Abstract
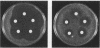
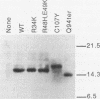
Heterotrimeric guanine nucleotide-binding proteins (G proteins) consisting of alpha, beta, and gamma subunits mediate signalling between cell surface receptors and intracellular effectors in eukaryotic cells. To define signalling functions of G gamma subunits (STE18 gene product) involved in pheromone response and mating in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae, we isolated and characterized dominant-negative STE18 alleles. We obtained dominant-negative mutations that disrupt C-terminal sequences required for prenylation of G gamma precursors (CAAX box) and that affect residues in the N-terminal half of Ste18p. Overexpression of mutant G gamma subunits in wild-type cells blocked signal transduction; this effect was suppressed upon overexpression of G beta subunits. Mutant G gamma subunits may therefore sequester G beta subunits into nonproductive G beta gamma dimers. Because mutant G gamma subunits blocked the constitutive signal resulting from disruption of the G alpha subunit gene (GPA1), they are defective in functions required for downstream signalling. Ste18p bearing a C107Y substitution in the CAAX box displayed reduced electrophoretic mobility, consistent with a prenylation defect. G gamma subunits carrying N-terminal substitutions had normal electrophoretic mobilities, suggesting that these proteins were prenylated. G gamma subunits bearing substitutions in their N-terminal region or C-terminal CAAX box (C107Y) supported receptor-G protein coupling in vitro, whereas C-terminal truncations caused partial defects in receptor coupling.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birnbaumer L. Receptor-to-effector signaling through G proteins: roles for beta gamma dimers as well as alpha subunits. Cell. 1992 Dec 24;71(7):1069–1072. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(05)80056-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blank J. L., Brattain K. A., Exton J. H. Activation of cytosolic phosphoinositide phospholipase C by G-protein beta gamma subunits. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 15;267(32):23069–23075. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blinder D., Bouvier S., Jenness D. D. Constitutive mutants in the yeast pheromone response: ordered function of the gene products. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):479–486. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90250-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumer K. J., Reneke J. E., Thorner J. The STE2 gene product is the ligand-binding component of the alpha-factor receptor of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 5;263(22):10836–10842. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumer K. J., Thorner J. Beta and gamma subunits of a yeast guanine nucleotide-binding protein are not essential for membrane association of the alpha subunit but are required for receptor coupling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(11):4363–4367. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.11.4363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer J. L., Waldo G. L., Harden T. K. Beta gamma-subunit activation of G-protein-regulated phospholipase C. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 15;267(35):25451–25456. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camps M., Carozzi A., Schnabel P., Scheer A., Parker P. J., Gierschik P. Isozyme-selective stimulation of phospholipase C-beta 2 by G protein beta gamma-subunits. Nature. 1992 Dec 17;360(6405):684–686. doi: 10.1038/360684a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke S. Protein isoprenylation and methylation at carboxyl-terminal cysteine residues. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:355–386. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.002035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole G. M., Stone D. E., Reed S. I. Stoichiometry of G protein subunits affects the Saccharomyces cerevisiae mating pheromone signal transduction pathway. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;10(2):510–517. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.2.510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietzel C., Kurjan J. The yeast SCG1 gene: a G alpha-like protein implicated in the a- and alpha-factor response pathway. Cell. 1987 Sep 25;50(7):1001–1010. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90166-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fawzi A. B., Fay D. S., Murphy E. A., Tamir H., Erdos J. J., Northup J. K. Rhodopsin and the retinal G-protein distinguish among G-protein beta gamma subunit forms. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 5;266(19):12194–12200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Federman A. D., Conklin B. R., Schrader K. A., Reed R. R., Bourne H. R. Hormonal stimulation of adenylyl cyclase through Gi-protein beta gamma subunits. Nature. 1992 Mar 12;356(6365):159–161. doi: 10.1038/356159a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finegold A. A., Schafer W. R., Rine J., Whiteway M., Tamanoi F. Common modifications of trimeric G proteins and ras protein: involvement of polyisoprenylation. Science. 1990 Jul 13;249(4965):165–169. doi: 10.1126/science.1695391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukada Y., Takao T., Ohguro H., Yoshizawa T., Akino T., Shimonishi Y. Farnesylated gamma-subunit of photoreceptor G protein indispensable for GTP-binding. Nature. 1990 Aug 16;346(6285):658–660. doi: 10.1038/346658a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins: transducers of receptor-generated signals. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:615–649. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herskowitz I. Functional inactivation of genes by dominant negative mutations. Nature. 1987 Sep 17;329(6136):219–222. doi: 10.1038/329219a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iñiguez-Lluhi J. A., Simon M. I., Robishaw J. D., Gilman A. G. G protein beta gamma subunits synthesized in Sf9 cells. Functional characterization and the significance of prenylation of gamma. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 15;267(32):23409–23417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz A., Wu D., Simon M. I. Subunits beta gamma of heterotrimeric G protein activate beta 2 isoform of phospholipase C. Nature. 1992 Dec 17;360(6405):686–689. doi: 10.1038/360686a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleuss C., Hescheler J., Ewel C., Rosenthal W., Schultz G., Wittig B. Assignment of G-protein subtypes to specific receptors inducing inhibition of calcium currents. Nature. 1991 Sep 5;353(6339):43–48. doi: 10.1038/353043a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleuss C., Scherübl H., Hescheler J., Schultz G., Wittig B. Selectivity in signal transduction determined by gamma subunits of heterotrimeric G proteins. Science. 1993 Feb 5;259(5096):832–834. doi: 10.1126/science.8094261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurjan J. Pheromone response in yeast. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:1097–1129. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.005313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai R. K., Perez-Sala D., Cañada F. J., Rando R. R. The gamma subunit of transducin is farnesylated. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7673–7677. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leberer E., Dignard D., Harcus D., Thomas D. Y., Whiteway M. The protein kinase homologue Ste20p is required to link the yeast pheromone response G-protein beta gamma subunits to downstream signalling components. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(13):4815–4824. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05587.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leberer E., Dignard D., Hougan L., Thomas D. Y., Whiteway M. Dominant-negative mutants of a yeast G-protein beta subunit identify two functional regions involved in pheromone signalling. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(13):4805–4813. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05586.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCaffrey G., Clay F. J., Kelsay K., Sprague G. F., Jr Identification and regulation of a gene required for cell fusion during mating of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2680–2690. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyajima I., Nakafuku M., Nakayama N., Brenner C., Miyajima A., Kaibuchi K., Arai K., Kaziro Y., Matsumoto K. GPA1, a haploid-specific essential gene, encodes a yeast homolog of mammalian G protein which may be involved in mating factor signal transduction. Cell. 1987 Sep 25;50(7):1011–1019. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90167-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muntz K. H., Sternweis P. C., Gilman A. G., Mumby S. M. Influence of gamma subunit prenylation on association of guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory proteins with membranes. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Jan;3(1):49–61. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.1.49. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomoto S., Nakayama N., Arai K., Matsumoto K. Regulation of the yeast pheromone response pathway by G protein subunits. EMBO J. 1990 Mar;9(3):691–696. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08161.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohguro H., Fukada Y., Takao T., Shimonishi Y., Yoshizawa T., Akino T. Carboxyl methylation and farnesylation of transducin gamma-subunit synergistically enhance its coupling with metarhodopsin II. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(12):3669–3674. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04934.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philippsen P., Stotz A., Scherf C. DNA of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:169–182. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94014-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein R. Targeting, disruption, replacement, and allele rescue: integrative DNA transformation in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:281–301. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94022-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schafer W. R., Rine J. Protein prenylation: genes, enzymes, targets, and functions. Annu Rev Genet. 1992;26:209–237. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.26.120192.001233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman F. Getting started with yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:3–21. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94004-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman F., Hicks J. Micromanipulation and dissection of asci. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:21–37. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94005-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikorski R. S., Boeke J. D. In vitro mutagenesis and plasmid shuffling: from cloned gene to mutant yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:302–318. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94023-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M. I., Strathmann M. P., Gautam N. Diversity of G proteins in signal transduction. Science. 1991 May 10;252(5007):802–808. doi: 10.1126/science.1902986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonds W. F., Butrynski J. E., Gautam N., Unson C. G., Spiegel A. M. G-protein beta gamma dimers. Membrane targeting requires subunit coexpression and intact gamma C-A-A-X domain. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 25;266(9):5363–5366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonds W. F., Manji H. K., Garritsen A., Lupas A. N. G proteins and beta ARK: a new twist for the coiled coil. Trends Biochem Sci. 1993 Sep;18(9):315–317. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(93)90062-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprague G. F., Jr Assay of yeast mating reaction. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:77–93. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94008-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang W. J., Gilman A. G. Type-specific regulation of adenylyl cyclase by G protein beta gamma subunits. Science. 1991 Dec 6;254(5037):1500–1503. doi: 10.1126/science.1962211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taussig R., Quarmby L. M., Gilman A. G. Regulation of purified type I and type II adenylylcyclases by G protein beta gamma subunits. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 5;268(1):9–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas B. J., Rothstein R. Elevated recombination rates in transcriptionally active DNA. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):619–630. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90584-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trueheart J., Boeke J. D., Fink G. R. Two genes required for cell fusion during yeast conjugation: evidence for a pheromone-induced surface protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;7(7):2316–2328. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.7.2316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vernet T., Dignard D., Thomas D. Y. A family of yeast expression vectors containing the phage f1 intergenic region. Gene. 1987;52(2-3):225–233. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90049-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whiteway M., Dignard D., Thomas D. Y. Mutagenesis of Ste18, a putative G gamma subunit in the Saccharomyces cerevisiae pheromone response pathway. Biochem Cell Biol. 1992 Oct-Nov;70(10-11):1230–1237. doi: 10.1139/o92-169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whiteway M., Hougan L., Dignard D., Thomas D. Y., Bell L., Saari G. C., Grant F. J., O'Hara P., MacKay V. L. The STE4 and STE18 genes of yeast encode potential beta and gamma subunits of the mating factor receptor-coupled G protein. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):467–477. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90249-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whiteway M., Hougan L., Thomas D. Y. Overexpression of the STE4 gene leads to mating response in haploid Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jan;10(1):217–222. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.1.217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wildman D. E., Tamir H., Leberer E., Northup J. K., Dennis M. Prenyl modification of guanine nucleotide regulatory protein gamma 2 subunits is not required for interaction with the transducin alpha subunit or rhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Feb 1;90(3):794–798. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.3.794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]