Abstract
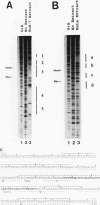
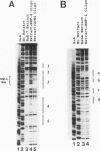
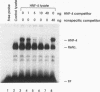
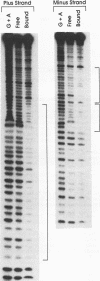
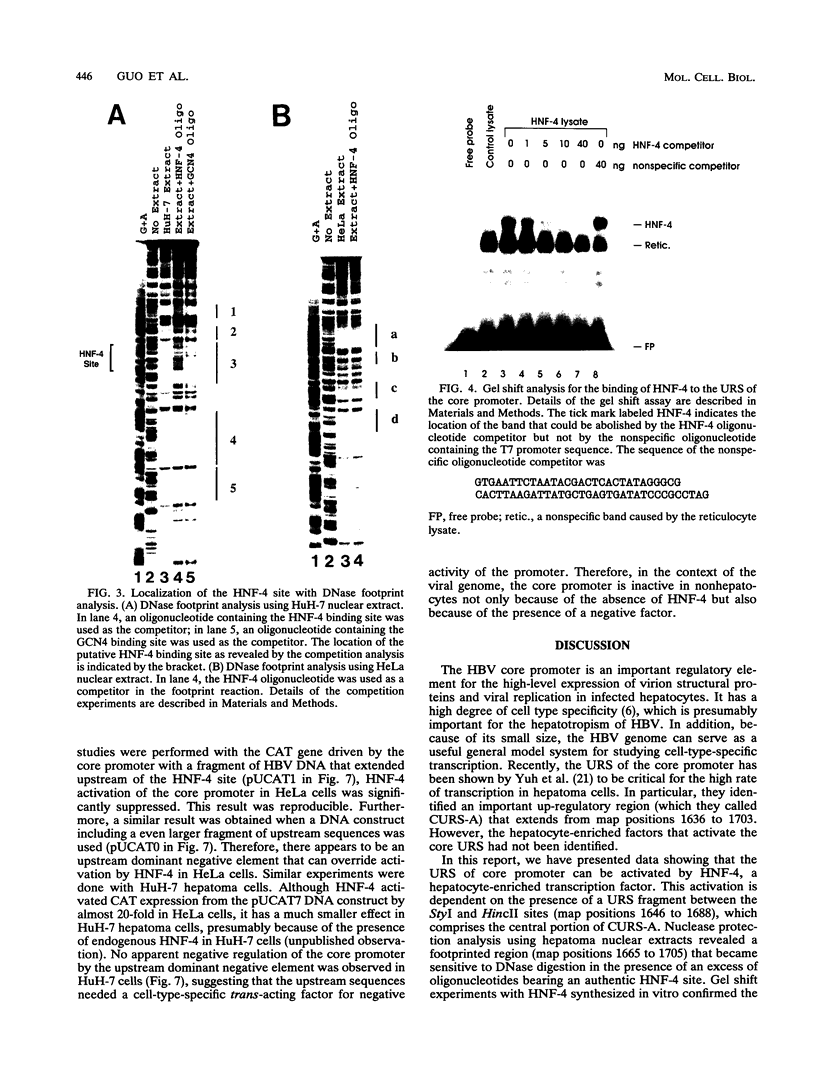
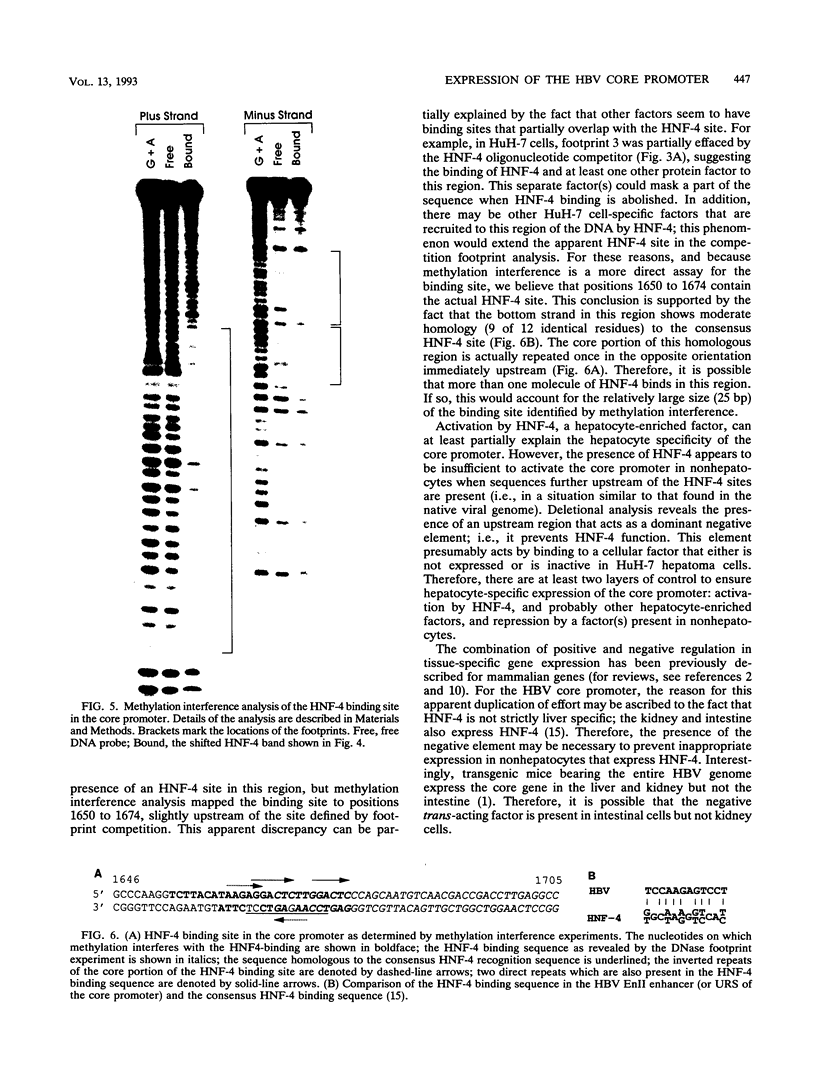
The core promoter of hepatitis B virus shows hepatocyte specificity, which is largely dependent on an upstream regulatory sequence that overlaps with viral enhancer II. Footprint analyses by numerous groups have shown binding by cellular proteins over a large stretch of DNA in this region, but the identity of these proteins and their role in core promoter function remain largely unknown. We present data showing that the transcription factor HNF-4 is one such factor, as it activates the core promoter approximately 20-fold via a binding site within the upstream regulatory sequence. Since HNF-4 is enriched in hepatocytes, its involvement at least partially explains the hepatocyte specificity of this promoter. In addition, however, we have found a region upstream of the HNF-4 site that suppresses activation by HNF-4 in HeLa cells but not in hepatoma cells. Therefore, the cell type specificity of the core promoter appears to result from a combination of activation by one or more factors specifically enriched in hepatocytes and repression by some other factor(s) present in nonhepatocytes, and it may provide a convenient model system for studying this type of tissue-specific transcriptional regulation in mammalian cells.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Farza H., Hadchouel M., Scotto J., Tiollais P., Babinet C., Pourcel C. Replication and gene expression of hepatitis B virus in a transgenic mouse that contains the complete viral genome. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4144–4152. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4144-4152.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foulkes N. S., Sassone-Corsi P. More is better: activators and repressors from the same gene. Cell. 1992 Feb 7;68(3):411–414. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90178-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman A. D., Landschulz W. H., McKnight S. L. CCAAT/enhancer binding protein activates the promoter of the serum albumin gene in cultured hepatoma cells. Genes Dev. 1989 Sep;3(9):1314–1322. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.9.1314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galas D. J., Schmitz A. DNAse footprinting: a simple method for the detection of protein-DNA binding specificity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Sep;5(9):3157–3170. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.9.3157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo W. T., Bell K. D., Ou J. H. Characterization of the hepatitis B virus EnhI enhancer and X promoter complex. J Virol. 1991 Dec;65(12):6686–6692. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.12.6686-6692.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honigwachs J., Faktor O., Dikstein R., Shaul Y., Laub O. Liver-specific expression of hepatitis B virus is determined by the combined action of the core gene promoter and the enhancer. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):919–924. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.919-924.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imagawa M., Osada S., Koyama Y., Suzuki T., Hirom P. C., Diccianni M. B., Morimura S., Muramatsu M. SF-B that binds to a negative element in glutathione transferase P gene is similar or identical to trans-activator LAP/IL6-DBP. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Aug 30;179(1):293–300. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91368-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- López-Cabrera M., Letovsky J., Hu K. Q., Siddiqui A. Multiple liver-specific factors bind to the hepatitis B virus core/pregenomic promoter: trans-activation and repression by CCAAT/enhancer binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(13):5069–5073. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.13.5069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- López-Cabrera M., Letovsky J., Hu K. Q., Siddiqui A. Transcriptional factor C/EBP binds to and transactivates the enhancer element II of the hepatitis B virus. Virology. 1991 Aug;183(2):825–829. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)91019-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Tjian R. Transcriptional regulation in mammalian cells by sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):371–378. doi: 10.1126/science.2667136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ou J. H., Bao H., Shih C., Tahara S. M. Preferred translation of human hepatitis B virus polymerase from core protein- but not from precore protein-specific transcript. J Virol. 1990 Sep;64(9):4578–4581. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.9.4578-4581.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pei D. Q., Shih C. H. Transcriptional activation and repression by cellular DNA-binding protein C/EBP. J Virol. 1990 Apr;64(4):1517–1522. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.4.1517-1522.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray M. B., Desmet V. J., Bradburne A. F., Desmyter J., Fevery J., De Groote J. Differential distribution of hepatitis B surface antigen and hepatitis B core antigen in the liver of hepatitis B patients. Gastroenterology. 1976 Sep;71(3):462–469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selden R. F., Howie K. B., Rowe M. E., Goodman H. M., Moore D. D. Human growth hormone as a reporter gene in regulation studies employing transient gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Sep;6(9):3173–3179. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.9.3173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sladek F. M., Zhong W. M., Lai E., Darnell J. E., Jr Liver-enriched transcription factor HNF-4 is a novel member of the steroid hormone receptor superfamily. Genes Dev. 1990 Dec;4(12B):2353–2365. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.12b.2353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su H., Yee J. K. Regulation of hepatitis B virus gene expression by its two enhancers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):2708–2712. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.2708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yee J. K. A liver-specific enhancer in the core promoter region of human hepatitis B virus. Science. 1989 Nov 3;246(4930):658–661. doi: 10.1126/science.2554495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuh C. H., Chang Y. L., Ting L. P. Transcriptional regulation of precore and pregenomic RNAs of hepatitis B virus. J Virol. 1992 Jul;66(7):4073–4084. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.7.4073-4084.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuh C. H., Ting L. P. C/EBP-like proteins binding to the functional box-alpha and box-beta of the second enhancer of hepatitis B virus. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):5044–5052. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.5044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou D. X., Yen T. S. Differential regulation of the hepatitis B virus surface gene promoters by a second viral enhancer. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 5;265(34):20731–20734. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]