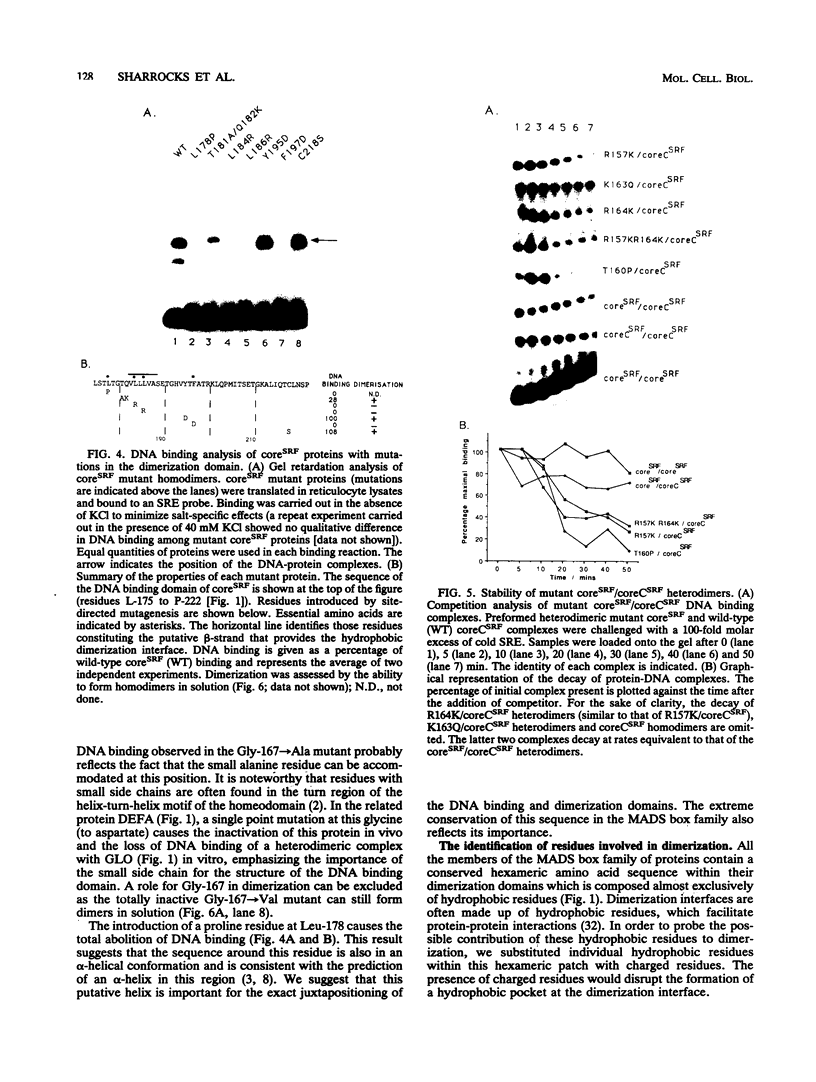
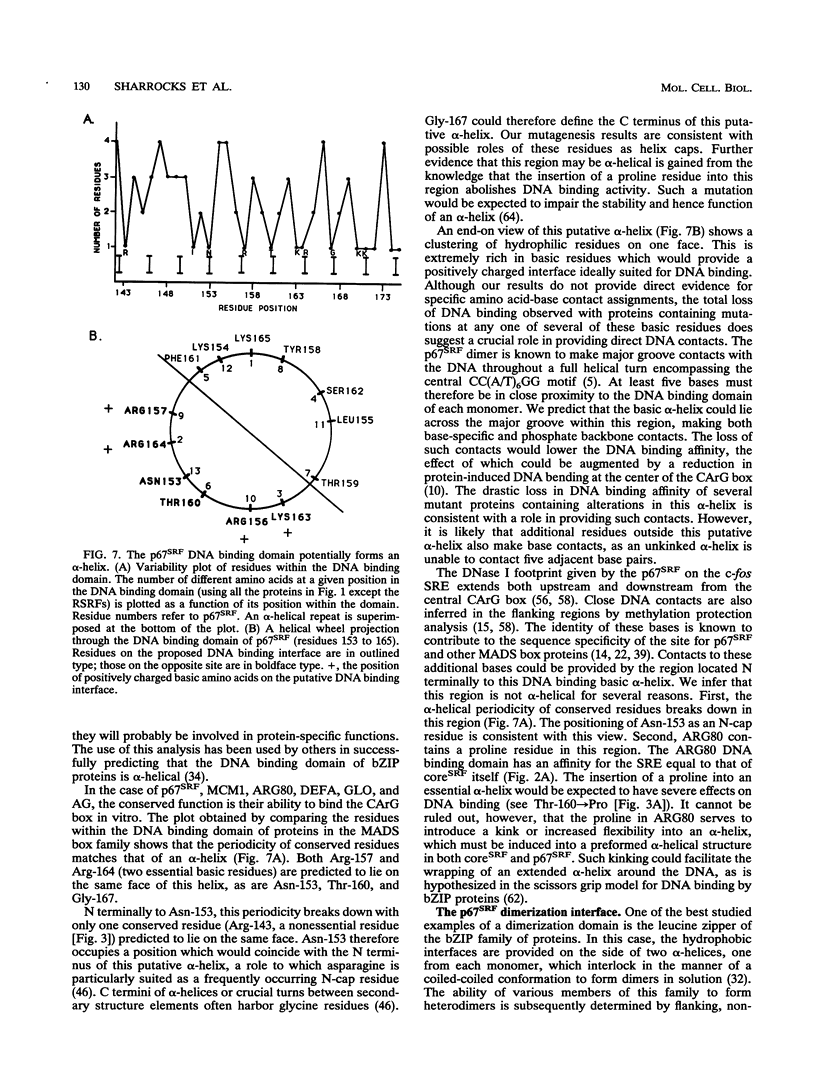
Abstract
The serum response factor (p67SRF) binds to a palindromic sequence in the c-fos serum response element (SRE). A second protein, p62TCF binds in conjunction with p67SRF to form a ternary complex, and it is through this complex that growth factor-induced transcriptional activation of c-fos is thought to take place. A 90-amino-acid peptide, coreSRF, is capable for dimerizing, binding DNA, and recruiting p62TCF. By using extensive site-directed mutagenesis we have investigated the role of individual coreSRF amino acids in DNA binding. Mutant phenotypes were defined by gel retardation and cross-linking analyses. Our results have identified residues essential for either DNA binding or dimerization. Three essential basic amino acids whose conservative mutation severely reduced DNA binding were identified. Evidence which is consistent with these residues being on the face of a DNA binding alpha-helix is presented. A phenylalanine residue and a hexameric hydrophobic box are identified as essential for dimerization. The amino acid phasing is consistent with the dimerization interface being presented as a continuous region on a beta-strand. A putative second alpha-helix acts as a linker between these two regions. This study indicates that p67SRF is a member of a protein family which, in common with many DNA binding proteins, utilize an alpha-helix for DNA binding. However, this alpha-helix is contained within a novel domain structure.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bender A., Sprague G. F., Jr MAT alpha 1 protein, a yeast transcription activator, binds synergistically with a second protein to a set of cell-type-specific genes. Cell. 1987 Aug 28;50(5):681–691. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90326-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Prediction of the secondary structure of proteins from their amino acid sequence. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1978;47:45–148. doi: 10.1002/9780470122921.ch2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coombs K., Brown D. T. Organization of the Sindbis virus nucleocapsid as revealed by bifunctional cross-linking agents. J Mol Biol. 1987 May 20;195(2):359–371. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90657-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalton S., Treisman R. Characterization of SAP-1, a protein recruited by serum response factor to the c-fos serum response element. Cell. 1992 Feb 7;68(3):597–612. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90194-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frampton J., Gibson T. J., Ness S. A., Döderlein G., Graf T. Proposed structure for the DNA-binding domain of the Myb oncoprotein based on model building and mutational analysis. Protein Eng. 1991 Dec;4(8):891–901. doi: 10.1093/protein/4.8.891. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Crothers D. M. Equilibria and kinetics of lac repressor-operator interactions by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6505–6525. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garnier J., Osguthorpe D. J., Robson B. Analysis of the accuracy and implications of simple methods for predicting the secondary structure of globular proteins. J Mol Biol. 1978 Mar 25;120(1):97–120. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90297-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham R., Gilman M. Distinct protein targets for signals acting at the c-fos serum response element. Science. 1991 Jan 11;251(4990):189–192. doi: 10.1126/science.1898992. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafson T. A., Taylor A., Kedes L. DNA bending is induced by a transcription factor that interacts with the human c-FOS and alpha-actin promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2162–2166. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutman A., Wasylyk C., Wasylyk B. Cell-specific regulation of oncogene-responsive sequences of the c-fos promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):5381–5387. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.5381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison S. C. A structural taxonomy of DNA-binding domains. Nature. 1991 Oct 24;353(6346):715–719. doi: 10.1038/353715a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison S. C., Aggarwal A. K. DNA recognition by proteins with the helix-turn-helix motif. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:933–969. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.004441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes T. E., Sengupta P., Cochran B. H. The human c-fos serum response factor and the yeast factors GRM/PRTF have related DNA-binding specificities. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12B):1713–1722. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12b.1713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrera R. E., Shaw P. E., Nordheim A. Occupation of the c-fos serum response element in vivo by a multi-protein complex is unaltered by growth factor induction. Nature. 1989 Jul 6;340(6228):68–70. doi: 10.1038/340068a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karim F. D., Urness L. D., Thummel C. S., Klemsz M. J., McKercher S. R., Celada A., Van Beveren C., Maki R. A., Gunther C. V., Nye J. A. The ETS-domain: a new DNA-binding motif that recognizes a purine-rich core DNA sequence. Genes Dev. 1990 Sep;4(9):1451–1453. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.9.1451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kissinger C. R., Liu B. S., Martin-Blanco E., Kornberg T. B., Pabo C. O. Crystal structure of an engrailed homeodomain-DNA complex at 2.8 A resolution: a framework for understanding homeodomain-DNA interactions. Cell. 1990 Nov 2;63(3):579–590. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90453-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kouzarides T., Ziff E. The role of the leucine zipper in the fos-jun interaction. Nature. 1988 Dec 15;336(6200):646–651. doi: 10.1038/336646a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krystek S. R., Jr, Bruccoleri R. E., Novotny J. Stabilities of leucine zipper dimers estimated by an empirical free energy method. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1991 Sep;38(3):229–236. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1991.tb01433.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung S., Miyamoto N. G. Point mutational analysis of the human c-fos serum response factor binding site. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Feb 11;17(3):1177–1195. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.3.1177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luisi B. F., Xu W. X., Otwinowski Z., Freedman L. P., Yamamoto K. R., Sigler P. B. Crystallographic analysis of the interaction of the glucocorticoid receptor with DNA. Nature. 1991 Aug 8;352(6335):497–505. doi: 10.1038/352497a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma H., Yanofsky M. F., Meyerowitz E. M. AGL1-AGL6, an Arabidopsis gene family with similarity to floral homeotic and transcription factor genes. Genes Dev. 1991 Mar;5(3):484–495. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.3.484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddox J. Towards synthetic self-replication. Nature. 1991 Dec 5;354(6352):351–351. doi: 10.1038/354351a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohun T. J., Chambers A. E., Towers N., Taylor M. V. Expression of genes encoding the transcription factor SRF during early development of Xenopus laevis: identification of a CArG box-binding activity as SRF. EMBO J. 1991 Apr;10(4):933–940. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08027.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller C. G., Nordheim A. A protein domain conserved between yeast MCM1 and human SRF directs ternary complex formation. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(13):4219–4229. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb05000.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murdoch F. E., Grunwald K. A., Gorski J. Marked effects of salt on estrogen receptor binding to DNA: biologically relevant discrimination between DNA sequences. Biochemistry. 1991 Nov 12;30(45):10838–10844. doi: 10.1021/bi00109a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murre C., McCaw P. S., Baltimore D. A new DNA binding and dimerization motif in immunoglobulin enhancer binding, daughterless, MyoD, and myc proteins. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):777–783. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90682-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakabeppu Y., Nathans D. The basic region of Fos mediates specific DNA binding. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3833–3841. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08561.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norman C., Runswick M., Pollock R., Treisman R. Isolation and properties of cDNA clones encoding SRF, a transcription factor that binds to the c-fos serum response element. Cell. 1988 Dec 23;55(6):989–1003. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90244-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neil K. T., Hoess R. H., DeGrado W. F. Design of DNA-binding peptides based on the leucine zipper motif. Science. 1990 Aug 17;249(4970):774–778. doi: 10.1126/science.2389143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oas T. G., McIntosh L. P., O'Shea E. K., Dahlquist F. W., Kim P. S. Secondary structure of a leucine zipper determined by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Biochemistry. 1990 Mar 27;29(12):2891–2894. doi: 10.1021/bi00464a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlendorf D. H., Anderson W. F., Lewis M., Pabo C. O., Matthews B. W. Comparison of the structures of cro and lambda repressor proteins from bacteriophage lambda. J Mol Biol. 1983 Sep 25;169(3):757–769. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80169-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Passmore S., Maine G. T., Elble R., Christ C., Tye B. K. Saccharomyces cerevisiae protein involved in plasmid maintenance is necessary for mating of MAT alpha cells. J Mol Biol. 1988 Dec 5;204(3):593–606. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90358-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel L., Abate C., Curran T. Altered protein conformation on DNA binding by Fos and Jun. Nature. 1990 Oct 11;347(6293):572–575. doi: 10.1038/347572a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavletich N. P., Pabo C. O. Zinc finger-DNA recognition: crystal structure of a Zif268-DNA complex at 2.1 A. Science. 1991 May 10;252(5007):809–817. doi: 10.1126/science.2028256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollock R., Treisman R. A sensitive method for the determination of protein-DNA binding specificities. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Nov 11;18(21):6197–6204. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.21.6197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollock R., Treisman R. Human SRF-related proteins: DNA-binding properties and potential regulatory targets. Genes Dev. 1991 Dec;5(12A):2327–2341. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.12a.2327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prywes R., Roeder R. G. Purification of the c-fos enhancer-binding protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;7(10):3482–3489. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pu W. T., Struhl K. Highly conserved residues in the bZIP domain of yeast GCN4 are not essential for DNA binding. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):4918–4926. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.4918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pu W. T., Struhl K. The leucine zipper symmetrically positions the adjacent basic regions for specific DNA binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):6901–6905. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.6901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rafferty J. B., Somers W. S., Saint-Girons I., Phillips S. E. Three-dimensional crystal structures of Escherichia coli met repressor with and without corepressor. Nature. 1989 Oct 26;341(6244):705–710. doi: 10.1038/341705a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ransone L. J., Wamsley P., Morley K. L., Verma I. M. Domain swapping reveals the modular nature of Fos, Jun, and CREB proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;10(9):4565–4573. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.9.4565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Record M. T., Jr, Ha J. H., Fisher M. A. Analysis of equilibrium and kinetic measurements to determine thermodynamic origins of stability and specificity and mechanism of formation of site-specific complexes between proteins and helical DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1991;208:291–343. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)08018-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson J. S., Richardson D. C. Amino acid preferences for specific locations at the ends of alpha helices. Science. 1988 Jun 17;240(4859):1648–1652. doi: 10.1126/science.3381086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld M. G. POU-domain transcription factors: pou-er-ful developmental regulators. Genes Dev. 1991 Jun;5(6):897–907. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.6.897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt-Dörr T., Oertel-Buchheit P., Pernelle C., Bracco L., Schnarr M., Granger-Schnarr M. Construction, purification, and characterization of a hybrid protein comprising the DNA binding domain of the LexA repressor and the Jun leucine zipper: a circular dichroism and mutagenesis study. Biochemistry. 1991 Oct 8;30(40):9657–9664. doi: 10.1021/bi00104a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröter H., Mueller C. G., Meese K., Nordheim A. Synergism in ternary complex formation between the dimeric glycoprotein p67SRF, polypeptide p62TCF and the c-fos serum response element. EMBO J. 1990 Apr;9(4):1123–1130. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08218.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröter H., Shaw P. E., Nordheim A. Purification of intercalator-released p67, a polypeptide that interacts specifically with the c-fos serum response element. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 23;15(24):10145–10158. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.24.10145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz-Sommer Z., Hue I., Huijser P., Flor P. J., Hansen R., Tetens F., Lönnig W. E., Saedler H., Sommer H. Characterization of the Antirrhinum floral homeotic MADS-box gene deficiens: evidence for DNA binding and autoregulation of its persistent expression throughout flower development. EMBO J. 1992 Jan;11(1):251–263. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05048.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz-Sommer Z., Huijser P., Nacken W., Saedler H., Sommer H. Genetic Control of Flower Development by Homeotic Genes in Antirrhinum majus. Science. 1990 Nov 16;250(4983):931–936. doi: 10.1126/science.250.4983.931. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharrocks A. D., Shaw P. E. Improved primer design for PCR-based, site-directed mutagenesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Mar 11;20(5):1147–1147. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.5.1147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw P. E., Frasch S., Nordheim A. Repression of c-fos transcription is mediated through p67SRF bound to the SRE. EMBO J. 1989 Sep;8(9):2567–2574. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08395.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw P. E., Schröter H., Nordheim A. The ability of a ternary complex to form over the serum response element correlates with serum inducibility of the human c-fos promoter. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):563–572. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90579-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw P. E. Ternary complex formation over the c-fos serum response element: p62TCF exhibits dual component specificity with contacts to DNA and an extended structure in the DNA-binding domain of p67SRF. EMBO J. 1992 Aug;11(8):3011–3019. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05371.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R. Identification of a protein-binding site that mediates transcriptional response of the c-fos gene to serum factors. Cell. 1986 Aug 15;46(4):567–574. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90882-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R. The SRE: a growth factor responsive transcriptional regulator. Semin Cancer Biol. 1990 Feb;1(1):47–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuil D., Clergue N., Montarras D., Pinset C., Kahn A., Phan-Dinh-Tuy F. CC Ar GG boxes, cis-acting elements with a dual specificity. Muscle-specific transcriptional activation and serum responsiveness. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jun 20;213(4):677–686. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80255-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner R., Tjian R. Leucine repeats and an adjacent DNA binding domain mediate the formation of functional cFos-cJun heterodimers. Science. 1989 Mar 31;243(4899):1689–1694. doi: 10.1126/science.2494701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinson C. R., Sigler P. B., McKnight S. L. Scissors-grip model for DNA recognition by a family of leucine zipper proteins. Science. 1989 Nov 17;246(4932):911–916. doi: 10.1126/science.2683088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss M. A., Ellenberger T., Wobbe C. R., Lee J. P., Harrison S. C., Struhl K. Folding transition in the DNA-binding domain of GCN4 on specific binding to DNA. Nature. 1990 Oct 11;347(6293):575–578. doi: 10.1038/347575a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams K. A., Deber C. M. Proline residues in transmembrane helices: structural or dynamic role? Biochemistry. 1991 Sep 17;30(37):8919–8923. doi: 10.1021/bi00101a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]