Abstract
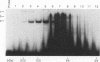
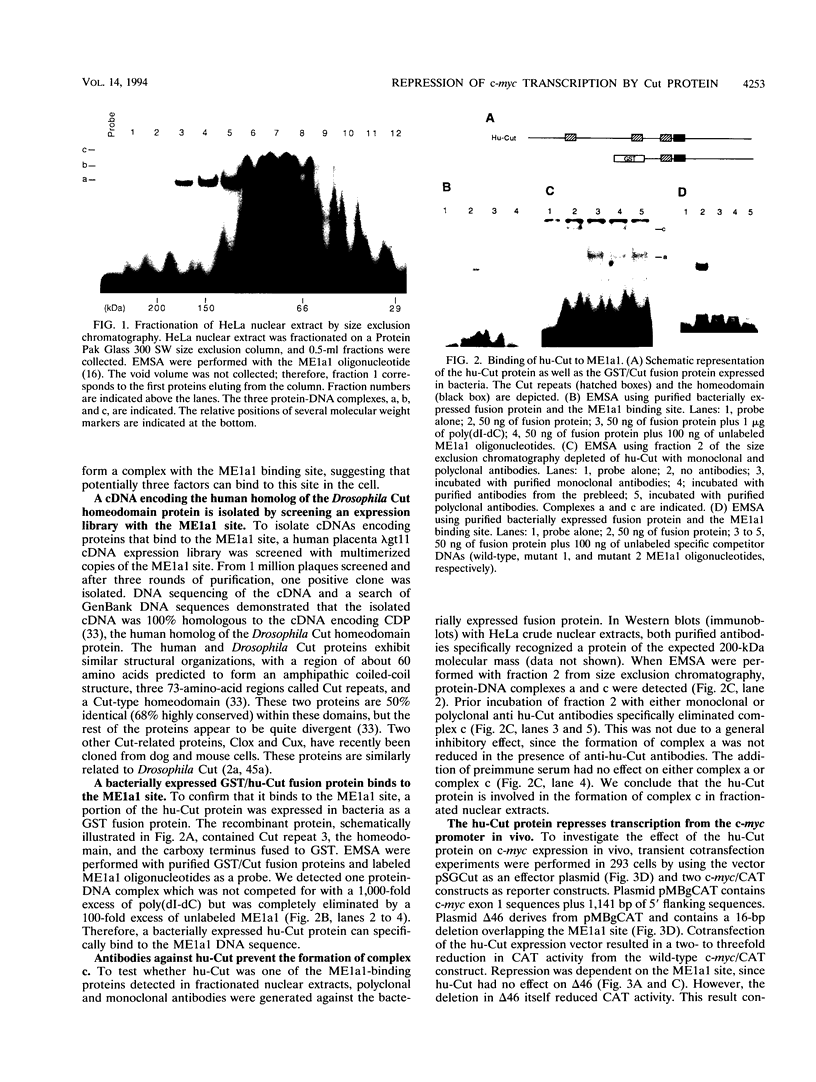
Studies of the c-myc promoter have shown that efficient transcription initiation at the P2 start site as well as the block to elongation of transcription require the presence of the ME1a1 protein binding site upstream of the P2 TATA box. Following fractionation by size exclusion chromatography, three protein-ME1a1 DNA complexes, a, b, and c, were detected by electrophoretic mobility shift assay. A cDNA encoding a protein present in complex c was isolated by screening of an expression library with an ME1a1 DNA probe. This cDNA was found to encode the human homolog of the Drosophila Cut homeodomain protein. The bacterially expressed human Cut (hu-Cut) protein bound to the ME1a1 site, and antibodies against hu-Cut inhibited the ME1a1 binding activity c in nuclear extracts. In cotransfection experiments, the hu-Cut protein repressed transcription from the c-myc promoter, and this repression was shown to be dependent on the presence of the ME1a1 site. Using a reporter construct with a heterologous promoter, we found that c-myc exon 1 sequences were also necessary, in addition to the ME1a1 site, for repression by Cut. Taken together, these results suggest that the human homolog of the Drosophila Cut homeodomain protein is involved in regulation of the c-myc gene.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almendral J. M., Sommer D., Macdonald-Bravo H., Burckhardt J., Perera J., Bravo R. Complexity of the early genetic response to growth factors in mouse fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):2140–2148. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.2140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andres V., Nadal-Ginard B., Mahdavi V. Clox, a mammalian homeobox gene related to Drosophila cut, encodes DNA-binding regulatory proteins differentially expressed during development. Development. 1992 Oct;116(2):321–334. doi: 10.1242/dev.116.2.321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrés V., Chiara M. D., Mahdavi V. A new bipartite DNA-binding domain: cooperative interaction between the cut repeat and homeo domain of the cut homeo proteins. Genes Dev. 1994 Jan;8(2):245–257. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.2.245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asselin C., Nepveu A., Marcu K. B. Molecular requirements for transcriptional initiation of the murine c-myc gene. Oncogene. 1989 May;4(5):549–558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barberis A., Superti-Furga G., Busslinger M. Mutually exclusive interaction of the CCAAT-binding factor and of a displacement protein with overlapping sequences of a histone gene promoter. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):347–359. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90489-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blochlinger K., Bodmer R., Jan L. Y., Jan Y. N. Patterns of expression of cut, a protein required for external sensory organ development in wild-type and cut mutant Drosophila embryos. Genes Dev. 1990 Aug;4(8):1322–1331. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.8.1322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blochlinger K., Jan L. Y., Jan Y. N. Postembryonic patterns of expression of cut, a locus regulating sensory organ identity in Drosophila. Development. 1993 Feb;117(2):441–450. doi: 10.1242/dev.117.2.441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodmer R., Barbel S., Sheperd S., Jack J. W., Jan L. Y., Jan Y. N. Transformation of sensory organs by mutations of the cut locus of D. melanogaster. Cell. 1987 Oct 23;51(2):293–307. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90156-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bossone S. A., Asselin C., Patel A. J., Marcu K. B. MAZ, a zinc finger protein, binds to c-MYC and C2 gene sequences regulating transcriptional initiation and termination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7452–7456. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffey R. J., Jr, Bascom C. C., Sipes N. J., Graves-Deal R., Weissman B. E., Moses H. L. Selective inhibition of growth-related gene expression in murine keratinocytes by transforming growth factor beta. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3088–3093. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3088. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole M. D. The myc oncogene: its role in transformation and differentiation. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:361–384. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.002045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coppola J. A., Parker J. M., Schuler G. D., Cole M. D. Continued withdrawal from the cell cycle and regulation of cellular genes in mouse erythroleukemia cells blocked in differentiation by the c-myc oncogene. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1714–1720. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1714. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean M., Levine R. A., Ran W., Kindy M. S., Sonenshein G. E., Campisi J. Regulation of c-myc transcription and mRNA abundance by serum growth factors and cell contact. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 15;261(20):9161–9166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Martin P. L., Shastry B. S., Roeder R. G. Eukaryotic gene transcription with purified components. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:582–598. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01039-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dmitrovsky E., Kuehl W. M., Hollis G. F., Kirsch I. R., Bender T. P., Segal S. Expression of a transfected human c-myc oncogene inhibits differentiation of a mouse erythroleukaemia cell line. Nature. 1986 Aug 21;322(6081):748–750. doi: 10.1038/322748a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dotto G. P., Gilman M. Z., Maruyama M., Weinberg R. A. c-myc and c-fos expression in differentiating mouse primary keratinocytes. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):2853–2857. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04579.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dufort D., Drolet M., Nepveu A. A protein binding site from the murine c-myc promoter contributes to transcriptional block. Oncogene. 1993 Jan;8(1):165–171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einat M., Resnitzky D., Kimchi A. Close link between reduction of c-myc expression by interferon and, G0/G1 arrest. Nature. 1985 Feb 14;313(6003):597–600. doi: 10.1038/313597a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evan G. I., Littlewood T. D. The role of c-myc in cell growth. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1993 Feb;3(1):44–49. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(05)80339-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han K., Manley J. L. Functional domains of the Drosophila Engrailed protein. EMBO J. 1993 Jul;12(7):2723–2733. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05934.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hann S. R., Thompson C. B., Eisenman R. N. c-myc oncogene protein synthesis is independent of the cell cycle in human and avian cells. 1985 Mar 28-Apr 3Nature. 314(6009):366–369. doi: 10.1038/314366a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada R., Dufort D., Denis-Larose C., Nepveu A. Conserved cut repeats in the human cut homeodomain protein function as DNA binding domains. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 21;269(3):2062–2067. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt J. T., Redner R. L., Nienhuis A. W. An oligomer complementary to c-myc mRNA inhibits proliferation of HL-60 promyelocytic cells and induces differentiation. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):963–973. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachman H. M., Cheng G. H., Skoultchi A. I. Transfection of mouse erythroleukemia cells with myc sequences changes the rate of induced commitment to differentiate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6480–6484. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachman H. M., Skoultchi A. I. Expression of c-myc changes during differentiation of mouse erythroleukaemia cells. Nature. 1984 Aug 16;310(5978):592–594. doi: 10.1038/310592a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Licht J. D., Grossel M. J., Figge J., Hansen U. M. Drosophila Krüppel protein is a transcriptional repressor. Nature. 1990 Jul 5;346(6279):76–79. doi: 10.1038/346076a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lillie J. W., Green M. R. Transcription activation by the adenovirus E1a protein. Nature. 1989 Mar 2;338(6210):39–44. doi: 10.1038/338039a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu S., McLeod E., Jack J. Four distinct regulatory regions of the cut locus and their effect on cell type specification in Drosophila. Genetics. 1991 Jan;127(1):151–159. doi: 10.1093/genetics/127.1.151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loke S. L., Stein C., Zhang X., Avigan M., Cohen J., Neckers L. M. Delivery of c-myc antisense phosphorothioate oligodeoxynucleotides to hematopoietic cells in culture by liposome fusion: specific reduction in c-myc protein expression correlates with inhibition of cell growth and DNA synthesis. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1988;141:282–289. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74006-0_38. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüscher B., Eisenman R. N. New light on Myc and Myb. Part I. Myc. Genes Dev. 1990 Dec;4(12A):2025–2035. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.12a.2025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcu K. B., Bossone S. A., Patel A. J. myc function and regulation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:809–860. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.004113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller H., Asselin C., Dufort D., Yang J. Q., Gupta K., Marcu K. B., Nepveu A. A cis-acting element in the promoter region of the murine c-myc gene is necessary for transcriptional block. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;9(12):5340–5349. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.12.5340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neufeld E. J., Skalnik D. G., Lievens P. M., Orkin S. H. Human CCAAT displacement protein is homologous to the Drosophila homeoprotein, cut. Nat Genet. 1992 Apr;1(1):50–55. doi: 10.1038/ng0492-50. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prochownik E. V., Kukowska J. Deregulated expression of c-myc by murine erythroleukaemia cells prevents differentiation. 1986 Aug 28-Sep 3Nature. 322(6082):848–850. doi: 10.1038/322848a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prochownik E. V., Kukowska J., Rodgers C. c-myc antisense transcripts accelerate differentiation and inhibit G1 progression in murine erythroleukemia cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;8(9):3683–3695. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.9.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pyrc J. J., Moberg K. H., Hall D. J. Isolation of a novel cDNA encoding a zinc-finger protein that binds to two sites within the c-myc promoter. Biochemistry. 1992 Apr 28;31(16):4102–4110. doi: 10.1021/bi00131a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabbitts P. H., Watson J. V., Lamond A., Forster A., Stinson M. A., Evan G., Fischer W., Atherton E., Sheppard R., Rabbitts T. H. Metabolism of c-myc gene products: c-myc mRNA and protein expression in the cell cycle. EMBO J. 1985 Aug;4(8):2009–2015. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03885.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reitsma P. H., Rothberg P. G., Astrin S. M., Trial J., Bar-Shavit Z., Hall A., Teitelbaum S. L., Kahn A. J. Regulation of myc gene expression in HL-60 leukaemia cells by a vitamin D metabolite. Nature. 1983 Dec 1;306(5942):492–494. doi: 10.1038/306492a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadowski I., Ma J., Triezenberg S., Ptashne M. GAL4-VP16 is an unusually potent transcriptional activator. Nature. 1988 Oct 6;335(6190):563–564. doi: 10.1038/335563a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadowski I., Ptashne M. A vector for expressing GAL4(1-147) fusions in mammalian cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Sep 25;17(18):7539–7539. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.18.7539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh H., LeBowitz J. H., Baldwin A. S., Jr, Sharp P. A. Molecular cloning of an enhancer binding protein: isolation by screening of an expression library with a recognition site DNA. Cell. 1988 Feb 12;52(3):415–423. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80034-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skalnik D. G., Strauss E. C., Orkin S. H. CCAAT displacement protein as a repressor of the myelomonocytic-specific gp91-phox gene promoter. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 5;266(25):16736–16744. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer C. A., Groudine M. Control of c-myc regulation in normal and neoplastic cells. Adv Cancer Res. 1991;56:1–48. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60476-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St-Arnaud R., Nepveu A., Marcu K. B., McBurney M. W. Two transient increases in c-myc gene expression during neuroectodermal differentiation of mouse embryonal carcinoma cells. Oncogene. 1988 Nov;3(5):553–559. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Superti-Furga G., Barberis A., Schaffner G., Busslinger M. The -117 mutation in Greek HPFH affects the binding of three nuclear factors to the CCAAT region of the gamma-globin gene. EMBO J. 1988 Oct;7(10):3099–3107. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03176.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Superti-Furga G., Barberis A., Schreiber E., Busslinger M. The protein CDP, but not CP1, footprints on the CCAAT region of the gamma-globin gene in unfractionated B-cell extracts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Mar 1;1007(2):237–242. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(89)90046-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson C. B., Challoner P. B., Neiman P. E., Groudine M. Levels of c-myc oncogene mRNA are invariant throughout the cell cycle. 1985 Mar 28-Apr 3Nature. 314(6009):363–366. doi: 10.1038/314363a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valarché I., Tissier-Seta J. P., Hirsch M. R., Martinez S., Goridis C., Brunet J. F. The mouse homeodomain protein Phox2 regulates Ncam promoter activity in concert with Cux/CDP and is a putative determinant of neurotransmitter phenotype. Development. 1993 Nov;119(3):881–896. doi: 10.1242/dev.119.3.881. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westin E. H., Wong-Staal F., Gelmann E. P., Dalla-Favera R., Papas T. S., Lautenberger J. A., Eva A., Reddy E. P., Tronick S. R., Aaronson S. A. Expression of cellular homologues of retroviral onc genes in human hematopoietic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(8):2490–2494. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.8.2490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Pellicer A., Silverstein S., Axel R., Urlaub G., Chasin L. DNA-mediated transfer of the adenine phosphoribosyltransferase locus into mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1373–1376. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang J. Q., Remmers E. F., Marcu K. B. The first exon of the c-myc proto-oncogene contains a novel positive control element. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 20;5(13):3553–3562. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04682.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokoyama K., Imamoto F. Transcriptional control of the endogenous MYC protooncogene by antisense RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7363–7367. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]