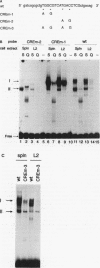
Abstract
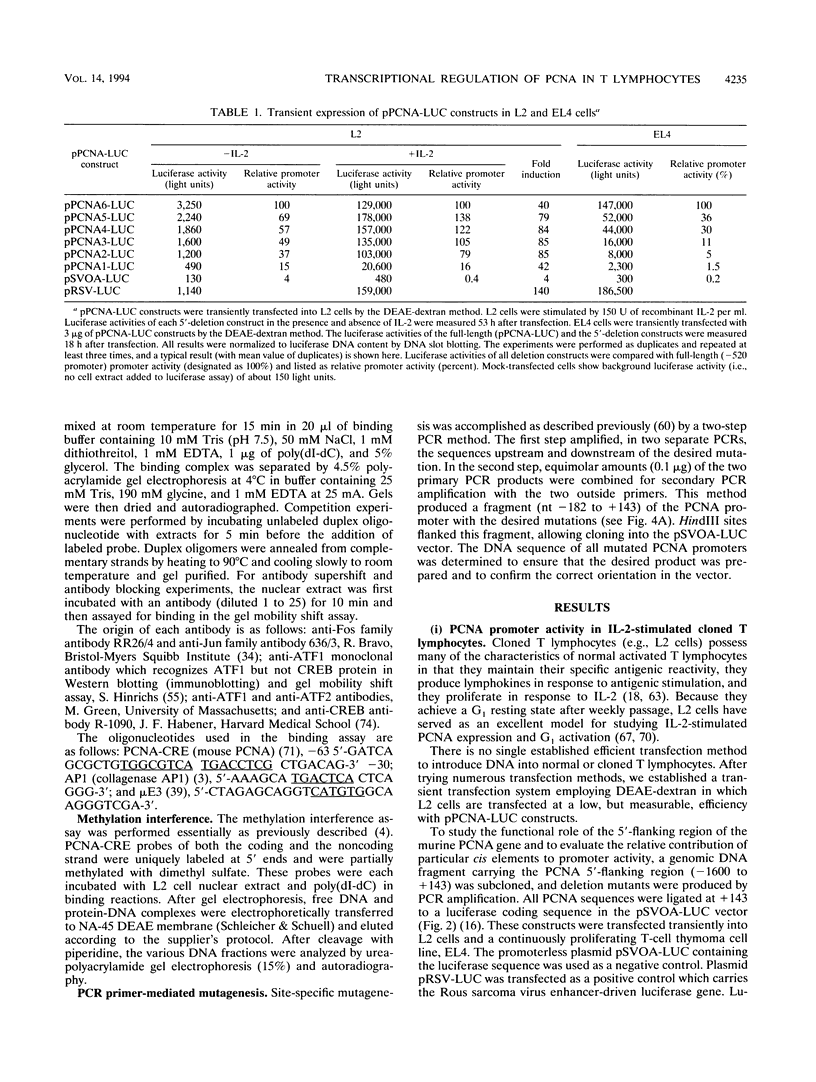
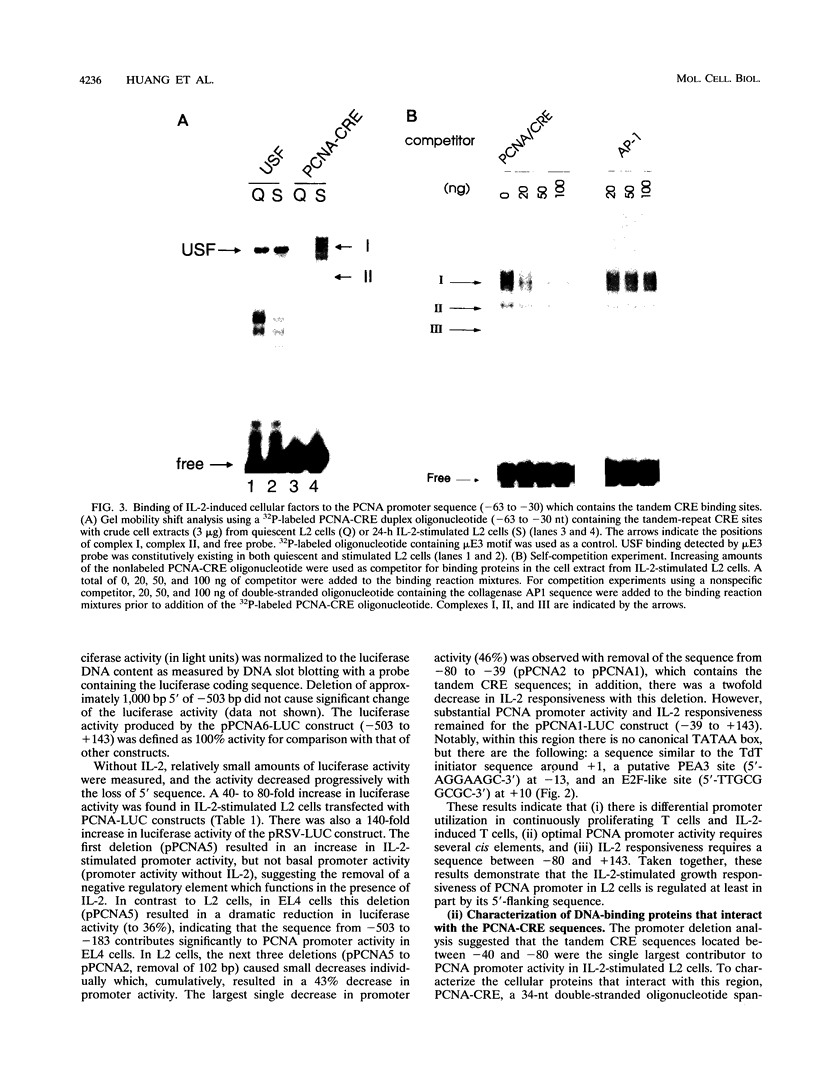
The proliferating-cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) gene encodes an auxiliary factor of DNA polymerase delta and functions in DNA replication during S phase. It is expressed at much higher levels in proliferating cells than in quiescent cells. We have studied the regulatory role of the 5'-flanking sequence of the murine PCNA gene in interleukin 2 (IL-2)-responsive cloned T cells (L2). Analysis of a set of deletion constructs in transient transfection assays measuring heterologous reporter gene (luciferase) activity demonstrated that the 182-bp 5'-flanking region provides full promoter activity in IL-2-stimulated L2 cells. While many elements contribute to PCNA promoter strength in IL-2-stimulated cells, the largest decrease in activity occurred with deletion of the tandem CRE (cyclic AMP response element) binding sites located at nucleotides -37 to -52. With a gel mobility shift assay, several IL-2-inducible DNA-protein complexes were detected, including CREB (CRE-binding) and ATF1 (activating transcription factor) proteins that are specific for the PCNA-CRE sequence. Methylation interference analysis confirmed specific binding of these proteins to the CRE sites. Mutation at the PCNA-CRE motif abolishes IL-2-inducible binding and reduces substantially PCNA promoter activity. These results indicate that IL-2-stimulated PCNA transcription may be partially mediated by these CRE-binding proteins.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alder H., Yoshinouchi M., Prystowsky M. B., Appasamy P., Baserga R. A conserved region in intron 1 negatively regulates the expression of the PCNA gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Apr 11;20(7):1769–1775. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.7.1769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almendral J. M., Huebsch D., Blundell P. A., Macdonald-Bravo H., Bravo R. Cloning and sequence of the human nuclear protein cyclin: homology with DNA-binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(6):1575–1579. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.6.1575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angel P., Imagawa M., Chiu R., Stein B., Imbra R. J., Rahmsdorf H. J., Jonat C., Herrlich P., Karin M. Phorbol ester-inducible genes contain a common cis element recognized by a TPA-modulated trans-acting factor. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):729–739. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90611-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer G. A., Burgers P. M. Molecular cloning, structure and expression of the yeast proliferating cell nuclear antigen gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jan 25;18(2):261–265. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.2.261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake M. C., Azizkhan J. C. Transcription factor E2F is required for efficient expression of the hamster dihydrofolate reductase gene in vitro and in vivo. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):4994–5002. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.4994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brasier A. R., Tate J. E., Habener J. F. Optimized use of the firefly luciferase assay as a reporter gene in mammalian cell lines. Biotechniques. 1989 Nov-Dec;7(10):1116–1122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bravo R., Celis J. E. A search for differential polypeptide synthesis throughout the cell cycle of HeLa cells. J Cell Biol. 1980 Mar;84(3):795–802. doi: 10.1083/jcb.84.3.795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bravo R., Frank R., Blundell P. A., Macdonald-Bravo H. Cyclin/PCNA is the auxiliary protein of DNA polymerase-delta. Nature. 1987 Apr 2;326(6112):515–517. doi: 10.1038/326515a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bravo R., Macdonald-Bravo H. Existence of two populations of cyclin/proliferating cell nuclear antigen during the cell cycle: association with DNA replication sites. J Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;105(4):1549–1554. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.4.1549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantrell D. A., Smith K. A. The interleukin-2 T-cell system: a new cell growth model. Science. 1984 Jun 22;224(4655):1312–1316. doi: 10.1126/science.6427923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. D., Ottavio L., Travali S., Lipson K. E., Baserga R. Transcriptional and posttranscriptional regulation of the proliferating cell nuclear antigen gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;10(7):3289–3296. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.7.3289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chellappan S. P., Hiebert S., Mudryj M., Horowitz J. M., Nevins J. R. The E2F transcription factor is a cellular target for the RB protein. Cell. 1991 Jun 14;65(6):1053–1061. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90557-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clevenger C. V., Altmann S. W., Prystowsky M. B. Requirement of nuclear prolactin for interleukin-2--stimulated proliferation of T lymphocytes. Science. 1991 Jul 5;253(5015):77–79. doi: 10.1126/science.2063207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutsch P. J., Hoeffler J. P., Jameson J. L., Lin J. C., Habener J. F. Structural determinants for transcriptional activation by cAMP-responsive DNA elements. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 5;263(34):18466–18472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flint K. J., Jones N. C. Differential regulation of three members of the ATF/CREB family of DNA-binding proteins. Oncogene. 1991 Nov;6(11):2019–2026. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita T., Shibuya H., Ohashi T., Yamanishi K., Taniguchi T. Regulation of human interleukin-2 gene: functional DNA sequences in the 5' flanking region for the gene expression in activated T lymphocytes. Cell. 1986 Aug 1;46(3):401–405. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90660-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner M. M., Revzin A. A gel electrophoresis method for quantifying the binding of proteins to specific DNA regions: application to components of the Escherichia coli lactose operon regulatory system. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):3047–3060. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.3047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregor P. D., Sawadogo M., Roeder R. G. The adenovirus major late transcription factor USF is a member of the helix-loop-helix group of regulatory proteins and binds to DNA as a dimer. Genes Dev. 1990 Oct;4(10):1730–1740. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.10.1730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habener J. F. Cyclic AMP response element binding proteins: a cornucopia of transcription factors. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Aug;4(8):1087–1094. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-8-1087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hai T. W., Liu F., Coukos W. J., Green M. R. Transcription factor ATF cDNA clones: an extensive family of leucine zipper proteins able to selectively form DNA-binding heterodimers. Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12B):2083–2090. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12b.2083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy S., Shenk T. Adenoviral control regions activated by E1A and the cAMP response element bind to the same factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4171–4175. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoeffler J. P., Meyer T. E., Yun Y., Jameson J. L., Habener J. F. Cyclic AMP-responsive DNA-binding protein: structure based on a cloned placental cDNA. Science. 1988 Dec 9;242(4884):1430–1433. doi: 10.1126/science.2974179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurst H. C., Totty N. F., Jones N. C. Identification and functional characterisation of the cellular activating transcription factor 43 (ATF-43) protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Sep 11;19(17):4601–4609. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.17.4601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivashkiv L. B., Liou H. C., Kara C. J., Lamph W. W., Verma I. M., Glimcher L. H. mXBP/CRE-BP2 and c-Jun form a complex which binds to the cyclic AMP, but not to the 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate, response element. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1609–1621. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaskulski D., Gatti C., Travali S., Calabretta B., Baserga R. Regulation of the proliferating cell nuclear antigen cyclin and thymidine kinase mRNA levels by growth factors. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 25;263(21):10175–10179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaskulski D., deRiel J. K., Mercer W. E., Calabretta B., Baserga R. Inhibition of cellular proliferation by antisense oligodeoxynucleotides to PCNA cyclin. Science. 1988 Jun 10;240(4858):1544–1546. doi: 10.1126/science.2897717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson K. W., Davis B. H., Smith K. A. cAMP antagonizes interleukin 2-promoted T-cell cycle progression at a discrete point in early G1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):6072–6076. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.6072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kammer G. M. The adenylate cyclase-cAMP-protein kinase A pathway and regulation of the immune response. Immunol Today. 1988 Jul-Aug;9(7-8):222–229. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(88)91220-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovary K., Bravo R. The jun and fos protein families are both required for cell cycle progression in fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Sep;11(9):4466–4472. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.9.4466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krönke M., Leonard W. J., Depper J. M., Greene W. C. Sequential expression of genes involved in human T lymphocyte growth and differentiation. J Exp Med. 1985 Jun 1;161(6):1593–1598. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.6.1593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ku D. H., Travali S., Calabretta B., Huebner K., Baserga R. Human gene for proliferating cell nuclear antigen has pseudogenes and localizes to chromosome 20. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1989 Jul;15(4):297–307. doi: 10.1007/BF01534969. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labrie C., Morris G. F., Mathews M. B. A complex promoter element mediates transactivation of the human proliferating cell nuclear antigen promoter by the 243-residue adenovirus E1A oncoprotein. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;13(3):1697–1707. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.3.1697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson E. L., Iscove N. N., Coutinho A. Two distinct factors are required for induction of T-cell growth. Nature. 1980 Feb 14;283(5748):664–666. doi: 10.1038/283664a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenardo M., Pierce J. W., Baltimore D. Protein-binding sites in Ig gene enhancers determine transcriptional activity and inducibility. Science. 1987 Jun 19;236(4808):1573–1577. doi: 10.1126/science.3109035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin Y. S., Green M. R. Interaction of a common cellular transcription factor, ATF, with regulatory elements in both E1a- and cyclic AMP-inducible promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3396–3400. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu F., Green M. R. A specific member of the ATF transcription factor family can mediate transcription activation by the adenovirus E1a protein. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1217–1224. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90686-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madsen P., Celis J. E. S-phase patterns of cyclin (PCNA) antigen staining resemble topographical patterns of DNA synthesis. A role for cyclin in DNA replication? FEBS Lett. 1985 Nov 25;193(1):5–11. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80068-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto K., Moriuchi T., Koji T., Nakane P. K. Molecular cloning of cDNA coding for rat proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA)/cyclin. EMBO J. 1987 Mar;6(3):637–642. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04802.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Means A. L., Farnham P. J. Transcription initiation from the dihydrofolate reductase promoter is positioned by HIP1 binding at the initiation site. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;10(2):653–661. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.2.653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Means A. L., Slansky J. E., McMahon S. L., Knuth M. W., Farnham P. J. The HIP1 binding site is required for growth regulation of the dihydrofolate reductase gene promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;12(3):1054–1063. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.3.1054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyachi K., Fritzler M. J., Tan E. M. Autoantibody to a nuclear antigen in proliferating cells. J Immunol. 1978 Dec;121(6):2228–2234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montminy M. R., Bilezikjian L. M. Binding of a nuclear protein to the cyclic-AMP response element of the somatostatin gene. Nature. 1987 Jul 9;328(6126):175–178. doi: 10.1038/328175a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore K. S., Sullivan K., Tan E. M., Prystowsky M. B. Proliferating cell nuclear antigen/cyclin is an interleukin 2-responsive gene. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 25;262(18):8447–8450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris G. F., Mathews M. B. Analysis of the proliferating cell nuclear antigen promoter and its response to adenovirus early region 1. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 25;265(27):16116–16125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris G. F., Mathews M. B. The adenovirus E1A transforming protein activates the proliferating cell nuclear antigen promoter via an activating transcription factor site. J Virol. 1991 Dec;65(12):6397–6406. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.12.6397-6406.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mudryj M., Hiebert S. W., Nevins J. R. A role for the adenovirus inducible E2F transcription factor in a proliferation dependent signal transduction pathway. EMBO J. 1990 Jul;9(7):2179–2184. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07387.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R. E2F: a link between the Rb tumor suppressor protein and viral oncoproteins. Science. 1992 Oct 16;258(5081):424–429. doi: 10.1126/science.1411535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohashi Y., Sawada Y., Moriuchi T., Fujinaga K. Analysis of the 5' flanking region of the rat proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) gene. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Mar 24;1130(2):175–181. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(92)90525-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottavio L., Chang C. D., Rizzo M. G., Petralia S., Travali S., Baserga R. The promoter of the proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) gene is active in serum-derived cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Jun 15;169(2):509–516. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)90360-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottavio L., Chang C. D., Rizzo M. G., Travali S., Casadevall C., Baserga R. Importance of introns in the growth regulation of mRNA levels of the proliferating cell nuclear antigen gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jan;10(1):303–309. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.1.303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardee A. B. G1 events and regulation of cell proliferation. Science. 1989 Nov 3;246(4930):603–608. doi: 10.1126/science.2683075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prelich G., Stillman B. Coordinated leading and lagging strand synthesis during SV40 DNA replication in vitro requires PCNA. Cell. 1988 Apr 8;53(1):117–126. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90493-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prystowsky M. B., Ely J. M., Beller D. I., Eisenberg L., Goldman J., Goldman M., Goldwasser E., Ihle J., Quintans J., Remold H. Alloreactive cloned T cell lines. VI. Multiple lymphokine activities secreted by helper and cytolytic cloned T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1982 Dec;129(6):2337–2344. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roesler W. J., Vandenbark G. R., Hanson R. W. Cyclic AMP and the induction of eukaryotic gene transcription. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 5;263(19):9063–9066. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg S. A., Grimm E. A., McGrogan M., Doyle M., Kawasaki E., Koths K., Mark D. F. Biological activity of recombinant human interleukin-2 produced in Escherichia coli. Science. 1984 Mar 30;223(4643):1412–1414. doi: 10.1126/science.6367046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabath D. E., Monos D. S., Lee S. C., Deutsch C., Prystowsky M. B. Cloned T-cell proliferation and synthesis of specific proteins are inhibited by quinine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4739–4743. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabath D. E., Podolin P. L., Comber P. G., Prystowsky M. B. cDNA cloning and characterization of interleukin 2-induced genes in a cloned T helper lymphocyte. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 25;265(21):12671–12678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheng M., Thompson M. A., Greenberg M. E. CREB: a Ca(2+)-regulated transcription factor phosphorylated by calmodulin-dependent kinases. Science. 1991 Jun 7;252(5011):1427–1430. doi: 10.1126/science.1646483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shipman-Appasamy P. M., Cohen K. S., Prystowsky M. B. Nucleotide sequence of murine PCNA: interspecies comparison of the cDNA and the 5' flanking region of the gene. DNA Seq. 1991;2(3):181–191. doi: 10.3109/10425179109039688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shipman-Appasamy P., Cohen K. S., Prystowsky M. B. Interleukin 2-induced expression of proliferating cell nuclear antigen is regulated by transcriptional and post-transcriptional mechanisms. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 5;265(31):19180–19184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shipman P. M., Sabath D. E., Fischer A. H., Comber P. G., Sullivan K., Tan E. M., Prystowsky M. B. Cyclin mRNA and protein expression in recombinant interleukin 2-stimulated cloned murine T lymphocytes. J Cell Biochem. 1988 Nov;38(3):189–198. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240380306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smale S. T., Baltimore D. The "initiator" as a transcription control element. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):103–113. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90176-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travali S., Ku D. H., Rizzo M. G., Ottavio L., Baserga R., Calabretta B. Structure of the human gene for the proliferating cell nuclear antigen. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 5;264(13):7466–7472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waeber G., Meyer T. E., LeSieur M., Hermann H. L., Gérard N., Habener J. F. Developmental stage-specific expression of cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate response element-binding protein CREB during spermatogenesis involves alternative exon splicing. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Oct;5(10):1418–1430. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-10-1418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang T., Sheppard J. R., Foker J. E. Rise and fall of cyclic AMP required for onset of lymphocyte DNA synthesis. Science. 1978 Jul 14;201(4351):155–157. doi: 10.1126/science.208147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong R. L., Katz M. E., Ogata K., Tan E. M., Cohen S. Inhibition of nuclear DNA synthesis by an autoantibody to proliferating cell nuclear antigen/cyclin. Cell Immunol. 1987 Dec;110(2):443–448. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(87)90137-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiong Y., Zhang H., Beach D. D type cyclins associate with multiple protein kinases and the DNA replication and repair factor PCNA. Cell. 1992 Oct 30;71(3):505–514. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90518-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi M., Nishida Y., Moriuchi T., Hirose F., Hui C. C., Suzuki Y., Matsukage A. Drosophila proliferating cell nuclear antigen (cyclin) gene: structure, expression during development, and specific binding of homeodomain proteins to its 5'-flanking region. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;10(3):872–879. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.3.872. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K. K., Gonzalez G. A., Biggs W. H., 3rd, Montminy M. R. Phosphorylation-induced binding and transcriptional efficacy of nuclear factor CREB. Nature. 1988 Aug 11;334(6182):494–498. doi: 10.1038/334494a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoo W., Martin M. E., Folk W. R. PEA1 and PEA3 enhancer elements are primary components of the polyomavirus late transcription initiator element. J Virol. 1991 Oct;65(10):5391–5400. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.10.5391-5400.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Wet J. R., Wood K. V., DeLuca M., Helinski D. R., Subramani S. Firefly luciferase gene: structure and expression in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):725–737. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]