Abstract
In the title compound, C7H5BrN2, fused six-membered pyridine and five-membered pyrrole rings form the essentially planar azaindole skeleton (r.m.s. deviation = 0.017 Å). In the crystal, pairs of N—H⋯N hydrogen bonds connect the molecules into inversion dimers.
Related literature
For the structure of 7-azaindole (C7H6N2), see: Dufour et al. (1990 ▶) and for the structure of 3-iodo-7-azaindole (C7H5IN2), see: Chou et al. (2000 ▶). For the utilization of the title compound as the N-donor carrier ligand of highly cytotoxic platinum(II) dichlorido complexes, see: Štarha et al. (2012 ▶).
Experimental
Crystal data
C7H5BrN2
M r = 197.04
Monoclinic,
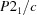
a = 8.9082 (4) Å
b = 13.3632 (6) Å
c = 5.8330 (3) Å
β = 103.403 (5)°
V = 675.47 (6) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 6.00 mm−1
T = 100 K
0.24 × 0.24 × 0.12 mm
Data collection
Oxford Diffraction Xcalibur Sapphire2 CCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis RED; Oxford Diffraction, 2009 ▶) T min = 0.327, T max = 0.533
3977 measured reflections
1185 independent reflections
1047 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.022
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.035
wR(F 2) = 0.092
S = 1.13
1185 reflections
91 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 1.69 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.33 e Å−3
Data collection: CrysAlis CCD (Oxford Diffraction, 2009 ▶); cell refinement: CrysAlis RED (Oxford Diffraction, 2009 ▶); data reduction: CrysAlis RED; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: DIAMOND (Brandenburg et al., 2011 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: publCIF (Westrip, 2010 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536813004157/tk5196sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536813004157/tk5196Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536813004157/tk5196Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1—H1⋯N7i | 0.88 | 2.12 | 2.960 (5) | 159 |
Symmetry code: (i) 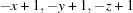 .
.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Palacký University (grant No. PrF_2012_009). The authors wish to thank Dr Igor Popa for carrying out the NMR spectroscopy measurements and Mr Tomáš Šilha for performing the CHN elemental analysis.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
The title compound 5-bromo-7-azaindole (5BrHaza), which is commercially available, was recently used, together with 3-chloro-7-azaindole and 3-iodo-7-azaindole, for the preparation of the platinum(II) dichlorido and oxalato (ox) complexes of the general formula cis-[PtCl2(nHaza)2], and [Pt(ox)(nHaza)2], respectively (Štarha et al., 2012); nHaza stands for the above-mentioned 7-azaindole halogeno-derivatives. The prepared Pt(II)-dichlorido complexes were found to be highly cytotoxic against the osteosarcoma (HOS), breast carcinoma (MCF7) and prostate carcinoma (LNCaP) human cancer cell lines. Particularly cis-[PtCl2(5BrHaza)2] exceeded the clinically applied platinum-based anticancer drug cisplatin, (cis-[PtCl2(NH3)2]), since its IC50 values (the concentration lethal for 50% of the tested cancer cells) equaled 2.5 µM (HOS; 34.2 µM for cisplatin), 2.0 µM (MCF7; 19.6 µM for cisplatin) and 1.5 µM (LNCaP; 3.8 µM for cisplatin).
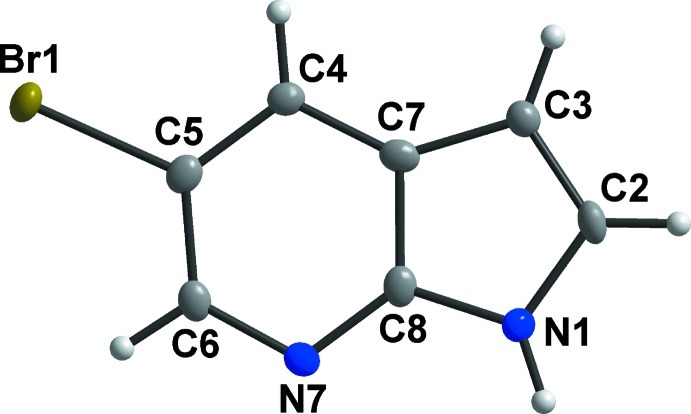
The discrete molecules (Fig. 1) of the title compound contain fused six-membered pyridine and five-membered pyrrole rings forming the 7-azaindole skeleton. The planes fitted through the atoms of both rings form a dihedral angle of 2.09 (14)° (Fig. 2). The most deviated atoms from the mentioned planes are C6 (-0.012 (4) Å) and C3 (-0.006 (4) Å), respectively, while the most deviated atom from the plane fitted through nonhydrogen atoms of the 7-azaindole moiety is C5 (0.025 (4) Å).
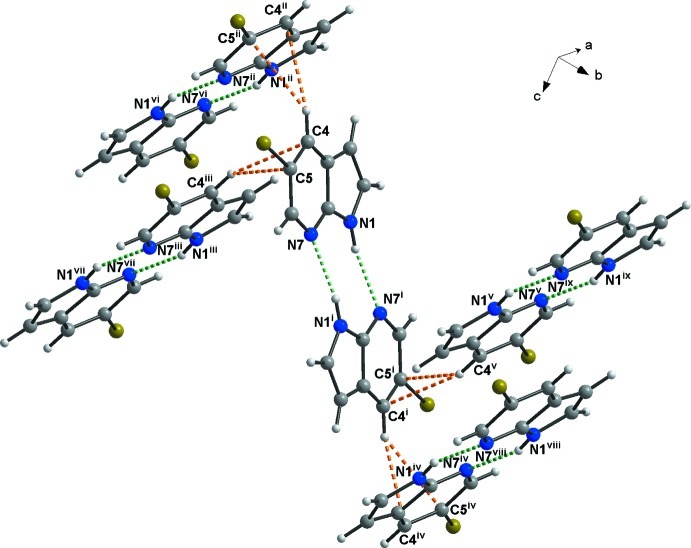
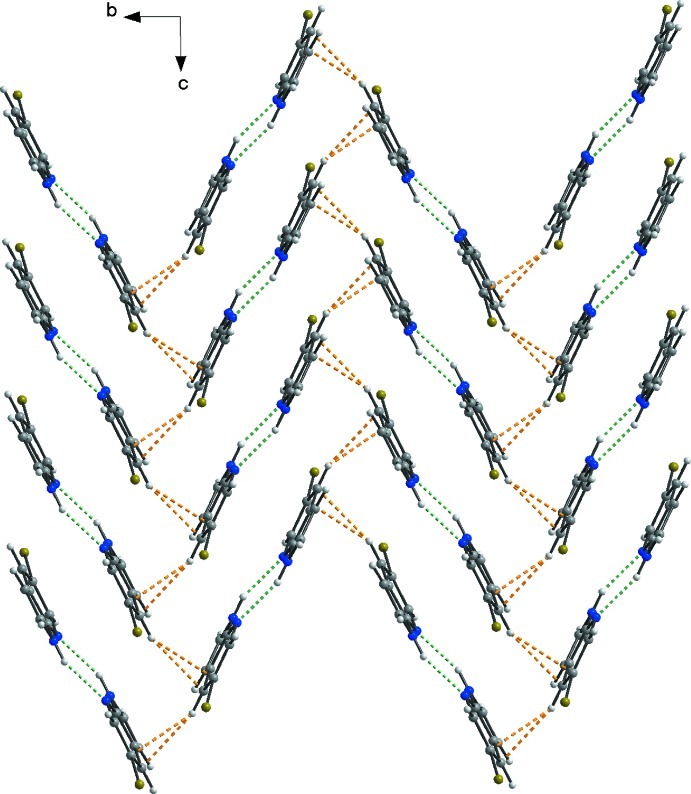
The crystal structure contains the N—H···N hydrogen bonds and C—H···C non-covalent contacts (Fig. 3). Two N1—H1···N7 hydrogen bonds (Table 1) bind together two 5BrHaza molecules into a centrosymmetric dimer. The dimers are connected by C4—H4···C4 and C4—H···C5 non-covalent contacts (see Hydrogen-bond geometry) with four other dimers, which results in the formation of a 2D supramolecular array (Fig. 4).
The molecular structure of the title compound resembles literature precedents: 7-azaindole (Dufour et al., 1990) and 3-iodo-7-azaindole (Chou et al., 2000).
Experimental
The title compound was employed as a starting compound of the syntheses of cis-[PtCl2(5BrHaza)2] and [Pt(ox)(5BrHaza)2].0.75H2O (Štarha et al., 2012). These complexes were prepared by the reactions of the appropriate platinum(II) salt (K2[PtCl4] or K2[Pt(ox)2].2H2O; water solution, 0.5 mmol) with 1.0 mmol of 5BrHaza dissolved in ethanol at 50 °C. Microcrystals obtained as a main product during 2 days of stirring were filtered off and the filtrate was left to crystalize at laboratory temperature in the case of the oxalato-5BrHaza complex. The colourless crystals, which formed as a by-product during a slow evaporation in next 2 weeks, were collected and characterized by elemental analysis, NMR spectroscopy and single-crystal X-ray analysis. 1H NMR (DMF-d7, TMS, 298 K, p.p.m.): δ 11.91 (bs, 1H, HN1), 8.30 (d, J = 2.2 Hz, 1H, HC6), 8.20 (d, J = 2.0 Hz, 1H, HC4), 7.63 (t, J = 2.8 Hz, 1H, HC2), 6.50 (m, 1H, HC3). 13C NMR (DMF-d7, TMS, 298 K, p.p.m.): δ 147.5 (C8), 142.9 (C6), 130.3 (C4), 128.2 (C2), 122.1 (C7), 111.1 (C5), 100.0 (C3). 15N NMR (DMF-d7, relative to DMF, 298 K, p.p.m.): δ 140.9 [s, 11.93, HN1; s, 7.63, HC2; s, 6.50, HC3 (N1)], 277.5 [s, 8.30, HC6 (N7)]. Analysis calculated for C7H6BrN2: C 42.67, H 2.56, N 14.22%; found: C 42.58, H 2.62, N 14.09%. Elemental analysis (C, H, N) was performed on a Thermo Scientific Flash 2000 CHNO-S Analyzer. The 1H, 13C and 15N NMR spectra of the DMF-d7 solutions were collected at 300 K on a Varian 400 spectrometer at 400.00 MHz, 100.58 MHz and 40.53 MHz, respectively. 1H and 13C spectra were calibrated using tetramethylsilane (TMS) as a reference. The 15N NMR spectrum was measured relative to the DMF signals.
Refinement
Hydrogen atoms were located in difference maps and refined using the riding model with C—H = 0.95 Å and N—H = 0.88 Å, and with Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(CH, NH). The maximum and minimum residual electron density peaks of 1.69 and -0.33 eÅ-3, respectively, were located 1.72 Å and 1.25 Å from the H6 and C6 atoms, respectively.
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of the title compound with the non-hydrogen atoms depicted as displacement ellipsoids at the 50% probability level and given with the atom numbering scheme.
Fig. 2.
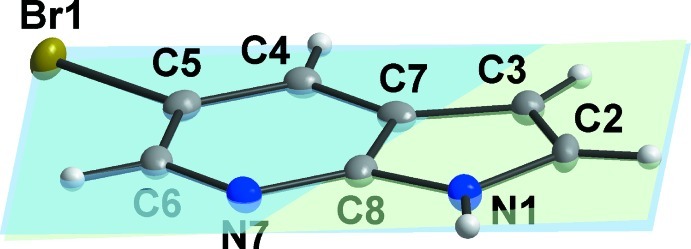
A view of the title compound showing the mutual orientation of the six-membered pyridine (least-squares plane created through the C4, C5, C6, N7, C8 and C7 atoms; in blue) and five-membered pyrrole rings (least-squares plane created through the N1, C2, C3, C7 and C8 atoms; in green). The planes are nearly coplanar forming the dihedral angle of 2.09 (14)°.
Fig. 3.
Part of the crystal structure of the title compound (ball-and-stick model) showing the N—H···N hydrogen bonds (dashed green lines) and C—H···C non-covalent contacts (dashed orange lines). [Symmetry codes: (i) 1 - x, 1 - y, 1 - z; (ii) x, 0.5 - y, z - 0.5; (iii) x, 0.5 - y, z + 0.5; (iv) 1 - x, y + 0.5, 1.5 - z; (v) 1 - x, y + 0.5, 0.5 - z; (vi) 1 - x, y - 0.5, 0.5 - z; (vii) 1 - x, y - 0.5, 1.5 - z; (viii) x, 1.5 - y, z + 0.5; (ix) x, 1.5 - y, z - 0.5].
Fig. 4.
Part of the crystal structure of the title compound (ball-and-stick model) showing the formation of zigzag chains; dashed green lines indicate the N—H···N hydrogen bonds and dashed orange lines indicate C—H···C non-covalent contacts.
Crystal data
| C7H5BrN2 | F(000) = 384 |
| Mr = 197.04 | Dx = 1.938 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Cell parameters from 4062 reflections |
| a = 8.9082 (4) Å | θ = 3.0–33.1° |
| b = 13.3632 (6) Å | µ = 6.00 mm−1 |
| c = 5.8330 (3) Å | T = 100 K |
| β = 103.403 (5)° | Prim, colourless |
| V = 675.47 (6) Å3 | 0.24 × 0.24 × 0.12 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Oxford Diffraction Xcalibur Sapphire2 CCD diffractometer | 1185 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: Enhance (Mo) X-ray Source | 1047 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.022 |
| Detector resolution: 8.3611 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 25.0°, θmin = 3.1° |
| ω scans | h = −10→9 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis RED; Oxford Diffraction, 2009) | k = −15→15 |
| Tmin = 0.327, Tmax = 0.533 | l = −6→6 |
| 3977 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.035 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.092 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.13 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0578P)2 + 1.0071P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 1185 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 91 parameters | Δρmax = 1.69 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.33 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Br1 | −0.02317 (5) | 0.34425 (3) | −0.26611 (7) | 0.0188 (2) | |
| N1 | 0.6033 (4) | 0.4228 (3) | 0.3167 (6) | 0.0151 (7) | |
| H1 | 0.6364 | 0.4519 | 0.4545 | 0.018* | |
| C2 | 0.6944 (5) | 0.3858 (3) | 0.1738 (8) | 0.0168 (9) | |
| H2 | 0.8039 | 0.3886 | 0.2096 | 0.020* | |
| C3 | 0.6054 (5) | 0.3447 (3) | −0.0253 (8) | 0.0151 (9) | |
| H3 | 0.6411 | 0.3135 | −0.1491 | 0.018* | |
| C4 | 0.3052 (5) | 0.3375 (3) | −0.1574 (7) | 0.0143 (9) | |
| H4 | 0.2942 | 0.3057 | −0.3060 | 0.017* | |
| C5 | 0.1780 (5) | 0.3665 (3) | −0.0748 (7) | 0.0153 (9) | |
| C6 | 0.1933 (5) | 0.4118 (3) | 0.1439 (7) | 0.0150 (9) | |
| H6 | 0.1023 | 0.4281 | 0.1944 | 0.018* | |
| N7 | 0.3299 (4) | 0.4335 (2) | 0.2865 (6) | 0.0153 (7) | |
| C7 | 0.4494 (5) | 0.3572 (3) | −0.0129 (7) | 0.0148 (9) | |
| C8 | 0.4527 (5) | 0.4061 (3) | 0.2052 (7) | 0.0150 (9) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Br1 | 0.0135 (3) | 0.0203 (3) | 0.0197 (3) | 0.00003 (15) | −0.00191 (18) | −0.00174 (16) |
| N1 | 0.0141 (19) | 0.0143 (16) | 0.0167 (18) | −0.0019 (13) | 0.0034 (15) | −0.0021 (14) |
| C2 | 0.011 (2) | 0.015 (2) | 0.025 (2) | 0.0024 (16) | 0.0054 (18) | 0.0023 (18) |
| C3 | 0.015 (2) | 0.013 (2) | 0.018 (2) | 0.0006 (15) | 0.0045 (17) | 0.0006 (16) |
| C4 | 0.018 (2) | 0.010 (2) | 0.015 (2) | −0.0014 (15) | 0.0040 (18) | 0.0003 (15) |
| C5 | 0.017 (2) | 0.010 (2) | 0.018 (2) | −0.0010 (15) | 0.0015 (18) | 0.0021 (15) |
| C6 | 0.014 (2) | 0.010 (2) | 0.022 (2) | 0.0001 (15) | 0.0050 (17) | 0.0028 (16) |
| N7 | 0.0166 (18) | 0.0121 (16) | 0.0179 (18) | −0.0007 (13) | 0.0057 (15) | −0.0016 (14) |
| C7 | 0.021 (2) | 0.0087 (19) | 0.016 (2) | 0.0007 (15) | 0.0063 (18) | 0.0006 (15) |
| C8 | 0.014 (2) | 0.010 (2) | 0.021 (2) | −0.0002 (15) | 0.0032 (17) | 0.0033 (16) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| Br1—C5 | 1.902 (4) | C4—C5 | 1.385 (6) |
| N1—C8 | 1.367 (6) | C4—C7 | 1.389 (6) |
| N1—C2 | 1.383 (5) | C4—H4 | 0.9500 |
| N1—H1 | 0.8800 | C5—C6 | 1.390 (6) |
| C2—C3 | 1.361 (6) | C6—N7 | 1.337 (5) |
| C2—H2 | 0.9500 | C6—H6 | 0.9500 |
| C3—C7 | 1.418 (6) | N7—C8 | 1.339 (5) |
| C3—H3 | 0.9500 | C7—C8 | 1.425 (6) |
| C8—N1—C2 | 107.6 (4) | C4—C5—Br1 | 119.2 (3) |
| C8—N1—H1 | 126.2 | C6—C5—Br1 | 119.0 (3) |
| C2—N1—H1 | 126.2 | N7—C6—C5 | 123.1 (4) |
| C3—C2—N1 | 110.6 (4) | N7—C6—H6 | 118.4 |
| C3—C2—H2 | 124.7 | C5—C6—H6 | 118.4 |
| N1—C2—H2 | 124.7 | C6—N7—C8 | 114.9 (3) |
| C2—C3—C7 | 107.0 (4) | C4—C7—C3 | 136.6 (4) |
| C2—C3—H3 | 126.5 | C4—C7—C8 | 116.9 (4) |
| C7—C3—H3 | 126.5 | C3—C7—C8 | 106.4 (4) |
| C5—C4—C7 | 116.9 (4) | N7—C8—N1 | 125.4 (4) |
| C5—C4—H4 | 121.5 | N7—C8—C7 | 126.3 (4) |
| C7—C4—H4 | 121.5 | N1—C8—C7 | 108.3 (4) |
| C4—C5—C6 | 121.8 (4) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N1—H1···N7i | 0.88 | 2.12 | 2.960 (5) | 159 |
| C4—H4···C4ii | 0.95 | 2.82 | 3.738 (6) | 162 |
| C4—H4···C5ii | 0.95 | 2.84 | 3.656 (6) | 144 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, −y+1, −z+1; (ii) x, −y+1/2, z−1/2.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: TK5196).
References
- Brandenburg, K. (2011). DIAMOND Crystal Impact GbR, Bonn, Germany.
- Chou, P. T., Liao, J. H., Wei, C. Y., Yang, C. Y., Yu, W. S. & Chou, Y. H. (2000). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 122, 986–987.
- Dufour, P., Dartiguenave, Y., Dartiguenave, M., Dufour, N., Lebuis, A. M., Belanger-Gariepy, F. & Beauchamp, A. L. (1990). Can. J. Chem. 68, 193–202.
- Oxford Diffraction (2009). CrysAlis CCD and CrysAlis RED Oxford Diffraction Ltd, Yarnton, England.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Štarha, P., Trávníček, Z., Popa, A., Popa, I., Muchová, T. & Brabec, V. (2012). J. Inorg. Biochem. 115, 57–63. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Westrip, S. P. (2010). J. Appl. Cryst. 43, 920–925.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536813004157/tk5196sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536813004157/tk5196Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536813004157/tk5196Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report