Abstract
In the crystal structure of the title compound, C8F16I2·C14H8N2, the molecules form infinite chains parallel to [2-11] through two symmetry-independent C—I⋯N halogen bonds (XBs). As commonly found, the perfluoroalkyl molecules segregate from the hydrocarbon ones, forming a layered structure. Apart from the XBs, the only contact below the sum of van der Waals radii is a weak H⋯F contact. The topology of the network is a nice example of the paradigm of the expansion of ditopic starting modules; the XB leads to the construction of infinite supramolecular chains along [2-11] formed by alternating XB donors and acceptors.
Related literature
For the use of bis-(4-pyridyl)buta-1,3-diine in crystal engeneering based on hydrogen bonding and transition metal binding, see: Nakamura et al. (2003 ▶); Curtis et al. (2005 ▶); Maekawa et al. (2000 ▶); Badruz Zaman et al. (2001 ▶); Allan et al. (1988 ▶). For N⋯I halogen bonds based on α,ω-diiodoperfluorocarbons, see: Neukirch et al. (2005 ▶); Navarrini et al. (2000 ▶); Liantonio et al. (2003 ▶); Bertani et al. (2002 ▶); Metrangolo et al. (2004 ▶, 2008 ▶); Fox et al. (2004 ▶); Dey et al. (2009 ▶). For segregation of perfluoroalkyl chains, see: Fox et al. (2008 ▶). For chirality and order/disorder of long perfluoroalkyl chains, see: Monde et al. (2006 ▶). For the synthesis of bis-(4-pyridyl)buta-1,3-diine, see: Della Ciana & Haim (1984 ▶).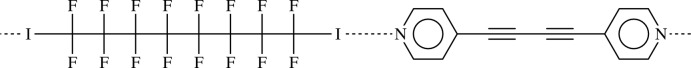
Experimental
Crystal data
C8F16I2·C14H8N2
M r = 858.10
Triclinic,
a = 5.4849 (11) Å
b = 14.302 (2) Å
c = 18.354 (3) Å
α = 111.40 (2)°
β = 90.35 (2)°
γ = 94.03 (2)°
V = 1336.4 (4) Å3
Z = 2
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 2.48 mm−1
T = 295 K
0.36 × 0.12 × 0.10 mm
Data collection
Bruker SMART CCD area detector diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2010 ▶) T min = 0.734, T max = 1.000
15067 measured reflections
6100 independent reflections
4600 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.026
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.039
wR(F 2) = 0.114
S = 1.02
6100 reflections
379 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.90 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.57 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2010 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2010 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SIR2002 (Burla et al., 2003 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 for Windows (Farrugia, 2012 ▶) and Mercury (Macrae et al., 2006 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: enCIFer (Allen et al., 2004 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536813001888/fy2080sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536813001888/fy2080Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536813001888/fy2080Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Halogen and hydrogen-bonding contacts (Å, °).
| C—X⋯Y | X⋯Y | C—X⋯Y |
|---|---|---|
| C1—I1⋯N1 | 2.863 (4) | 177.93 (16) |
| C8—I2⋯N2i | 2.887 (4) | 175.39 (16) |
| C1—F1⋯H9ii | 2.60 | 145.3 |
Symmetry codes: (i) = −2 + x, 1 + y, −1 + z; (ii) = −x, 1 − y, 1 − z.
Acknowledgments
GC, PM and GT acknowledge the Fondazione Cariplo (projects 2009–2550 and 2010–1351) for financial support.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Bis-(4-pyridyl)buta-1,3-diine (1) (Allan et al., 1988) has been used as ditopic hydrogen bonding (HB) acceptor in crystal engineering (Nakamura et al., 2003; Curtis et al., 2005) and in transition metals complexes (Badruz Zaman et al., 2001; Maekawa et al., 2000), but it has never been used in halogen bonding (XB) adducts formation. Our group has shown that α,ω-diiodoperfluorocarbons are very good ditopic XB donors, both towards neutral (Fox et al., 2004) and ionic (Metrangolo et al., 2008) electron-donors. As expected, when solutions of (1) and 1,1,2,2,3,3,4,4,5,5,6,6,7,7,8,8-hexadecafluoro-1,8-diiodooctane (2), are mixed, the (1)···(2) adduct quickly precipitates (Fig. 1). It forms an infinite one-dimensional and non-covalent polymer through short XBs (Table 1). In our experience, this kind of nearly linear adduct has normally Z' = 1/2, that is, both molecules lie on crystallographic elements of symmetry, more frequently Ci, but also C2 (see Table 2). Here instead, both molecules are in general position and Z' is 1. The cause of the molecular symmetry breaking is an F···H contact, the only interaction shorter than the sum of the van der Waals radii beside the I···N XBs. (Table 1). As happens in most structures containing perfluorocarbons and hydrocarbons moieties (see for example Fox et al., 2008), the two components segregate and a layered structure is formed (Fig. 2).
Experimental
(1) was synthetized according to Della Ciana & Haim (1984); (2) was from Aldrich. The adduct was obtained by slow evaporation from a 1:1 solution of the two components in chloroform.
Refinement
The lowest energy conformation of long perfluoroalkanes is chiral in due to the sterically hindered F···F contacts between 1,3 positioned CF2 groups (Monde et al., 2006). Their crystals frequently show a superposition, in the same crystallographic site, of the two more common conformers: all-trans+ and all-trans- (see, for example, Dey <i1,4-bis(pyridin-4-yl)buta-1,3-diyne–1,1,2,2,3,3,4,4,5,5,6,6,7,7,8,8-hexadecafluoro-1,8-diiodooctane (1/1)>et al., 2009), which in some cases have unequal occupancy factors. This is particularly visible for –CF3 terminated chains, that is, for α,ω-dihaloperfluorocarbons, which have the two endings strongly interacting with any electron-donor site. This type of disorder is difficult to observe, at least at room temperature, because it is masked by the large ADPs of perfluoroalkyl chains. This is due to the very weak interactions that their chains give with any environment. In the present study, splitting of some fluorine atoms was suggested by SHELXL but did not give good results. In spite of the use of a lot of restraints and constraints, at the price of a large increase of refined parameters, the final R1, wR2 and Δρ did not change significantly. The correlations between couples of parameters involving split atoms were very high, many of them being in the range 0.95–0.99. For these reasons we decided to use the ordered model of refinement. All H atoms were placed in geometrically calculated positions with C—H = 0.93 Å and Uiso(H) = 1.2 Ueq(C).
Figures
Fig. 1.
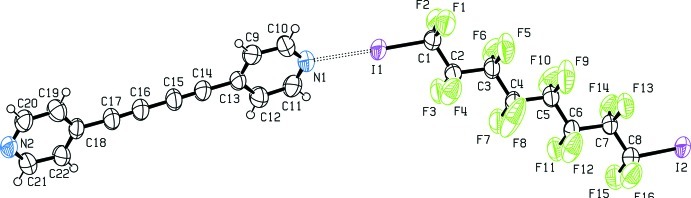
The asymmetric unit of the title compound. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at 50% probability level.
Fig. 2.
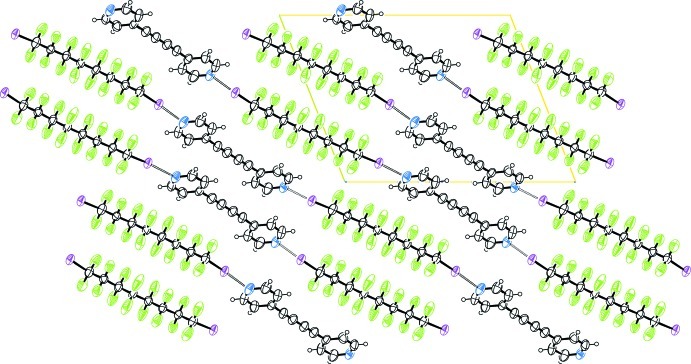
Crystal packing of the title compound viewed along the a axis, showing the alternating perfluorocarbon/hydrocarbon layers.
Crystal data
| C8F16I2·C14H8N2 | Z = 2 |
| Mr = 858.10 | F(000) = 808 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 2.132 Mg m−3 |
| a = 5.4849 (11) Å | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| b = 14.302 (2) Å | Cell parameters from 981 reflections |
| c = 18.354 (3) Å | θ = 2.4–27.4° |
| α = 111.40 (2)° | µ = 2.48 mm−1 |
| β = 90.35 (2)° | T = 295 K |
| γ = 94.03 (2)° | Elongated prism, colourless |
| V = 1336.4 (4) Å3 | 0.36 × 0.12 × 0.10 mm |
Data collection
| Bruker SMART CCD area detector diffractometer | 4600 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| ω and φ scans | Rint = 0.026 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2010) | θmax = 27.5°, θmin = 2.3° |
| Tmin = 0.734, Tmax = 1.000 | h = −7→7 |
| 15067 measured reflections | k = −18→18 |
| 6100 independent reflections | l = −23→23 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | 0 restraints |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.039 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.114 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0662P)2 + 0.5679P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.02 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.002 |
| 6100 reflections | Δρmax = 0.90 e Å−3 |
| 379 parameters | Δρmin = −0.57 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| I1 | 0.11335 (6) | 0.46492 (2) | 0.32421 (2) | 0.06421 (11) | |
| C1 | −0.0850 (8) | 0.5404 (4) | 0.2631 (3) | 0.0616 (10) | |
| F1 | −0.1957 (7) | 0.6162 (3) | 0.3136 (2) | 0.1019 (12) | |
| F2 | −0.2603 (6) | 0.4751 (3) | 0.2165 (2) | 0.0938 (10) | |
| C2 | 0.0789 (7) | 0.5809 (3) | 0.2117 (2) | 0.0525 (9) | |
| F3 | 0.2403 (6) | 0.6512 (3) | 0.25989 (19) | 0.0936 (10) | |
| F4 | 0.1996 (6) | 0.5068 (2) | 0.16550 (18) | 0.0852 (9) | |
| C3 | −0.0565 (8) | 0.6289 (3) | 0.1613 (2) | 0.0598 (10) | |
| F5 | −0.1913 (8) | 0.6966 (3) | 0.2048 (2) | 0.1254 (16) | |
| F6 | −0.2101 (6) | 0.5560 (3) | 0.1115 (2) | 0.1027 (12) | |
| C4 | 0.1092 (8) | 0.6720 (3) | 0.1114 (2) | 0.0558 (9) | |
| F7 | 0.2517 (11) | 0.7470 (4) | 0.1598 (3) | 0.170 (3) | |
| F8 | 0.2464 (7) | 0.6031 (4) | 0.0697 (3) | 0.1272 (17) | |
| C5 | −0.0268 (8) | 0.7128 (3) | 0.0561 (2) | 0.0569 (10) | |
| F9 | −0.1635 (10) | 0.7821 (4) | 0.0985 (2) | 0.152 (2) | |
| F10 | −0.1735 (7) | 0.6388 (3) | 0.0088 (2) | 0.1142 (14) | |
| C6 | 0.1400 (8) | 0.7555 (3) | 0.0062 (2) | 0.0546 (9) | |
| F11 | 0.2902 (7) | 0.8298 (3) | 0.0525 (2) | 0.1111 (13) | |
| F12 | 0.2741 (6) | 0.6821 (3) | −0.0373 (2) | 0.0963 (11) | |
| C7 | 0.0006 (7) | 0.7947 (3) | −0.0502 (2) | 0.0519 (9) | |
| F13 | −0.1322 (6) | 0.8675 (2) | −0.00739 (17) | 0.0850 (9) | |
| F14 | −0.1497 (6) | 0.7197 (2) | −0.09729 (17) | 0.0826 (9) | |
| C8 | 0.1623 (9) | 0.8356 (4) | −0.1016 (3) | 0.0651 (11) | |
| F15 | 0.3155 (6) | 0.9102 (3) | −0.0564 (2) | 0.1065 (12) | |
| F16 | 0.2988 (7) | 0.7622 (3) | −0.1455 (2) | 0.1068 (13) | |
| I2 | −0.04797 (6) | 0.88682 (2) | −0.17707 (2) | 0.06339 (11) | |
| C9 | 0.4885 (9) | 0.3202 (4) | 0.5119 (3) | 0.0669 (12) | |
| H1B | 0.4645 | 0.3284 | 0.5639 | 0.080* | |
| C10 | 0.3452 (9) | 0.3656 (4) | 0.4747 (3) | 0.0758 (13) | |
| H10 | 0.2236 | 0.4041 | 0.5031 | 0.091* | |
| N1 | 0.3700 (8) | 0.3578 (3) | 0.4013 (3) | 0.0730 (11) | |
| C11 | 0.5425 (10) | 0.3021 (5) | 0.3621 (3) | 0.0775 (14) | |
| H11 | 0.5607 | 0.2952 | 0.3101 | 0.093* | |
| C12 | 0.6971 (9) | 0.2536 (4) | 0.3932 (3) | 0.0689 (12) | |
| H12 | 0.8175 | 0.2160 | 0.3634 | 0.083* | |
| C13 | 0.6682 (7) | 0.2623 (3) | 0.4706 (2) | 0.0553 (9) | |
| C14 | 0.8229 (8) | 0.2136 (4) | 0.5068 (3) | 0.0616 (10) | |
| C15 | 0.9543 (9) | 0.1761 (4) | 0.5378 (3) | 0.0651 (11) | |
| C16 | 1.1066 (9) | 0.1343 (4) | 0.5753 (3) | 0.0646 (11) | |
| C17 | 1.2428 (9) | 0.0982 (4) | 0.6076 (3) | 0.0654 (11) | |
| C18 | 1.3964 (8) | 0.0545 (3) | 0.6481 (2) | 0.0565 (10) | |
| C19 | 1.3530 (9) | 0.0648 (4) | 0.7250 (3) | 0.0678 (11) | |
| H19 | 1.2238 | 0.0998 | 0.7514 | 0.081* | |
| C20 | 1.5051 (9) | 0.0220 (4) | 0.7606 (3) | 0.0674 (11) | |
| H20 | 1.4754 | 0.0291 | 0.8121 | 0.081* | |
| N2 | 1.6933 (7) | −0.0291 (3) | 0.7268 (2) | 0.0699 (10) | |
| C21 | 1.7289 (9) | −0.0398 (4) | 0.6527 (3) | 0.0743 (13) | |
| H21 | 1.8567 | −0.0769 | 0.6274 | 0.089* | |
| C22 | 1.5882 (9) | 0.0006 (4) | 0.6113 (3) | 0.0706 (13) | |
| H22 | 1.6214 | −0.0082 | 0.5597 | 0.085* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| I1 | 0.06808 (19) | 0.0752 (2) | 0.06554 (19) | 0.00504 (14) | −0.00501 (13) | 0.04518 (15) |
| C1 | 0.065 (3) | 0.071 (3) | 0.062 (2) | 0.017 (2) | 0.009 (2) | 0.037 (2) |
| F1 | 0.132 (3) | 0.111 (2) | 0.094 (2) | 0.070 (2) | 0.056 (2) | 0.0628 (19) |
| F2 | 0.0727 (18) | 0.119 (3) | 0.116 (3) | −0.0210 (18) | −0.0270 (17) | 0.079 (2) |
| C2 | 0.054 (2) | 0.057 (2) | 0.052 (2) | 0.0110 (18) | 0.0002 (17) | 0.0243 (18) |
| F3 | 0.108 (2) | 0.100 (2) | 0.084 (2) | −0.0334 (19) | −0.0355 (18) | 0.0554 (18) |
| F4 | 0.103 (2) | 0.101 (2) | 0.0805 (18) | 0.0584 (18) | 0.0315 (16) | 0.0569 (16) |
| C3 | 0.068 (3) | 0.067 (2) | 0.056 (2) | 0.021 (2) | 0.006 (2) | 0.034 (2) |
| F5 | 0.171 (4) | 0.146 (3) | 0.112 (3) | 0.114 (3) | 0.073 (3) | 0.091 (2) |
| F6 | 0.091 (2) | 0.135 (3) | 0.110 (3) | −0.040 (2) | −0.0437 (19) | 0.087 (2) |
| C4 | 0.061 (2) | 0.058 (2) | 0.060 (2) | 0.0006 (19) | −0.0104 (18) | 0.0354 (19) |
| F7 | 0.238 (5) | 0.165 (4) | 0.139 (3) | −0.132 (4) | −0.127 (4) | 0.120 (3) |
| F8 | 0.122 (3) | 0.180 (4) | 0.158 (3) | 0.098 (3) | 0.080 (3) | 0.138 (3) |
| C5 | 0.067 (2) | 0.060 (2) | 0.049 (2) | 0.021 (2) | 0.0048 (18) | 0.0245 (18) |
| F9 | 0.222 (5) | 0.187 (4) | 0.122 (3) | 0.158 (4) | 0.109 (3) | 0.118 (3) |
| F10 | 0.107 (3) | 0.161 (3) | 0.101 (2) | −0.058 (2) | −0.046 (2) | 0.092 (3) |
| C6 | 0.061 (2) | 0.057 (2) | 0.053 (2) | 0.0073 (18) | −0.0054 (18) | 0.0279 (18) |
| F11 | 0.130 (3) | 0.118 (3) | 0.105 (2) | −0.055 (2) | −0.068 (2) | 0.077 (2) |
| F12 | 0.101 (2) | 0.128 (3) | 0.102 (2) | 0.069 (2) | 0.0459 (18) | 0.081 (2) |
| C7 | 0.057 (2) | 0.054 (2) | 0.050 (2) | 0.0100 (17) | −0.0028 (17) | 0.0253 (17) |
| F13 | 0.105 (2) | 0.098 (2) | 0.0755 (17) | 0.0553 (18) | 0.0257 (16) | 0.0516 (16) |
| F14 | 0.095 (2) | 0.0869 (19) | 0.0769 (18) | −0.0257 (16) | −0.0342 (16) | 0.0497 (15) |
| C8 | 0.062 (3) | 0.079 (3) | 0.070 (3) | 0.009 (2) | −0.001 (2) | 0.045 (2) |
| F15 | 0.093 (2) | 0.131 (3) | 0.123 (3) | −0.044 (2) | −0.047 (2) | 0.089 (2) |
| F16 | 0.110 (2) | 0.147 (3) | 0.109 (2) | 0.073 (2) | 0.051 (2) | 0.090 (2) |
| I2 | 0.07009 (19) | 0.0747 (2) | 0.06057 (18) | 0.00691 (14) | −0.00418 (13) | 0.04264 (15) |
| C9 | 0.061 (2) | 0.090 (3) | 0.062 (3) | 0.006 (2) | 0.000 (2) | 0.042 (2) |
| C10 | 0.066 (3) | 0.093 (3) | 0.088 (3) | 0.026 (3) | 0.008 (2) | 0.052 (3) |
| N1 | 0.064 (2) | 0.091 (3) | 0.086 (3) | 0.011 (2) | −0.005 (2) | 0.058 (2) |
| C11 | 0.078 (3) | 0.110 (4) | 0.066 (3) | 0.006 (3) | −0.002 (2) | 0.057 (3) |
| C12 | 0.068 (3) | 0.087 (3) | 0.063 (3) | 0.017 (2) | 0.004 (2) | 0.038 (2) |
| C13 | 0.050 (2) | 0.064 (2) | 0.060 (2) | 0.0001 (18) | −0.0102 (17) | 0.034 (2) |
| C14 | 0.062 (2) | 0.073 (3) | 0.062 (2) | 0.003 (2) | −0.0062 (19) | 0.039 (2) |
| C15 | 0.067 (3) | 0.069 (3) | 0.070 (3) | 0.010 (2) | −0.009 (2) | 0.038 (2) |
| C16 | 0.067 (3) | 0.071 (3) | 0.067 (3) | 0.008 (2) | −0.006 (2) | 0.038 (2) |
| C17 | 0.066 (3) | 0.071 (3) | 0.069 (3) | 0.010 (2) | −0.008 (2) | 0.038 (2) |
| C18 | 0.061 (2) | 0.057 (2) | 0.062 (2) | 0.0009 (18) | −0.0117 (19) | 0.0348 (19) |
| C19 | 0.070 (3) | 0.076 (3) | 0.057 (2) | 0.012 (2) | −0.007 (2) | 0.023 (2) |
| C20 | 0.075 (3) | 0.080 (3) | 0.055 (2) | 0.002 (2) | −0.010 (2) | 0.036 (2) |
| N2 | 0.064 (2) | 0.086 (3) | 0.077 (3) | −0.001 (2) | −0.0163 (19) | 0.051 (2) |
| C21 | 0.066 (3) | 0.091 (3) | 0.081 (3) | 0.020 (3) | −0.002 (2) | 0.047 (3) |
| C22 | 0.064 (3) | 0.104 (4) | 0.062 (3) | 0.016 (3) | 0.000 (2) | 0.051 (3) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| I1—C1 | 2.154 (4) | C9—C10 | 1.376 (6) |
| C1—F1 | 1.330 (5) | C9—C13 | 1.377 (7) |
| C1—F2 | 1.345 (6) | C9—H1B | 0.9300 |
| C1—C2 | 1.540 (6) | C10—N1 | 1.320 (7) |
| C2—F4 | 1.316 (5) | C10—H10 | 0.9300 |
| C2—F3 | 1.338 (5) | N1—C11 | 1.321 (7) |
| C2—C3 | 1.552 (5) | C11—C12 | 1.376 (7) |
| C3—F5 | 1.290 (5) | C11—H11 | 0.9300 |
| C3—F6 | 1.344 (6) | C12—C13 | 1.390 (6) |
| C3—C4 | 1.545 (6) | C12—H12 | 0.9300 |
| C4—F8 | 1.298 (6) | C13—C14 | 1.436 (6) |
| C4—F7 | 1.315 (5) | C14—C15 | 1.185 (6) |
| C4—C5 | 1.552 (6) | C15—C16 | 1.375 (6) |
| C5—F9 | 1.303 (5) | C16—C17 | 1.204 (6) |
| C5—F10 | 1.312 (6) | C17—C18 | 1.434 (6) |
| C5—C6 | 1.546 (6) | C18—C22 | 1.378 (7) |
| C6—F11 | 1.319 (5) | C18—C19 | 1.389 (6) |
| C6—F12 | 1.336 (5) | C19—C20 | 1.362 (6) |
| C6—C7 | 1.563 (5) | C19—H19 | 0.9300 |
| C7—F13 | 1.322 (5) | C20—N2 | 1.330 (7) |
| C7—F14 | 1.330 (5) | C20—H20 | 0.9300 |
| C7—C8 | 1.536 (6) | N2—C21 | 1.329 (6) |
| C8—F15 | 1.324 (6) | C21—C22 | 1.372 (6) |
| C8—F16 | 1.346 (6) | C21—H21 | 0.9300 |
| C8—I2 | 2.151 (4) | C22—H22 | 0.9300 |
| F1—C1—F2 | 107.3 (4) | F15—C8—F16 | 107.0 (4) |
| F1—C1—C2 | 109.0 (4) | F15—C8—C7 | 109.4 (4) |
| F2—C1—C2 | 108.1 (4) | F16—C8—C7 | 108.8 (4) |
| F1—C1—I1 | 110.5 (3) | F15—C8—I2 | 109.8 (3) |
| F2—C1—I1 | 108.9 (3) | F16—C8—I2 | 109.3 (3) |
| C2—C1—I1 | 112.9 (3) | C7—C8—I2 | 112.5 (3) |
| F4—C2—F3 | 108.4 (4) | C10—C9—C13 | 118.7 (4) |
| F4—C2—C1 | 108.5 (3) | C10—C9—H1B | 120.6 |
| F3—C2—C1 | 107.0 (3) | C13—C9—H1B | 120.6 |
| F4—C2—C3 | 109.1 (3) | N1—C10—C9 | 123.9 (5) |
| F3—C2—C3 | 108.2 (3) | N1—C10—H10 | 118.1 |
| C1—C2—C3 | 115.4 (3) | C9—C10—H10 | 118.1 |
| F5—C3—F6 | 106.3 (4) | C10—N1—C11 | 117.0 (4) |
| F5—C3—C4 | 110.6 (4) | N1—C11—C12 | 124.2 (5) |
| F6—C3—C4 | 107.1 (3) | N1—C11—H11 | 117.9 |
| F5—C3—C2 | 110.1 (4) | C12—C11—H11 | 117.9 |
| F6—C3—C2 | 107.0 (4) | C11—C12—C13 | 118.1 (5) |
| C4—C3—C2 | 115.2 (3) | C11—C12—H12 | 120.9 |
| F8—C4—F7 | 108.2 (5) | C13—C12—H12 | 120.9 |
| F8—C4—C3 | 109.2 (3) | C9—C13—C12 | 118.1 (4) |
| F7—C4—C3 | 107.6 (4) | C9—C13—C14 | 120.8 (4) |
| F8—C4—C5 | 108.6 (4) | C12—C13—C14 | 121.1 (4) |
| F7—C4—C5 | 107.7 (4) | C15—C14—C13 | 178.1 (5) |
| C3—C4—C5 | 115.4 (4) | C14—C15—C16 | 178.8 (6) |
| F9—C5—F10 | 107.2 (5) | C17—C16—C15 | 179.1 (6) |
| F9—C5—C6 | 109.6 (4) | C16—C17—C18 | 177.5 (5) |
| F10—C5—C6 | 108.5 (3) | C22—C18—C19 | 118.6 (4) |
| F9—C5—C4 | 108.2 (4) | C22—C18—C17 | 120.8 (4) |
| F10—C5—C4 | 107.9 (4) | C19—C18—C17 | 120.6 (4) |
| C6—C5—C4 | 115.2 (4) | C20—C19—C18 | 118.1 (5) |
| F11—C6—F12 | 108.1 (4) | C20—C19—H19 | 121.0 |
| F11—C6—C5 | 109.6 (4) | C18—C19—H19 | 121.0 |
| F12—C6—C5 | 107.9 (3) | N2—C20—C19 | 124.4 (4) |
| F11—C6—C7 | 108.4 (3) | N2—C20—H20 | 117.8 |
| F12—C6—C7 | 108.0 (3) | C19—C20—H20 | 117.8 |
| C5—C6—C7 | 114.7 (3) | C21—N2—C20 | 116.6 (4) |
| F13—C7—F14 | 108.4 (4) | N2—C21—C22 | 123.8 (5) |
| F13—C7—C8 | 108.1 (3) | N2—C21—H21 | 118.1 |
| F14—C7—C8 | 107.8 (3) | C22—C21—H21 | 118.1 |
| F13—C7—C6 | 108.2 (3) | C21—C22—C18 | 118.4 (4) |
| F14—C7—C6 | 108.5 (3) | C21—C22—H22 | 120.8 |
| C8—C7—C6 | 115.6 (3) | C18—C22—H22 | 120.8 |
| F1—C1—C2—F4 | 176.0 (4) | F10—C5—C6—F12 | −62.3 (5) |
| F2—C1—C2—F4 | −67.7 (4) | C4—C5—C6—F12 | 58.8 (5) |
| I1—C1—C2—F4 | 52.8 (4) | F9—C5—C6—C7 | −58.7 (5) |
| F1—C1—C2—F3 | 59.2 (5) | F10—C5—C6—C7 | 58.1 (5) |
| F2—C1—C2—F3 | 175.5 (4) | C4—C5—C6—C7 | 179.1 (3) |
| I1—C1—C2—F3 | −64.0 (4) | F11—C6—C7—F13 | −63.1 (5) |
| F1—C1—C2—C3 | −61.3 (5) | F12—C6—C7—F13 | −179.9 (4) |
| F2—C1—C2—C3 | 55.0 (5) | C5—C6—C7—F13 | 59.8 (5) |
| I1—C1—C2—C3 | 175.5 (3) | F11—C6—C7—F14 | 179.6 (4) |
| F4—C2—C3—F5 | 175.0 (4) | F12—C6—C7—F14 | 62.7 (5) |
| F3—C2—C3—F5 | −67.2 (5) | C5—C6—C7—F14 | −57.6 (5) |
| C1—C2—C3—F5 | 52.6 (6) | F11—C6—C7—C8 | 58.3 (5) |
| F4—C2—C3—F6 | 59.9 (5) | F12—C6—C7—C8 | −58.5 (5) |
| F3—C2—C3—F6 | 177.6 (4) | C5—C6—C7—C8 | −178.8 (4) |
| C1—C2—C3—F6 | −62.6 (5) | F13—C7—C8—F15 | 63.4 (5) |
| F4—C2—C3—C4 | −59.1 (5) | F14—C7—C8—F15 | −179.7 (4) |
| F3—C2—C3—C4 | 58.7 (5) | C6—C7—C8—F15 | −58.0 (5) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 178.5 (4) | F13—C7—C8—F16 | 180.0 (4) |
| F5—C3—C4—F8 | 178.5 (4) | F14—C7—C8—F16 | −63.1 (4) |
| F6—C3—C4—F8 | −66.0 (5) | C6—C7—C8—F16 | 58.5 (5) |
| C2—C3—C4—F8 | 52.9 (5) | F13—C7—C8—I2 | −58.8 (4) |
| F5—C3—C4—F7 | 61.3 (6) | F14—C7—C8—I2 | 58.1 (4) |
| F6—C3—C4—F7 | 176.8 (4) | C6—C7—C8—I2 | 179.7 (3) |
| C2—C3—C4—F7 | −64.3 (5) | C13—C9—C10—N1 | −0.5 (8) |
| F5—C3—C4—C5 | −58.9 (5) | C9—C10—N1—C11 | 0.6 (8) |
| F6—C3—C4—C5 | 56.6 (5) | C10—N1—C11—C12 | −0.8 (8) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 175.5 (4) | N1—C11—C12—C13 | 1.0 (9) |
| F8—C4—C5—F9 | −179.8 (4) | C10—C9—C13—C12 | 0.6 (7) |
| F7—C4—C5—F9 | −62.9 (6) | C10—C9—C13—C14 | 179.8 (5) |
| C3—C4—C5—F9 | 57.2 (6) | C11—C12—C13—C9 | −0.8 (7) |
| F8—C4—C5—F10 | 64.5 (5) | C11—C12—C13—C14 | 179.9 (5) |
| F7—C4—C5—F10 | −178.6 (4) | C22—C18—C19—C20 | 0.9 (7) |
| C3—C4—C5—F10 | −58.5 (5) | C17—C18—C19—C20 | −179.8 (5) |
| F8—C4—C5—C6 | −56.9 (5) | C18—C19—C20—N2 | 0.0 (8) |
| F7—C4—C5—C6 | 60.1 (6) | C19—C20—N2—C21 | −1.3 (8) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | −179.8 (3) | C20—N2—C21—C22 | 1.7 (8) |
| F9—C5—C6—F11 | 63.5 (5) | N2—C21—C22—C18 | −0.8 (9) |
| F10—C5—C6—F11 | −179.7 (4) | C19—C18—C22—C21 | −0.5 (7) |
| C4—C5—C6—F11 | −58.7 (5) | C17—C18—C22—C21 | −179.8 (5) |
| F9—C5—C6—F12 | −179.0 (4) |
Halogen and hydrogen-bonding contacts (Å, °).
| C—X···Y | X···Y | C—X···Y |
| C1—I1···N1 | 2.863 (4) | 177.93 (16) |
| C8—I2···N2i | 2.887 (4) | 175.39 (16) |
| C1—F1···H9ii | 2.60 | 145.3 |
Symmetry codes: (i) = -2+x, 1+y, -1+z; (ii) = -x, 1-y, 1-z.
Crystallographic symmetry site of single molecules in one-dimensional adducts between some molecules containg two basic N atoms and α,ω-diiodoperfluoroalkanes previously studied by our group.
| Molecule A | Molecul B | A site | B site |
| C14H8N2a | I-(CF2)8-I | C1 | C1 |
| C10H16N2b | I-(CF2)8-Ic | C1 | C1 |
| C12H26N2O2d | I-(CF2)8-I | Ci | C2 |
| C10H16N2e | Br-(CF2)8-Br | C2 | Ci |
| C13H14N2f | I-(CF2)8-I | Ci | Ci |
| CN-(CH2)4-CNg | I-(CF2)2-I | Ci | Ci |
| CN-(CH2)4-CNg | I-(CF2)4-I | Ci | Ci |
| CN-(CH2)6-CNg | I-(CF2)4-I | Ci | Ci |
| CN-(CH2)4-CNg | I-(CF2)6-I | Ci | Ci |
| CN-(CH2)6-CNg | I-(CF2)6-I | Ci | Ci |
| CN-(CH2)4-CNg | I-(CF2)8-I | Ci | Ci |
| CN-(CH2)6-CNg | I-(CF2)8-I | Ci | Ci |
| C10H8N4h | I-(CF2)8-I | C1 | Ci |
| C10H8N4i | I-(CF2)4-I | C1 | Ci |
(a) This work. (b) N,N,N',N'-tetramethyl-p-phenylenediamine (Neukirch et al., 2005). (c) Unusually, the conformation of I-(CF2)8-I is ttgtt. (d) 1,7,10,16-tetraoxa-4,13-diazacyclo-octadecane (Navarrini et al., 2000). (e) 1,7,10,16-tetraoxa-4,13-diazacyclo-octadecane (Liantonio et al., 2003). (f) 1,3-di-(4-pyridyl)propane (Bertani et al., 2002). (g) Metrangolo et al. (2004). (h) 4,4'-azobispyridine (Fox et al., 2004). (i) 1,7,10,16-tetraoxa-4,13-diazacyclo-octadecane (Dey et al., 2009).
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: FY2080).
References
- Allan, J. R., Barrow, M. J., Beaumont, P. C., Macindoe, L. A., Milburn, G. H. W. & Werninck, A. R. (1988). Inorg. Chim. Acta, 148, 85–90.
- Allen, F. H., Johnson, O., Shields, G. P., Smith, B. R. & Towler, M. (2004). J. Appl. Cryst. 37, 335–338.
- Badruz Zaman, M. D., Smith, M. D. & Zur Loye, H.-C. (2001). Chem. Mater. 13, 3534–3541.
- Bertani, R., Metrangolo, P., Moiana, A., Perez, E., Pilati, T., Resnati, G., Rico-Lattes, I. & Sassi, A. (2002). Adv. Mater. 14, 1197–1201.
- Bruker (2010). APEX2, SAINT and SADABS Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Burla, M. C., Camalli, M., Carrozzini, B., Cascarano, G. L., Giacovazzo, C., Polidori, G. & Spagna, R. (2003). J. Appl. Cryst. 36, 1103.
- Curtis, S. M., Le, N., Fowler, F. W. & Lauher, J. W. (2005). Cryst. Growth Des. 5, 2313–2321.
- Della Ciana, L. & Haim, A. (1984). J. Heterocycl. Chem. 21, 607–608.
- Dey, A., Metrangolo, P., Pilati, T., Resnati, G., Terraneo, G. & Wlassics, I. (2009). J. Fluorine Chem. 130, 816–823.
- Farrugia, L. J. (2012). J. Appl. Cryst. 45, 849–854.
- Fox, D. B., Liantonio, R., Metrangolo, P., Pilati, T. & Resnati, G. (2004). J. Fluorine Chem. 125, 271–281.
- Fox, D., Metrangolo, P., Pasini, D., Pilati, T., Resnati, G. & Terraneo, G. (2008). CrystEngComm, 10, 1132–1136.
- Liantonio, R., Metrangolo, P., Pilati, T., Resnati, G. & Stevenazzi, A. (2003). Cryst. Growth Des. 3, 799–803.
- Macrae, C. F., Edgington, P. R., McCabe, P., Pidcock, E., Shields, G. P., Taylor, R., Towler, M. & van de Streek, J. (2006). J. Appl. Cryst. 39, 453–457.
- Maekawa, M., Konaka, H., Suenaga, Y., Takayoshi Kuroda-Sowa, T. & Munakata, M. (2000). J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. pp. 4160–4166.
- Metrangolo, P., Meyer, F., Pilati, T. & Resnati, G. (2008). Chem. Commun. pp. 1635–1637. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Metrangolo, P., Pilati, T., Resnati, G. & Stevenazzi, A. (2004). Chem. Commun. pp. 1492–1493. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Monde, K., Miura, N., Hashimoto, M., Taniguchi, T. & Inabe, T. (2006). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 128, 6000–6001. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, A., Sato, T. & Kuroda, R. (2003). CrystEngComm, 5, 318–325.
- Navarrini, W., Metrangolo, P., Pilati, T. & Resnati, G. (2000). New J. Chem. 24, 777–780.
- Neukirch, H., Guido, E., Liantonio, R., Metrangolo, P., Pilati, T. & Resnati, G. (2005). Chem. Commun. pp. 1534–1536. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536813001888/fy2080sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536813001888/fy2080Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536813001888/fy2080Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report


