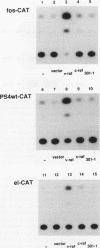
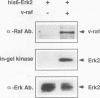
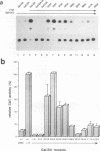
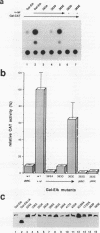
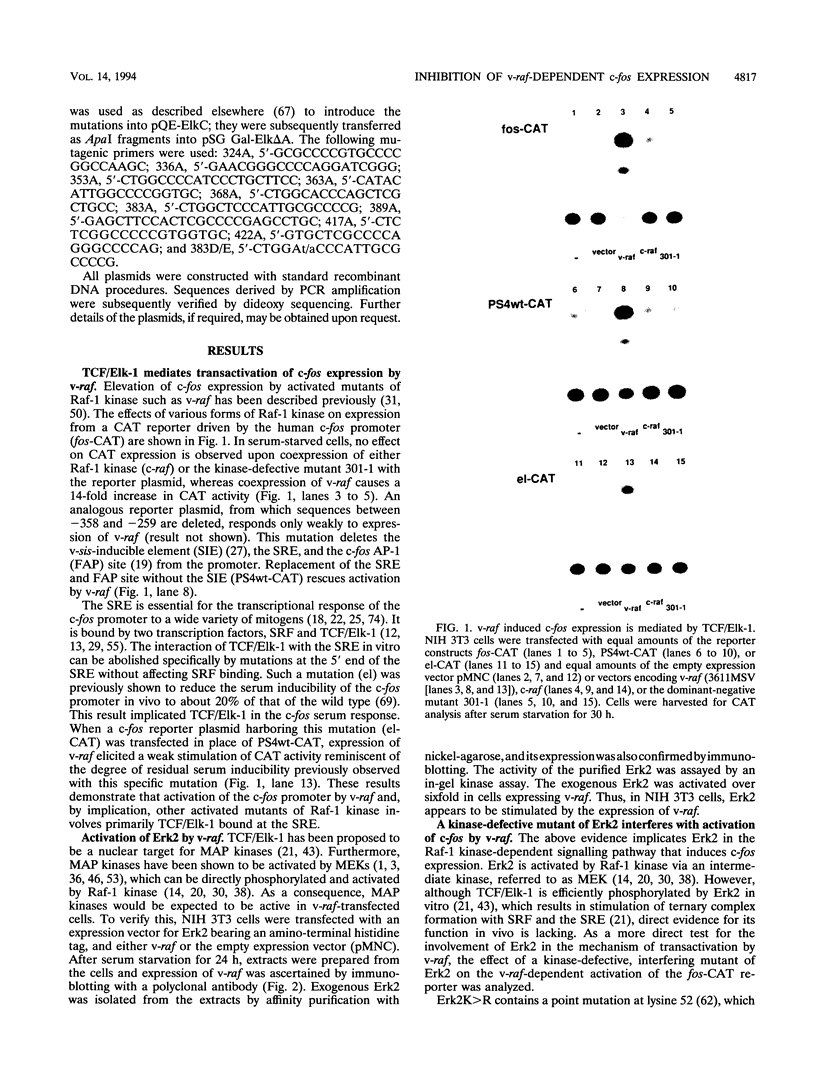
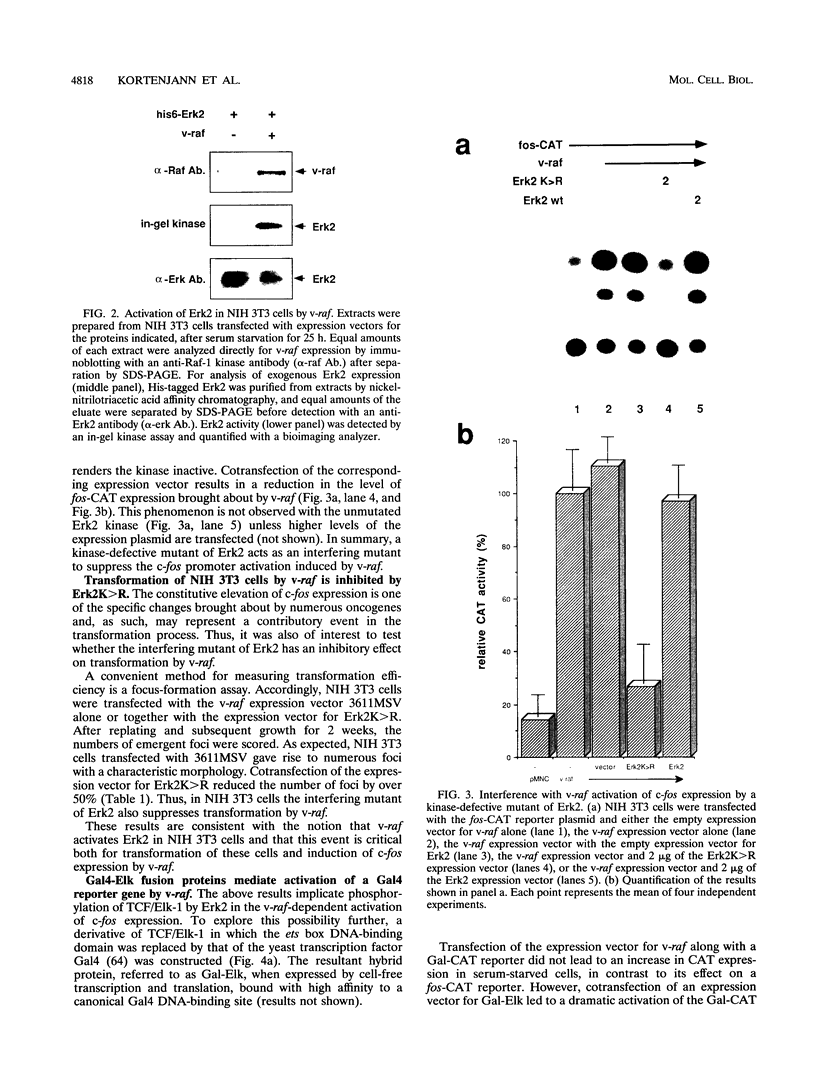
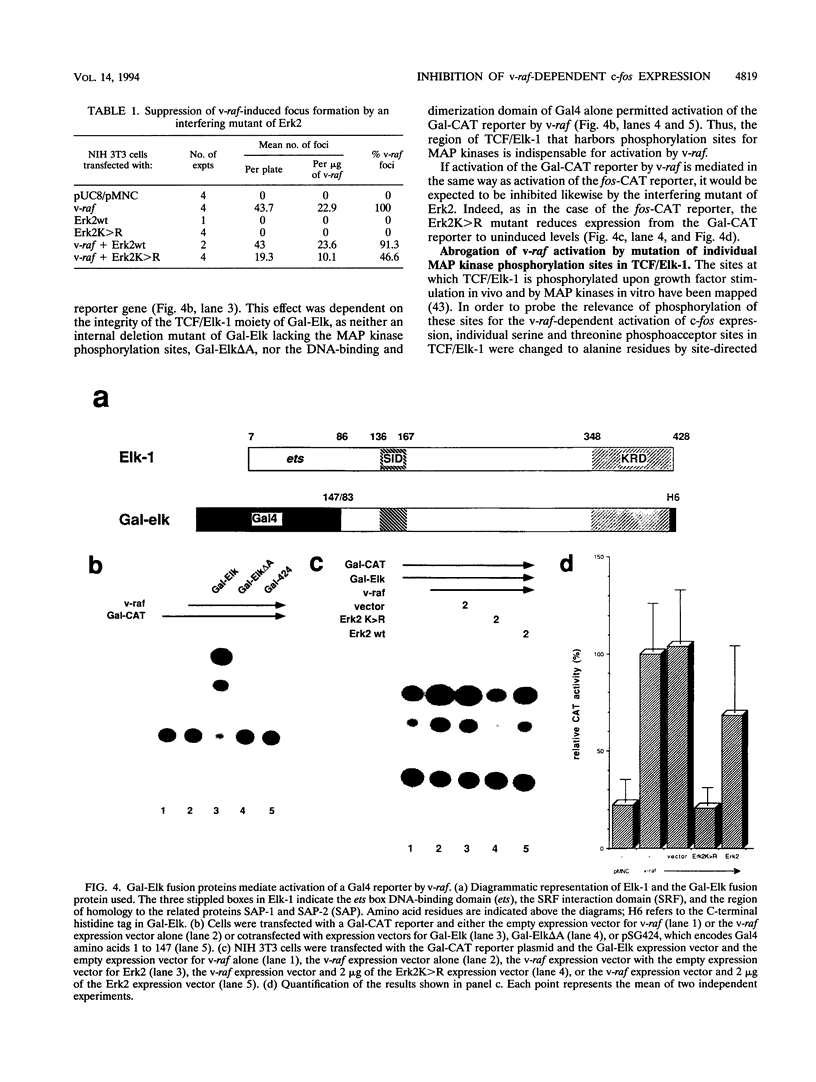
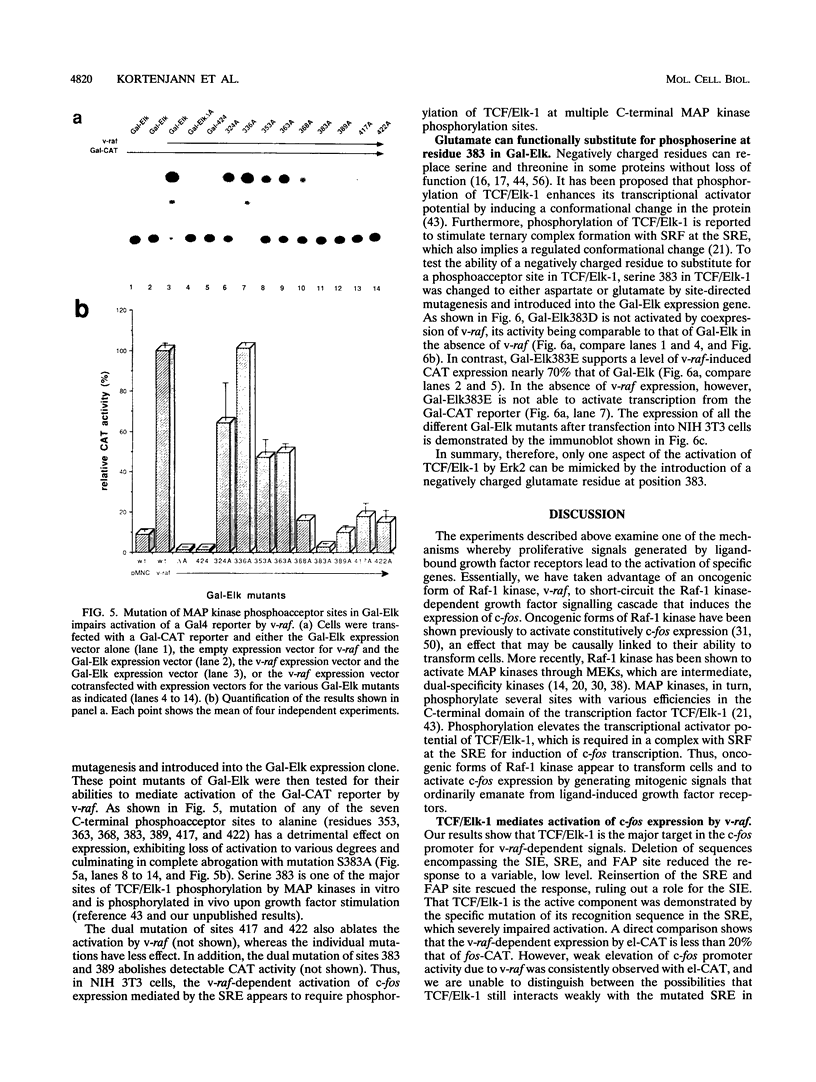
Abstract
Receptor-bound growth factors elicit intracellular signals that lead to the phosphorylation and activation of numerous intracellular kinases and transcription factors with consequent changes in patterns of gene expression. Several oncogene products are able to mimic these signals, resulting in cell transformation and proliferation. For example, the introduction of oncogenic forms of Raf-1 kinase into fibroblasts induces transformation and leads to the constitutive expression of, among others, the c-fos proto-oncogene. Here it is shown that the elevation of c-fos promoter activity brought about by v-raf is mediated by TCF/Elk-1, which forms a ternary complex with SRF at the serum response element and is a substrate for mitogen-activating protein kinases in vitro. In NIH 3T3 fibroblasts, v-raf activates Erk2, and overexpression of an interfering mutant of Erk2 both blocks the ability of v-raf to activate the c-fos promoter and suppresses transformation. Mutation of individual mitogen-activating protein kinase phosphoacceptor sites in TCF/Elk-1 also compromises v-raf-activated expression of a Gal-Elk/Gal-chloramphenicol acetyltransferase reporter system. However, in at least one instance the introduction of glutamate, but not aspartate, at a phosphoacceptor site is compatible with activation. These results provide compelling evidence that phosphorylation of TCF/Elk-1 by Erk2 is a major link in the Raf-1 kinase-dependent signal transduction pathway that activates c-fos expression.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams P. D., Parker P. J. Activation of mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase by a MAP kinase-kinase. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 5;267(19):13135–13137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahn N. G., Seger R., Krebs E. G. The mitogen-activated protein kinase activator. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;4(6):992–999. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(92)90131-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alessandrini A., Crews C. M., Erikson R. L. Phorbol ester stimulates a protein-tyrosine/threonine kinase that phosphorylates and activates the Erk-1 gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 1;89(17):8200–8204. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.17.8200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson S., Davis D. L., Dahlbäck H., Jörnvall H., Russell D. W. Cloning, structure, and expression of the mitochondrial cytochrome P-450 sterol 26-hydroxylase, a bile acid biosynthetic enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 15;264(14):8222–8229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. M. Molecular themes in oncogenesis. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):235–248. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90636-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulton T. G., Nye S. H., Robbins D. J., Ip N. Y., Radziejewska E., Morgenbesser S. D., DePinho R. A., Panayotatos N., Cobb M. H., Yancopoulos G. D. ERKs: a family of protein-serine/threonine kinases that are activated and tyrosine phosphorylated in response to insulin and NGF. Cell. 1991 May 17;65(4):663–675. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90098-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buday L., Downward J. Epidermal growth factor regulates p21ras through the formation of a complex of receptor, Grb2 adapter protein, and Sos nucleotide exchange factor. Cell. 1993 May 7;73(3):611–620. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90146-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cadena D. L., Gill G. N. Receptor tyrosine kinases. FASEB J. 1992 Mar;6(6):2332–2337. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.6.6.1312047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chardin P., Camonis J. H., Gale N. W., van Aelst L., Schlessinger J., Wigler M. H., Bar-Sagi D. Human Sos1: a guanine nucleotide exchange factor for Ras that binds to GRB2. Science. 1993 May 28;260(5112):1338–1343. doi: 10.1126/science.8493579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen D. R., Curran T. The structure and function of the fos proto-oncogene. Crit Rev Oncog. 1989;1(1):65–88. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran T., Franza B. R., Jr Fos and Jun: the AP-1 connection. Cell. 1988 Nov 4;55(3):395–397. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90024-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalton S., Marais R., Wynne J., Treisman R. Isolation and characterization of SRF accessory proteins. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1993 Jun 29;340(1293):325–332. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1993.0074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalton S., Treisman R. Characterization of SAP-1, a protein recruited by serum response factor to the c-fos serum response element. Cell. 1992 Feb 7;68(3):597–612. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90194-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dent P., Haser W., Haystead T. A., Vincent L. A., Roberts T. M., Sturgill T. W. Activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase by v-Raf in NIH 3T3 cells and in vitro. Science. 1992 Sep 4;257(5075):1404–1407. doi: 10.1126/science.1326789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dony C., Gruss P. Proto-oncogene c-fos expression in growth regions of fetal bone and mesodermal web tissue. Nature. 1987 Aug 20;328(6132):711–714. doi: 10.1038/328711a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari S., Pearson R. B., Siegmann M., Kozma S. C., Thomas G. The immunosuppressant rapamycin induces inactivation of p70s6k through dephosphorylation of a novel set of sites. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 5;268(22):16091–16094. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firzlaff J. M., Lüscher B., Eisenman R. N. Negative charge at the casein kinase II phosphorylation site is important for transformation but not for Rb protein binding by the E7 protein of human papillomavirus type 16. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 15;88(12):5187–5191. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.12.5187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisch T. M., Prywes R., Roeder R. G. c-fos sequence necessary for basal expression and induction by epidermal growth factor, 12-O-tetradecanoyl phorbol-13-acetate and the calcium ionophore. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;7(10):3490–3502. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisch T. M., Prywes R., Simon M. C., Roeder R. G. Multiple sequence elements in the c-fos promoter mediate induction by cAMP. Genes Dev. 1989 Feb;3(2):198–211. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.2.198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallego C., Gupta S. K., Heasley L. E., Qian N. X., Johnson G. L. Mitogen-activated protein kinase activation resulting from selective oncogene expression in NIH 3T3 and rat 1a cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7355–7359. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gille H., Sharrocks A. D., Shaw P. E. Phosphorylation of transcription factor p62TCF by MAP kinase stimulates ternary complex formation at c-fos promoter. Nature. 1992 Jul 30;358(6385):414–417. doi: 10.1038/358414a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman M. Z. The c-fos serum response element responds to protein kinase C-dependent and -independent signals but not to cyclic AMP. Genes Dev. 1988 Apr;2(4):394–402. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.4.394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez F. A., Seth A., Raden D. L., Bowman D. S., Fay F. S., Davis R. J. Serum-induced translocation of mitogen-activated protein kinase to the cell surface ruffling membrane and the nucleus. J Cell Biol. 1993 Sep;122(5):1089–1101. doi: 10.1083/jcb.122.5.1089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotoh Y., Nishida E., Yamashita T., Hoshi M., Kawakami M., Sakai H. Microtubule-associated-protein (MAP) kinase activated by nerve growth factor and epidermal growth factor in PC12 cells. Identity with the mitogen-activated MAP kinase of fibroblastic cells. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Nov 13;193(3):661–669. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19384.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. E., Siegfried Z., Ziff E. B. Mutation of the c-fos gene dyad symmetry element inhibits serum inducibility of transcription in vivo and the nuclear regulatory factor binding in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;7(3):1217–1225. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.3.1217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. E., Ziff E. B. Stimulation of 3T3 cells induces transcription of the c-fos proto-oncogene. Nature. 1984 Oct 4;311(5985):433–438. doi: 10.1038/311433a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes T. E., Kitchen A. M., Cochran B. H. Inducible binding of a factor to the c-fos regulatory region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(5):1272–1276. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.5.1272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill C. S., Marais R., John S., Wynne J., Dalton S., Treisman R. Functional analysis of a growth factor-responsive transcription factor complex. Cell. 1993 Apr 23;73(2):395–406. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90238-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hipskind R. A., Rao V. N., Mueller C. G., Reddy E. S., Nordheim A. Ets-related protein Elk-1 is homologous to the c-fos regulatory factor p62TCF. Nature. 1991 Dec 19;354(6354):531–534. doi: 10.1038/354531a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe L. R., Leevers S. J., Gómez N., Nakielny S., Cohen P., Marshall C. J. Activation of the MAP kinase pathway by the protein kinase raf. Cell. 1992 Oct 16;71(2):335–342. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90361-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jamal S., Ziff E. Transactivation of c-fos and beta-actin genes by raf as a step in early response to transmembrane signals. Nature. 1990 Mar 29;344(6265):463–466. doi: 10.1038/344463a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. S., Spiegelman B. M., Papaioannou V. Pleiotropic effects of a null mutation in the c-fos proto-oncogene. Cell. 1992 Nov 13;71(4):577–586. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90592-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kameshita I., Fujisawa H. A sensitive method for detection of calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II activity in sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel. Anal Biochem. 1989 Nov 15;183(1):139–143. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(89)90181-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolch W., Heidecker G., Kochs G., Hummel R., Vahidi H., Mischak H., Finkenzeller G., Marmé D., Rapp U. R. Protein kinase C alpha activates RAF-1 by direct phosphorylation. Nature. 1993 Jul 15;364(6434):249–252. doi: 10.1038/364249a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolch W., Heidecker G., Lloyd P., Rapp U. R. Raf-1 protein kinase is required for growth of induced NIH/3T3 cells. Nature. 1991 Jan 31;349(6308):426–428. doi: 10.1038/349426a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosako H., Gotoh Y., Matsuda S., Ishikawa M., Nishida E. Xenopus MAP kinase activator is a serine/threonine/tyrosine kinase activated by threonine phosphorylation. EMBO J. 1992 Aug;11(8):2903–2908. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05359.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruijer W., Cooper J. A., Hunter T., Verma I. M. Platelet-derived growth factor induces rapid but transient expression of the c-fos gene and protein. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):711–716. doi: 10.1038/312711a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyriakis J. M., App H., Zhang X. F., Banerjee P., Brautigan D. L., Rapp U. R., Avruch J. Raf-1 activates MAP kinase-kinase. Nature. 1992 Jul 30;358(6385):417–421. doi: 10.1038/358417a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange-Carter C. A., Pleiman C. M., Gardner A. M., Blumer K. J., Johnson G. L. A divergence in the MAP kinase regulatory network defined by MEK kinase and Raf. Science. 1993 Apr 16;260(5106):315–319. doi: 10.1126/science.8385802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li N., Batzer A., Daly R., Yajnik V., Skolnik E., Chardin P., Bar-Sagi D., Margolis B., Schlessinger J. Guanine-nucleotide-releasing factor hSos1 binds to Grb2 and links receptor tyrosine kinases to Ras signalling. Nature. 1993 May 6;363(6424):85–88. doi: 10.1038/363085a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lillie J. W., Green M. R. Transcription activation by the adenovirus E1a protein. Nature. 1989 Mar 2;338(6210):39–44. doi: 10.1038/338039a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowenstein E. J., Daly R. J., Batzer A. G., Li W., Margolis B., Lammers R., Ullrich A., Skolnik E. Y., Bar-Sagi D., Schlessinger J. The SH2 and SH3 domain-containing protein GRB2 links receptor tyrosine kinases to ras signaling. Cell. 1992 Aug 7;70(3):431–442. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90167-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marais R., Wynne J., Treisman R. The SRF accessory protein Elk-1 contains a growth factor-regulated transcriptional activation domain. Cell. 1993 Apr 23;73(2):381–393. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90237-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus F., Rittenhouse J., Moberly L., Edelstein I., Hiller E., Rogers D. T. Yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase. Properties of phospho and dephospho forms and of two mutants in which serine 11 has been changed by site-directed mutagenesis. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 5;263(13):6058–6062. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis B., Rhee S. G., Felder S., Mervic M., Lyall R., Levitzki A., Ullrich A., Zilberstein A., Schlessinger J. EGF induces tyrosine phosphorylation of phospholipase C-II: a potential mechanism for EGF receptor signaling. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1101–1107. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90047-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda S., Kosako H., Takenaka K., Moriyama K., Sakai H., Akiyama T., Gotoh Y., Nishida E. Xenopus MAP kinase activator: identification and function as a key intermediate in the phosphorylation cascade. EMBO J. 1992 Mar;11(3):973–982. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05136.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meisenhelder J., Suh P. G., Rhee S. G., Hunter T. Phospholipase C-gamma is a substrate for the PDGF and EGF receptor protein-tyrosine kinases in vivo and in vitro. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1109–1122. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90048-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moodie S. A., Willumsen B. M., Weber M. J., Wolfman A. Complexes of Ras.GTP with Raf-1 and mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase. Science. 1993 Jun 11;260(5114):1658–1661. doi: 10.1126/science.8503013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan J. I., Curran T. Role of ion flux in the control of c-fos expression. Nature. 1986 Aug 7;322(6079):552–555. doi: 10.1038/322552a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. K., Kaplan D. R., Escobedo J. A., Rapp U. R., Roberts T. M., Williams L. T. Direct activation of the serine/threonine kinase activity of Raf-1 through tyrosine phosphorylation by the PDGF beta-receptor. Cell. 1989 Aug 25;58(4):649–657. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90100-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller C. G., Nordheim A. A protein domain conserved between yeast MCM1 and human SRF directs ternary complex formation. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(13):4219–4229. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb05000.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller R., Bravo R., Burckhardt J., Curran T. Induction of c-fos gene and protein by growth factors precedes activation of c-myc. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):716–720. doi: 10.1038/312716a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakielny S., Cohen P., Wu J., Sturgill T. MAP kinase activator from insulin-stimulated skeletal muscle is a protein threonine/tyrosine kinase. EMBO J. 1992 Jun;11(6):2123–2129. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05271.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishida E., Gotoh Y. The MAP kinase cascade is essential for diverse signal transduction pathways. Trends Biochem Sci. 1993 Apr;18(4):128–131. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(93)90019-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norman C., Runswick M., Pollock R., Treisman R. Isolation and properties of cDNA clones encoding SRF, a transcription factor that binds to the c-fos serum response element. Cell. 1988 Dec 23;55(6):989–1003. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90244-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ofir R., Dwarki V. J., Rashid D., Verma I. M. Phosphorylation of the C terminus of Fos protein is required for transcriptional transrepression of the c-fos promoter. Nature. 1990 Nov 1;348(6296):80–82. doi: 10.1038/348080a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panayotou G., Waterfield M. D. The assembly of signalling complexes by receptor tyrosine kinases. Bioessays. 1993 Mar;15(3):171–177. doi: 10.1002/bies.950150305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawson T., Schlessingert J. SH2 and SH3 domains. Curr Biol. 1993 Jul 1;3(7):434–442. doi: 10.1016/0960-9822(93)90350-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelech S. L., Sanghera J. S. Mitogen-activated protein kinases: versatile transducers for cell signaling. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Jun;17(6):233–238. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0004(00)80005-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelicci G., Lanfrancone L., Grignani F., McGlade J., Cavallo F., Forni G., Nicoletti I., Grignani F., Pawson T., Pelicci P. G. A novel transforming protein (SHC) with an SH2 domain is implicated in mitogenic signal transduction. Cell. 1992 Jul 10;70(1):93–104. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90536-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapp U. R., Goldsborough M. D., Mark G. E., Bonner T. I., Groffen J., Reynolds F. H., Jr, Stephenson J. R. Structure and biological activity of v-raf, a unique oncogene transduced by a retrovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4218–4222. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins D. J., Zhen E., Owaki H., Vanderbilt C. A., Ebert D., Geppert T. D., Cobb M. H. Regulation and properties of extracellular signal-regulated protein kinases 1 and 2 in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 5;268(7):5097–5106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rüther U., Garber C., Komitowski D., Müller R., Wagner E. F. Deregulated c-fos expression interferes with normal bone development in transgenic mice. 1987 Jan 29-Feb 4Nature. 325(6103):412–416. doi: 10.1038/325412a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadowski I., Ptashne M. A vector for expressing GAL4(1-147) fusions in mammalian cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Sep 25;17(18):7539–7539. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.18.7539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlessinger J., Ullrich A. Growth factor signaling by receptor tyrosine kinases. Neuron. 1992 Sep;9(3):383–391. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90177-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröter H., Mueller C. G., Meese K., Nordheim A. Synergism in ternary complex formation between the dimeric glycoprotein p67SRF, polypeptide p62TCF and the c-fos serum response element. EMBO J. 1990 Apr;9(4):1123–1130. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08218.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharrocks A. D., Shaw P. E. Improved primer design for PCR-based, site-directed mutagenesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Mar 11;20(5):1147–1147. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.5.1147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw P. E., Schröter H., Nordheim A. The ability of a ternary complex to form over the serum response element correlates with serum inducibility of the human c-fos promoter. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):563–572. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90579-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw P. E. Ternary complex formation over the c-fos serum response element: p62TCF exhibits dual component specificity with contacts to DNA and an extended structure in the DNA-binding domain of p67SRF. EMBO J. 1992 Aug;11(8):3011–3019. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05371.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki M. SPXX, a frequent sequence motif in gene regulatory proteins. J Mol Biol. 1989 May 5;207(1):61–84. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90441-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sözeri O., Vollmer K., Liyanage M., Frith D., Kour G., Mark G. E., 3rd, Stabel S. Activation of the c-Raf protein kinase by protein kinase C phosphorylation. Oncogene. 1992 Nov;7(11):2259–2262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R. Identification of a protein-binding site that mediates transcriptional response of the c-fos gene to serum factors. Cell. 1986 Aug 15;46(4):567–574. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90882-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R. The SRE: a growth factor responsive transcriptional regulator. Semin Cancer Biol. 1990 Feb;1(1):47–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R. Transient accumulation of c-fos RNA following serum stimulation requires a conserved 5' element and c-fos 3' sequences. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):889–902. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90285-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner B. J., Hayes T. E., Hoban C. J., Cochran B. H. The SIF binding element confers sis/PDGF inducibility onto the c-fos promoter. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(13):4477–4484. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07898.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Z. Q., Ovitt C., Grigoriadis A. E., Möhle-Steinlein U., Rüther U., Wagner E. F. Bone and haematopoietic defects in mice lacking c-fos. Nature. 1992 Dec 24;360(6406):741–745. doi: 10.1038/360741a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warne P. H., Viciana P. R., Downward J. Direct interaction of Ras and the amino-terminal region of Raf-1 in vitro. Nature. 1993 Jul 22;364(6435):352–355. doi: 10.1038/364352a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilmot C. M., Thornton J. M. Analysis and prediction of the different types of beta-turn in proteins. J Mol Biol. 1988 Sep 5;203(1):221–232. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90103-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood K. W., Sarnecki C., Roberts T. M., Blenis J. ras mediates nerve growth factor receptor modulation of three signal-transducing protein kinases: MAP kinase, Raf-1, and RSK. Cell. 1992 Mar 20;68(6):1041–1050. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90076-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X. F., Settleman J., Kyriakis J. M., Takeuchi-Suzuki E., Elledge S. J., Marshall M. S., Bruder J. T., Rapp U. R., Avruch J. Normal and oncogenic p21ras proteins bind to the amino-terminal regulatory domain of c-Raf-1. Nature. 1993 Jul 22;364(6435):308–313. doi: 10.1038/364308a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]