852a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sung P., Higgins D., Prakash L., Prakash S. Mutation of lysine-48 to arginine in the yeast RAD3 protein abolishes its ATPase and DNA helicase activities but not the ability to bind ATP. EMBO J. 1988 Oct;7(10):3263–3269. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03193.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tian G. C., Yan H. G., Jiang R. T., Kishi F., Nakazawa A., Tsai M. D. Mechanism of adenylate kinase. Are the essential lysines essential? Biochemistry. 1990 May 8;29(18):4296–4304. doi: 10.1021/bi00470a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troelstra C., van Gool A., de Wit J., Vermeulen W., Bootsma D., Hoeijmakers J. H. ERCC6, a member of a subfamily of putative helicases, is involved in Cockayne's syndrome and preferential repair of active genes. Cell. 1992 Dec 11;71(6):939–953. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90390-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vermeulen W., Stefanini M., Giliani S., Hoeijmakers J. H., Bootsma D. Xeroderma pigmentosum complementation group H falls into complementation group D. Mutat Res. 1991 Sep;255(2):201–208. doi: 10.1016/0921-8777(91)90054-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. E., Saraste M., Runswick M. J., Gay N. J. Distantly related sequences in the alpha- and beta-subunits of ATP synthase, myosin, kinases and other ATP-requiring enzymes and a common nucleotide binding fold. EMBO J. 1982;1(8):945–951. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01276.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J., Grossman L. Mutations in the helix-turn-helix motif of the Escherichia coli UvrA protein eliminate its specificity for UV-damaged DNA. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 5;268(7):5323–5331. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber C. A., Salazar E. P., Stewart S. A., Thompson L. H. ERCC2: cDNA cloning and molecular characterization of a human nucleotide excision repair gene with high homology to yeast RAD3. EMBO J. 1990 May;9(5):1437–1447. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08260.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeda G., Ma L. B., van Ham R. C., van der Eb A. J., Hoeijmakers J. H. Structure and expression of the human XPBC/ERCC-3 gene involved in DNA repair disorders xeroderma pigmentosum and Cockayne's syndrome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Nov 25;19(22):6301–6308. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.22.6301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeda G., Ma L., van Ham R. C., Bootsma D., van der Eb A. J., Hoeijmakers J. H. Characterization of the mouse homolog of the XPBC/ERCC-3 gene implicated in xeroderma pigmentosum and Cockayne's syndrome. Carcinogenesis. 1991 Dec;12(12):2361–2368. doi: 10.1093/carcin/12.12.2361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeda G., van Ham R. C., Masurel R., Westerveld A., Odijk H., de Wit J., Bootsma D., van der Eb A. J., Hoeijmakers J. H. Molecular cloning and biological characterization of the human excision repair gene ERCC-3. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2570–2581. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeda G., van Ham R. C., Vermeulen W., Bootsma D., van der Eb A. J., Hoeijmakers J. H. A presumed DNA helicase encoded by ERCC-3 is involved in the human repair disorders xeroderma pigmentosum and Cockayne's syndrome. Cell. 1990 Aug 24;62(4):777–791. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90122-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zantema A., Schrier P. I., Davis-Olivier A., van Laar T., Vaessen R. T., van der EB A. J. Adenovirus serotype determines association and localization of the large E1B tumor antigen with cellular tumor antigen p53 in transformed cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;5(11):3084–3091. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.11.3084. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu L. A., Weller S. K. The six conserved helicase motifs of the UL5 gene product, a component of the herpes simplex virus type 1 helicase-primase, are essential for its function. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):469–479. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.469-479.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Duin M., de Wit J., Odijk H., Westerveld A., Yasui A., Koken M. H., Hoeijmakers J. H., Bootsma D. Molecular characterization of the human excision repair gene ERCC-1: cDNA cloning and amino acid homology with the yeast DNA repair gene RAD10. Cell. 1986 Mar 28;44(6):913–923. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90014-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Eb A. J., Graham F. L. Assay of transforming activity of tumor virus DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):826–839. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65077-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]