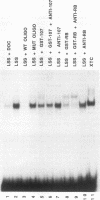
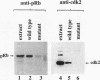
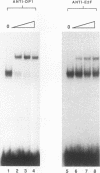
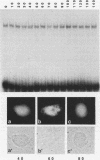
Abstract
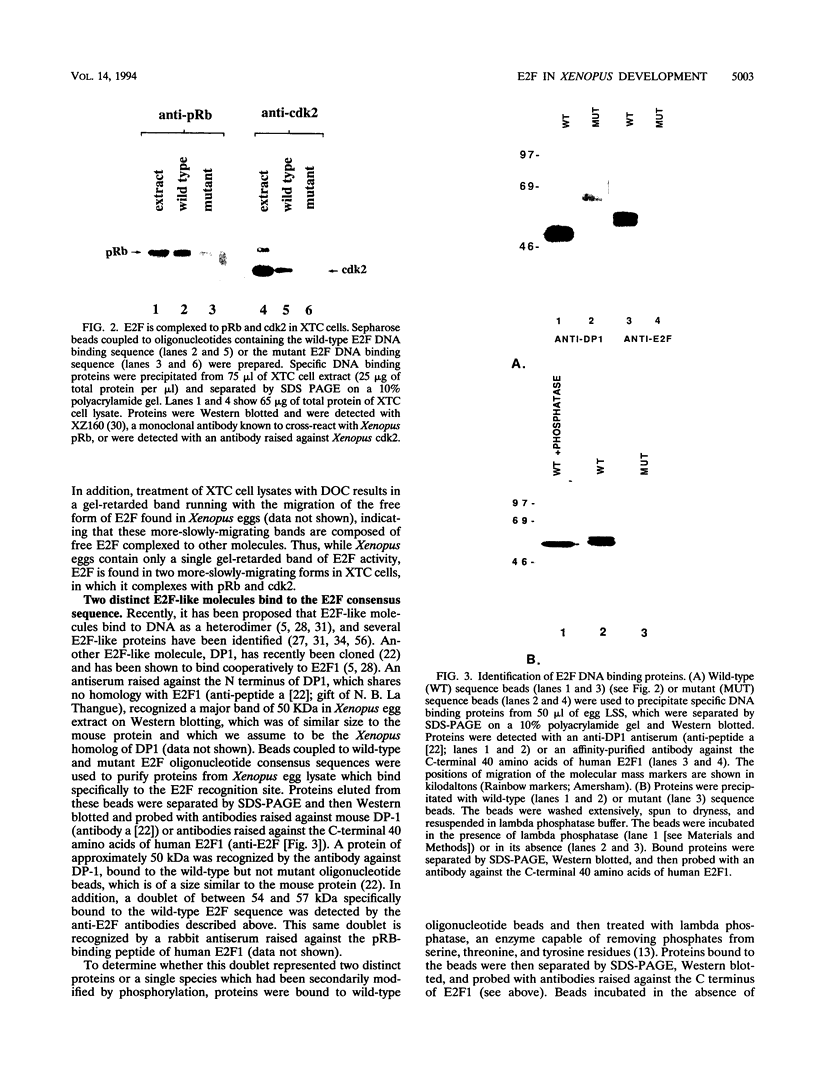
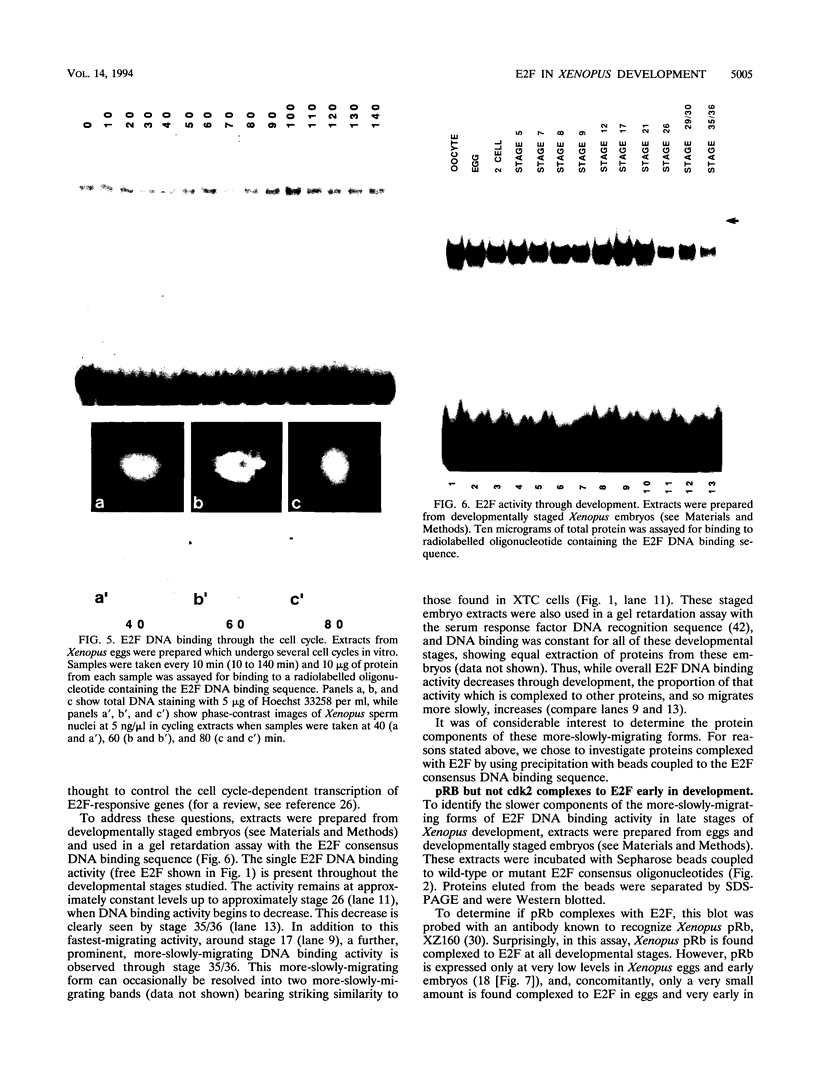
The transcription factor E2F has been implicated in cell cycle control by virtue of its association with cyclins, cyclin-dependent kinases, and pRb-related tumor suppressor gene products. Eggs and embryos from the frog Xenopus laevis have been used to investigate the characteristics of E2F-like molecules in the Xenopus cell cycle and throughout early development. We find multiple E2F species in Xenopus eggs, at least one of which is modified by phosphorylation. The vast majority of E2F remains in the free form throughout the very early embryonic cell cycle, and it also remains predominantly free until some time after the mid-blastula transition, the onset of zygotic transcription. At this time, E2F complexes significantly to pRb but not to cdk2, although cdk2 binding is found in tissue culture cells from a very advanced stage in embryogenesis. This suggests that the complexing of E2F to cyclins, cyclin-dependent kinases, and tumor suppressor gene products may be controlled separately in early Xenopus development. Thus, the association of E2F with other molecules may not result solely from processes affecting cell cycle progression but may also reflect developmental and differentiation cues.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baeuerle P. A., Baltimore D. Activation of DNA-binding activity in an apparently cytoplasmic precursor of the NF-kappa B transcription factor. Cell. 1988 Apr 22;53(2):211–217. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90382-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagchi S., Raychaudhuri P., Nevins J. R. Adenovirus E1A proteins can dissociate heteromeric complexes involving the E2F transcription factor: a novel mechanism for E1A trans-activation. Cell. 1990 Aug 24;62(4):659–669. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90112-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagchi S., Weinmann R., Raychaudhuri P. The retinoblastoma protein copurifies with E2F-I, an E1A-regulated inhibitor of the transcription factor E2F. Cell. 1991 Jun 14;65(6):1063–1072. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90558-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bandara L. R., Adamczewski J. P., Hunt T., La Thangue N. B. Cyclin A and the retinoblastoma gene product complex with a common transcription factor. Nature. 1991 Jul 18;352(6332):249–251. doi: 10.1038/352249a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bandara L. R., Buck V. M., Zamanian M., Johnston L. H., La Thangue N. B. Functional synergy between DP-1 and E2F-1 in the cell cycle-regulating transcription factor DRTF1/E2F. EMBO J. 1993 Nov;12(11):4317–4324. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06116.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blow J. J., Laskey R. A. Initiation of DNA replication in nuclei and purified DNA by a cell-free extract of Xenopus eggs. Cell. 1986 Nov 21;47(4):577–587. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90622-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchkovich K., Duffy L. A., Harlow E. The retinoblastoma protein is phosphorylated during specific phases of the cell cycle. Cell. 1989 Sep 22;58(6):1097–1105. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90508-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cao L., Faha B., Dembski M., Tsai L. H., Harlow E., Dyson N. Independent binding of the retinoblastoma protein and p107 to the transcription factor E2F. Nature. 1992 Jan 9;355(6356):176–179. doi: 10.1038/355176a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chellappan S. P., Hiebert S., Mudryj M., Horowitz J. M., Nevins J. R. The E2F transcription factor is a cellular target for the RB protein. Cell. 1991 Jun 14;65(6):1053–1061. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90557-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chittenden T., Livingston D. M., Kaelin W. G., Jr The T/E1A-binding domain of the retinoblastoma product can interact selectively with a sequence-specific DNA-binding protein. Cell. 1991 Jun 14;65(6):1073–1082. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90559-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobrinik D., Whyte P., Peeper D. S., Jacks T., Weinberg R. A. Cell cycle-specific association of E2F with the p130 E1A-binding protein. Genes Dev. 1993 Dec;7(12A):2392–2404. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.12a.2392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. T., Cohen P. Discovery of a protein phosphatase activity encoded in the genome of bacteriophage lambda. Probable identity with open reading frame 221. Biochem J. 1989 Jun 15;260(3):931–934. doi: 10.1042/bj2600931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Whyte P. RB and the cell cycle: entrance or exit? Cell. 1989 Sep 22;58(6):1009–1011. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90495-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalton S. Cell cycle regulation of the human cdc2 gene. EMBO J. 1992 May;11(5):1797–1804. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05231.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeCaprio J. A., Ludlow J. W., Lynch D., Furukawa Y., Griffin J., Piwnica-Worms H., Huang C. M., Livingston D. M. The product of the retinoblastoma susceptibility gene has properties of a cell cycle regulatory element. Cell. 1989 Sep 22;58(6):1085–1095. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90507-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DePamphilis M. L. Transcriptional elements as components of eukaryotic origins of DNA replication. Cell. 1988 Mar 11;52(5):635–638. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90398-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Destrée O. H., Lam K. T., Peterson-Maduro L. J., Eizema K., Diller L., Gryka M. A., Frebourg T., Shibuya E., Friend S. H. Structure and expression of the Xenopus retinoblastoma gene. Dev Biol. 1992 Sep;153(1):141–149. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(92)90098-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devoto S. H., Mudryj M., Pines J., Hunter T., Nevins J. R. A cyclin A-protein kinase complex possesses sequence-specific DNA binding activity: p33cdk2 is a component of the E2F-cyclin A complex. Cell. 1992 Jan 10;68(1):167–176. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90215-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewen M. E., Faha B., Harlow E., Livingston D. M. Interaction of p107 with cyclin A independent of complex formation with viral oncoproteins. Science. 1992 Jan 3;255(5040):85–87. doi: 10.1126/science.1532457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fang F., Newport J. W. Evidence that the G1-S and G2-M transitions are controlled by different cdc2 proteins in higher eukaryotes. Cell. 1991 Aug 23;66(4):731–742. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90117-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girling R., Partridge J. F., Bandara L. R., Burden N., Totty N. F., Hsuan J. J., La Thangue N. B. A new component of the transcription factor DRTF1/E2F. Nature. 1993 Mar 4;362(6415):83–87. doi: 10.1038/362083a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamel P. A., Gill R. M., Phillips R. A., Gallie B. L. Transcriptional repression of the E2-containing promoters EIIaE, c-myc, and RB1 by the product of the RB1 gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;12(8):3431–3438. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.8.3431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heintz N. H., Dailey L., Held P., Heintz N. Eukaryotic replication origins as promoters of bidirectional DNA synthesis. Trends Genet. 1992 Nov;8(11):376–381. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(92)90298-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helin K., Ed H. The retinoblastoma protein as a transcriptional repressor. Trends Cell Biol. 1993 Feb;3(2):43–46. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(93)90150-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helin K., Lees J. A., Vidal M., Dyson N., Harlow E., Fattaey A. A cDNA encoding a pRB-binding protein with properties of the transcription factor E2F. Cell. 1992 Jul 24;70(2):337–350. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90107-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helin K., Wu C. L., Fattaey A. R., Lees J. A., Dynlacht B. D., Ngwu C., Harlow E. Heterodimerization of the transcription factors E2F-1 and DP-1 leads to cooperative trans-activation. Genes Dev. 1993 Oct;7(10):1850–1861. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.10.1850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiebert S. W., Chellappan S. P., Horowitz J. M., Nevins J. R. The interaction of RB with E2F coincides with an inhibition of the transcriptional activity of E2F. Genes Dev. 1992 Feb;6(2):177–185. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.2.177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu Q. J., Bautista C., Edwards G. M., Defeo-Jones D., Jones R. E., Harlow E. Antibodies specific for the human retinoblastoma protein identify a family of related polypeptides. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;11(11):5792–5799. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.11.5792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber H. E., Edwards G., Goodhart P. J., Patrick D. R., Huang P. S., Ivey-Hoyle M., Barnett S. F., Oliff A., Heimbrook D. C. Transcription factor E2F binds DNA as a heterodimer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3525–3529. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivey-Hoyle M., Conroy R., Huber H. E., Goodhart P. J., Oliff A., Heimbrook D. C. Cloning and characterization of E2F-2, a novel protein with the biochemical properties of transcription factor E2F. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Dec;13(12):7802–7812. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.12.7802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. G., Schwarz J. K., Cress W. D., Nevins J. R. Expression of transcription factor E2F1 induces quiescent cells to enter S phase. Nature. 1993 Sep 23;365(6444):349–352. doi: 10.1038/365349a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaelin W. G., Jr, Krek W., Sellers W. R., DeCaprio J. A., Ajchenbaum F., Fuchs C. S., Chittenden T., Li Y., Farnham P. J., Blanar M. A. Expression cloning of a cDNA encoding a retinoblastoma-binding protein with E2F-like properties. Cell. 1992 Jul 24;70(2):351–364. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90108-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaelin W. G., Jr, Pallas D. C., DeCaprio J. A., Kaye F. J., Livingston D. M. Identification of cellular proteins that can interact specifically with the T/E1A-binding region of the retinoblastoma gene product. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):521–532. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90236-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimelman D., Kirschner M., Scherson T. The events of the midblastula transition in Xenopus are regulated by changes in the cell cycle. Cell. 1987 Feb 13;48(3):399–407. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90191-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovesdi I., Reichel R., Nevins J. R. Identification of a cellular transcription factor involved in E1A trans-activation. Cell. 1986 Apr 25;45(2):219–228. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90386-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Thangue N. B., Rigby P. W. An adenovirus E1A-like transcription factor is regulated during the differentiation of murine embryonal carcinoma stem cells. Cell. 1987 May 22;49(4):507–513. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90453-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Thangue N. B., Thimmappaya B., Rigby P. W. The embryonal carcinoma stem cell Ela-like activity involves a differentiation-regulated transcription factor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 May 25;18(10):2929–2938. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.10.2929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lees E., Faha B., Dulic V., Reed S. I., Harlow E. Cyclin E/cdk2 and cyclin A/cdk2 kinases associate with p107 and E2F in a temporally distinct manner. Genes Dev. 1992 Oct;6(10):1874–1885. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.10.1874. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lees J. A., Saito M., Vidal M., Valentine M., Look T., Harlow E., Dyson N., Helin K. The retinoblastoma protein binds to a family of E2F transcription factors. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Dec;13(12):7813–7825. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.12.7813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohun T. J., Garrett N., Taylor M. V. Temporal and tissue-specific expression of the proto-oncogene c-fos during development in Xenopus laevis. Development. 1989 Dec;107(4):835–846. doi: 10.1242/dev.107.4.835. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mudryj M., Devoto S. H., Hiebert S. W., Hunter T., Pines J., Nevins J. R. Cell cycle regulation of the E2F transcription factor involves an interaction with cyclin A. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1243–1253. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90019-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray A. W. Cell cycle extracts. Methods Cell Biol. 1991;36:581–605. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray A. W., Kirschner M. W. Cyclin synthesis drives the early embryonic cell cycle. Nature. 1989 May 25;339(6222):275–280. doi: 10.1038/339275a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray A. W., Solomon M. J., Kirschner M. W. The role of cyclin synthesis and degradation in the control of maturation promoting factor activity. Nature. 1989 May 25;339(6222):280–286. doi: 10.1038/339280a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R. Transcriptional regulation. A closer look at E2F. Nature. 1992 Jul 30;358(6385):375–376. doi: 10.1038/358375a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newport J., Kirschner M. A major developmental transition in early Xenopus embryos: I. characterization and timing of cellular changes at the midblastula stage. Cell. 1982 Oct;30(3):675–686. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newport J., Kirschner M. A major developmental transition in early Xenopus embryos: II. Control of the onset of transcription. Cell. 1982 Oct;30(3):687–696. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90273-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagano M., Draetta G., Jansen-Dürr P. Association of cdk2 kinase with the transcription factor E2F during S phase. Science. 1992 Feb 28;255(5048):1144–1147. doi: 10.1126/science.1312258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pudney M., Varma M. G., Leake C. J. Establishment of a cell line (XTC-2) from the South African clawed toad, Xenopus laevis. Experientia. 1973 Apr 15;29(4):466–467. doi: 10.1007/BF01926785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray S. K., Arroyo M., Bagchi S., Raychaudhuri P. Identification of a 60-kilodalton Rb-binding protein, RBP60, that allows the Rb-E2F complex to bind DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;12(10):4327–4333. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.10.4327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichel R., Kovesdi I., Nevins J. R. Developmental control of a promoter-specific factor that is also regulated by the E1A gene product. Cell. 1987 Feb 13;48(3):501–506. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90200-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz J. K., Devoto S. H., Smith E. J., Chellappan S. P., Jakoi L., Nevins J. R. Interactions of the p107 and Rb proteins with E2F during the cell proliferation response. EMBO J. 1993 Mar;12(3):1013–1020. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05742.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shan B., Zhu X., Chen P. L., Durfee T., Yang Y., Sharp D., Lee W. H. Molecular cloning of cellular genes encoding retinoblastoma-associated proteins: identification of a gene with properties of the transcription factor E2F. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;12(12):5620–5631. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.12.5620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheehan M. A., Mills A. D., Sleeman A. M., Laskey R. A., Blow J. J. Steps in the assembly of replication-competent nuclei in a cell-free system from Xenopus eggs. J Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;106(1):1–12. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirodkar S., Ewen M., DeCaprio J. A., Morgan J., Livingston D. M., Chittenden T. The transcription factor E2F interacts with the retinoblastoma product and a p107-cyclin A complex in a cell cycle-regulated manner. Cell. 1992 Jan 10;68(1):157–166. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90214-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor M. V., Gurdon J. B., Hopwood N. D., Towers N., Mohun T. J. Xenopus embryos contain a somite-specific, MyoD-like protein that binds to a promoter site required for muscle actin expression. Genes Dev. 1991 Jul;5(7):1149–1160. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.7.1149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub S. J., Prater C. A., Dean D. C. Retinoblastoma protein switches the E2F site from positive to negative element. Nature. 1992 Jul 16;358(6383):259–261. doi: 10.1038/358259a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zamanian M., La Thangue N. B. Adenovirus E1a prevents the retinoblastoma gene product from repressing the activity of a cellular transcription factor. EMBO J. 1992 Jul;11(7):2603–2610. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05325.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]