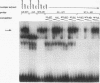
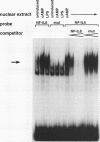
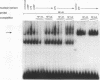
Abstract
Induction of interleukin-6 (IL-6) gene expression is mediated by numerous agents involving all major signal transduction pathways. We have compared the effects of prostaglandins and their second messenger cyclic AMP (cAMP) with the effect of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) on IL-6 gene expression. We demonstrate that secretion of IL-6 is induced by cAMP in murine monocytic PU5-1.8 cells, even though to a lesser extent than by LPS. Nevertheless, cAMP and prostaglandins of the E series in the presence of theophylline induce transcription of the IL-6 promoter more strongly than LPS, suggesting distinctive effects of cAMP and LPS on posttranscriptional events. Mutations within four regulatory elements, namely, the multiple response element (MRE), AP-1, NF-IL6, and NF-kappa B sites, significantly reduce, but do not completely abrogate, inducibility by cAMP and prostaglandin E1, whereas alterations of four additional sites have no effects. LPS-induced promoter activity, however, is almost completely abolished by mutations in the NF-kappa B site, suggesting that a single regulatory element is crucial for inducibility by LPS. Stimulation by cAMP is correlated with the binding of inducible factors to the AP-1, NF-IL6, and NF-kappa B elements, whereas factors binding to the MRE are constitutively expressed. Recombinant cAMP response element-binding protein binds to the MRE, indicating a potential role for this factor in the cAMP response. Our results suggest that cAMP and prostaglandins act through multiple, partially redundant regulatory elements to induce IL-6 expression in monocytic cells. Nuclear events that overlap partially with the LPS response but also exhibit distinctive features are involved.
Full text
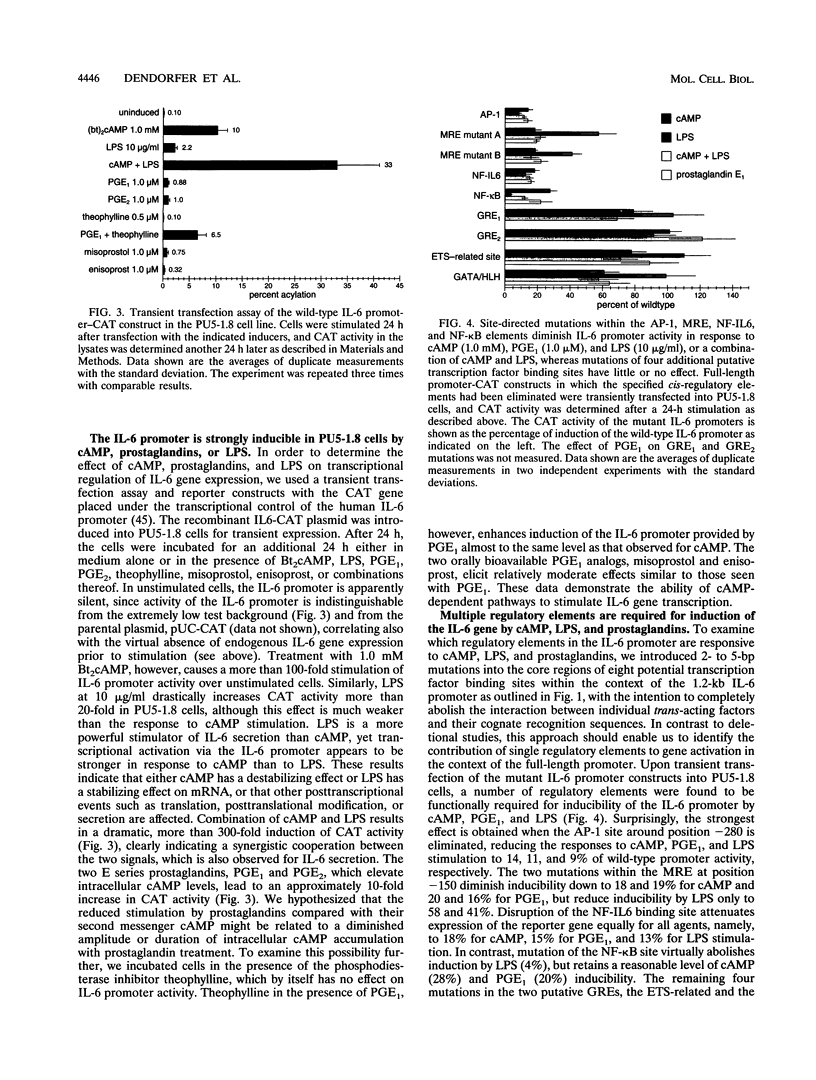
PDF

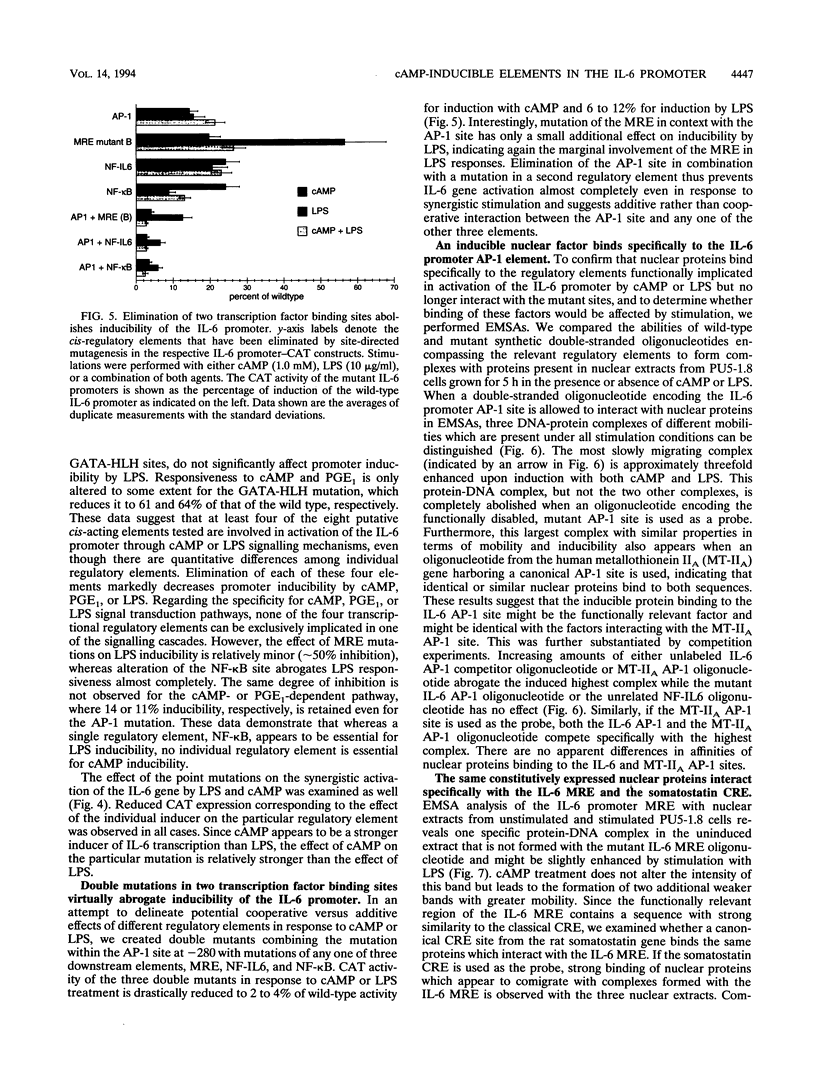
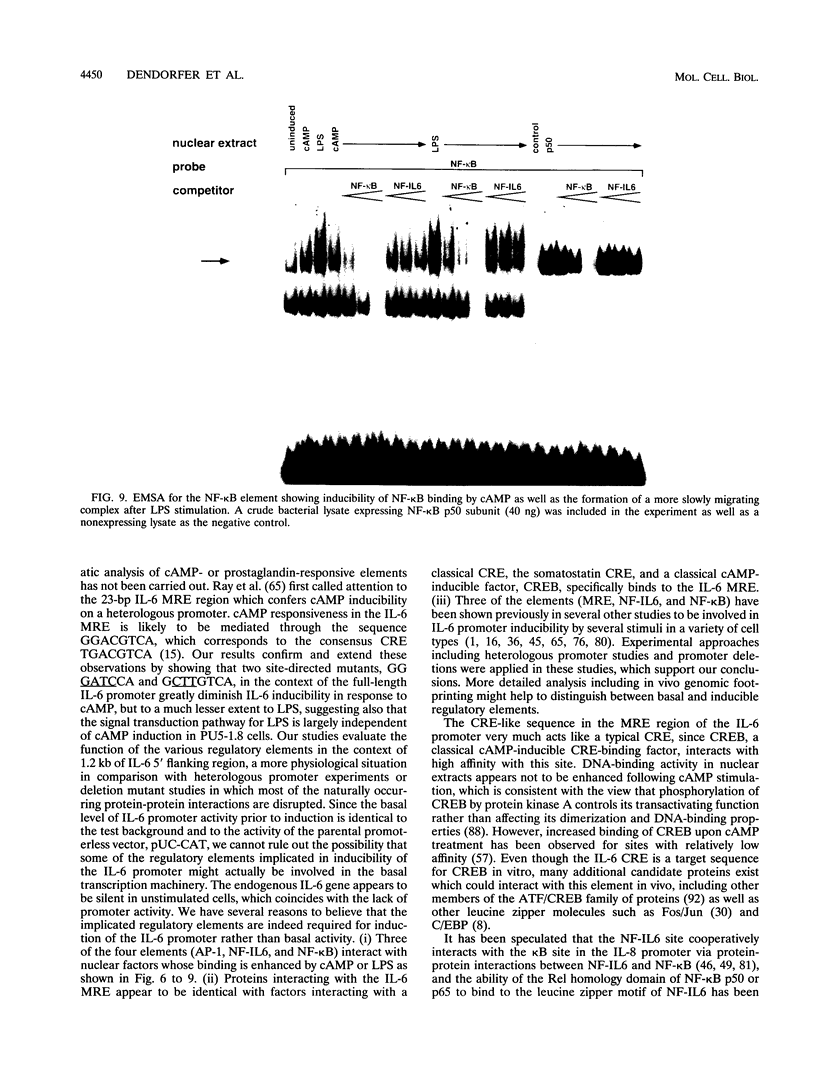




Images in this article
Selected References
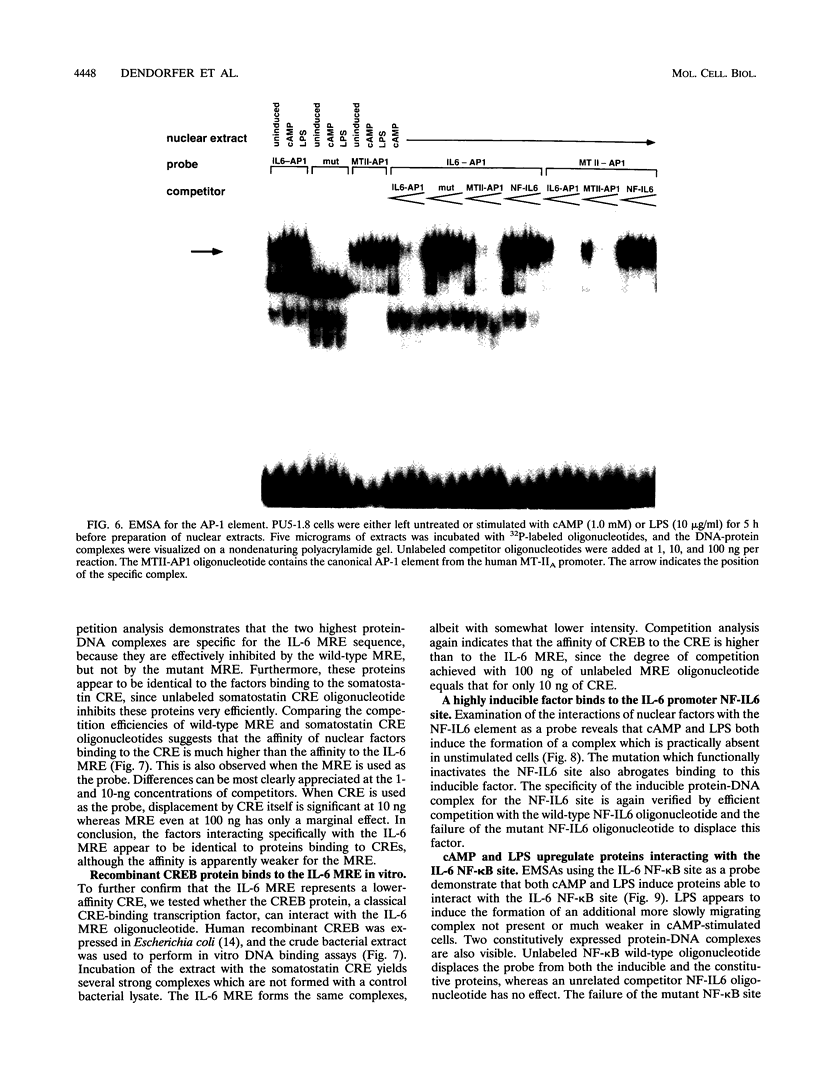
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
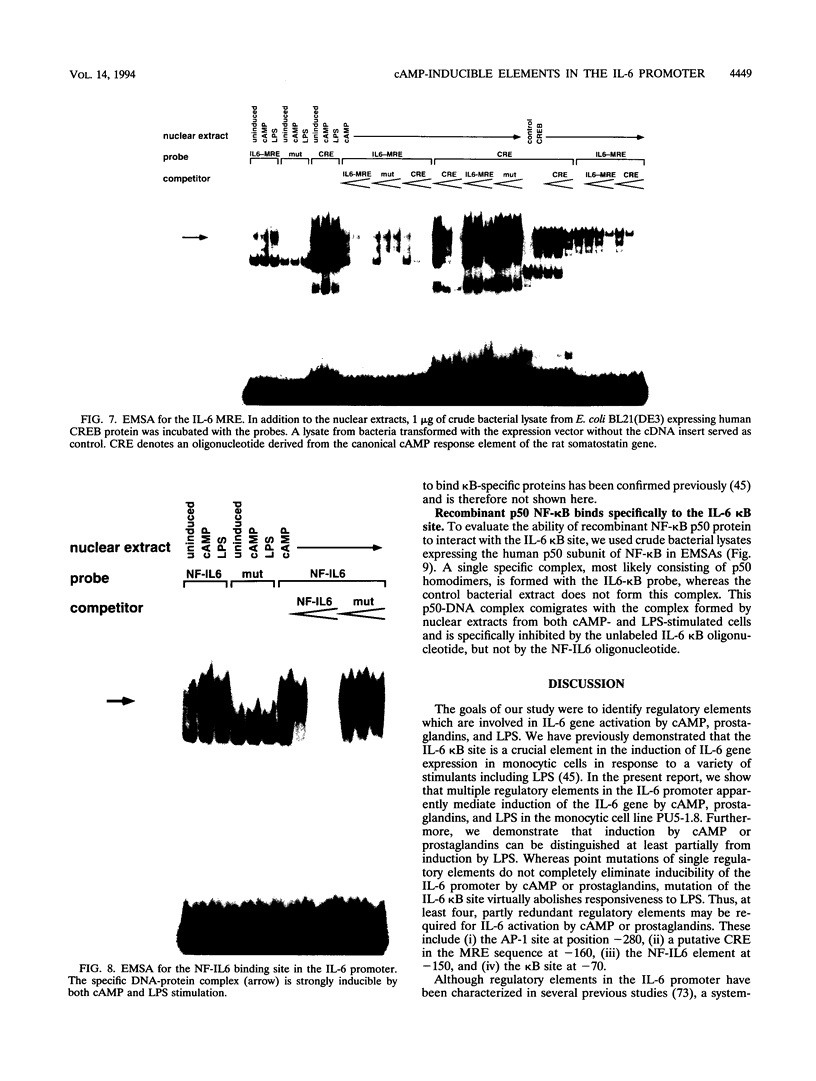
- Akira S., Isshiki H., Nakajima T., Kinoshita S., Nishio Y., Natsuka S., Kishimoto T. Regulation of expression of the interleukin 6 gene: structure and function of the transcription factor NF-IL6. Ciba Found Symp. 1992;167:47–67. doi: 10.1002/9780470514269.ch4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akira S., Isshiki H., Sugita T., Tanabe O., Kinoshita S., Nishio Y., Nakajima T., Hirano T., Kishimoto T. A nuclear factor for IL-6 expression (NF-IL6) is a member of a C/EBP family. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):1897–1906. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08316.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akira S., Kishimoto T. IL-6 and NF-IL6 in acute-phase response and viral infection. Immunol Rev. 1992 Jun;127:25–50. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1992.tb01407.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alberts A. S., Deng T., Lin A., Meinkoth J. L., Schönthal A., Mumby M. C., Karin M., Feramisco J. R. Protein phosphatase 2A potentiates activity of promoters containing AP-1-binding elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;13(4):2104–2112. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.4.2104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auwerx J., Sassone-Corsi P. AP-1 (Fos-Jun) regulation by IP-1: effect of signal transduction pathways and cell growth. Oncogene. 1992 Nov;7(11):2271–2280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auwerx J., Sassone-Corsi P. IP-1: a dominant inhibitor of Fos/Jun whose activity is modulated by phosphorylation. Cell. 1991 Mar 8;64(5):983–993. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90322-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailly S., Ferrua B., Fay M., Gougerot-Pocidalo M. A. Differential regulation of IL 6, IL 1 A, IL 1 beta and TNF alpha production in LPS-stimulated human monocytes: role of cyclic AMP. Cytokine. 1990 May;2(3):205–210. doi: 10.1016/1043-4666(90)90017-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakker O., Parker M. G. CAAT/enhancer binding protein is able to bind to ATF/CRE elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Mar 25;19(6):1213–1217. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.6.1213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer J., Ganter U., Geiger T., Jacobshagen U., Hirano T., Matsuda T., Kishimoto T., Andus T., Acs G., Gerok W. Regulation of interleukin-6 expression in cultured human blood monocytes and monocyte-derived macrophages. Blood. 1988 Oct;72(4):1134–1140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkowitz L. A., Riabowol K. T., Gilman M. Z. Multiple sequence elements of a single functional class are required for cyclic AMP responsiveness of the mouse c-fos promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;9(10):4272–4281. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.10.4272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betz M., Fox B. S. Prostaglandin E2 inhibits production of Th1 lymphokines but not of Th2 lymphokines. J Immunol. 1991 Jan 1;146(1):108–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B. Application of transcriptional and posttranscriptional reporter constructs to the analysis of tumor necrosis factor gene regulation. Am J Med Sci. 1992 Feb;303(2):129–133. doi: 10.1097/00000441-199202000-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Brown T. A CAT reporter construct allows ultrasensitive estimation of TNF synthesis, and suggests that the TNF gene has been silenced in non-macrophage cell lines. J Clin Invest. 1991 Apr;87(4):1336–1344. doi: 10.1172/JCI115137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanar M. A., Rutter W. J. Interaction cloning: identification of a helix-loop-helix zipper protein that interacts with c-Fos. Science. 1992 May 15;256(5059):1014–1018. doi: 10.1126/science.1589769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borrelli E., Montmayeur J. P., Foulkes N. S., Sassone-Corsi P. Signal transduction and gene control: the cAMP pathway. Crit Rev Oncog. 1992;3(4):321–338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brach M. A., Gruss H. J., Kaisho T., Asano Y., Hirano T., Herrmann F. Ionizing radiation induces expression of interleukin 6 by human fibroblasts involving activation of nuclear factor-kappa B. J Biol Chem. 1993 Apr 25;268(12):8466–8472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brach M. A., Herrmann F. Interleukin 6: presence and future. Int J Clin Lab Res. 1992;22(3):143–151. doi: 10.1007/BF02591414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farr A., Roman A. A pitfall of using a second plasmid to determine transfection efficiency. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Feb 25;20(4):920–920. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.4.920. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiorentino D. F., Zlotnik A., Mosmann T. R., Howard M., O'Garra A. IL-10 inhibits cytokine production by activated macrophages. J Immunol. 1991 Dec 1;147(11):3815–3822. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisch T. M., Prywes R., Simon M. C., Roeder R. G. Multiple sequence elements in the c-fos promoter mediate induction by cAMP. Genes Dev. 1989 Feb;3(2):198–211. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.2.198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman M. Z. The c-fos serum response element responds to protein kinase C-dependent and -independent signals but not to cyclic AMP. Genes Dev. 1988 Apr;2(4):394–402. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.4.394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman M. Z., Wilson R. N., Weinberg R. A. Multiple protein-binding sites in the 5'-flanking region regulate c-fos expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4305–4316. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez G. A., Montminy M. R. Cyclic AMP stimulates somatostatin gene transcription by phosphorylation of CREB at serine 133. Cell. 1989 Nov 17;59(4):675–680. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90013-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosschedl R., Baltimore D. Cell-type specificity of immunoglobulin gene expression is regulated by at least three DNA sequence elements. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):885–897. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80069-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hai T., Curran T. Cross-family dimerization of transcription factors Fos/Jun and ATF/CREB alters DNA binding specificity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3720–3724. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han J., Huez G., Beutler B. Interactive effects of the tumor necrosis factor promoter and 3'-untranslated regions. J Immunol. 1991 Mar 15;146(6):1843–1848. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haynes D. R., Whitehouse M. W., Vernon-Roberts B. The prostaglandin E1 analogue, misoprostol, regulates inflammatory cytokines and immune functions in vitro like the natural prostaglandins E1, E2 and E3. Immunology. 1992 Jun;76(2):251–257. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano T. Interleukin-6 and its relation to inflammation and disease. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1992 Jan;62(1 Pt 2):S60–S65. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(92)90042-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano T. The biology of interleukin-6. Chem Immunol. 1992;51:153–180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Karin M. The regulation of transcription by phosphorylation. Cell. 1992 Aug 7;70(3):375–387. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90162-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isshiki H., Akira S., Tanabe O., Nakajima T., Shimamoto T., Hirano T., Kishimoto T. Constitutive and interleukin-1 (IL-1)-inducible factors interact with the IL-1-responsive element in the IL-6 gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2757–2764. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janaswami P. M., Kalvakolanu D. V., Zhang Y., Sen G. C. Transcriptional repression of interleukin-6 gene by adenoviral E1A proteins. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 5;267(34):24886–24891. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kammer G. M. The adenylate cyclase-cAMP-protein kinase A pathway and regulation of the immune response. Immunol Today. 1988 Jul-Aug;9(7-8):222–229. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(88)91220-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto T., Akira S., Taga T. Interleukin-6 and its receptor: a paradigm for cytokines. Science. 1992 Oct 23;258(5082):593–597. doi: 10.1126/science.1411569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto T. Interleukin-6 and its receptor in autoimmunity. J Autoimmun. 1992 Apr;5 (Suppl A):123–132. doi: 10.1016/0896-8411(92)90027-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel S. L., Spengler M., May M. A., Spengler R., Larrick J., Remick D. Prostaglandin E2 regulates macrophage-derived tumor necrosis factor gene expression. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 15;263(11):5380–5384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeClair K. P., Blanar M. A., Sharp P. A. The p50 subunit of NF-kappa B associates with the NF-IL6 transcription factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 1;89(17):8145–8149. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.17.8145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee F. D. The role of interleukin-6 in development. Dev Biol. 1992 Jun;151(2):331–338. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(92)90173-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W., Haslinger A., Karin M., Tjian R. Activation of transcription by two factors that bind promoter and enhancer sequences of the human metallothionein gene and SV40. Nature. 1987 Jan 22;325(6102):368–372. doi: 10.1038/325368a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Libermann T. A., Baltimore D. Activation of interleukin-6 gene expression through the NF-kappa B transcription factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):2327–2334. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.2327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahé Y., Mukaida N., Kuno K., Akiyama M., Ikeda N., Matsushima K., Murakami S. Hepatitis B virus X protein transactivates human interleukin-8 gene through acting on nuclear factor kB and CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein-like cis-elements. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 25;266(21):13759–13763. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin C. A., Dorf M. E. Differential regulation of interleukin-6, macrophage inflammatory protein-1, and JE/MCP-1 cytokine expression in macrophage cell lines. Cell Immunol. 1991 Jun;135(1):245–258. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(91)90269-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masquilier D., Sassone-Corsi P. Transcriptional cross-talk: nuclear factors CREM and CREB bind to AP-1 sites and inhibit activation by Jun. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 5;267(31):22460–22466. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsusaka T., Fujikawa K., Nishio Y., Mukaida N., Matsushima K., Kishimoto T., Akira S. Transcription factors NF-IL6 and NF-kappa B synergistically activate transcription of the inflammatory cytokines, interleukin 6 and interleukin 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Nov 1;90(21):10193–10197. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.21.10193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehmet H., Morris C., Rozengurt E. Multiple synergistic signal transduction pathways regulate c-fos expression in Swiss 3T3 cells: the role of cyclic AMP. Cell Growth Differ. 1990 Jun;1(6):293–298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metz R., Ziff E. cAMP stimulates the C/EBP-related transcription factor rNFIL-6 to trans-locate to the nucleus and induce c-fos transcription. Genes Dev. 1991 Oct;5(10):1754–1766. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.10.1754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minty A., Chalon P., Derocq J. M., Dumont X., Guillemot J. C., Kaghad M., Labit C., Leplatois P., Liauzun P., Miloux B. Interleukin-13 is a new human lymphokine regulating inflammatory and immune responses. Nature. 1993 Mar 18;362(6417):248–250. doi: 10.1038/362248a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montminy M. R., Sevarino K. A., Wagner J. A., Mandel G., Goodman R. H. Identification of a cyclic-AMP-responsive element within the rat somatostatin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):6682–6686. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.6682. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura T., Datta R., Sherman M. L., Kufe D. Regulation of c-jun gene expression by cAMP in HL-60 myeloid leukemia cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 15;265(35):22011–22015. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nibbering P. H., van Furth R. Quantitative immunocytochemical characterization of four murine macrophage-like cell lines. Immunobiology. 1988 Mar;176(4-5):432–439. doi: 10.1016/S0171-2985(88)80024-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols M., Weih F., Schmid W., DeVack C., Kowenz-Leutz E., Luckow B., Boshart M., Schütz G. Phosphorylation of CREB affects its binding to high and low affinity sites: implications for cAMP induced gene transcription. EMBO J. 1992 Sep;11(9):3337–3346. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05412.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novak T. J., Rothenberg E. V. cAMP inhibits induction of interleukin 2 but not of interleukin 4 in T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(23):9353–9357. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.23.9353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orkin S. H. GATA-binding transcription factors in hematopoietic cells. Blood. 1992 Aug 1;80(3):575–581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papavassiliou A. G., Treier M., Chavrier C., Bohmann D. Targeted degradation of c-Fos, but not v-Fos, by a phosphorylation-dependent signal on c-Jun. Science. 1992 Dec 18;258(5090):1941–1944. doi: 10.1126/science.1470918. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul-Eugene N., Kolb J. P., Abadie A., Gordon J., Delespesse G., Sarfati M., Mencia-Huerta J. M., Braquet P., Dugas B. Ligation of CD23 triggers cAMP generation and release of inflammatory mediators in human monocytes. J Immunol. 1992 Nov 1;149(9):3066–3071. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phipps R. P., Stein S. H., Roper R. L. A new view of prostaglandin E regulation of the immune response. Immunol Today. 1991 Oct;12(10):349–352. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(91)90064-Z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralph P., Moore M. A., Nilsson K. Lysozyme synthesis by established human and murine histiocytic lymphoma cell lines. J Exp Med. 1976 Jun 1;143(6):1528–1533. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.6.1528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray A., LaForge K. S., Sehgal P. B. On the mechanism for efficient repression of the interleukin-6 promoter by glucocorticoids: enhancer, TATA box, and RNA start site (Inr motif) occlusion. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;10(11):5736–5746. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.11.5736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray A., Sassone-Corsi P., Sehgal P. B. A multiple cytokine- and second messenger-responsive element in the enhancer of the human interleukin-6 gene: similarities with c-fos gene regulation. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;9(12):5537–5547. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.12.5537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray A., Tatter S. B., May L. T., Sehgal P. B. Activation of the human "beta 2-interferon/hepatocyte-stimulating factor/interleukin 6" promoter by cytokines, viruses, and second messenger agonists. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6701–6705. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renz H., Gong J. H., Schmidt A., Nain M., Gemsa D. Release of tumor necrosis factor-alpha from macrophages. Enhancement and suppression are dose-dependently regulated by prostaglandin E2 and cyclic nucleotides. J Immunol. 1988 Oct 1;141(7):2388–2393. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roux P., Blanchard J. M., Fernandez A., Lamb N., Jeanteur P., Piechaczyk M. Nuclear localization of c-Fos, but not v-Fos proteins, is controlled by extracellular signals. Cell. 1990 Oct 19;63(2):341–351. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90167-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santhanam U., Ray A., Sehgal P. B. Repression of the interleukin 6 gene promoter by p53 and the retinoblastoma susceptibility gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7605–7609. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schandené L., Vandenbussche P., Crusiaux A., Alègre M. L., Abramowicz D., Dupont E., Content J., Goldman M. Differential effects of pentoxifylline on the production of tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) and interleukin-6 (IL-6) by monocytes and T cells. Immunology. 1992 May;76(1):30–34. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seed B., Sheen J. Y. A simple phase-extraction assay for chloramphenicol acyltransferase activity. Gene. 1988 Jul 30;67(2):271–277. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90403-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sehgal P. B. Interleukin-6: a regulator of plasma protein gene expression in hepatic and non-hepatic tissues. Mol Biol Med. 1990 Apr;7(2):117–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sehgal P. B. Regulation of IL6 gene expression. Res Immunol. 1992 Sep;143(7):724–734. doi: 10.1016/0923-2494(92)80011-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sehgal P. B., Walther Z., Tamm I. Rapid enhancement of beta 2-interferon/B-cell differentiation factor BSF-2 gene expression in human fibroblasts by diacylglycerols and the calcium ionophore A23187. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3663–3667. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seth A., Ascione R., Fisher R. J., Mavrothalassitis G. J., Bhat N. K., Papas T. S. The ets gene family. Cell Growth Differ. 1992 May;3(5):327–334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu H., Mitomo K., Watanabe T., Okamoto S., Yamamoto K. Involvement of a NF-kappa B-like transcription factor in the activation of the interleukin-6 gene by inflammatory lymphokines. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;10(2):561–568. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.2.561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirai A., Holmes K., Klinman D. Detection and quantitation of cells secreting IL-6 under physiologic conditions in BALB/c mice. J Immunol. 1993 Feb 1;150(3):793–799. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirakawa F., Mizel S. B. In vitro activation and nuclear translocation of NF-kappa B catalyzed by cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase and protein kinase C. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;9(6):2424–2430. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.6.2424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snijdewint F. G., Kaliński P., Wierenga E. A., Bos J. D., Kapsenberg M. L. Prostaglandin E2 differentially modulates cytokine secretion profiles of human T helper lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1993 Jun 15;150(12):5321–5329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparacio S. M., Zhang Y., Vilcek J., Benveniste E. N. Cytokine regulation of interleukin-6 gene expression in astrocytes involves activation of an NF-kappa B-like nuclear protein. J Neuroimmunol. 1992 Aug;39(3):231–242. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(92)90257-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein B., Baldwin A. S., Jr Distinct mechanisms for regulation of the interleukin-8 gene involve synergism and cooperativity between C/EBP and NF-kappa B. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Nov;13(11):7191–7198. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.11.7191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart G. S., Dovey S., O'Rourke D. M. A rapid method for site directed mutagenesis of plasmid DNA. Biotechniques. 1988 Jun;6(6):511-2, 517-8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sung S. S., Walters J. A. Increased cyclic AMP levels enhance IL-1 alpha and IL-1 beta mRNA expression and protein production in human myelomonocytic cell lines and monocytes. J Clin Invest. 1991 Dec;88(6):1915–1923. doi: 10.1172/JCI115515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanabe O., Akira S., Kamiya T., Wong G. G., Hirano T., Kishimoto T. Genomic structure of the murine IL-6 gene. High degree conservation of potential regulatory sequences between mouse and human. J Immunol. 1988 Dec 1;141(11):3875–3881. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Snick J. Interleukin-6: an overview. Annu Rev Immunol. 1990;8:253–278. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.08.040190.001345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vellenga E., van der Vinne B., De Wolf J. T., Halie M. R. Simultaneous expression and regulation of G-CSF and IL-6 mRNA in adherent human monocytes and fibroblasts. Br J Haematol. 1991 May;78(1):14–18. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1991.tb04375.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K. K., Gonzalez G. A., Biggs W. H., 3rd, Montminy M. R. Phosphorylation-induced binding and transcriptional efficacy of nuclear factor CREB. Nature. 1988 Aug 11;334(6182):494–498. doi: 10.1038/334494a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y. H., Lin J. X., Vilcek J. Interleukin-6 induction by tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-1 in human fibroblasts involves activation of a nuclear factor binding to a kappa B-like sequence. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;10(7):3818–3823. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.7.3818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y. H., Lin J. X., Yip Y. K., Vilcek J. Enhancement of cAMP levels and of protein kinase activity by tumor necrosis factor and interleukin 1 in human fibroblasts: role in the induction of interleukin 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6802–6805. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y., Lin J. X., Vilcek J. Synthesis of interleukin 6 (interferon-beta 2/B cell stimulatory factor 2) in human fibroblasts is triggered by an increase in intracellular cyclic AMP. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 5;263(13):6177–6182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziff E. B. Transcription factors: a new family gathers at the cAMP response site. Trends Genet. 1990 Mar;6(3):69–72. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90081-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Groot R. P., Sassone-Corsi P. Activation of Jun/AP-1 by protein kinase A. Oncogene. 1992 Nov;7(11):2281–2286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Waal Malefyt R., Abrams J., Bennett B., Figdor C. G., de Vries J. E. Interleukin 10(IL-10) inhibits cytokine synthesis by human monocytes: an autoregulatory role of IL-10 produced by monocytes. J Exp Med. 1991 Nov 1;174(5):1209–1220. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.5.1209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]