Abstract
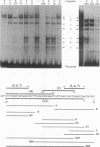
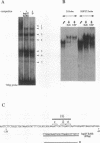
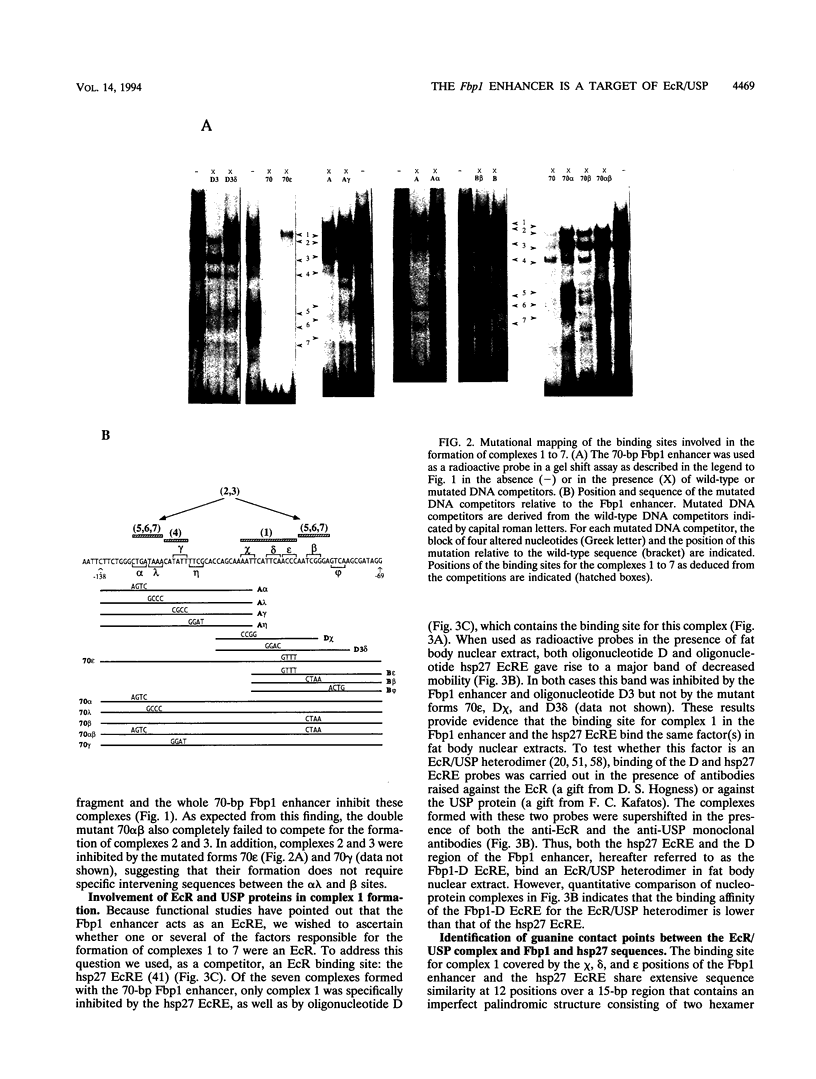
The transcription of the Drosophila melanogaster Fbp1 gene is induced by the steroid hormone 20-hydroxyecdysone and restricted to the late-third-instar fat body tissue. In a previous study we showed that the -68 to -138 region relative to the transcription start site acts as an ecdysone-dependent third-instar fat body-specific enhancer in a transgenic assay. Here we report that seven nucleoprotein complexes are formed in vitro on this enhancer when a nuclear extract from late-third-instar fat body is used in a gel shift assay. Accurate mapping of the binding sites of the complexes revealed a remarkably symmetrical organization. Using specific antibodies, one of the complexes was identified as a heterodimer consisting of the ecdysone receptor (EcR) and Ultraspiracle (USP) proteins. The binding site of the heterodimer as defined by mutagenesis and methylation interference experiments bears strong sequence similarity to the canonical hsp27 ecdysone response element, including an imperfect palindromic structure. The two elements diverge at three positions in both half-sites, indicating that the structure of an active EcR/USP binding site allows considerable sequence variations. In vivo footprinting experiments using ligation-mediated PCR and wild-type or ecdysteroid-deficient larvae show that occupancy of the Fbp1 EcR/USP binding site and adjacent region is dependent on a high concentration of ecdysteroids. These results provide strong evidence for a direct role of the EcR/USP heterodimer in driving gene expression in response to changes of the ecdysteroid titer during Drosophila larval development.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andres A. J., Fletcher J. C., Karim F. D., Thummel C. S. Molecular analysis of the initiation of insect metamorphosis: a comparative study of Drosophila ecdysteroid-regulated transcription. Dev Biol. 1993 Dec;160(2):388–404. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1993.1315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andres A. J., Thummel C. S. Hormones, puffs and flies: the molecular control of metamorphosis by ecdysone. Trends Genet. 1992 Apr;8(4):132–138. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(92)90371-A. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antoniewski C., Laval M., Lepesant J. A. Structural features critical to the activity of an ecdysone receptor binding site. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 1993 Jan;23(1):105–114. doi: 10.1016/0965-1748(93)90088-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashburner M., Chihara C., Meltzer P., Richards G. Temporal control of puffing activity in polytene chromosomes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1974;38:655–662. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.038.01.070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker P. B., Gloss B., Schmid W., Strähle U., Schütz G. In vivo protein-DNA interactions in a glucocorticoid response element require the presence of the hormone. Nature. 1986 Dec 18;324(6098):686–688. doi: 10.1038/324686a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burtis K. C., Thummel C. S., Jones C. W., Karim F. D., Hogness D. S. The Drosophila 74EF early puff contains E74, a complex ecdysone-inducible gene that encodes two ets-related proteins. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):85–99. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90217-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherbas L., Lee K., Cherbas P. Identification of ecdysone response elements by analysis of the Drosophila Eip28/29 gene. Genes Dev. 1991 Jan;5(1):120–131. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.1.120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christianson A. M., King D. L., Hatzivassiliou E., Casas J. E., Hallenbeck P. L., Nikodem V. M., Mitsialis S. A., Kafatos F. C. DNA binding and heteromerization of the Drosophila transcription factor chorion factor 1/ultraspiracle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 1;89(23):11503–11507. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.23.11503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobens L., Rudolph K., Berger E. M. Ecdysterone regulatory elements function as both transcriptional activators and repressors. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):1846–1853. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.1846. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garen A., Kauvar L., Lepesant J. A. Roles of ecdysone in Drosophila development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):5099–5103. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.5099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves B. J., Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. Homologous recognition of a promoter domain common to the MSV LTR and the HSV tk gene. Cell. 1986 Feb 28;44(4):565–576. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90266-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross-Bellard M., Oudet P., Chambon P. Isolation of high-molecular-weight DNA from mammalian cells. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Jul 2;36(1):32–38. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02881.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henrich V. C., Sliter T. J., Lubahn D. B., MacIntyre A., Gilbert L. I. A steroid/thyroid hormone receptor superfamily member in Drosophila melanogaster that shares extensive sequence similarity with a mammalian homologue. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jul 25;18(14):4143–4148. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.14.4143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huet F., Ruiz C., Richards G. Puffs and PCR: the in vivo dynamics of early gene expression during ecdysone responses in Drosophila. Development. 1993 Jun;118(2):613–627. doi: 10.1242/dev.118.2.613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurban P., Thummel C. S. Isolation and characterization of fifteen ecdysone-inducible Drosophila genes reveal unexpected complexities in ecdysone regulation. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Nov;13(11):7101–7111. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.11.7101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Härd T., Kellenbach E., Boelens R., Maler B. A., Dahlman K., Freedman L. P., Carlstedt-Duke J., Yamamoto K. R., Gustafsson J. A., Kaptein R. Solution structure of the glucocorticoid receptor DNA-binding domain. Science. 1990 Jul 13;249(4965):157–160. doi: 10.1126/science.2115209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. F., Landschulz W. H., Graves B. J., McKnight S. L. Identification of a rat liver nuclear protein that binds to the enhancer core element of three animal viruses. Genes Dev. 1987 Apr;1(2):133–146. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.2.133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karim F. D., Thummel C. S. Temporal coordination of regulatory gene expression by the steroid hormone ecdysone. EMBO J. 1992 Nov;11(11):4083–4093. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05501.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koelle M. R., Talbot W. S., Segraves W. A., Bender M. T., Cherbas P., Hogness D. S. The Drosophila EcR gene encodes an ecdysone receptor, a new member of the steroid receptor superfamily. Cell. 1991 Oct 4;67(1):59–77. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90572-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar V., Chambon P. The estrogen receptor binds tightly to its responsive element as a ligand-induced homodimer. Cell. 1988 Oct 7;55(1):145–156. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90017-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laval M., Pourrain F., Deutsch J., Lepesant J. A. In vivo functional characterization of an ecdysone response enhancer in the proximal upstream region of the Fbp1 gene of D. melanogaster. Mech Dev. 1993 Dec;44(2-3):123–138. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(93)90062-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lepesant J. A., Kejzlarova-Lepesant J., Garen A. Ecdysone-inducible functions of larval fat bodies in Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5570–5574. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luisi B. F., Xu W. X., Otwinowski Z., Freedman L. P., Yamamoto K. R., Sigler P. B. Crystallographic analysis of the interaction of the glucocorticoid receptor with DNA. Nature. 1991 Aug 8;352(6335):497–505. doi: 10.1038/352497a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luo Y., Amin J., Voellmy R. Ecdysterone receptor is a sequence-specific transcription factor involved in the developmental regulation of heat shock genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;11(7):3660–3675. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.7.3660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez E., Givel F., Wahli W. A common ancestor DNA motif for invertebrate and vertebrate hormone response elements. EMBO J. 1991 Feb;10(2):263–268. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07946.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maschat F., Dubertret M. L., Thérond P., Claverie J. M., Lepesant J. A. Structure of the ecdysone-inducible P1 gene of Drosophila melanogaster. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jul 20;214(2):359–372. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90186-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller P. R., Wold B. In vivo footprinting of a muscle specific enhancer by ligation mediated PCR. Science. 1989 Nov 10;246(4931):780–786. doi: 10.1126/science.2814500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Natzle J. E. Temporal regulation of Drosophila imaginal disc morphogenesis: a hierarchy of primary and secondary 20-hydroxyecdysone-responsive loci. Dev Biol. 1993 Feb;155(2):516–532. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1993.1049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oro A. E., McKeown M., Evans R. M. Relationship between the product of the Drosophila ultraspiracle locus and the vertebrate retinoid X receptor. Nature. 1990 Sep 20;347(6290):298–301. doi: 10.1038/347298a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oyhar A., Strangmann-Diekmann M., Kiltz H. H., Pongs O. Characterization of a specific ecdysteroid receptor-DNA complex reveals common properties for invertebrate and vertebrate hormone-receptor/DNA interactions. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Sep 1;200(2):329–335. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb16189.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oźyhar A., Pongs O. Mutational analysis of the interaction between ecdysteroid receptor and its response element. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 1993 Aug;46(2):135–145. doi: 10.1016/0960-0760(93)90288-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paco-Larson M. L., Nakanishi Y., Levine M., Garen A. Histochemical analysis of the ecdysterone-regulated expression of the Drosophila genes P1 and LSP-2. Dev Genet. 1986;7(4):197–203. doi: 10.1002/dvg.1020070405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riddihough G., Pelham H. R. Activation of the Drosophila hsp27 promoter by heat shock and by ecdysone involves independent and remote regulatory sequences. EMBO J. 1986 Jul;5(7):1653–1658. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04408.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riddihough G., Pelham H. R. An ecdysone response element in the Drosophila hsp27 promoter. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 1;6(12):3729–3734. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02707.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigaud G., Roux J., Pictet R., Grange T. In vivo footprinting of rat TAT gene: dynamic interplay between the glucocorticoid receptor and a liver-specific factor. Cell. 1991 Nov 29;67(5):977–986. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90370-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakonju S., Brown D. D. Contact points between a positive transcription factor and the Xenopus 5S RNA gene. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(2 Pt 1):395–405. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90133-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleif R. DNA looping. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:199–223. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.001215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwabe J. W., Neuhaus D., Rhodes D. Solution structure of the DNA-binding domain of the oestrogen receptor. Nature. 1990 Nov 29;348(6300):458–461. doi: 10.1038/348458a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segraves W. A., Hogness D. S. The E75 ecdysone-inducible gene responsible for the 75B early puff in Drosophila encodes two new members of the steroid receptor superfamily. Genes Dev. 1990 Feb;4(2):204–219. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.2.204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shea M. J., King D. L., Conboy M. J., Mariani B. D., Kafatos F. C. Proteins that bind to Drosophila chorion cis-regulatory elements: a new C2H2 zinc finger protein and a C2C2 steroid receptor-like component. Genes Dev. 1990 Jul;4(7):1128–1140. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.7.1128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone B. L., Thummel C. S. The Drosophila 78C early late puff contains E78, an ecdysone-inducible gene that encodes a novel member of the nuclear hormone receptor superfamily. Cell. 1993 Oct 22;75(2):307–320. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)80072-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talbot W. S., Swyryd E. A., Hogness D. S. Drosophila tissues with different metamorphic responses to ecdysone express different ecdysone receptor isoforms. Cell. 1993 Jul 2;73(7):1323–1337. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90359-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas H. E., Stunnenberg H. G., Stewart A. F. Heterodimerization of the Drosophila ecdysone receptor with retinoid X receptor and ultraspiracle. Nature. 1993 Apr 1;362(6419):471–475. doi: 10.1038/362471a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thummel C. S., Burtis K. C., Hogness D. S. Spatial and temporal patterns of E74 transcription during Drosophila development. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):101–111. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90218-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thummel C. S. Puffs and gene regulation--molecular insights into the Drosophila ecdysone regulatory hierarchy. Bioessays. 1990 Dec;12(12):561–568. doi: 10.1002/bies.950121202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai S. Y., Carlstedt-Duke J., Weigel N. L., Dahlman K., Gustafsson J. A., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Molecular interactions of steroid hormone receptor with its enhancer element: evidence for receptor dimer formation. Cell. 1988 Oct 21;55(2):361–369. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90059-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urness L. D., Thummel C. S. Molecular interactions within the ecdysone regulatory hierarchy: DNA binding properties of the Drosophila ecdysone-inducible E74A protein. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):47–61. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90287-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrange O., Eriksson P., Perlmann T. The purified activated glucocorticoid receptor is a homodimer. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 25;264(9):5253–5259. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yao T. P., Segraves W. A., Oro A. E., McKeown M., Evans R. M. Drosophila ultraspiracle modulates ecdysone receptor function via heterodimer formation. Cell. 1992 Oct 2;71(1):63–72. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90266-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]