Abstract
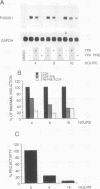
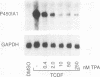
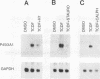
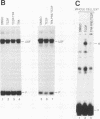
Signal transduction by dioxin (2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin) is mediated by the intracellular dioxin receptor which, in its dioxin-activated state, regulates transcription of target genes encoding drug-metabolizing enzymes, such as cytochrome P-450IA1 and glutathione S-transferase Ya. Exposure of the dioxin receptor to dioxin leads to an apparent translocation of the receptor to the nucleus in vivo and to a rapid conversion of the receptor from a latent, non-DNA-binding form to a species that binds to dioxin-responsive positive control elements in vitro. This DNA-binding form of receptor appears to be a heterodimeric complex with the helix-loop-helix factor Arnt. In this study, we show that activation of the cytochrome P-450IA1 gene and minimal dioxin-responsive reporter constructs by the dioxin receptor was inhibited following prolonged treatment of human keratinocytes with the phorbol ester 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate. Inhibition of the receptor-mediated activation response was also achieved by treatment of the cells with a number of protein kinase inhibitors, one of which, calphostin C, shows selectivity for protein kinase C. Taken together, these data suggest that protein kinase C-dependent phosphorylation may play an essential role in the dioxin signaling pathway. This hypothesis is supported by the observation that pretreatment of the cells with 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate inhibited the DNA-binding activity of the dioxin receptor in vivo. In vivo, the dioxin receptor was found to be a phosphoprotein. In vitro, dephosphorylation of the ligand-activated, heteromeric dioxin receptor form or dephosphorylation of the individual ligand-binding and Arnt receptor subunits inhibited the xenobiotic response element-binding activity. Moreover, dephosphorylation experiments with the individual receptor subunits prior to assembly of the xenobiotic response element-binding receptor form indicated that phosphorylation seemed to be important for the DNA-binding activity per se of the receptor, whereas Arnt appeared to require phosphorylation to interact with the receptor. Finally, a protein kinase C inhibitor-sensitive cytosolic catalytic activity that could restore the DNA-binding activity of the dephosphorylated dioxin receptor form was identified.
Full text
PDF



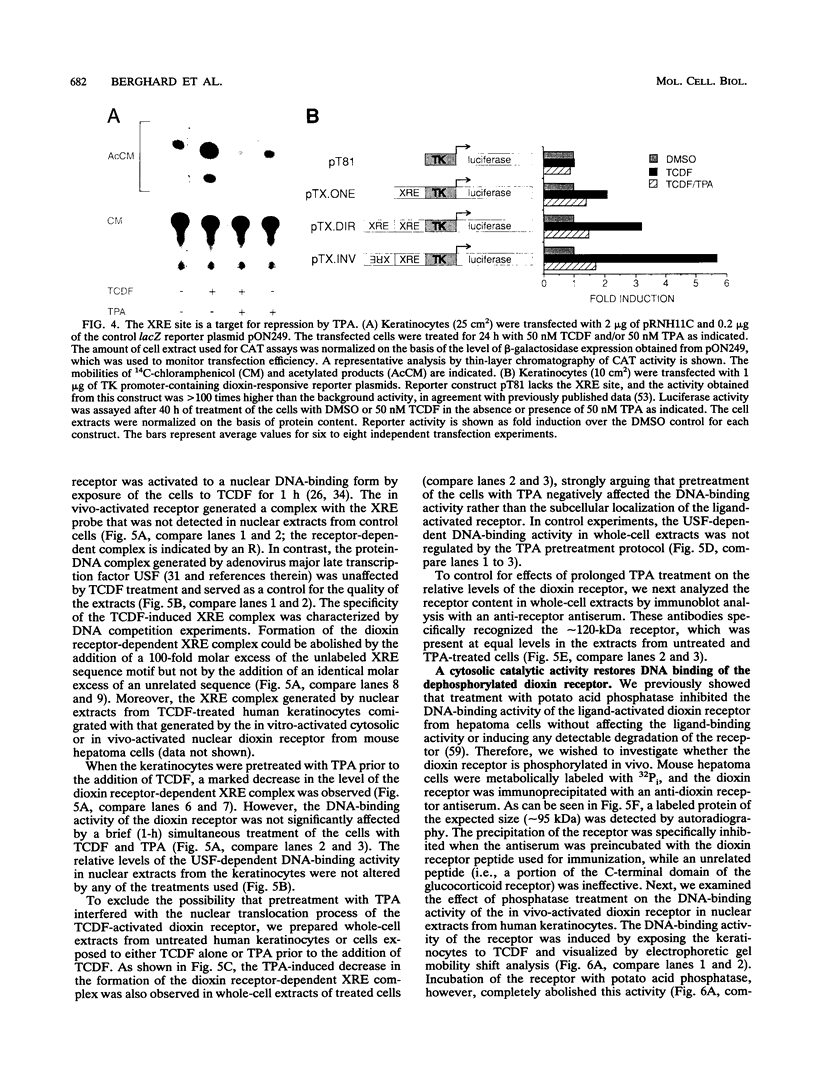
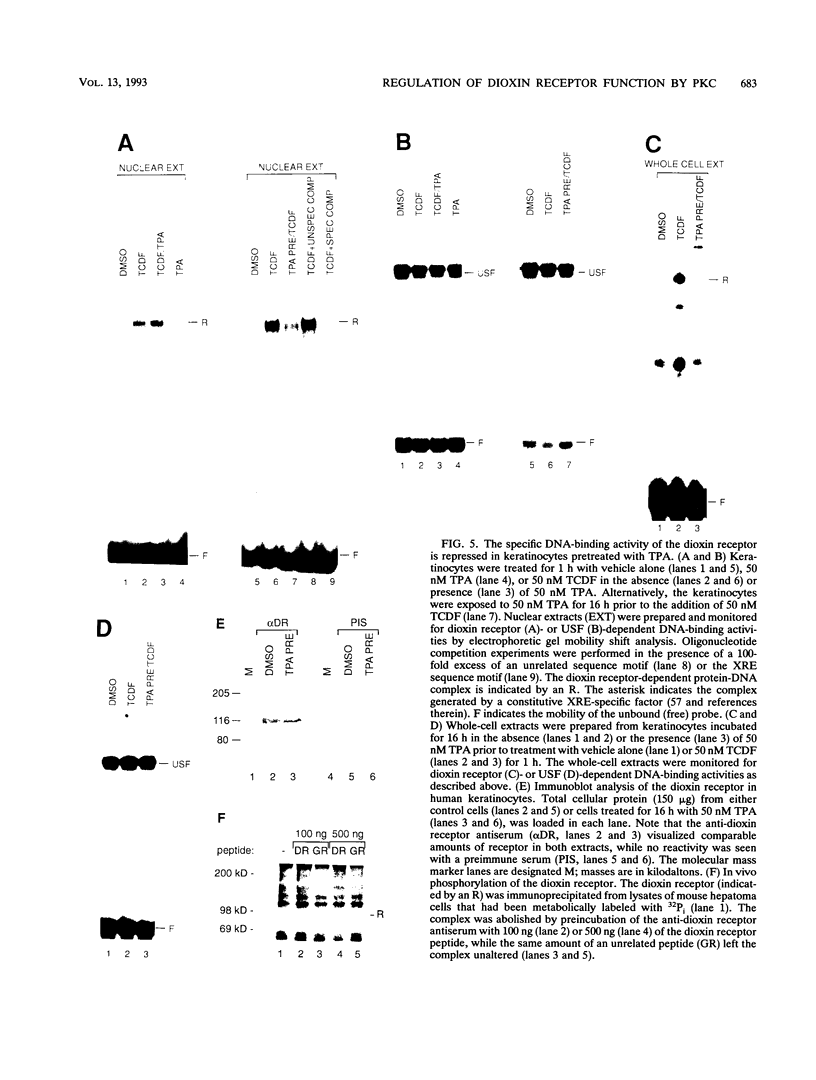

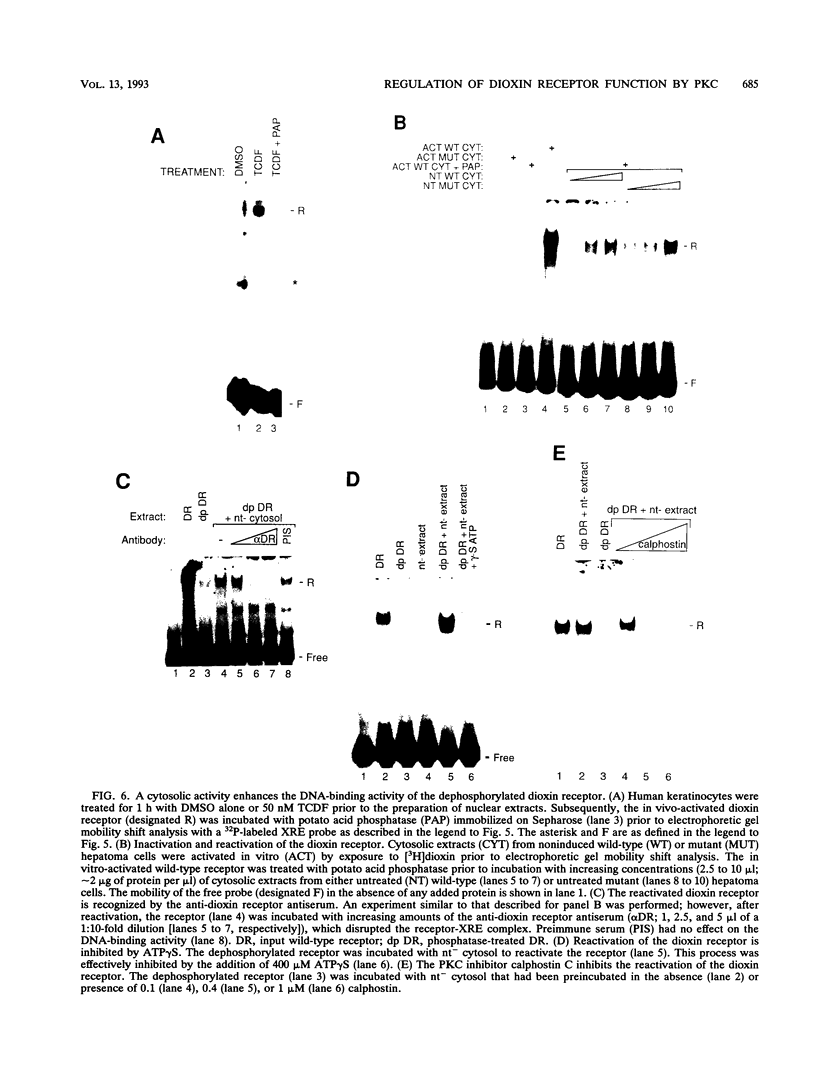
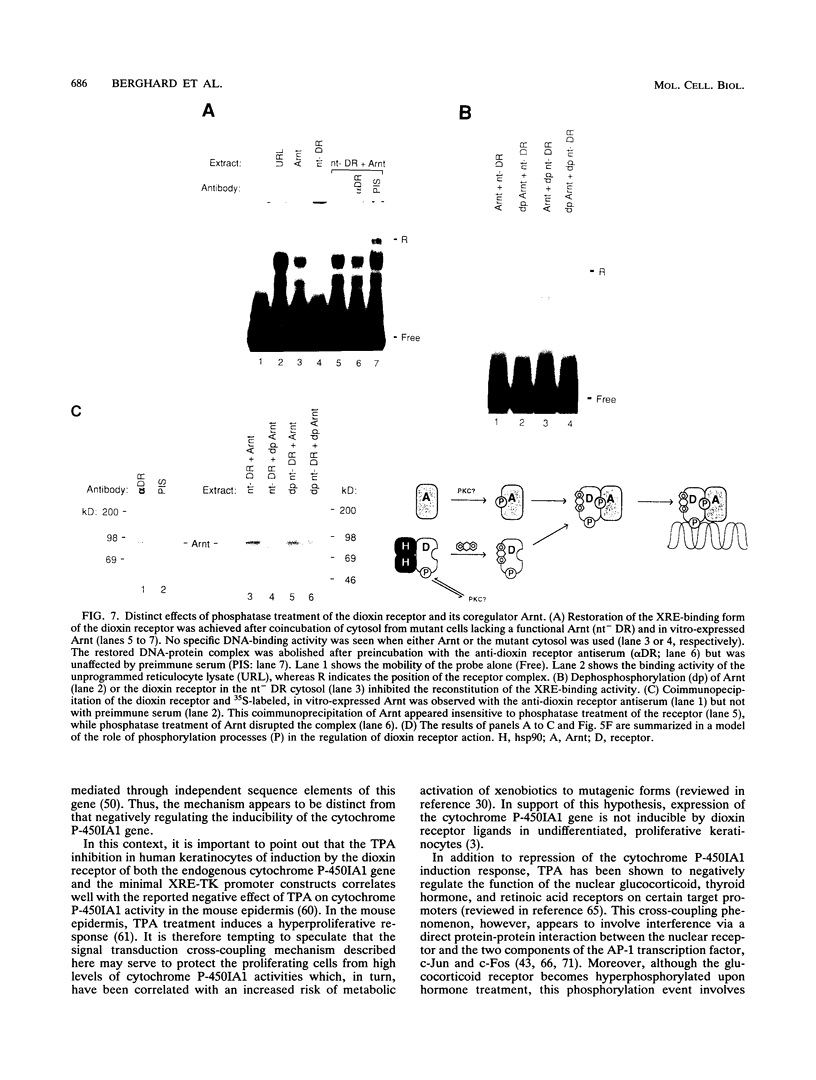



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adamo S., Caporale C., Nervi C., Ceci R., Molinaro M. Activity and regulation of calcium-, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase in differentiating chick myogenic cells. J Cell Biol. 1989 Jan;108(1):153–158. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.1.153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auwerx J., Sassone-Corsi P. IP-1: a dominant inhibitor of Fos/Jun whose activity is modulated by phosphorylation. Cell. 1991 Mar 8;64(5):983–993. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90322-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
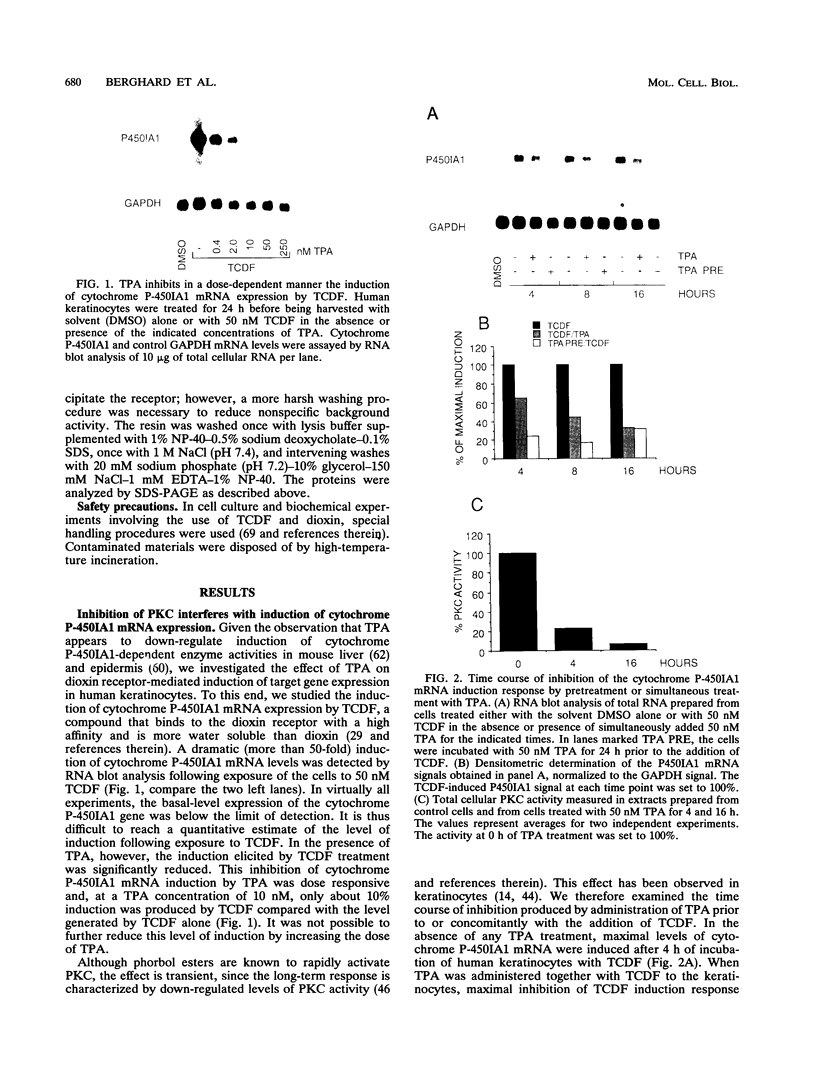
- Berghard A., Gradin K., Toftgård R. Serum and extracellular calcium modulate induction of cytochrome P-450IA1 in human keratinocytes. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 5;265(34):21086–21090. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumberg P. M. Complexities of the protein kinase C pathway. Mol Carcinog. 1991;4(5):339–344. doi: 10.1002/mc.2940040502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodwell J. E., Ortí E., Coull J. M., Pappin D. J., Smith L. I., Swift F. Identification of phosphorylated sites in the mouse glucocorticoid receptor. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 25;266(12):7549–7555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle W. J., Smeal T., Defize L. H., Angel P., Woodgett J. R., Karin M., Hunter T. Activation of protein kinase C decreases phosphorylation of c-Jun at sites that negatively regulate its DNA-binding activity. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):573–584. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90241-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruns R. F., Miller F. D., Merriman R. L., Howbert J. J., Heath W. F., Kobayashi E., Takahashi I., Tamaoki T., Nakano H. Inhibition of protein kinase C by calphostin C is light-dependent. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Apr 15;176(1):288–293. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)90922-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchner K., Otto H., Hilbert R., Lindschau C., Haller H., Hucho F. Properties of protein kinase C associated with nuclear membranes. Biochem J. 1992 Sep 1;286(Pt 2):369–375. doi: 10.1042/bj2860369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrier F., Owens R. A., Nebert D. W., Puga A. Dioxin-dependent activation of murine Cyp1a-1 gene transcription requires protein kinase C-dependent phosphorylation. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;12(4):1856–1863. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.4.1856. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chauchereau A., Loosfelt H., Milgrom E. Phosphorylation of transfected wild type and mutated progesterone receptors. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 25;266(27):18280–18286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherrington J. M., Mocarski E. S. Human cytomegalovirus ie1 transactivates the alpha promoter-enhancer via an 18-base-pair repeat element. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1435–1440. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1435-1440.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chida K., Kato N., Kuroki T. Down regulation of phorbol diester receptors by proteolytic degradation of protein kinase C in a cultured cell line of fetal rat skin keratinocytes. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 5;261(28):13013–13018. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuthill S., Wilhelmsson A., Poellinger L. Role of the ligand in intracellular receptor function: receptor affinity determines activation in vitro of the latent dioxin receptor to a DNA-binding form. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;11(1):401–411. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.1.401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denis M., Poellinger L., Wikstöm A. C., Gustafsson J. A. Requirement of hormone for thermal conversion of the glucocorticoid receptor to a DNA-binding state. Nature. 1988 Jun 16;333(6174):686–688. doi: 10.1038/333686a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denison M. S., Fisher J. M., Whitlock J. P., Jr Inducible, receptor-dependent protein-DNA interactions at a dioxin-responsive transcriptional enhancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2528–2532. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denner L. A., Weigel N. L., Maxwell B. L., Schrader W. T., O'Malley B. W. Regulation of progesterone receptor-mediated transcription by phosphorylation. Science. 1990 Dec 21;250(4988):1740–1743. doi: 10.1126/science.2176746. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckstein F. Nucleoside phosphorothioates. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:367–402. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.002055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ema M., Sogawa K., Watanabe N., Chujoh Y., Matsushita N., Gotoh O., Funae Y., Fujii-Kuriyama Y. cDNA cloning and structure of mouse putative Ah receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Apr 15;184(1):246–253. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91185-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felgner P. L., Gadek T. R., Holm M., Roman R., Chan H. W., Wenz M., Northrop J. P., Ringold G. M., Danielsen M. Lipofection: a highly efficient, lipid-mediated DNA-transfection procedure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7413–7417. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fort P., Marty L., Piechaczyk M., el Sabrouty S., Dani C., Jeanteur P., Blanchard J. M. Various rat adult tissues express only one major mRNA species from the glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate-dehydrogenase multigenic family. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Mar 11;13(5):1431–1442. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.5.1431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujisawa-Sehara A., Sogawa K., Yamane M., Fujii-Kuriyama Y. Characterization of xenobiotic responsive elements upstream from the drug-metabolizing cytochrome P-450c gene: a similarity to glucocorticoid regulatory elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 May 26;15(10):4179–4191. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.10.4179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujisawa-Sehara A., Yamane M., Fujii-Kuriyama Y. A DNA-binding factor specific for xenobiotic responsive elements of P-450c gene exists as a cryptic form in cytoplasm: its possible translocation to nucleus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):5859–5863. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.5859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauthier-Rouvière C., Basset M., Blanchard J. M., Cavadore J. C., Fernandez A., Lamb N. J. Casein kinase II induces c-fos expression via the serum response element pathway and p67SRF phosphorylation in living fibroblasts. EMBO J. 1991 Oct;10(10):2921–2930. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07842.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh S., Baltimore D. Activation in vitro of NF-kappa B by phosphorylation of its inhibitor I kappa B. Nature. 1990 Apr 12;344(6267):678–682. doi: 10.1038/344678a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillner M., Bergman J., Cambillau C., Fernström B., Gustafsson J. A. Interactions of indoles with specific binding sites for 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin in rat liver. Mol Pharmacol. 1985 Oct;28(4):357–363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez F. J., Nebert D. W. Evolution of the P450 gene superfamily: animal-plant 'warfare', molecular drive and human genetic differences in drug oxidation. Trends Genet. 1990 Jun;6(6):182–186. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90174-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregor P. D., Sawadogo M., Roeder R. G. The adenovirus major late transcription factor USF is a member of the helix-loop-helix group of regulatory proteins and binds to DNA as a dimer. Genes Dev. 1990 Oct;4(10):1730–1740. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.10.1730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hankinson O. Dominant and recessive aryl hydrocarbon hydroxylase-deficient mutants of mouse hepatoma line, Hepa-1, and assignment of recessive mutants to three complementation groups. Somatic Cell Genet. 1983 Jul;9(4):497–514. doi: 10.1007/BF01543050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannun Y. A., Loomis C. R., Bell R. M. Activation of protein kinase C by Triton X-100 mixed micelles containing diacylglycerol and phosphatidylserine. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 25;260(18):10039–10043. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hapgood J., Cuthill S., Denis M., Poellinger L., Gustafsson J. A. Specific protein-DNA interactions at a xenobiotic-responsive element: copurification of dioxin receptor and DNA-binding activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(1):60–64. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.1.60. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennings H., Michael D., Cheng C., Steinert P., Holbrook K., Yuspa S. H. Calcium regulation of growth and differentiation of mouse epidermal cells in culture. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):245–254. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90406-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrick-Davis K., Camussi G., Bussolino F., Baglioni C. Modulation of neurite outgrowth in neuroblastoma cells by protein kinase C and platelet-activating factor. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 5;266(28):18620–18625. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hines R. N., Mathis J. M., Jacob C. S. Identification of multiple regulatory elements on the human cytochrome P450IA1 gene. Carcinogenesis. 1988 Sep;9(9):1599–1605. doi: 10.1093/carcin/9.9.1599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoeck W., Groner B. Hormone-dependent phosphorylation of the glucocorticoid receptor occurs mainly in the amino-terminal transactivation domain. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 5;265(10):5403–5408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman E. C., Reyes H., Chu F. F., Sander F., Conley L. H., Brooks B. A., Hankinson O. Cloning of a factor required for activity of the Ah (dioxin) receptor. Science. 1991 May 17;252(5008):954–958. doi: 10.1126/science.1852076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Karin M. The regulation of transcription by phosphorylation. Cell. 1992 Aug 7;70(3):375–387. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90162-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaiswal A. K., Gonzalez F. J., Nebert D. W. Human dioxin-inducible cytochrome P1-450: complementary DNA and amino acid sequence. Science. 1985 Apr 5;228(4695):80–83. doi: 10.1126/science.3838385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonat C., Rahmsdorf H. J., Park K. K., Cato A. C., Gebel S., Ponta H., Herrlich P. Antitumor promotion and antiinflammation: down-modulation of AP-1 (Fos/Jun) activity by glucocorticoid hormone. Cell. 1990 Sep 21;62(6):1189–1204. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90395-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kast R., Fürstenberger G., Marks F. Activation of a keratinocyte phospholipase A2 by bradykinin and 4 beta-phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate. Evidence for a receptor-GTP-binding protein versus a protein-kinase-C mediated mechanism. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Dec 18;202(3):941–950. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb16454.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawajiri K., Watanabe J., Gotoh O., Tagashira Y., Sogawa K., Fujii-Kuriyama Y. Structure and drug inducibility of the human cytochrome P-450c gene. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Sep 1;159(2):219–225. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09857.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikkawa U., Nishizuka Y. The role of protein kinase C in transmembrane signalling. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2:149–178. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.02.110186.001053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landers J. P., Bunce N. J. The Ah receptor and the mechanism of dioxin toxicity. Biochem J. 1991 Jun 1;276(Pt 2):273–287. doi: 10.1042/bj2760273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manak J. R., de Bisschop N., Kris R. M., Prywes R. Casein kinase II enhances the DNA binding activity of serum response factor. Genes Dev. 1990 Jun;4(6):955–967. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.6.955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miesfeld R., Rusconi S., Godowski P. J., Maler B. A., Okret S., Wikström A. C., Gustafsson J. A., Yamamoto K. R. Genetic complementation of a glucocorticoid receptor deficiency by expression of cloned receptor cDNA. Cell. 1986 Aug 1;46(3):389–399. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90659-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore C. C., Brentano S. T., Miller W. L. Human P450scc gene transcription is induced by cyclic AMP and repressed by 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate and A23187 through independent cis elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;10(11):6013–6023. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.11.6013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuhold L. A., Shirayoshi Y., Ozato K., Jones J. E., Nebert D. W. Regulation of mouse CYP1A1 gene expression by dioxin: requirement of two cis-acting elements during induction. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;9(6):2378–2386. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.6.2378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The molecular heterogeneity of protein kinase C and its implications for cellular regulation. Nature. 1988 Aug 25;334(6184):661–665. doi: 10.1038/334661a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordeen S. K. Luciferase reporter gene vectors for analysis of promoters and enhancers. Biotechniques. 1988 May;6(5):454–458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okino S. T., Pendurthi U. R., Tukey R. H. Phorbol esters inhibit the dioxin receptor-mediated transcriptional activation of the mouse Cyp1a-1 and Cyp1a-2 genes by 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 5;267(10):6991–6998. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulson K. E., Darnell J. E., Jr, Rushmore T., Pickett C. B. Analysis of the upstream elements of the xenobiotic compound-inducible and positionally regulated glutathione S-transferase Ya gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):1841–1852. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.1841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard D., Salser S. J., Yamamoto K. R. A movable and regulable inactivation function within the steroid binding domain of the glucocorticoid receptor. Cell. 1988 Sep 23;54(7):1073–1080. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90122-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poellinger L., Göttlicher M., Gustafsson J. A. The dioxin and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors: nuclear receptors in search of endogenous ligands. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1992 Jun;13(6):241–245. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(92)90076-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poland A., Knutson J. C. 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin and related halogenated aromatic hydrocarbons: examination of the mechanism of toxicity. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1982;22:517–554. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.22.040182.002505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pongratz I., Strömstedt P. E., Mason G. G., Poellinger L. Inhibition of the specific DNA binding activity of the dioxin receptor by phosphatase treatment. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 5;266(25):16813–16817. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puhvel S. M., Ertl D. C. Decreased induction of aryl hydrocarbon hydroxylase activity in hyperproliferative hairless mouse epidermis. Br J Dermatol. 1984 Jan;110(1):29–35. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1984.tb07308.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raick A. N. Ultrastructural, histological, and biochemical alterations produced by 12-O-tetradecanoyl-phorbol-13-acetate on mouse epidermis and their relevance to skin tumor promotion. Cancer Res. 1973 Feb;33(2):269–286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raunio H., Pelkonen O. Effect of polycyclic aromatic compounds and phorbol esters on ornithine decarboxylase and aryl hydrocarbon hydroxylase activities in mouse liver. Cancer Res. 1983 Feb;43(2):782–786. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reyes H., Reisz-Porszasz S., Hankinson O. Identification of the Ah receptor nuclear translocator protein (Arnt) as a component of the DNA binding form of the Ah receptor. Science. 1992 May 22;256(5060):1193–1195. doi: 10.1126/science.256.5060.1193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schüle R., Evans R. M. Cross-coupling of signal transduction pathways: zinc finger meets leucine zipper. Trends Genet. 1991 Nov-Dec;7(11-12):377–381. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(91)90259-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schüle R., Rangarajan P., Kliewer S., Ransone L. J., Bolado J., Yang N., Verma I. M., Evans R. M. Functional antagonism between oncoprotein c-Jun and the glucocorticoid receptor. Cell. 1990 Sep 21;62(6):1217–1226. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90397-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamaoki T., Nakano H. Potent and specific inhibitors of protein kinase C of microbial origin. Biotechnology (N Y) 1990 Aug;8(8):732–735. doi: 10.1038/nbt0890-732. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H., Davis R., Tapscott S., Thayer M., Krause M., Benezra R., Blackwell T. K., Turner D., Rupp R., Hollenberg S. The myoD gene family: nodal point during specification of the muscle cell lineage. Science. 1991 Feb 15;251(4995):761–766. doi: 10.1126/science.1846704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilhelmsson A., Cuthill S., Denis M., Wikström A. C., Gustafsson J. A., Poellinger L. The specific DNA binding activity of the dioxin receptor is modulated by the 90 kd heat shock protein. EMBO J. 1990 Jan;9(1):69–76. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08081.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K. K., Gonzalez G. A., Biggs W. H., 3rd, Montminy M. R. Phosphorylation-induced binding and transcriptional efficacy of nuclear factor CREB. Nature. 1988 Aug 11;334(6182):494–498. doi: 10.1038/334494a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang-Yen H. F., Chambard J. C., Sun Y. L., Smeal T., Schmidt T. J., Drouin J., Karin M. Transcriptional interference between c-Jun and the glucocorticoid receptor: mutual inhibition of DNA binding due to direct protein-protein interaction. Cell. 1990 Sep 21;62(6):1205–1215. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90396-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]