Abstract
In the crystal structure of the title hydrated quinolinium salt of ferron (8-hydroxy-7-iodoquinoline-5-sulfonic acid), C9H7N+·C9H5INO4S−·0.8H2O, the quinolinium cation is fully disordered over two sites (occupancy factors fixed at 0.63 and 0.37) lying essentially within a common plane and with the ferron anions forming π–π-associated stacks down the b axis [minimum ring centroid separation = 3.462 (6) Å]. The cations and anions are linked into chains extending along c through hydroxy O—H⋯O and quinolinium N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds to sulfonate O-atom acceptors which are also involved in water O—H⋯O hydrogen-bonding interactions along b, giving a two-dimensional network.
Related literature
For the crystal structure of ferron, see: Balasubramanian & Muthiah (1996 ▶). For analytical applications of ferron, see: Vogel (1964 ▶). For the crystal structures of other non-zwitterionic compounds of ferron, see: Hemamalini et al. (2004 ▶); Smith et al. (2004 ▶, 2007 ▶).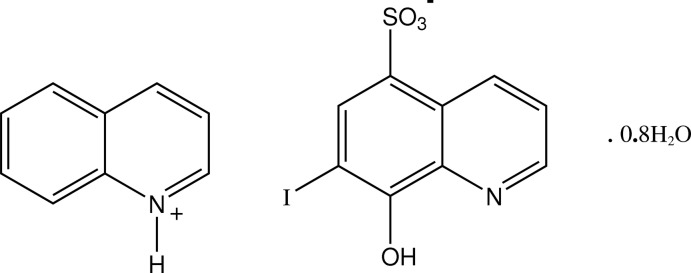
Experimental
Crystal data
C9H8N+·C9H5INO4S−·0.8H2O
M r = 494.69
Orthorhombic,

a = 16.2403 (5) Å
b = 7.1539 (3) Å
c = 15.2458 (5) Å
V = 1771.28 (11) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 1.96 mm−1
T = 200 K
0.32 × 0.25 × 0.12 mm
Data collection
Oxford Diffraction Gemini-S CCD-detector diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Agilent, 2012 ▶) T min = 0.906, T max = 0.980
6143 measured reflections
3207 independent reflections
2709 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.028
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.040
wR(F 2) = 0.082
S = 1.18
3207 reflections
244 parameters
1 restraint
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.65 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.66 e Å−3
Absolute structure: Flack (1983 ▶), 789 Friedel pairs
Flack parameter: 0.01 (3)
Data collection: CrysAlis PRO (Agilent, 2012 ▶); cell refinement: CrysAlis PRO; data reduction: CrysAlis PRO; program(s) used to solve structure: SIR92 (Altomare et al., 1993 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶) within WinGX (Farrugia, 2012 ▶); molecular graphics: PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: PLATON.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812046247/su2523sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812046247/su2523Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812046247/su2523Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1A—H1A⋯O53i | 0.86 | 1.97 | 2.783 (10) | 157 |
| N1B—H1B⋯O53i | 0.86 | 1.88 | 2.725 (16) | 166 |
| O8—H8⋯O52ii | 0.81 | 2.13 | 2.769 (7) | 135 |
| O1W—H11W⋯O52 | 0.89 | 2.18 | 3.066 (9) | 179 |
| O1W—H12W⋯O51iii | 0.90 | 2.18 | 3.080 (8) | 178 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  ; (iii)
; (iii)  .
.
Acknowledgments
The author acknowledges financial support from the Science and Engineering Faculty and the University Library, Queensland University of Technology.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Ferron (8-hydroxy-7-iodoquinoline-5-sulfonic acid) is a bidentate complexing agent which has analytical applications as a selective colour reagent for the detection of iron(III) but not iron(II) (Vogel, 1964). The crystal structure of ferron (Balasubramanian & Muthiah, 1996) has shown that the molecule exists as a sulfonate-quinolinium zwitterion. As a sulfonic acid, ferron is potentially capable of protonating most Lewis bases, but the crystal structures of only a small number of such salts have been reported. With 8-hydroxyquinoline, a 1:1 sesquihydrate is formed (Smith et al., 2004) and with bifunctional 4,4'-bipyridine (Hemamalini et al., 2004) a monoprotonated 1:1 dihydrate is found. A common structural feature in these ferron proton-transfer salts is the presence of R22(10) cyclic hydrogen-bonded ferron···ferron dimers involving the 8-hydroxy donor and hetero-N acceptor groups. Reaction of ferron with quinoline gave the title chemically stable 1:1 hydrated salt, whose crystal structure is reported on herein.
In the title compound, Fig. 1, the quinolinium cation is fully disordered over two sites A and B with occupancy factors fixed at 0.63 and 0.37, lying essentially within a common plane. These cations are linked to the anions through both quinolinium N—H···O and hydroxyl O—H···O and hydrogen bonds to sulfonate O-atom acceptors (Table 1), forming chains extending along c. Water O—H···Osulfonate hydrogen-bonding interactions together with cation–anion ring π–π associations [minimum ring centroid separation = 3.462 (6) Å] link the chains down the b axial direction, giving a two-dimensional network structure (Figs. 2 and 3). The ferron–ferron dimeric association is not present. In the crystal, there are relatively short intra-anionic I7···O51iv interactions [3.027 (5) Å] [symmetry code (iv): x + 1/2,-y, z].
With the ferron anion, the short intra-anionic O8—H8···N1 association [2.693 (7) Å] is present, similar to that found in other non-zwitterionic compounds of ferron (Hemamalini et al., 2004; Smith et al., 2004, 2007). Also the common aromatic ring C6–H6···O51sulfonate association [2.827 (8) Å] maintains the S5–O51 bond close to the extended plane of the aromatic ring [torsion angle C10—C5—S5—O51, 171.1 (5) °].
Experimental
The title compound was synthesized by heating a solution containing 1 mmol of 8-hydroxy-7-iodoquinoline-5-sulfonic acid (ferron) and 1 mmol of quinoline in 50 ml of 50% ethanol-water for 10 min under reflux. After concentration to ca. 40 ml, partial room temperature evaporation of the hot-filtered solution gave yellow flat prisms of the title compound (m.p. 460.6–462.3 K) from which a specimen was cleaved for the X-ray analysis.
Refinement
Hydrogen atoms on the water molecule and the hydroxyl group were located in a difference-Fourier synthesis but were subsequently allowed to ride in the refinement with Uiso(H) = 1.5Ueq(O). Other H-atoms were included in the refinement in calculated positions with N—H = 0.86 Å or C—H = 0.93 Å and were also treated as riding, with Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C). The site occupancy of the water molecule was determined as 0.801 (12) and was subsequently fixed as 0.80. The quinolinium cation was completely disordered laterally within a common plane and the minor component (B) was subsequently located and its occupancy determined as 0.373 (14). Because of the instability in the anisotropic displacement parameters for both components, these were refined isotropically. The maximum difference peak was 0.64 e Å-3 1.07 Å from I7.
Figures
Fig. 1.
Molecular configuration and atom naming for the individual cation, the disordered anion components (A and B) and the water species in the title compound. The minor-occupancy B anion is shown with broken bonds and displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 30% probability level. The intra- and inter-species hydrogen bonds are shown as a dashed lines.
Fig. 2.
The stacking of the cation and anion rings down the b axis in the crystal of the title compound.
Fig. 3.
A perspective view of the crystal packing of the title compound viewed along the a axis, showing the inter-chain water hydrogen-bonding associations (dashed lines; see Table for details; symmetry codes: (i) -x+1, -y+1, z+1/2; (ii) -x+1, -y+2, z+1/2; (iii) x, y+1, z).
Crystal data
| C9H8N+·C9H5INO4S−·0.8H2O | F(000) = 976 |
| Mr = 494.69 | Dx = 1.855 Mg m−3 |
| Orthorhombic, Pca21 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: P 2c -2ac | Cell parameters from 1806 reflections |
| a = 16.2403 (5) Å | θ = 3.4–28.9° |
| b = 7.1539 (3) Å | µ = 1.96 mm−1 |
| c = 15.2458 (5) Å | T = 200 K |
| V = 1771.28 (11) Å3 | Flat prism, yellow |
| Z = 4 | 0.32 × 0.25 × 0.12 mm |
Data collection
| Oxford Diffraction Gemini-S CCD-detector diffractometer | 3207 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 2709 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.028 |
| Detector resolution: 16.077 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 28.9°, θmin = 3.4° |
| ω scans | h = −22→15 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Agilent, 2012) | k = −6→9 |
| Tmin = 0.906, Tmax = 0.980 | l = −19→19 |
| 6143 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.040 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.082 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0181P)2 + 3.2291P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.18 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.004 |
| 3207 reflections | Δρmax = 0.65 e Å−3 |
| 244 parameters | Δρmin = −0.66 e Å−3 |
| 1 restraint | Absolute structure: Flack (1983), 789 Friedel pairs |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Flack parameter: 0.01 (3) |
Special details
| Geometry. Bond distances, angles etc. have been calculated using the rounded fractional coordinates. All su's are estimated from the variances of the (full) variance-covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account in the estimation of distances, angles and torsion angles |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | Occ. (<1) | |
| N1A | 0.5706 (6) | 0.4412 (12) | 0.3693 (6) | 0.020 (2)* | 0.630 |
| C2A | 0.6389 (9) | 0.4939 (16) | 0.3279 (9) | 0.025 (3)* | 0.630 |
| C3A | 0.6447 (7) | 0.4807 (15) | 0.2359 (9) | 0.019 (2)* | 0.630 |
| C4A | 0.5784 (8) | 0.4161 (17) | 0.1888 (8) | 0.026 (3)* | 0.630 |
| C5A | 0.4375 (7) | 0.2937 (15) | 0.1920 (9) | 0.023 (3)* | 0.630 |
| C6A | 0.3681 (8) | 0.2443 (17) | 0.2377 (9) | 0.030 (2)* | 0.630 |
| C7A | 0.3664 (8) | 0.2600 (17) | 0.3288 (10) | 0.026 (2)* | 0.630 |
| C8A | 0.4325 (10) | 0.3261 (17) | 0.3750 (8) | 0.026 (3)* | 0.630 |
| C9A | 0.5015 (8) | 0.3760 (17) | 0.3272 (8) | 0.021 (3)* | 0.630 |
| C10A | 0.5084 (11) | 0.356 (3) | 0.2307 (12) | 0.022 (5)* | 0.630 |
| C8B | 0.6037 (15) | 0.466 (3) | 0.3434 (14) | 0.020 (4)* | 0.370 |
| C9B | 0.5273 (13) | 0.388 (3) | 0.3220 (12) | 0.013 (4)* | 0.370 |
| C10B | 0.4986 (15) | 0.362 (3) | 0.2426 (16) | 0.006 (6)* | 0.370 |
| C3B | 0.3682 (13) | 0.254 (3) | 0.2889 (17) | 0.029 (4)* | 0.370 |
| C4B | 0.4180 (12) | 0.288 (3) | 0.2210 (14) | 0.020 (4)* | 0.370 |
| C5B | 0.5542 (14) | 0.390 (3) | 0.1688 (15) | 0.032 (5)* | 0.370 |
| C6B | 0.6308 (13) | 0.451 (3) | 0.1885 (15) | 0.030 (4)* | 0.370 |
| C7B | 0.6552 (12) | 0.496 (3) | 0.2747 (15) | 0.022 (4)* | 0.370 |
| N1B | 0.4736 (11) | 0.341 (2) | 0.3879 (10) | 0.022 (3)* | 0.370 |
| C2B | 0.4005 (15) | 0.285 (3) | 0.3719 (14) | 0.028 (5)* | 0.370 |
| I7 | 0.30996 (2) | 0.75195 (7) | 0.45473 (4) | 0.0259 (1) | |
| S5 | 0.38785 (10) | 0.7547 (3) | 0.09027 (10) | 0.0232 (4) | |
| O8 | 0.4943 (2) | 0.8886 (6) | 0.4574 (4) | 0.0265 (11) | |
| O51 | 0.3101 (3) | 0.6580 (7) | 0.0999 (3) | 0.0327 (16) | |
| O52 | 0.3807 (3) | 0.9388 (7) | 0.0506 (3) | 0.0280 (16) | |
| O53 | 0.4497 (3) | 0.6391 (7) | 0.0466 (3) | 0.0323 (16) | |
| N1 | 0.6037 (3) | 0.9565 (7) | 0.3285 (4) | 0.0220 (17) | |
| C2 | 0.6580 (4) | 0.9911 (9) | 0.2656 (5) | 0.027 (2) | |
| C3 | 0.6418 (4) | 0.9684 (9) | 0.1760 (5) | 0.0233 (19) | |
| C4 | 0.5659 (4) | 0.9043 (9) | 0.1505 (4) | 0.0223 (19) | |
| C5 | 0.4255 (4) | 0.7936 (7) | 0.1981 (4) | 0.0150 (17) | |
| C6 | 0.3719 (4) | 0.7600 (9) | 0.2665 (4) | 0.0183 (17) | |
| C7 | 0.3948 (4) | 0.7926 (7) | 0.3545 (4) | 0.0147 (17) | |
| C8 | 0.4722 (4) | 0.8578 (8) | 0.3737 (4) | 0.0173 (17) | |
| C9 | 0.5289 (4) | 0.8920 (8) | 0.3042 (4) | 0.0157 (17) | |
| C10 | 0.5063 (4) | 0.8627 (8) | 0.2143 (4) | 0.0167 (17) | |
| O1W | 0.2775 (5) | 1.2846 (9) | 0.0055 (5) | 0.057 (3) | 0.800 |
| H4A | 0.58090 | 0.41330 | 0.12790 | 0.0310* | 0.630 |
| H5A | 0.43630 | 0.28440 | 0.13110 | 0.0270* | 0.630 |
| H6A | 0.32210 | 0.20010 | 0.20780 | 0.0360* | 0.630 |
| H7A | 0.31910 | 0.22470 | 0.35900 | 0.0310* | 0.630 |
| H8A | 0.43110 | 0.33690 | 0.43570 | 0.0310* | 0.630 |
| H1A | 0.56960 | 0.44830 | 0.42560 | 0.0240* | 0.630 |
| H2A | 0.68320 | 0.53980 | 0.35990 | 0.0300* | 0.630 |
| H3A | 0.69290 | 0.51530 | 0.20730 | 0.0220* | 0.630 |
| H1B | 0.48960 | 0.34940 | 0.44150 | 0.0260* | 0.370 |
| H2B | 0.36610 | 0.26310 | 0.41960 | 0.0330* | 0.370 |
| H3B | 0.31450 | 0.21280 | 0.28100 | 0.0350* | 0.370 |
| H4B | 0.40210 | 0.26440 | 0.16340 | 0.0240* | 0.370 |
| H5B | 0.53800 | 0.36630 | 0.11140 | 0.0380* | 0.370 |
| H6B | 0.66890 | 0.46380 | 0.14340 | 0.0360* | 0.370 |
| H7B | 0.70690 | 0.54790 | 0.28460 | 0.0270* | 0.370 |
| H8B | 0.61840 | 0.49450 | 0.40080 | 0.0250* | 0.370 |
| H2 | 0.71010 | 1.03290 | 0.28190 | 0.0320* | |
| H3 | 0.68190 | 0.99650 | 0.13450 | 0.0280* | |
| H4 | 0.55400 | 0.88840 | 0.09130 | 0.0270* | |
| H6 | 0.31940 | 0.71470 | 0.25440 | 0.0220* | |
| H8 | 0.54190 | 0.92330 | 0.45790 | 0.0390* | |
| H11W | 0.30700 | 1.18390 | 0.01810 | 0.0850* | 0.800 |
| H12W | 0.28600 | 1.39490 | 0.03310 | 0.0850* | 0.800 |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| I7 | 0.0229 (2) | 0.0360 (2) | 0.0189 (2) | −0.0052 (2) | 0.0053 (2) | −0.0028 (2) |
| S5 | 0.0250 (8) | 0.0290 (8) | 0.0156 (6) | −0.0017 (8) | −0.0034 (6) | 0.0023 (7) |
| O8 | 0.025 (2) | 0.036 (2) | 0.0184 (18) | −0.0057 (18) | −0.006 (3) | −0.007 (3) |
| O51 | 0.030 (3) | 0.043 (3) | 0.025 (2) | −0.017 (2) | −0.010 (2) | 0.003 (2) |
| O52 | 0.028 (3) | 0.031 (3) | 0.025 (2) | 0.000 (2) | −0.003 (2) | 0.010 (2) |
| O53 | 0.045 (3) | 0.031 (3) | 0.021 (2) | 0.006 (3) | 0.000 (2) | −0.009 (2) |
| N1 | 0.017 (3) | 0.022 (3) | 0.027 (3) | −0.005 (2) | −0.003 (2) | −0.001 (3) |
| C2 | 0.018 (3) | 0.023 (4) | 0.041 (4) | 0.002 (3) | −0.007 (3) | 0.007 (3) |
| C3 | 0.018 (3) | 0.017 (3) | 0.035 (4) | 0.006 (3) | 0.005 (3) | 0.003 (3) |
| C4 | 0.028 (4) | 0.016 (3) | 0.023 (3) | 0.005 (3) | 0.004 (3) | 0.004 (3) |
| C5 | 0.025 (3) | 0.008 (3) | 0.012 (3) | 0.000 (2) | 0.001 (2) | 0.000 (2) |
| C6 | 0.018 (3) | 0.019 (3) | 0.018 (3) | −0.003 (3) | −0.002 (2) | 0.004 (3) |
| C7 | 0.013 (3) | 0.011 (3) | 0.020 (3) | −0.001 (2) | 0.006 (2) | 0.001 (2) |
| C8 | 0.020 (3) | 0.014 (3) | 0.018 (3) | 0.001 (2) | 0.001 (3) | −0.004 (3) |
| C9 | 0.013 (3) | 0.009 (3) | 0.025 (3) | 0.000 (2) | 0.001 (2) | −0.001 (2) |
| C10 | 0.018 (3) | 0.012 (3) | 0.020 (3) | −0.001 (2) | 0.000 (3) | 0.008 (3) |
| O1W | 0.070 (5) | 0.027 (4) | 0.073 (5) | 0.023 (4) | −0.034 (4) | −0.010 (4) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| I7—C7 | 2.078 (6) | C8A—C9A | 1.38 (2) |
| S5—O52 | 1.454 (5) | C8B—C9B | 1.40 (3) |
| S5—O51 | 1.447 (5) | C9A—C10A | 1.48 (2) |
| S5—O53 | 1.462 (5) | C9B—C10B | 1.31 (3) |
| S5—C5 | 1.776 (6) | C2A—H2A | 0.9300 |
| O8—C8 | 1.344 (8) | C2B—H2B | 0.9300 |
| O8—H8 | 0.8100 | C3A—H3A | 0.9300 |
| O1W—H12W | 0.9000 | C3B—H3B | 0.9300 |
| O1W—H11W | 0.8900 | C4A—H4A | 0.9300 |
| N1A—C2A | 1.331 (17) | C4B—H4B | 0.9300 |
| N1A—C9A | 1.374 (16) | C5A—H5A | 0.9300 |
| N1B—C9B | 1.37 (3) | C5B—H5B | 0.9300 |
| N1B—C2B | 1.28 (3) | C6A—H6A | 0.9300 |
| N1A—H1A | 0.8600 | C6B—H6B | 0.9300 |
| N1B—H1B | 0.8600 | C7A—H7A | 0.9300 |
| N1—C2 | 1.326 (9) | C7B—H7B | 0.9300 |
| N1—C9 | 1.351 (8) | C8A—H8A | 0.9300 |
| C2A—C3A | 1.409 (19) | C8B—H8B | 0.9300 |
| C2B—C3B | 1.39 (3) | C2—C3 | 1.401 (11) |
| C3A—C4A | 1.374 (17) | C3—C4 | 1.371 (9) |
| C3B—C4B | 1.34 (3) | C4—C10 | 1.404 (9) |
| C4A—C10A | 1.37 (2) | C5—C6 | 1.380 (9) |
| C4B—C10B | 1.45 (3) | C5—C10 | 1.424 (9) |
| C5A—C10A | 1.37 (2) | C6—C7 | 1.412 (9) |
| C5A—C6A | 1.371 (18) | C7—C8 | 1.372 (9) |
| C5B—C6B | 1.35 (3) | C8—C9 | 1.425 (9) |
| C5B—C10B | 1.46 (3) | C9—C10 | 1.434 (9) |
| C6A—C7A | 1.39 (2) | C2—H2 | 0.9300 |
| C6B—C7B | 1.41 (3) | C3—H3 | 0.9300 |
| C7A—C8A | 1.37 (2) | C4—H4 | 0.9300 |
| C7B—C8B | 1.36 (3) | C6—H6 | 0.9300 |
| O51—S5—O52 | 113.9 (3) | C4B—C3B—H3B | 122.00 |
| O51—S5—O53 | 112.1 (3) | C10A—C4A—H4A | 120.00 |
| O51—S5—C5 | 106.3 (3) | C3A—C4A—H4A | 120.00 |
| O52—S5—O53 | 112.2 (3) | C3B—C4B—H4B | 122.00 |
| O52—S5—C5 | 105.7 (3) | C10B—C4B—H4B | 122.00 |
| O53—S5—C5 | 105.9 (3) | C10A—C5A—H5A | 118.00 |
| C8—O8—H8 | 108.00 | C6A—C5A—H5A | 118.00 |
| H11W—O1W—H12W | 122.00 | C10B—C5B—H5B | 122.00 |
| C2A—N1A—C9A | 123.7 (10) | C6B—C5B—H5B | 122.00 |
| C2B—N1B—C9B | 121.9 (17) | C5A—C6A—H6A | 120.00 |
| C9A—N1A—H1A | 118.00 | C7A—C6A—H6A | 120.00 |
| C2A—N1A—H1A | 118.00 | C5B—C6B—H6B | 119.00 |
| C9B—N1B—H1B | 119.00 | C7B—C6B—H6B | 119.00 |
| C2B—N1B—H1B | 119.00 | C8A—C7A—H7A | 119.00 |
| C2—N1—C9 | 117.6 (6) | C6A—C7A—H7A | 119.00 |
| N1A—C2A—C3A | 120.6 (12) | C8B—C7B—H7B | 120.00 |
| N1B—C2B—C3B | 125 (2) | C6B—C7B—H7B | 120.00 |
| C2A—C3A—C4A | 119.4 (11) | C7A—C8A—H8A | 121.00 |
| C2B—C3B—C4B | 117 (2) | C9A—C8A—H8A | 122.00 |
| C3A—C4A—C10A | 120.7 (13) | C9B—C8B—H8B | 122.00 |
| C3B—C4B—C10B | 116 (2) | C7B—C8B—H8B | 122.00 |
| C6A—C5A—C10A | 123.8 (14) | N1—C2—C3 | 124.0 (6) |
| C6B—C5B—C10B | 116 (2) | C2—C3—C4 | 119.0 (6) |
| C5A—C6A—C7A | 120.1 (12) | C3—C4—C10 | 119.6 (6) |
| C5B—C6B—C7B | 123 (2) | C6—C5—C10 | 120.7 (6) |
| C6A—C7A—C8A | 121.7 (12) | S5—C5—C6 | 117.1 (5) |
| C6B—C7B—C8B | 120.7 (19) | S5—C5—C10 | 122.2 (5) |
| C7A—C8A—C9A | 117.0 (12) | C5—C6—C7 | 121.6 (6) |
| C7B—C8B—C9B | 115.4 (19) | I7—C7—C8 | 119.9 (4) |
| C8A—C9A—C10A | 124.0 (13) | I7—C7—C6 | 120.1 (5) |
| N1A—C9A—C10A | 115.8 (12) | C6—C7—C8 | 120.0 (6) |
| N1A—C9A—C8A | 120.2 (11) | O8—C8—C9 | 120.4 (5) |
| N1B—C9B—C8B | 119.4 (17) | O8—C8—C7 | 120.2 (5) |
| C8B—C9B—C10B | 126 (2) | C7—C8—C9 | 119.5 (6) |
| N1B—C9B—C10B | 115 (2) | N1—C9—C10 | 122.8 (6) |
| C4A—C10A—C9A | 119.6 (15) | C8—C9—C10 | 121.3 (6) |
| C4A—C10A—C5A | 126.7 (16) | N1—C9—C8 | 115.8 (6) |
| C5A—C10A—C9A | 113.3 (14) | C4—C10—C9 | 117.0 (6) |
| C5B—C10B—C9B | 118 (2) | C4—C10—C5 | 126.1 (6) |
| C4B—C10B—C5B | 116 (2) | C5—C10—C9 | 116.9 (6) |
| C4B—C10B—C9B | 126 (2) | N1—C2—H2 | 118.00 |
| C3A—C2A—H2A | 120.00 | C3—C2—H2 | 118.00 |
| N1A—C2A—H2A | 120.00 | C4—C3—H3 | 121.00 |
| C3B—C2B—H2B | 117.00 | C2—C3—H3 | 120.00 |
| N1B—C2B—H2B | 118.00 | C3—C4—H4 | 120.00 |
| C2A—C3A—H3A | 120.00 | C10—C4—H4 | 120.00 |
| C4A—C3A—H3A | 120.00 | C5—C6—H6 | 119.00 |
| C2B—C3B—H3B | 122.00 | C7—C6—H6 | 119.00 |
| O53—S5—C5—C6 | −130.4 (5) | C8A—C9A—C10A—C4A | 177.6 (14) |
| O53—S5—C5—C10 | 51.8 (5) | N1—C2—C3—C4 | −0.9 (10) |
| O52—S5—C5—C6 | 110.4 (5) | C2—C3—C4—C10 | −0.1 (9) |
| O51—S5—C5—C6 | −11.0 (5) | C3—C4—C10—C5 | −179.3 (6) |
| O51—S5—C5—C10 | 171.1 (5) | C3—C4—C10—C9 | 0.5 (9) |
| O52—S5—C5—C10 | −67.4 (5) | S5—C5—C6—C7 | −177.8 (5) |
| C2A—N1A—C9A—C10A | 3.5 (18) | C10—C5—C6—C7 | 0.0 (9) |
| C9A—N1A—C2A—C3A | −1.6 (17) | S5—C5—C10—C4 | −1.5 (8) |
| C2A—N1A—C9A—C8A | −179.2 (11) | S5—C5—C10—C9 | 178.7 (4) |
| C9—N1—C2—C3 | 1.4 (9) | C6—C5—C10—C4 | −179.2 (6) |
| C2—N1—C9—C8 | −179.6 (5) | C6—C5—C10—C9 | 1.0 (8) |
| C2—N1—C9—C10 | −0.9 (9) | C5—C6—C7—I7 | 177.1 (4) |
| N1A—C2A—C3A—C4A | 1.3 (17) | C5—C6—C7—C8 | −0.5 (9) |
| C2A—C3A—C4A—C10A | −3 (2) | I7—C7—C8—O8 | 2.6 (7) |
| C3A—C4A—C10A—C5A | 178.0 (15) | I7—C7—C8—C9 | −177.6 (4) |
| C3A—C4A—C10A—C9A | 5 (2) | C6—C7—C8—O8 | −179.9 (5) |
| C6A—C5A—C10A—C4A | −176.6 (16) | C6—C7—C8—C9 | 0.0 (8) |
| C6A—C5A—C10A—C9A | −4 (2) | O8—C8—C9—N1 | −0.4 (8) |
| C10A—C5A—C6A—C7A | 1 (2) | O8—C8—C9—C10 | −179.1 (5) |
| C5A—C6A—C7A—C8A | 0.7 (19) | C7—C8—C9—N1 | 179.8 (5) |
| C6A—C7A—C8A—C9A | −0.3 (19) | C7—C8—C9—C10 | 1.1 (9) |
| C7A—C8A—C9A—C10A | −2 (2) | N1—C9—C10—C4 | 0.0 (9) |
| C7A—C8A—C9A—N1A | −179.1 (11) | N1—C9—C10—C5 | 179.8 (5) |
| N1A—C9A—C10A—C4A | −5 (2) | C8—C9—C10—C4 | 178.6 (6) |
| C8A—C9A—C10A—C5A | 4 (2) | C8—C9—C10—C5 | −1.5 (8) |
| N1A—C9A—C10A—C5A | −179.0 (13) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N1A—H1A···O53i | 0.86 | 1.97 | 2.783 (10) | 157 |
| N1B—H1B···O53i | 0.86 | 1.88 | 2.725 (16) | 166 |
| O8—H8···N1 | 0.81 | 2.23 | 2.693 (7) | 117 |
| O8—H8···O52ii | 0.81 | 2.13 | 2.769 (7) | 135 |
| O1W—H11W···O52 | 0.89 | 2.18 | 3.066 (9) | 179 |
| O1W—H12W···O51iii | 0.90 | 2.18 | 3.080 (8) | 178 |
| C4—H4···O53 | 0.93 | 2.55 | 3.110 (8) | 119 |
| C6—H6···O51 | 0.93 | 2.39 | 2.827 (8) | 108 |
| C8A—H8A···O53i | 0.93 | 2.58 | 3.251 (14) | 130 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, −y+1, z+1/2; (ii) −x+1, −y+2, z+1/2; (iii) x, y+1, z.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: SU2523).
References
- Agilent (2012). CrysAlis PRO Agilent Technologies, Yarnton, England.
- Altomare, A., Cascarano, G., Giacovazzo, C. & Guagliardi, A. (1993). J. Appl. Cryst. 26, 343–350.
- Balasubramanian, T. & Muthiah, P. T. (1996). Acta Cryst. C52, 2072–2073. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Farrugia, L. J. (2012). J. Appl. Cryst. 45, 849–854.
- Flack, H. D. (1983). Acta Cryst. A39, 876–881.
- Hemamalini, M., Muthiah, P. T., Bocelli, G. & Cantoni, A. (2004). Acta Cryst. C60, o284–o286. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Smith, G., Wermuth, U. D. & Healy, P. C. (2004). Acta Cryst. C60, o600–o603. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Smith, G., Wermuth, U. D. & Healy, P. C. (2007). Acta Cryst. C63, o405–o407. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Vogel, A. I. (1964). Textbook of Macro and Semi-Micro Qualitative Inorganic Analysis, 4th ed., p. 266. London: Longmans.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812046247/su2523sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812046247/su2523Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812046247/su2523Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report





