Abstract
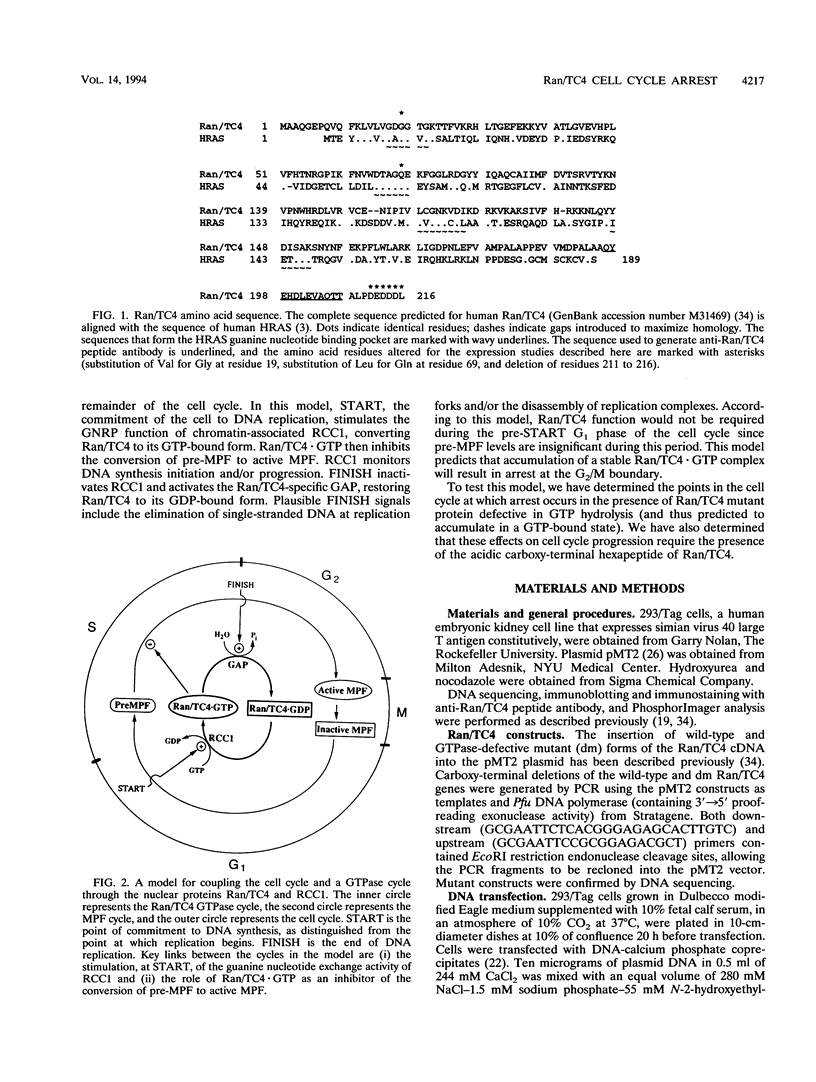
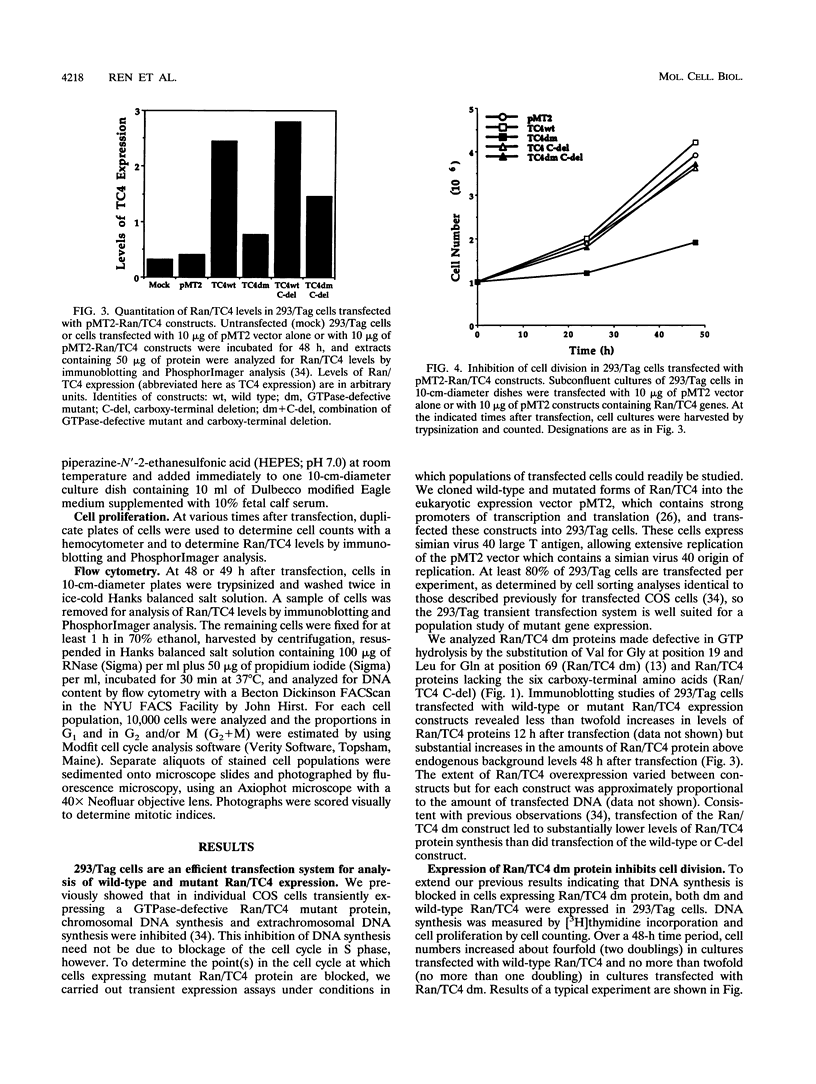
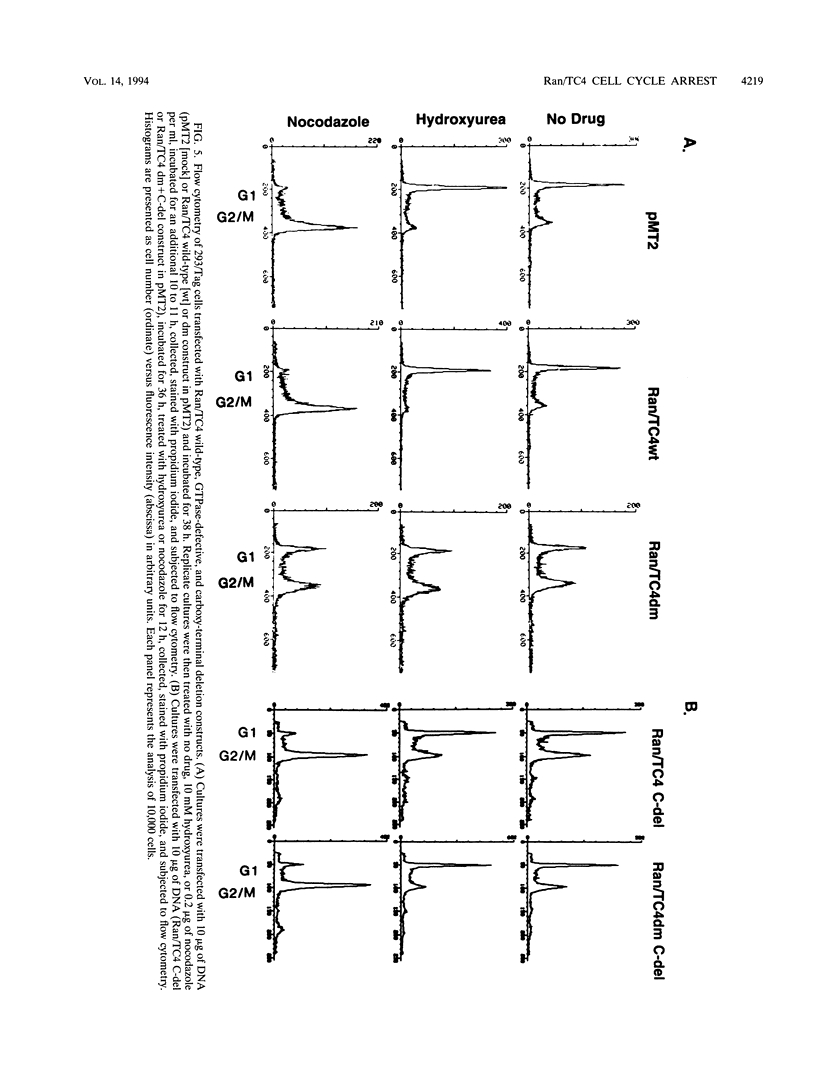
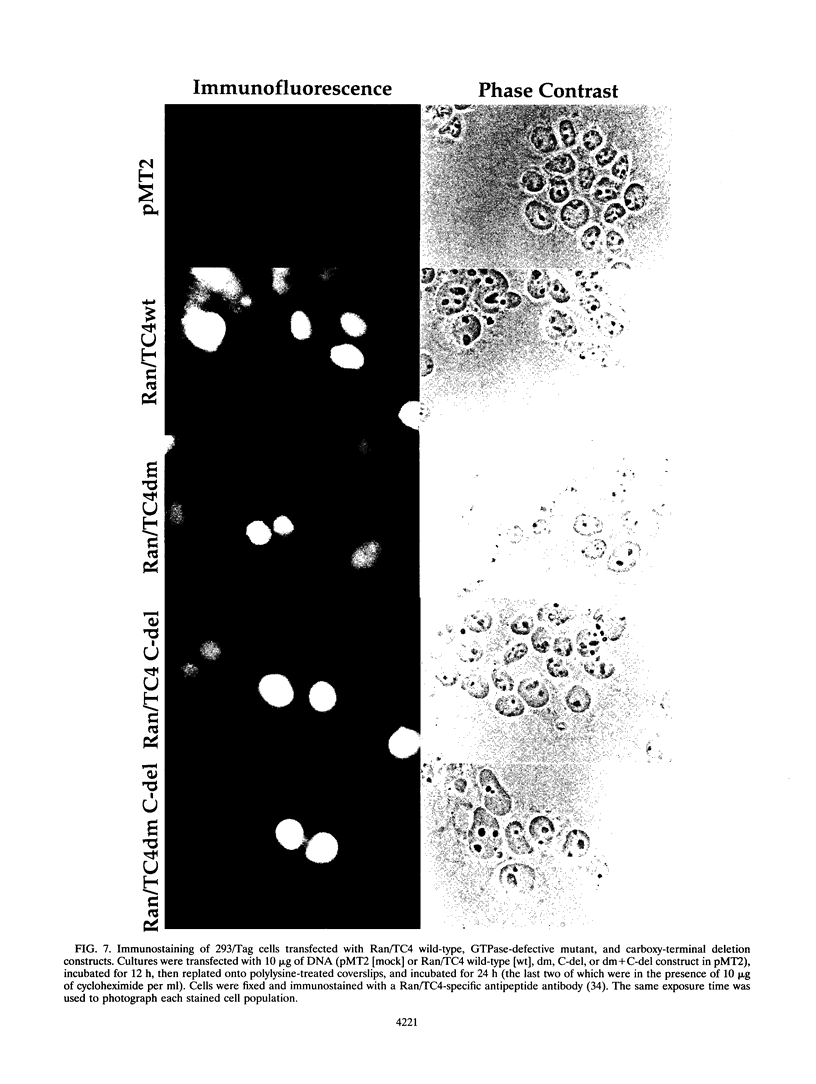
Ran/TC4, a member of the RAS gene superfamily, encodes an abundant nuclear protein that binds and hydrolyzes GTP. Transient expression of a Ran/TC4 mutant protein deficient in GTP hydrolysis blocked DNA replication, suggesting a role for Ran/TC4 in the regulation of cell cycle progression. To test this possibility, we exploited an efficient transfection system, involving the introduction of cDNAs in the pMT2 vector into 293/Tag cells, to analyze phenotypes associated with mutant and wild-type Ran/TC4 expression. Expression of a Ran/TC4 mutant protein deficient in GTP hydrolysis inhibited proliferation of transfected cells by arresting them predominantly in the G2, but also in the G1, phase of the cell cycle. Deletion of an acidic carboxy-terminal hexapeptide from the Ran/TC4 mutant did not alter its nuclear localization but did block its inhibitory effect on cell cycle progression. These data suggest that normal progression of the cell cycle is coupled to the operation of a Ran/TC4 GTPase cycle. Mediators of this coupling are likely to include the nuclear regulator of chromosome condensation 1 protein and the mitosis-promoting factor complex.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aebi M., Clark M. W., Vijayraghavan U., Abelson J. A yeast mutant, PRP20, altered in mRNA metabolism and maintenance of the nuclear structure, is defective in a gene homologous to the human gene RCC1 which is involved in the control of chromosome condensation. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 Oct;224(1):72–80. doi: 10.1007/BF00259453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amberg D. C., Fleischmann M., Stagljar I., Cole C. N., Aebi M. Nuclear PRP20 protein is required for mRNA export. EMBO J. 1993 Jan;12(1):233–241. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05649.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbacid M. ras genes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:779–827. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.004023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belhumeur P., Lee A., Tam R., DiPaolo T., Fortin N., Clark M. W. GSP1 and GSP2, genetic suppressors of the prp20-1 mutant in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: GTP-binding proteins involved in the maintenance of nuclear organization. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;13(4):2152–2161. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.4.2152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertram J. F., Nurcombe V. Counting cells with the new stereology. Trends Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;2(6):177–180. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(92)90038-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bischoff F. R., Maier G., Tilz G., Ponstingl H. A 47-kDa human nuclear protein recognized by antikinetochore autoimmune sera is homologous with the protein encoded by RCC1, a gene implicated in onset of chromosome condensation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8617–8621. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bischoff F. R., Ponstingl H. Catalysis of guanine nucleotide exchange on Ran by the mitotic regulator RCC1. Nature. 1991 Nov 7;354(6348):80–82. doi: 10.1038/354080a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bischoff F. R., Ponstingl H. Mitotic regulator protein RCC1 is complexed with a nuclear ras-related polypeptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10830–10834. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10830. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R., Sanders D. A., McCormick F. The GTPase superfamily: a conserved switch for diverse cell functions. Nature. 1990 Nov 8;348(6297):125–132. doi: 10.1038/348125a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R., Sanders D. A., McCormick F. The GTPase superfamily: conserved structure and molecular mechanism. Nature. 1991 Jan 10;349(6305):117–127. doi: 10.1038/349117a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chardin P. Small GTP-binding proteins of the ras family: a conserved functional mechanism? Cancer Cells. 1991 Apr;3(4):117–126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coutavas E., Ren M., Oppenheim J. D., D'Eustachio P., Rush M. G. Characterization of proteins that interact with the cell-cycle regulatory protein Ran/TC4. Nature. 1993 Dec 9;366(6455):585–587. doi: 10.1038/366585a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dasso M., Nishitani H., Kornbluth S., Nishimoto T., Newport J. W. RCC1, a regulator of mitosis, is essential for DNA replication. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;12(8):3337–3345. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.8.3337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dasso M. RCC1 in the cell cycle: the regulator of chromosome condensation takes on new roles. Trends Biochem Sci. 1993 Mar;18(3):96–101. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(93)90161-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downward J. Regulatory mechanisms for ras proteins. Bioessays. 1992 Mar;14(3):177–184. doi: 10.1002/bies.950140308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downward J. Signal transduction. Rac and Rho in tune. Nature. 1992 Sep 24;359(6393):273–274. doi: 10.1038/359273a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drivas G. T., Shih A., Coutavas E., Rush M. G., D'Eustachio P. Characterization of four novel ras-like genes expressed in a human teratocarcinoma cell line. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1793–1798. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drivas G., Massey R., Chang H. Y., Rush M. G., D'Eustachio P. Ras-like genes and gene families in the mouse. Mamm Genome. 1991;1(2):112–117. doi: 10.1007/BF02443787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forrester W., Stutz F., Rosbash M., Wickens M. Defects in mRNA 3'-end formation, transcription initiation, and mRNA transport associated with the yeast mutation prp20: possible coupling of mRNA processing and chromatin structure. Genes Dev. 1992 Oct;6(10):1914–1926. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.10.1914. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman R. S., Donoghue D. J. Protein kinases and protooncogenes: biochemical regulators of the eukaryotic cell cycle. Biochemistry. 1991 Mar 5;30(9):2293–2302. doi: 10.1021/bi00223a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C., Padmanabhan R., Howard B. H. High efficiency DNA-mediated transformation of primate cells. Science. 1983 Aug 5;221(4610):551–553. doi: 10.1126/science.6306768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt T. Summary: put out more flags. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1991;56:757–769. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1991.056.01.085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurwitz J., Dean F. B., Kwong A. D., Lee S. H. The in vitro replication of DNA containing the SV40 origin. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 25;265(30):18043–18046. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadowaki T., Goldfarb D., Spitz L. M., Tartakoff A. M., Ohno M. Regulation of RNA processing and transport by a nuclear guanine nucleotide release protein and members of the Ras superfamily. EMBO J. 1993 Jul;12(7):2929–2937. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05955.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman R. J. Vectors used for expression in mammalian cells. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:487–511. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85041-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto T., Beach D. Premature initiation of mitosis in yeast lacking RCC1 or an interacting GTPase. Cell. 1991 Jul 26;66(2):347–360. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90624-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick F. Coupling of ras p21 signalling and GTP hydrolysis by GTPase activating proteins. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1992 Apr 29;336(1276):43–48. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1992.0042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore M. S., Blobel G. The GTP-binding protein Ran/TC4 is required for protein import into the nucleus. Nature. 1993 Oct 14;365(6447):661–663. doi: 10.1038/365661a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore M. S., Blobel G. The two steps of nuclear import, targeting to the nuclear envelope and translocation through the nuclear pore, require different cytosolic factors. Cell. 1992 Jun 12;69(6):939–950. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90613-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray A. W. Creative blocks: cell-cycle checkpoints and feedback controls. Nature. 1992 Oct 15;359(6396):599–604. doi: 10.1038/359599a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishitani H., Ohtsubo M., Yamashita K., Iida H., Pines J., Yasudo H., Shibata Y., Hunter T., Nishimoto T. Loss of RCC1, a nuclear DNA-binding protein, uncouples the completion of DNA replication from the activation of cdc2 protein kinase and mitosis. EMBO J. 1991 Jun;10(6):1555–1564. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07675.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ren M., Drivas G., D'Eustachio P., Rush M. G. Ran/TC4: a small nuclear GTP-binding protein that regulates DNA synthesis. J Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;120(2):313–323. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.2.313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seki T., Yamashita K., Nishitani H., Takagi T., Russell P., Nishimoto T. Chromosome condensation caused by loss of RCC1 function requires the cdc25C protein that is located in the cytoplasm. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Dec;3(12):1373–1388. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.12.1373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherr C. J. Mammalian G1 cyclins. Cell. 1993 Jun 18;73(6):1059–1065. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90636-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]