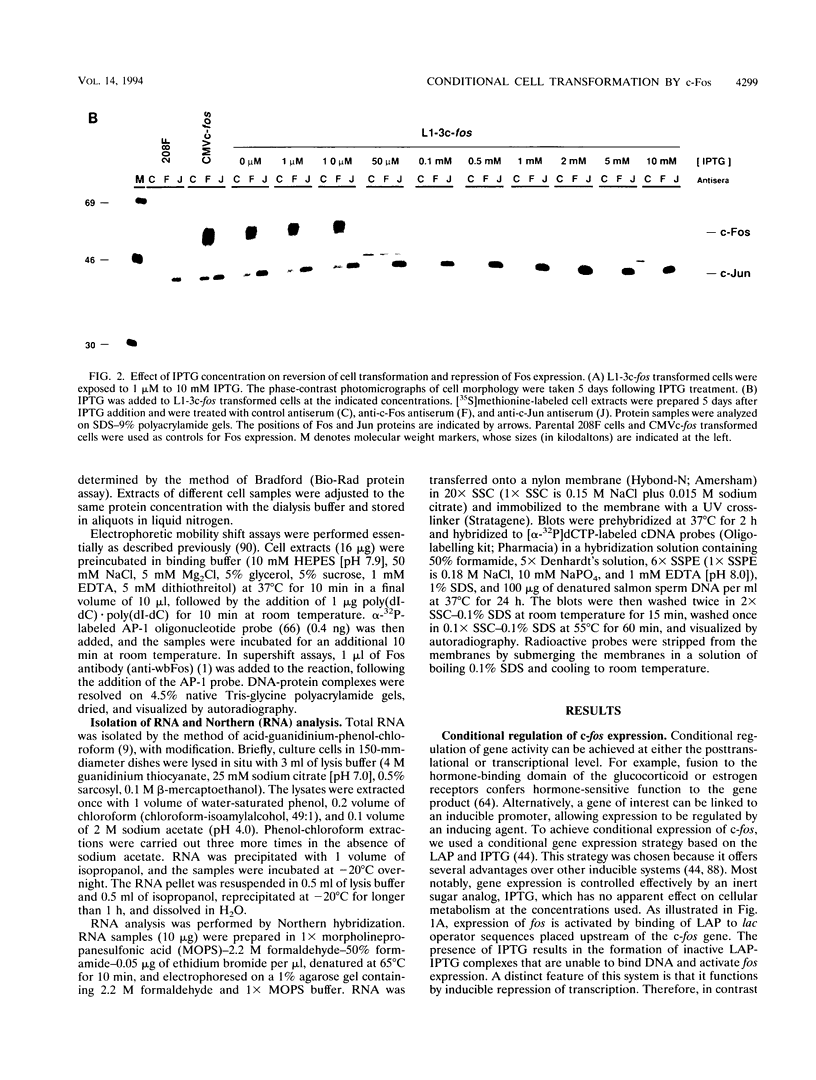
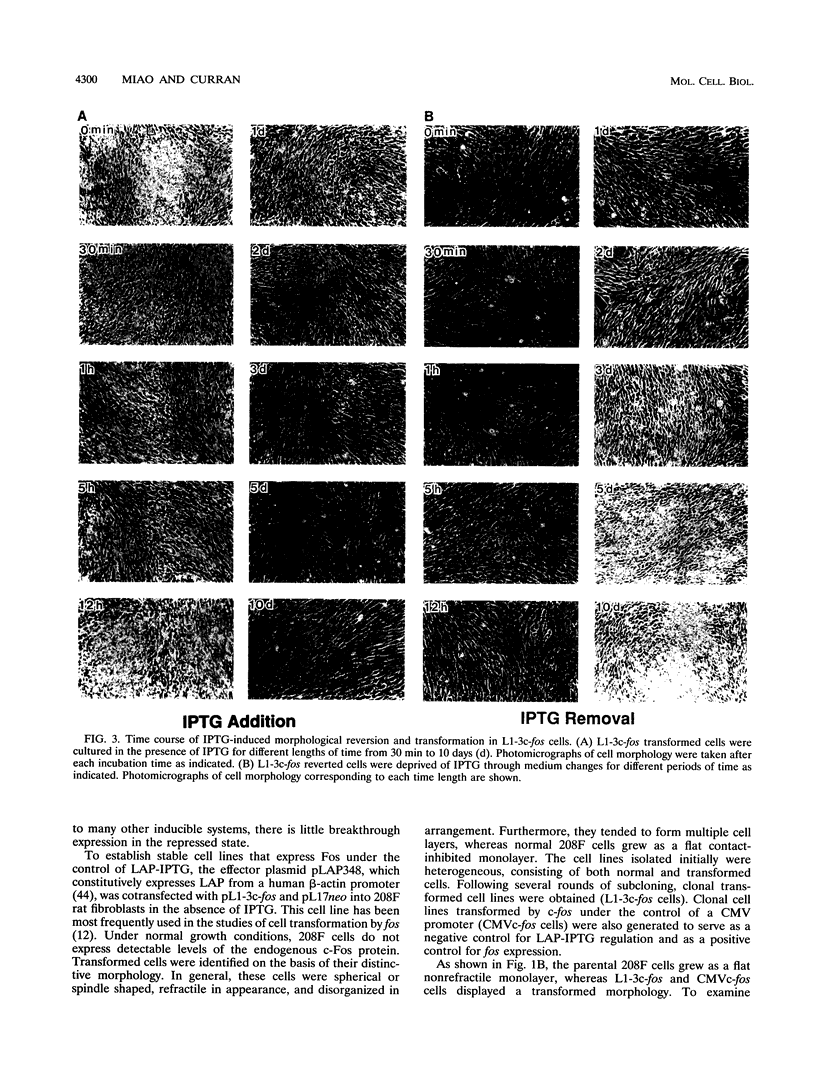
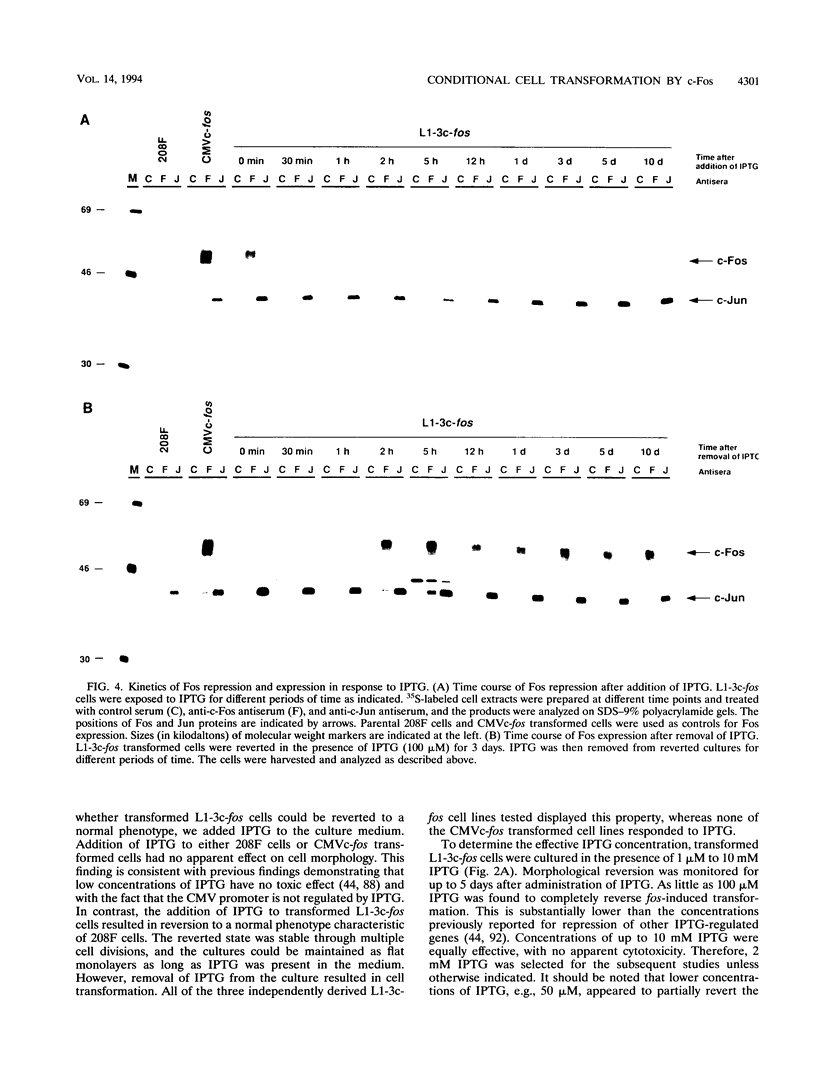
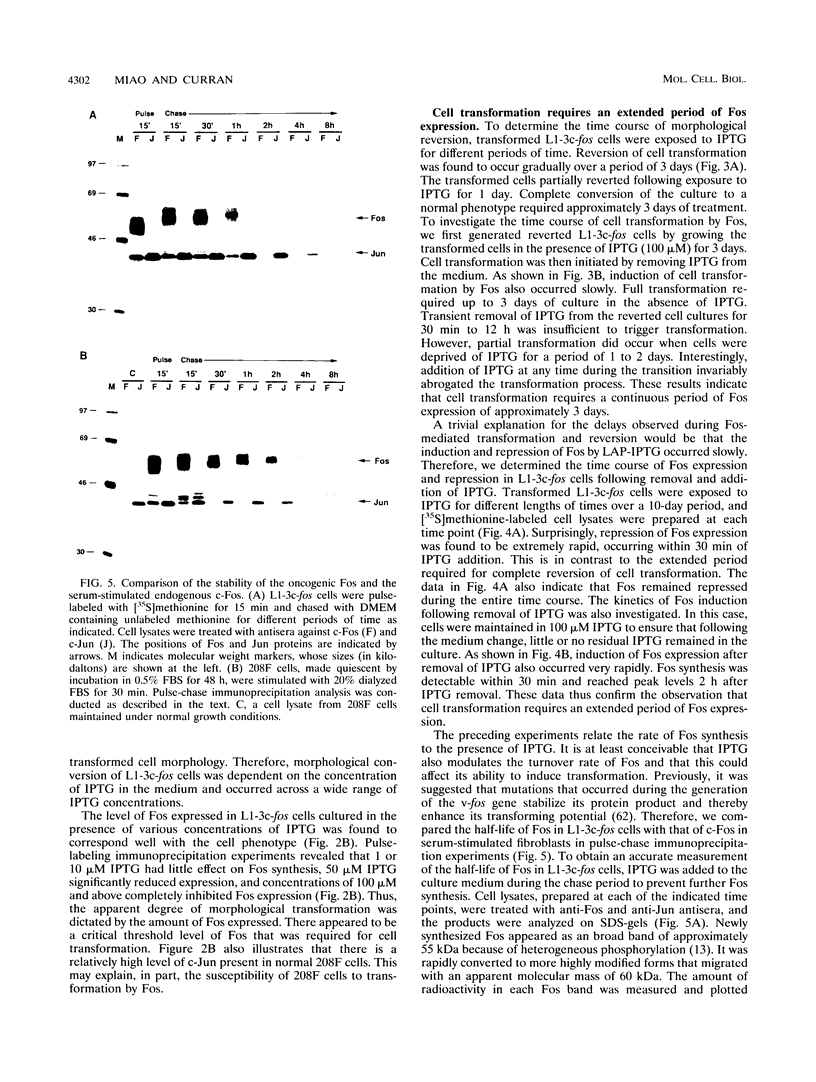
Abstract
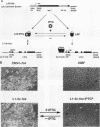
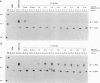
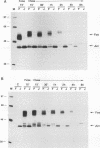
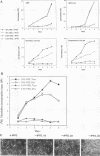
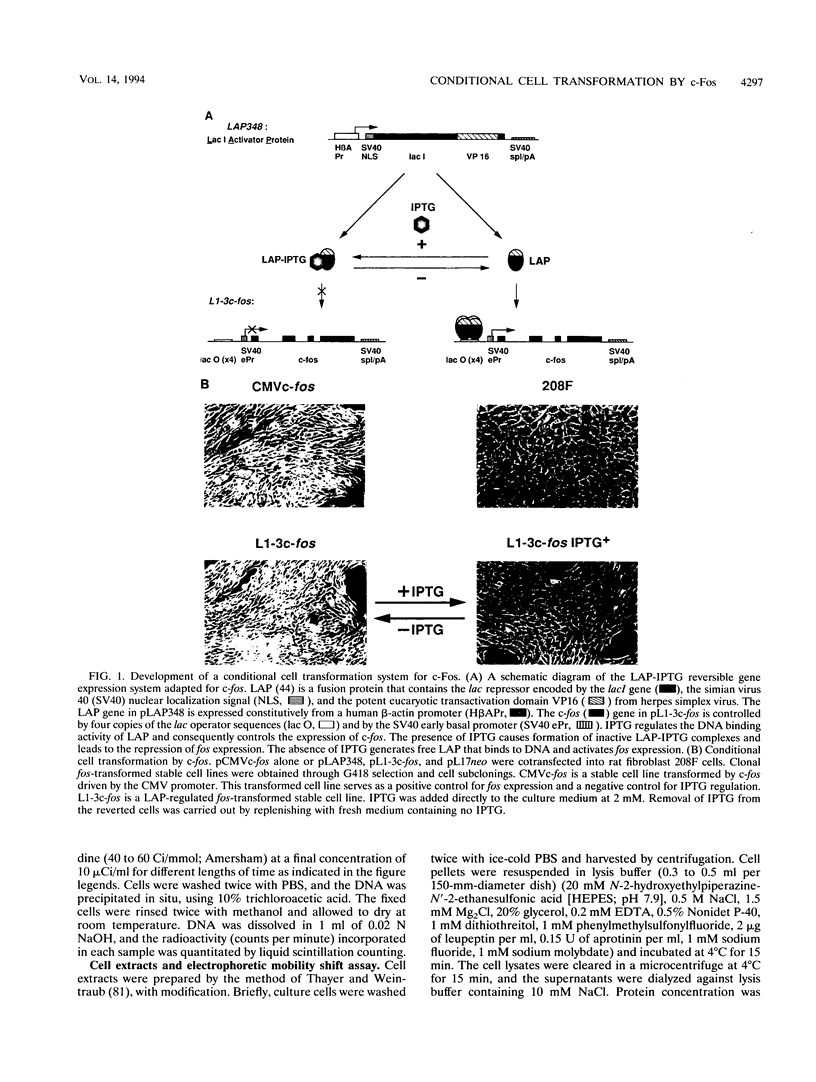
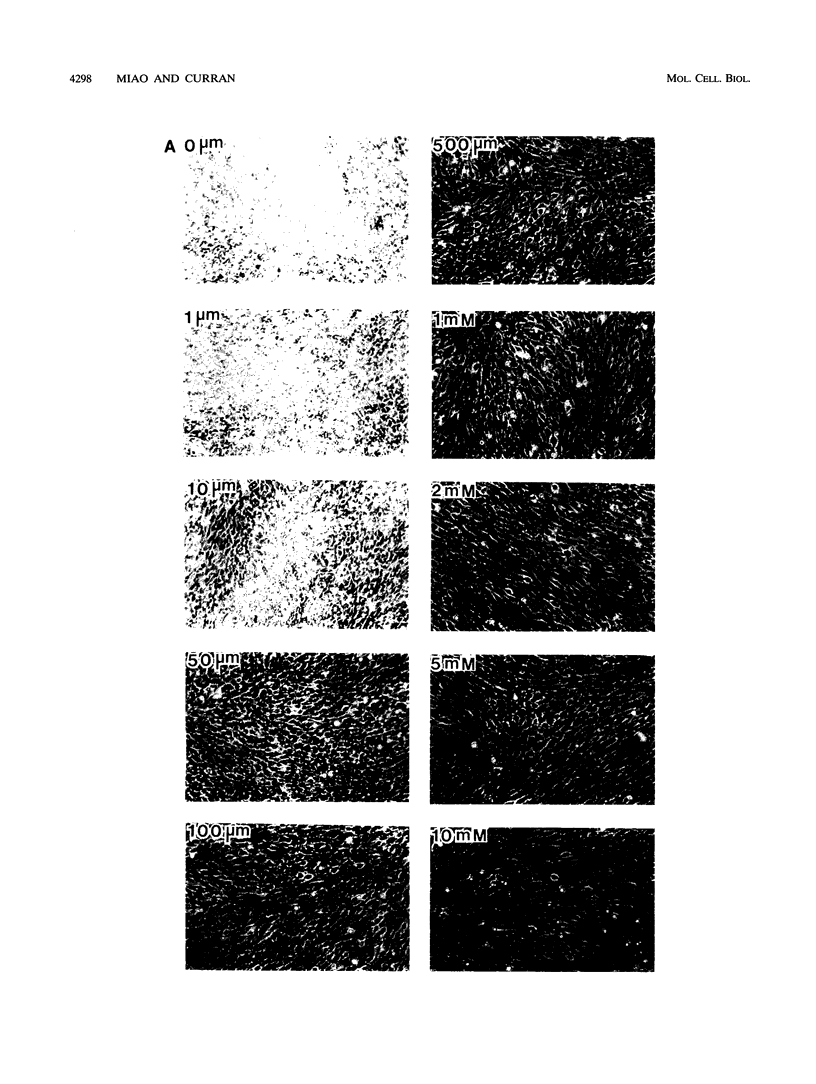
The proto-oncogene transcription factors Fos and Jun form a heterodimeric complex that binds to DNA and regulates expression of specific target genes. Continuous expression of c-fos causes transformation of cultured fibroblasts and induces osteogenic sarcoma in mice. To investigate the molecular basis of fos-mediated oncogenesis, we developed a conditional cell transformation system in which Fos expression was regulated by isopropyl-beta-D-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG). Synthesis or repression of Fos in L1-3c-fos cells occurred rapidly, within 30 min, after the removal or addition of IPTG to the culture medium. However, there was a significant delay between the induction of Fos expression and the appearance of morphological transformation. No effect was observed after 12 h of Fos expression, partial transformation was detected after 24 h, and full transformation required approximately 3 days of continuous Fos expression. Similarly, the transformed cell morphology persisted for at least 2 days after repression of Fos, and a normal phenotype was observed only after 3 days. Fos-Jun complexes, capable of binding to AP-1 sequences, were present continuously during the delay in morphological transformation. Furthermore, increased expression of several candidate Fos target genes, including those encoding Fra-1, transin (stromelysin), collagenase, and ornithine decarboxylase, was detected shortly after Fos induction. The induction of morphological transformation was not dependent on the cell cycle, as it occurred in both cycling and noncycling cells. Thus, the Fos-Jun complexes present before L1-3c-fos cells become fully transformed are transcriptionally active. These complexes disappeared, and the Fos target genes were repressed at least 2 days prior to reversion. Our results suggest that cell transformation by Fos requires increased expression of a target gene(s) with a long-lived product(s) that must reach a critical level.
Full text
PDF


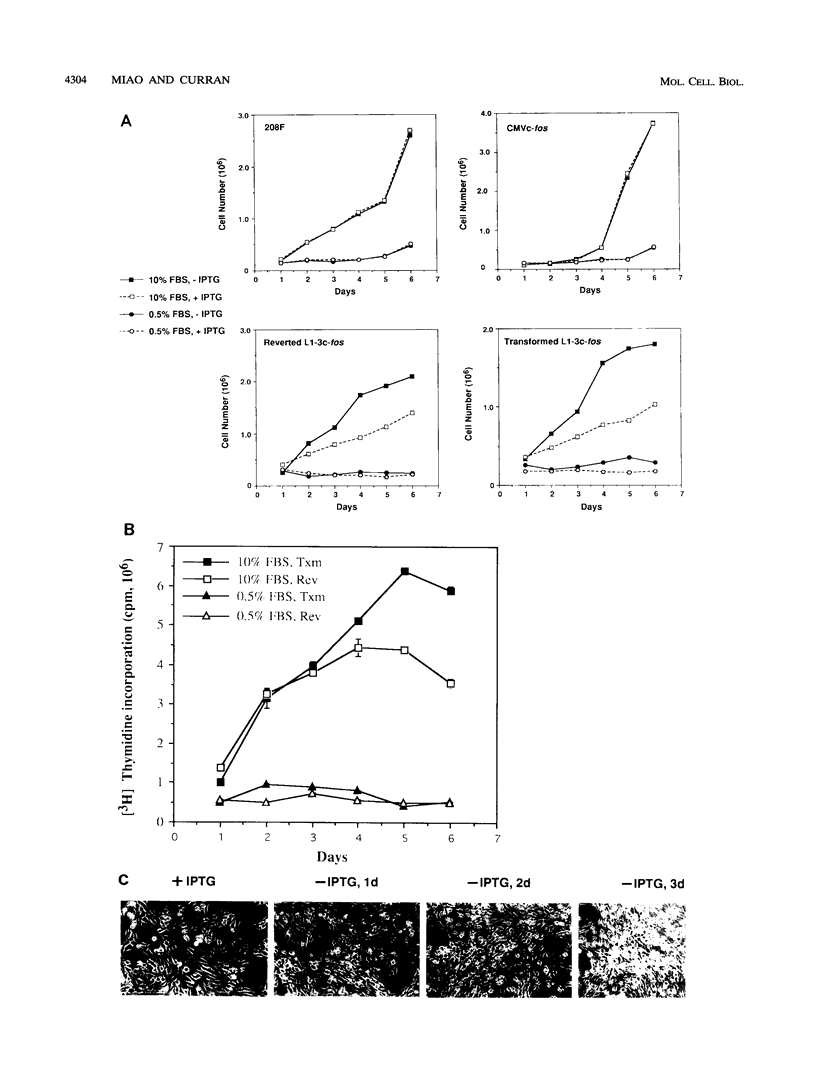

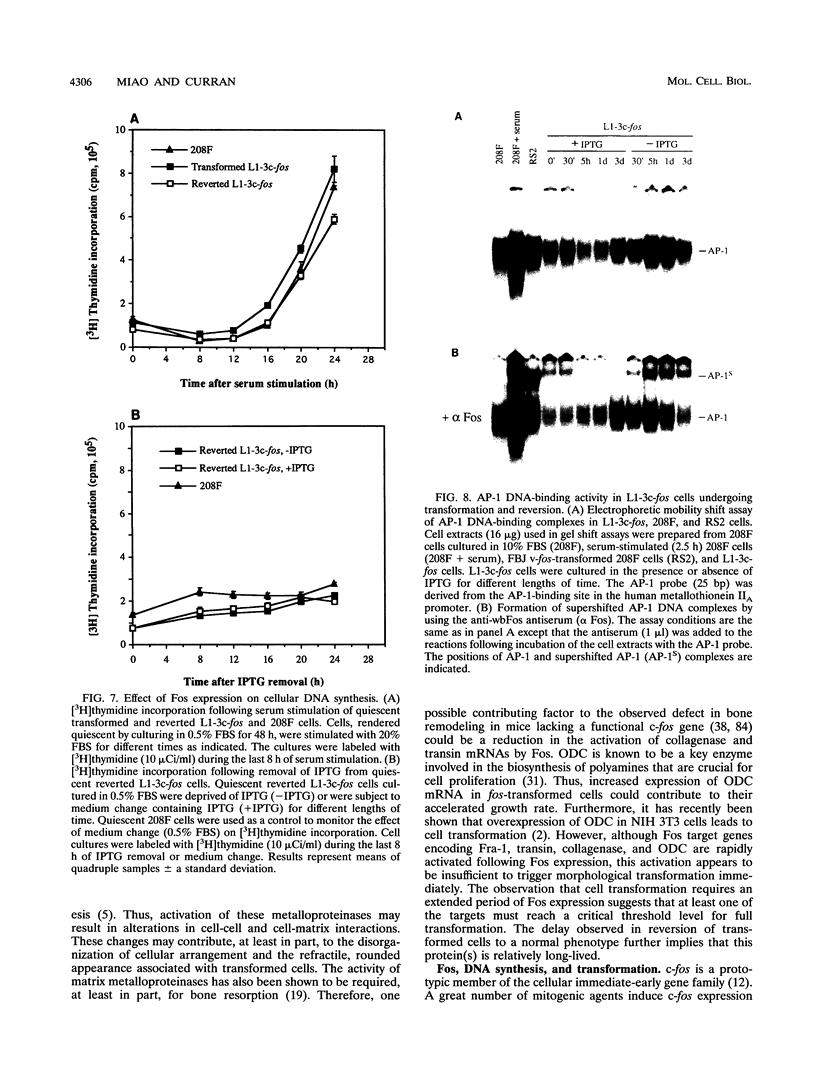




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abate C., Luk D., Gentz R., Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Curran T. Expression and purification of the leucine zipper and DNA-binding domains of Fos and Jun: both Fos and Jun contact DNA directly. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):1032–1036. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.1032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auvinen M., Paasinen A., Andersson L. C., Hölttä E. Ornithine decarboxylase activity is critical for cell transformation. Nature. 1992 Nov 26;360(6402):355–358. doi: 10.1038/360355a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell J. G., Wyke J. A., Macpherson I. A. Transformation by a temperature sensitive mutant of Rous sarcoma virus in the absence of serum. J Gen Virol. 1975 May;27(2):127–134. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-27-2-127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bravo R., Burckhardt J., Curran T., Müller R. Expression of c-fos in NIH3T3 cells is very low but inducible throughout the cell cycle. EMBO J. 1986 Apr;5(4):695–700. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04269.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown P. H., Alani R., Preis L. H., Szabo E., Birrer M. J. Suppression of oncogene-induced transformation by a deletion mutant of c-jun. Oncogene. 1993 Apr;8(4):877–886. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catling A. D., Wyke J. A., Frame M. C. Mitogenesis of quiescent chick fibroblasts by v-Src: dependence on events at the membrane leading to early changes in AP-1. Oncogene. 1993 Jul;8(7):1875–1886. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C., Okayama H. High-efficiency transformation of mammalian cells by plasmid DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2745–2752. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen D. R., Curran T. Analysis of dimerization and DNA binding functions in Fos and Jun by domain-swapping: involvement of residues outside the leucine zipper/basic region. Oncogene. 1990 Jun;5(6):929–939. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran T., Miller A. D., Zokas L., Verma I. M. Viral and cellular fos proteins: a comparative analysis. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90219-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran T., Peters G., Van Beveren C., Teich N. M., Verma I. M. FBJ murine osteosarcoma virus: identification and molecular cloning of biologically active proviral DNA. J Virol. 1982 Nov;44(2):674–682. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.2.674-682.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran T., Teich N. M. Candidate product of the FBJ murine osteosarcoma virus oncogene: characterization of a 55,000-dalton phosphoprotein. J Virol. 1982 Apr;42(1):114–122. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.1.114-122.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran T., Teich N. M. Identification of a 39,000-dalton protein in cells transformed by the FBJ murine osteosarcoma virus. Virology. 1982 Jan 15;116(1):221–235. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90415-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran T., Verma I. M. FBR murine osteosarcoma virus. I. Molecular analysis and characterization of a 75,000-Da gag-fos fusion product. Virology. 1984 May;135(1):218–228. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90132-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everts V., Delaissé J. M., Korper W., Niehof A., Vaes G., Beertsen W. Degradation of collagen in the bone-resorbing compartment underlying the osteoclast involves both cysteine-proteinases and matrix metalloproteinases. J Cell Physiol. 1992 Feb;150(2):221–231. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041500202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field S. J., Johnson R. S., Mortensen R. M., Papaioannou V. E., Spiegelman B. M., Greenberg M. E. Growth and differentiation of embryonic stem cells that lack an intact c-fos gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 1;89(19):9306–9310. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.19.9306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkel M. P., Biskis B. O., Jinkins P. B. Virus induction of osteosarcomas in mice. Science. 1966 Feb 11;151(3711):698–701. doi: 10.1126/science.151.3711.698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franza B. R., Jr, Sambucetti L. C., Cohen D. R., Curran T. Analysis of Fos protein complexes and Fos-related antigens by high-resolution two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. Oncogene. 1987 May;1(2):213–221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friis R. R., Jockusch B. M., Boschek C. B., Ziemiecki A., Rübsamen H., Bauer H. Transformation-defective, temperature-sensitive mutants of Rous sarcoma virus have a reversibly defective src-gene product. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1980;44(Pt 2):1007–1012. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1980.044.01.108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujii M., Shalloway D., Verma I. M. Gene regulation by tyrosine kinases: src protein activates various promoters, including c-fos. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;9(6):2493–2499. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.6.2493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauthier-Rouvière C., Fernandez A., Lamb N. J. ras-induced c-fos expression and proliferation in living rat fibroblasts involves C-kinase activation and the serum response element pathway. EMBO J. 1990 Jan;9(1):171–180. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08093.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentz R., Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Abate C., Curran T. Parallel association of Fos and Jun leucine zippers juxtaposes DNA binding domains. Science. 1989 Mar 31;243(4899):1695–1699. doi: 10.1126/science.2494702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. E., Ziff E. B. Stimulation of 3T3 cells induces transcription of the c-fos proto-oncogene. Nature. 1984 Oct 4;311(5985):433–438. doi: 10.1038/311433a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grigoriadis A. E., Schellander K., Wang Z. Q., Wagner E. F. Osteoblasts are target cells for transformation in c-fos transgenic mice. J Cell Biol. 1993 Aug;122(3):685–701. doi: 10.1083/jcb.122.3.685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawker K. L., Pintzas A., Hennigan R. F., Gillespie D. A., Ozanne B. W. Transformation by the fos or jun oncogene does not increase AP-1 DNA-binding activity. J Virol. 1993 Sep;67(9):5487–5495. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.9.5487-5495.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heby O., Persson L. Molecular genetics of polyamine synthesis in eukaryotic cells. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Apr;15(4):153–158. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90216-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt J. T., Gopal T. V., Moulton A. D., Nienhuis A. W. Inducible production of c-fos antisense RNA inhibits 3T3 cell proliferation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4794–4798. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hölttä E., Auvinen M., Andersson L. C. Polyamines are essential for cell transformation by pp60v-src: delineation of molecular events relevant for the transformed phenotype. J Cell Biol. 1993 Aug;122(4):903–914. doi: 10.1083/jcb.122.4.903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hölttä E., Sistonen L., Alitalo K. The mechanisms of ornithine decarboxylase deregulation in c-Ha-ras oncogene-transformed NIH 3T3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 25;263(9):4500–4507. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jamal S., Ziff E. Transactivation of c-fos and beta-actin genes by raf as a step in early response to transmembrane signals. Nature. 1990 Mar 29;344(6265):463–466. doi: 10.1038/344463a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenuwein T., Müller D., Curran T., Müller R. Extended life span and tumorigenicity of nonestablished mouse connective tissue cells transformed by the fos oncogene of FBR-MuSV. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):629–637. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80035-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenuwein T., Müller R. Structure-function analysis of fos protein: a single amino acid change activates the immortalizing potential of v-fos. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):647–657. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90243-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. S., Spiegelman B. M., Papaioannou V. Pleiotropic effects of a null mutation in the c-fos proto-oncogene. Cell. 1992 Nov 13;71(4):577–586. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90592-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr L. D., Holt J. T., Matrisian L. M. Growth factors regulate transin gene expression by c-fos-dependent and c-fos-independent pathways. Science. 1988 Dec 9;242(4884):1424–1427. doi: 10.1126/science.2462278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kouzarides T., Ziff E. The role of the leucine zipper in the fos-jun interaction. Nature. 1988 Dec 15;336(6200):646–651. doi: 10.1038/336646a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovary K., Bravo R. Existence of different Fos/Jun complexes during the G0-to-G1 transition and during exponential growth in mouse fibroblasts: differential role of Fos proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;12(11):5015–5023. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.11.5015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovary K., Bravo R. The jun and fos protein families are both required for cell cycle progression in fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Sep;11(9):4466–4472. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.9.4466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruijer W., Cooper J. A., Hunter T., Verma I. M. Platelet-derived growth factor induces rapid but transient expression of the c-fos gene and protein. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):711–716. doi: 10.1038/312711a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labow M. A., Baim S. B., Shenk T., Levine A. J. Conversion of the lac repressor into an allosterically regulated transcriptional activator for mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;10(7):3343–3356. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.7.3343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landschulz W. H., Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. The leucine zipper: a hypothetical structure common to a new class of DNA binding proteins. Science. 1988 Jun 24;240(4860):1759–1764. doi: 10.1126/science.3289117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd A. C., Paterson H. F., Morris J. D., Hall A., Marshall C. J. p21H-ras-induced morphological transformation and increases in c-myc expression are independent of functional protein kinase C. EMBO J. 1989 Apr;8(4):1099–1104. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03479.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd A., Yancheva N., Wasylyk B. Transformation suppressor activity of a Jun transcription factor lacking its activation domain. Nature. 1991 Aug 15;352(6336):635–638. doi: 10.1038/352635a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall C. J. How does p21ras transform cells? Trends Genet. 1991 Mar;7(3):91–95. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(91)90278-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin G. S., Venuta S., Weber M., Rubin H. Temperature-dependent alterations in sugar transport in cells infected by a temperature-sensitive mutant of Rous sarcoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Nov;68(11):2739–2741. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.11.2739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matrisian L. M., Bowden G. T., Krieg P., Fürstenberger G., Briand J. P., Leroy P., Breathnach R. The mRNA coding for the secreted protease transin is expressed more abundantly in malignant than in benign tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9413–9417. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matrisian L. M., Glaichenhaus N., Gesnel M. C., Breathnach R. Epidermal growth factor and oncogenes induce transcription of the same cellular mRNA in rat fibroblasts. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1435–1440. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03799.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonnell S. E., Kerr L. D., Matrisian L. M. Epidermal growth factor stimulation of stromelysin mRNA in rat fibroblasts requires induction of proto-oncogenes c-fos and c-jun and activation of protein kinase C. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):4284–4293. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.4284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meijlink F., Curran T., Miller A. D., Verma I. M. Removal of a 67-base-pair sequence in the noncoding region of protooncogene fos converts it to a transforming gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):4987–4991. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.4987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan J. I., Curran T. Stimulus-transcription coupling in the nervous system: involvement of the inducible proto-oncogenes fos and jun. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1991;14:421–451. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.14.030191.002225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris J. D., Price B., Lloyd A. C., Self A. J., Marshall C. J., Hall A. Scrape-loading of Swiss 3T3 cells with ras protein rapidly activates protein kinase C in the absence of phosphoinositide hydrolysis. Oncogene. 1989 Jan;4(1):27–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller R., Bravo R., Burckhardt J., Curran T. Induction of c-fos gene and protein by growth factors precedes activation of c-myc. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):716–720. doi: 10.1038/312716a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakabeppu Y., Oda S., Sekiguchi M. Proliferative activation of quiescent Rat-1A cells by delta FosB. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jul;13(7):4157–4166. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.7.4157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuberg M., Schuermann M., Müller R. Mutagenesis of the DNA contact site in Fos protein: compatibility with the scissors grip model and requirement for transformation. Oncogene. 1991 Aug;6(8):1325–1333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishikura K., Murray J. M. Antisense RNA of proto-oncogene c-fos blocks renewed growth of quiescent 3T3 cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):639–649. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizawa M., Goto N., Kawai S. An avian transforming retrovirus isolated from a nephroblastoma that carries the fos gene as the oncogene. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):3733–3740. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.3733-3740.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papavassiliou A. G., Treier M., Chavrier C., Bohmann D. Targeted degradation of c-Fos, but not v-Fos, by a phosphorylation-dependent signal on c-Jun. Science. 1992 Dec 18;258(5090):1941–1944. doi: 10.1126/science.1470918. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patwardhan S., Gashler A., Siegel M. G., Chang L. C., Joseph L. J., Shows T. B., Le Beau M. M., Sukhatme V. P. EGR3, a novel member of the Egr family of genes encoding immediate-early transcription factors. Oncogene. 1991 Jun;6(6):917–928. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard D. Steroid-binding domains for regulating the functions of heterologous proteins in cis. Trends Cell Biol. 1993 Aug;3(8):278–280. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(93)90057-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quade K. Transformation of mammalian cells by avian myelocytomatosis virus and avian erythroblastosis virus. Virology. 1979 Oct 30;98(2):461–465. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90569-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Sambucetti L. C., Curran T., Distel R. J., Spiegelman B. M. Common DNA binding site for Fos protein complexes and transcription factor AP-1. Cell. 1988 Feb 12;52(3):471–480. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80039-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riabowol K. T., Vosatka R. J., Ziff E. B., Lamb N. J., Feramisco J. R. Microinjection of fos-specific antibodies blocks DNA synthesis in fibroblast cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1670–1676. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohrschneider L. R. Localization of pp60src within normal rat kidney cells infected with temperature-sensitive mutants (T-class) of Rous sarcoma virus. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1980;44(Pt 2):1013–1022. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1980.044.01.109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuermann M., Hennig G., Müller R. Transcriptional activation and transformation by chimaeric Fos-estrogen receptor proteins: altered properties as a consequence of gene fusion. Oncogene. 1993 Oct;8(10):2781–2790. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuermann M., Jooss K., Müller R. fosB is a transforming gene encoding a transcriptional activator. Oncogene. 1991 Apr;6(4):567–576. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuermann M., Neuberg M., Hunter J. B., Jenuwein T., Ryseck R. P., Bravo R., Müller R. The leucine repeat motif in Fos protein mediates complex formation with Jun/AP-1 and is required for transformation. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):507–516. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90253-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schönthal A., Herrlich P., Rahmsdorf H. J., Ponta H. Requirement for fos gene expression in the transcriptional activation of collagenase by other oncogenes and phorbol esters. Cell. 1988 Jul 29;54(3):325–334. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90195-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smeyne R. J., Schilling K., Robertson L., Luk D., Oberdick J., Curran T., Morgan J. I. fos-lacZ transgenic mice: mapping sites of gene induction in the central nervous system. Neuron. 1992 Jan;8(1):13–23. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90105-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smeyne R. J., Vendrell M., Hayward M., Baker S. J., Miao G. G., Schilling K., Robertson L. M., Curran T., Morgan J. I. Continuous c-fos expression precedes programmed cell death in vivo. Nature. 1993 May 13;363(6425):166–169. doi: 10.1038/363166a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stacey D. W., Kung H. F. Transformation of NIH 3T3 cells by microinjection of Ha-ras p21 protein. Nature. 1984 Aug 9;310(5977):508–511. doi: 10.1038/310508a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stacey D. W., Watson T., Kung H. F., Curran T. Microinjection of transforming ras protein induces c-fos expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):523–527. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Superti-Furga G., Bergers G., Picard D., Busslinger M. Hormone-dependent transcriptional regulation and cellular transformation by Fos-steroid receptor fusion proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 15;88(12):5114–5118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.12.5114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki T., Murakami M., Onai N., Fukuda E., Hashimoto Y., Sonobe M. H., Kameda T., Ichinose M., Miki K., Iba H. Analysis of AP-1 function in cellular transformation pathways. J Virol. 1994 Jun;68(6):3527–3535. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.6.3527-3535.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thayer M. J., Weintraub H. A cellular factor stimulates the DNA-binding activity of MyoD and E47. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 15;90(14):6483–6487. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.14.6483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner R., Tjian R. Leucine repeats and an adjacent DNA binding domain mediate the formation of functional cFos-cJun heterodimers. Science. 1989 Mar 31;243(4899):1689–1694. doi: 10.1126/science.2494701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Z. Q., Grigoriadis A. E., Möhle-Steinlein U., Wagner E. F. A novel target cell for c-fos-induced oncogenesis: development of chondrogenic tumours in embryonic stem cell chimeras. EMBO J. 1991 Sep;10(9):2437–2450. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07783.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Z. Q., Ovitt C., Grigoriadis A. E., Möhle-Steinlein U., Rüther U., Wagner E. F. Bone and haematopoietic defects in mice lacking c-fos. Nature. 1992 Dec 24;360(6406):741–745. doi: 10.1038/360741a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wick M., Lucibello F. C., Müller R. Inhibition of Fos- and Ras-induced transformation by mutant Fos proteins with structural alterations in functionally different domains. Oncogene. 1992 May;7(5):859–867. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisdon R., Verma I. M. Transformation by Fos proteins requires a C-terminal transactivation domain. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Dec;13(12):7429–7438. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.12.7429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrighton C., Busslinger M. Direct transcriptional stimulation of the ornithine decarboxylase gene by Fos in PC12 cells but not in fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Aug;13(8):4657–4669. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.8.4657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyborski D. L., Short J. M. Analysis of inducers of the E.coli lac repressor system in mammalian cells and whole animals. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Sep 11;19(17):4647–4653. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.17.4647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyke A. W., Cushley W., Wyke J. A. Mitogenesis by v-Src: a need for active oncoprotein both in leaving G0 and in completing G1 phases of the cell cycle. Cell Growth Differ. 1993 Aug;4(8):671–678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xanthoudakis S., Miao G., Wang F., Pan Y. C., Curran T. Redox activation of Fos-Jun DNA binding activity is mediated by a DNA repair enzyme. EMBO J. 1992 Sep;11(9):3323–3335. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05411.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida T., Shindo Y., Ohta K., Iba H. Identification of a small region of the v-fos gene product that is sufficient for transforming potential and growth-stimulating activity. Oncogene Res. 1989;5(2):79–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zambetti G. P., Olson D., Labow M., Levine A. J. A mutant p53 protein is required for maintenance of the transformed phenotype in cells transformed with p53 plus ras cDNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 1;89(9):3952–3956. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.9.3952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]