Abstract
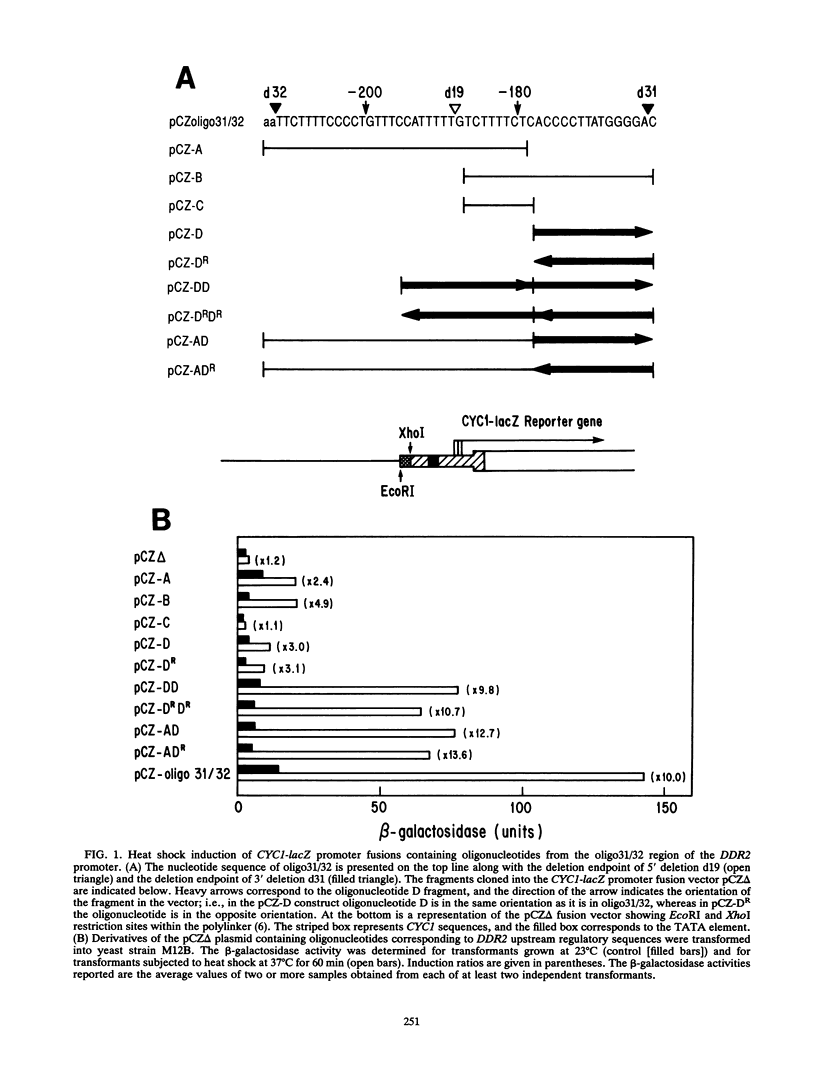
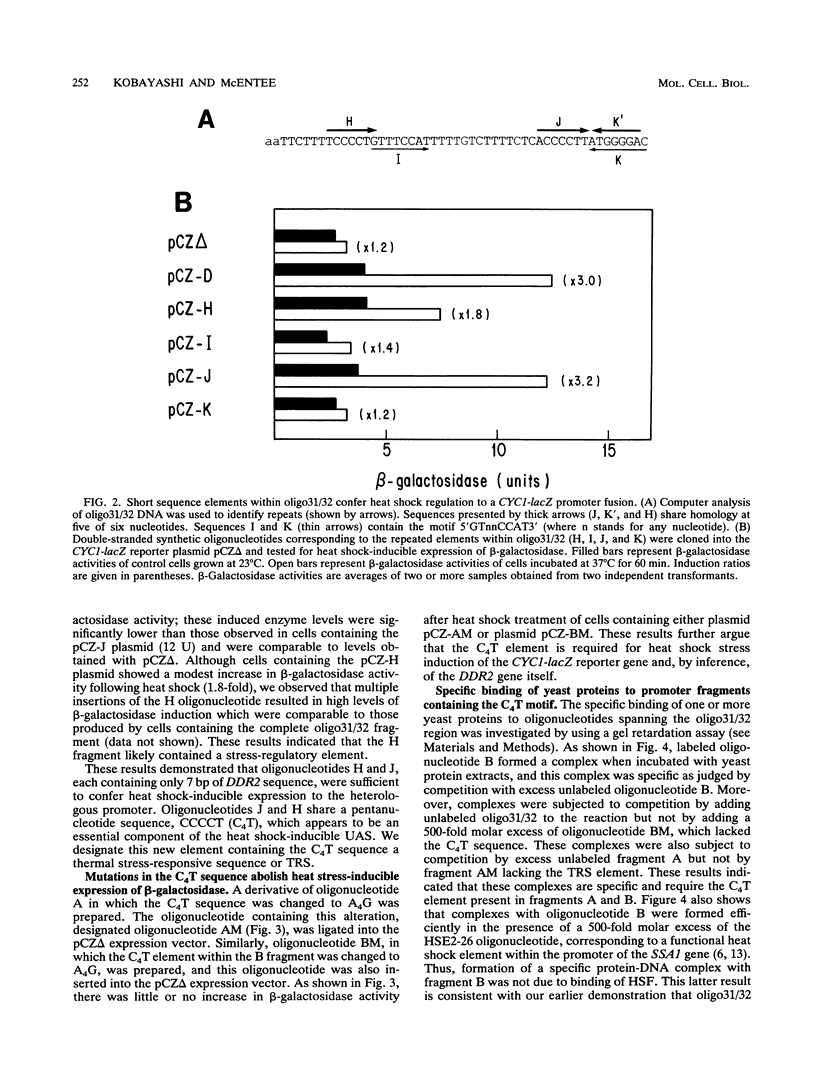
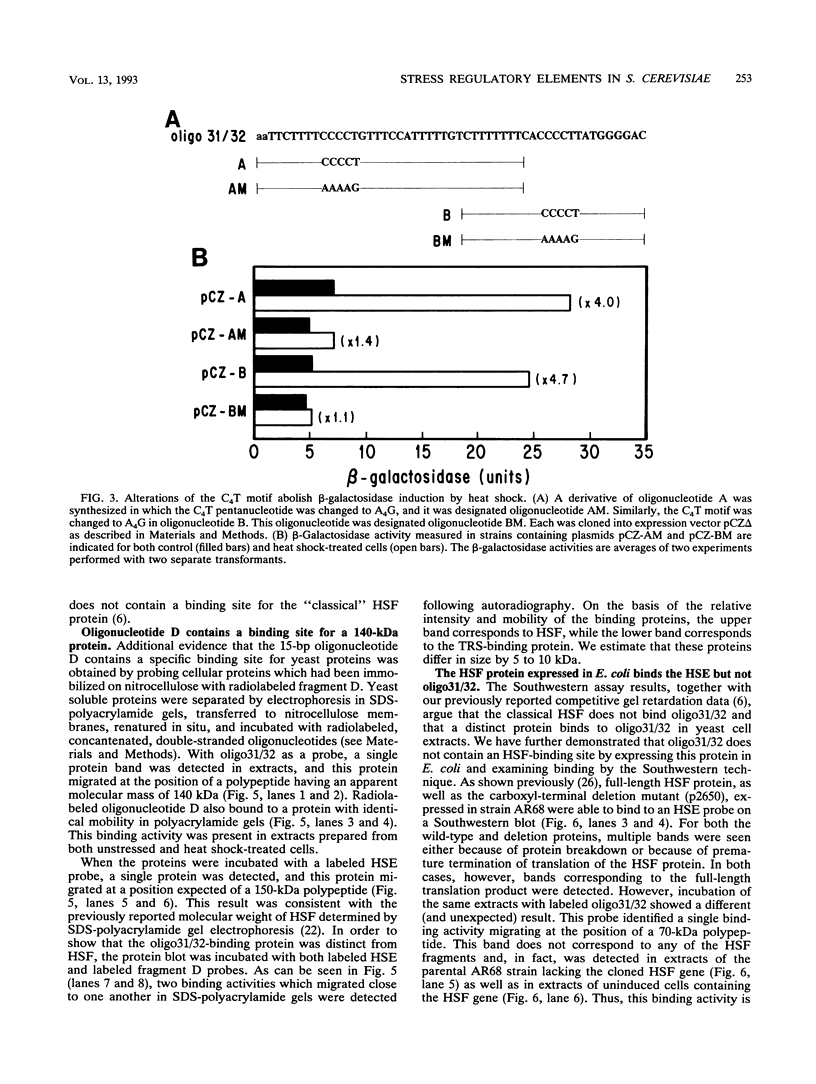
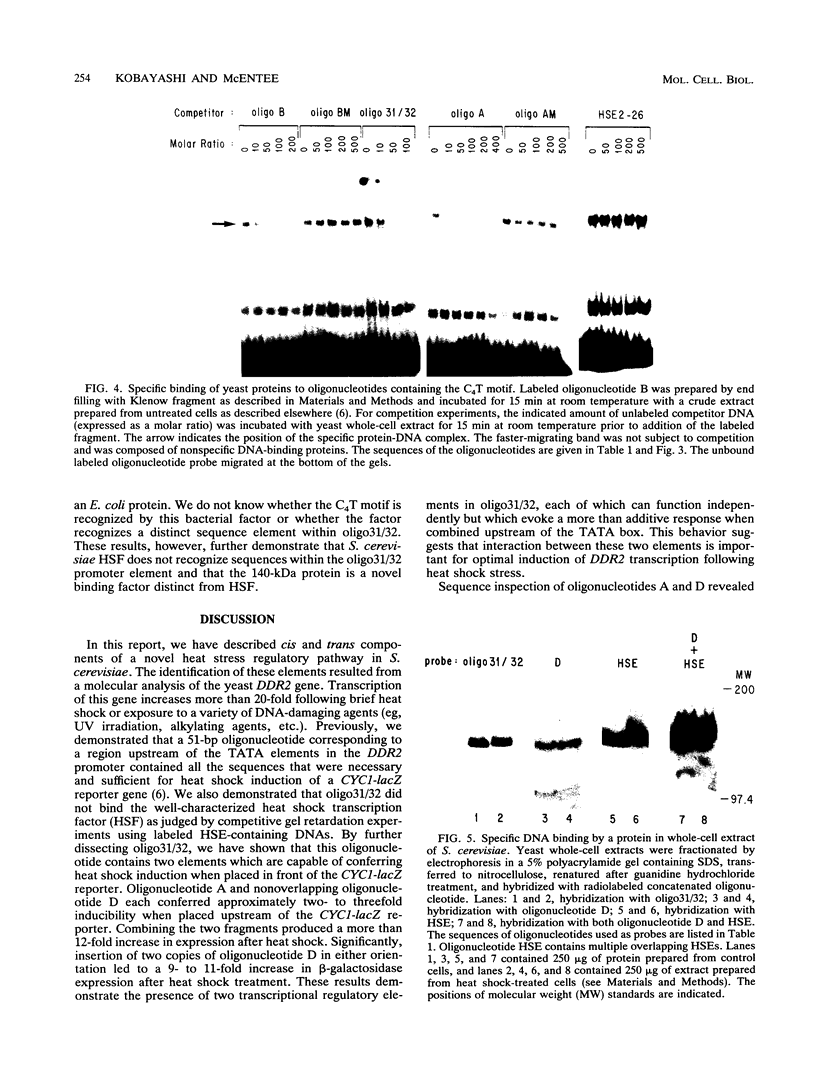
The stress-responsive DDR2 gene (previously called DDRA2) of Saccharomyces cerevisiae is transcribed at elevated levels following stress caused by heat shock or DNA damage. Previously, we identified a 51-bp promoter fragment, oligo31/32, which conferred heat shock inducibility on the heterologous CYC1-lacZ reporter gene in S. cerevisiae (N. Kobayashi and K. McEntee, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 87:6550-6554, 1990). Using a series of synthetic oligonucleotides, we have identified a pentanucleotide, CCCCT (C4T), as an essential component of this stress response sequence. This element is not a binding site for the well-characterized heat shock transcription factor which recognizes a distinct cis-acting heat shock element in the promoters of many heat shock genes. Here we demonstrate the ability of oligonucleotides containing the C4T sequence to confer heat shock inducibility on the reporter gene and show that the presence of two such elements produces more than additive effects on induction. Gel retardation experiments have been used to demonstrate specific complex formation between C4T-containing fragments and one or more yeast proteins. Formation of these complexes was not competed by fragments containing mutations in the C4T sequence nor by heat shock element-containing competitor DNAs. Fragments containing the C4T element bound to a single 140-kDa polypeptide, distinct from heat shock transcription factors in yeast crude extracts. These experiments identify key cis- and trans-acting components of a novel heat shock stress response pathway in S. cerevisiae.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amin J., Ananthan J., Voellmy R. Key features of heat shock regulatory elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;8(9):3761–3769. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.9.3761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clos J., Westwood J. T., Becker P. B., Wilson S., Lambert K., Wu C. Molecular cloning and expression of a hexameric Drosophila heat shock factor subject to negative regulation. Cell. 1990 Nov 30;63(5):1085–1097. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90511-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson J. W., Gross C. A. Identification of the sigma E subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase: a second alternate sigma factor involved in high-temperature gene expression. Genes Dev. 1989 Sep;3(9):1462–1471. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.9.1462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldenberg C. J., Luo Y., Fenna M., Baler R., Weinmann R., Voellmy R. Purified human factor activates heat shock promoter in a HeLa cell-free transcription system. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 25;263(36):19734–19739. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadonaga J. T., Tjian R. Affinity purification of sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5889–5893. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi N., McEntee K. Evidence for a heat shock transcription factor-independent mechanism for heat shock induction of transcription in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(17):6550–6554. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krueger J. H., Walker G. C. groEL and dnaK genes of Escherichia coli are induced by UV irradiation and nalidixic acid in an htpR+-dependent fashion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(5):1499–1503. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.5.1499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lue N. F., Kornberg R. D. Accurate initiation at RNA polymerase II promoters in extracts from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):8839–8843. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.8839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClanahan T., McEntee K. DNA damage and heat shock dually regulate genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;6(1):90–96. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.1.90. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ota I. M., Varshavsky A. A gene encoding a putative tyrosine phosphatase suppresses lethality of an N-end rule-dependent mutant. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 15;89(6):2355–2359. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.6.2355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park H. O., Craig E. A. Positive and negative regulation of basal expression of a yeast HSP70 gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 May;9(5):2025–2033. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.5.2025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R. A regulatory upstream promoter element in the Drosophila hsp 70 heat-shock gene. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):517–528. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90249-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perisic O., Xiao H., Lis J. T. Stable binding of Drosophila heat shock factor to head-to-head and tail-to-tail repeats of a conserved 5 bp recognition unit. Cell. 1989 Dec 1;59(5):797–806. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90603-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Praekelt U. M., Meacock P. A. HSP12, a new small heat shock gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: analysis of structure, regulation and function. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 Aug;223(1):97–106. doi: 10.1007/BF00315801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabindran S. K., Giorgi G., Clos J., Wu C. Molecular cloning and expression of a human heat shock factor, HSF1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):6906–6910. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.6906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarge K. D., Zimarino V., Holm K., Wu C., Morimoto R. I. Cloning and characterization of two mouse heat shock factors with distinct inducible and constitutive DNA-binding ability. Genes Dev. 1991 Oct;5(10):1902–1911. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.10.1902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scharf K. D., Rose S., Zott W., Schöffl F., Nover L., Schöff F. Three tomato genes code for heat stress transcription factors with a region of remarkable homology to the DNA-binding domain of the yeast HSF. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(13):4495–4501. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07900.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuetz T. J., Gallo G. J., Sheldon L., Tempst P., Kingston R. E. Isolation of a cDNA for HSF2: evidence for two heat shock factor genes in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):6911–6915. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.6911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorger P. K., Lewis M. J., Pelham H. R. Heat shock factor is regulated differently in yeast and HeLa cells. Nature. 1987 Sep 3;329(6134):81–84. doi: 10.1038/329081a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorger P. K., Pelham H. R. Purification and characterization of a heat-shock element binding protein from yeast. EMBO J. 1987 Oct;6(10):3035–3041. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02609.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorger P. K., Pelham H. R. Yeast heat shock factor is an essential DNA-binding protein that exhibits temperature-dependent phosphorylation. Cell. 1988 Sep 9;54(6):855–864. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)91219-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinson C. R., LaMarco K. L., Johnson P. F., Landschulz W. H., McKnight S. L. In situ detection of sequence-specific DNA binding activity specified by a recombinant bacteriophage. Genes Dev. 1988 Jul;2(7):801–806. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.7.801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Q. P., Kaguni J. M. A novel sigma factor is involved in expression of the rpoH gene of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1989 Aug;171(8):4248–4253. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.8.4248-4253.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiederrecht G., Seto D., Parker C. S. Isolation of the gene encoding the S. cerevisiae heat shock transcription factor. Cell. 1988 Sep 9;54(6):841–853. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)91197-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiederrecht G., Shuey D. J., Kibbe W. A., Parker C. S. The Saccharomyces and Drosophila heat shock transcription factors are identical in size and DNA binding properties. Cell. 1987 Feb 13;48(3):507–515. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90201-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieser R., Adam G., Wagner A., Schüller C., Marchler G., Ruis H., Krawiec Z., Bilinski T. Heat shock factor-independent heat control of transcription of the CTT1 gene encoding the cytosolic catalase T of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 5;266(19):12406–12411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. Two protein-binding sites in chromatin implicated in the activation of heat-shock genes. Nature. 1984 May 17;309(5965):229–234. doi: 10.1038/309229a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C., Wilson S., Walker B., Dawid I., Paisley T., Zimarino V., Ueda H. Purification and properties of Drosophila heat shock activator protein. Science. 1987 Nov 27;238(4831):1247–1253. doi: 10.1126/science.3685975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiao H., Lis J. T. Germline transformation used to define key features of heat-shock response elements. Science. 1988 Mar 4;239(4844):1139–1142. doi: 10.1126/science.3125608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimarino V., Wu C. Induction of sequence-specific binding of Drosophila heat shock activator protein without protein synthesis. 1987 Jun 25-Jul 1Nature. 327(6124):727–730. doi: 10.1038/327727a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]