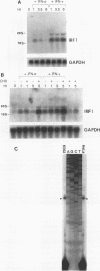
Abstract
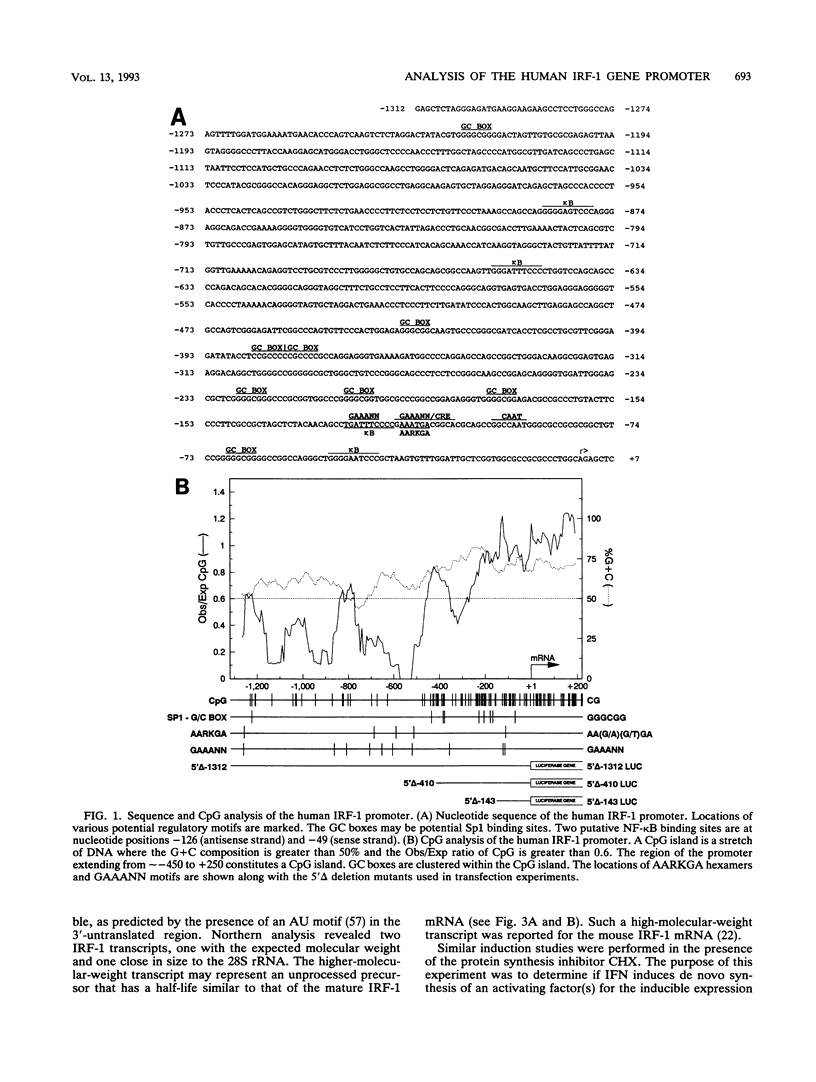
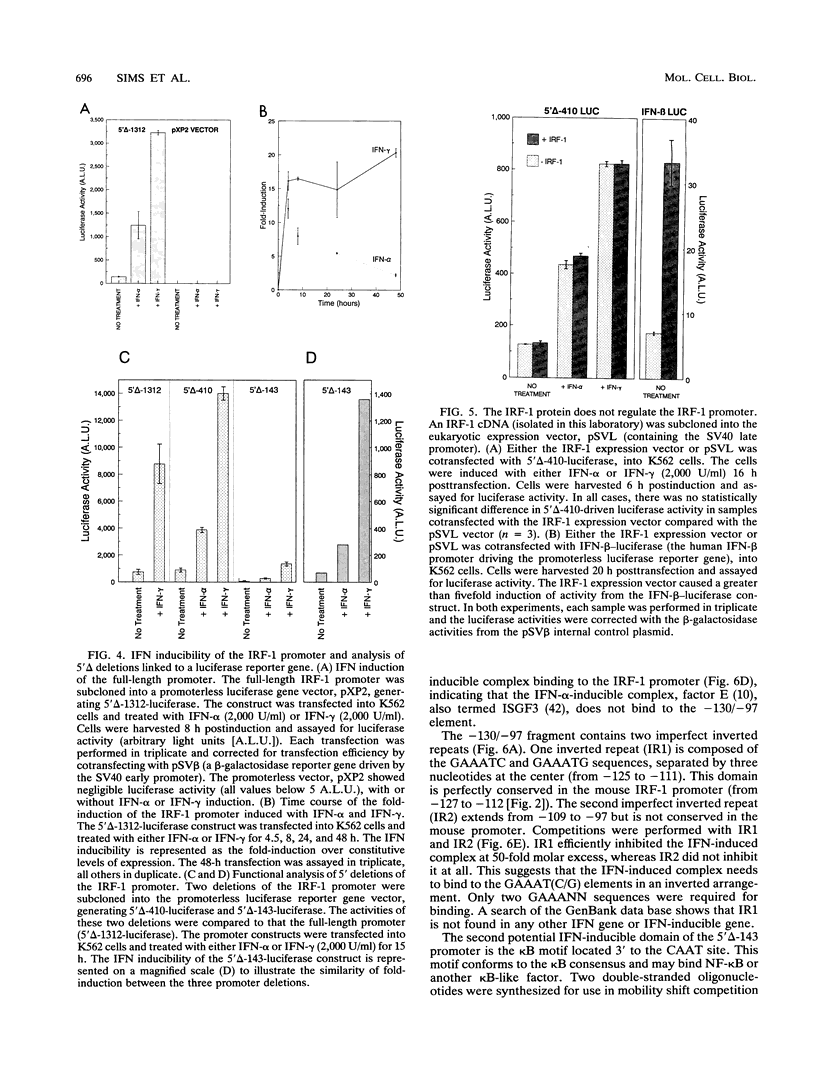
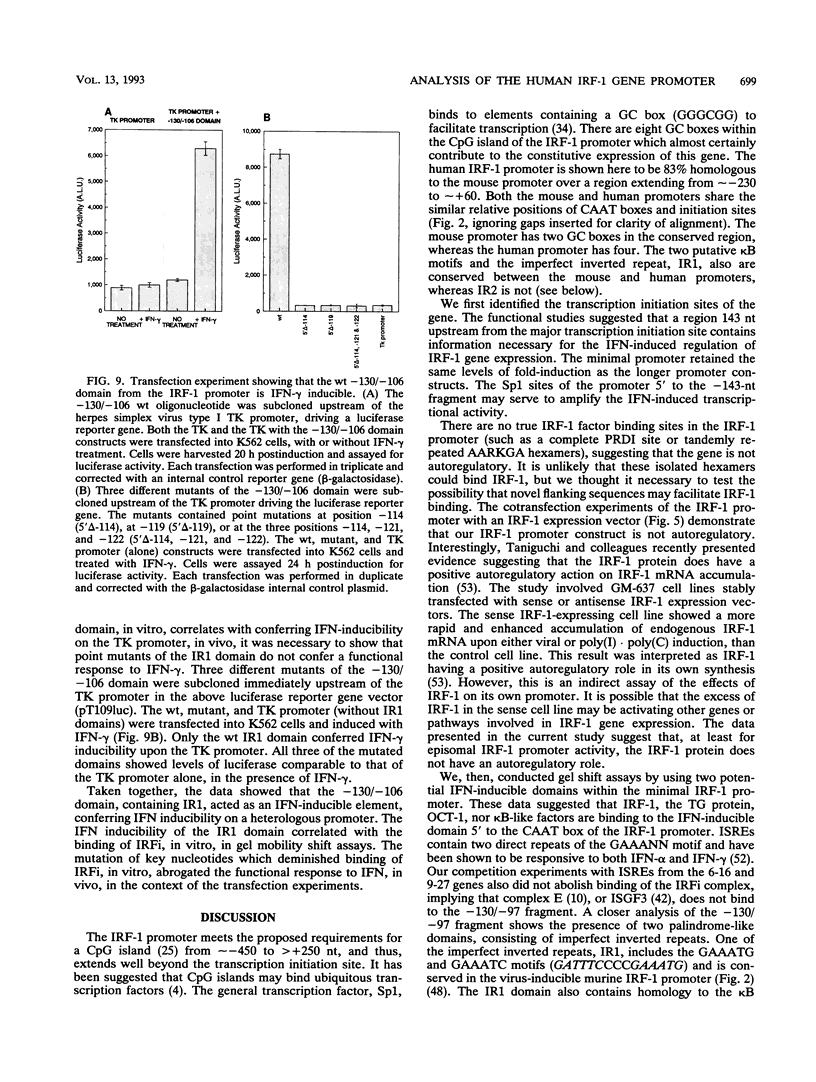
We have cloned and functionally characterized the human interferon regulatory factor 1 (IRF-1) gene promoter. The promoter contains a CpG island, with several GC boxes, a CAAT box, but no TATA box. IRF-1 mRNA is strongly induced by gamma interferon (IFN-gamma) but more weakly and transiently by IFN-alpha. There are several putative kappa B motifs and numerous AA(G/A)G(G/T)A and GAAANN motifs throughout the promoter. The IRF-1 promoter is not autoregulated by the IRF-1 gene product. IFN inducibility of the promoter was studied with 5' deletion mutants linked to a heterologous reporter gene. Gel mobility shift assays were used to show IFN-inducible factor binding to the IRF-1 promoter. These studies showed that IFN inducibility is conferred by a novel imperfect inverted-repeat arrangement of two GAAANN motifs within a domain, 130 nucleotides upstream of transcription initiation. This inverted repeat binds a factor upon induction with IFN and can confer IFN inducibility on a heterologous promoter. Conversely, point mutations of the inverted repeat are not IFN inducible when linked to the same heterologous promoter.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abdollahi A., Lord K. A., Hoffman-Liebermann B., Liebermann D. A. Interferon regulatory factor 1 is a myeloid differentiation primary response gene induced by interleukin 6 and leukemia inhibitory factor: role in growth inhibition. Cell Growth Differ. 1991 Aug;2(8):401–407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baeuerle P. A. The inducible transcription activator NF-kappa B: regulation by distinct protein subunits. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Apr 16;1072(1):63–80. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(91)90007-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basta P. V., Sherman P. A., Ting J. P. Detailed delineation of an interferon-gamma-responsive element important in human HLA-DRA gene expression in a glioblastoma multiform line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8618–8622. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird A. P. CpG-rich islands and the function of DNA methylation. Nature. 1986 May 15;321(6067):209–213. doi: 10.1038/321209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanar M. A., Baldwin A. S., Jr, Flavell R. A., Sharp P. A. A gamma-interferon-induced factor that binds the interferon response sequence of the MHC class I gene, H-2Kb. EMBO J. 1989 Apr;8(4):1139–1144. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03484.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang D. C. Cell poration and cell fusion using an oscillating electric field. Biophys J. 1989 Oct;56(4):641–652. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82711-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang D. C., Gao P. Q., Maxwell B. L. High efficiency gene transfection by electroporation using a radio-frequency electric field. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Apr 17;1092(2):153–160. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(91)90149-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Yen T. J. Multiple determinants of eukaryotic mRNA stability. New Biol. 1989 Nov;1(2):121–126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale T. C., Imam A. M., Kerr I. M., Stark G. R. Rapid activation by interferon alpha of a latent DNA-binding protein present in the cytoplasm of untreated cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(4):1203–1207. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.4.1203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale T. C., Rosen J. M., Guille M. J., Lewin A. R., Porter A. G., Kerr I. M., Stark G. R. Overlapping sites for constitutive and induced DNA binding factors involved in interferon-stimulated transcription. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):831–839. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03444.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker T., Lew D. J., Mirkovitch J., Darnell J. E., Jr Cytoplasmic activation of GAF, an IFN-gamma-regulated DNA-binding factor. EMBO J. 1991 Apr;10(4):927–932. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08026.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driggers P. H., Ennist D. L., Gleason S. L., Mak W. H., Marks M. S., Levi B. Z., Flanagan J. R., Appella E., Ozato K. An interferon gamma-regulated protein that binds the interferon-inducible enhancer element of major histocompatibility complex class I genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(10):3743–3747. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.10.3743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. Control of eukaryotic messenger RNA synthesis by sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins. 1985 Aug 29-Sep 4Nature. 316(6031):774–778. doi: 10.1038/316774a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan C. M., Maniatis T. A DNA-binding protein containing two widely separated zinc finger motifs that recognize the same DNA sequence. Genes Dev. 1990 Jan;4(1):29–42. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.1.29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan C. M., Maniatis T. Two different virus-inducible elements are required for human beta-interferon gene regulation. EMBO J. 1989 Jan;8(1):101–110. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03353.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita T., Kimura Y., Miyamoto M., Barsoumian E. L., Taniguchi T. Induction of endogenous IFN-alpha and IFN-beta genes by a regulatory transcription factor, IRF-1. Nature. 1989 Jan 19;337(6204):270–272. doi: 10.1038/337270a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita T., Miyamoto M., Kimura Y., Hammer J., Taniguchi T. Involvement of a cis-element that binds an H2TF-1/NF kappa B like factor(s) in the virus-induced interferon-beta gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 May 11;17(9):3335–3346. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.9.3335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita T., Ohno S., Yasumitsu H., Taniguchi T. Delimitation and properties of DNA sequences required for the regulated expression of human interferon-beta gene. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):489–496. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80022-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita T., Reis L. F., Watanabe N., Kimura Y., Taniguchi T., Vilcek J. Induction of the transcription factor IRF-1 and interferon-beta mRNAs by cytokines and activators of second-messenger pathways. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):9936–9940. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.9936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita T., Sakakibara J., Sudo Y., Miyamoto M., Kimura Y., Taniguchi T. Evidence for a nuclear factor(s), IRF-1, mediating induction and silencing properties to human IFN-beta gene regulatory elements. EMBO J. 1988 Nov;7(11):3397–3405. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03213.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita T., Shibuya H., Hotta H., Yamanishi K., Taniguchi T. Interferon-beta gene regulation: tandemly repeated sequences of a synthetic 6 bp oligomer function as a virus-inducible enhancer. Cell. 1987 May 8;49(3):357–367. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90288-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardiner-Garden M., Frommer M. CpG islands in vertebrate genomes. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jul 20;196(2):261–282. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90689-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gidoni D., Dynan W. S., Tjian R. Multiple specific contacts between a mammalian transcription factor and its cognate promoters. 1984 Nov 29-Dec 5Nature. 312(5993):409–413. doi: 10.1038/312409a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodbourn S., Burstein H., Maniatis T. The human beta-interferon gene enhancer is under negative control. Cell. 1986 May 23;45(4):601–610. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90292-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodbourn S., Maniatis T. Overlapping positive and negative regulatory domains of the human beta-interferon gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1447–1451. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodbourn S. The regulation of beta-interferon gene expression. Semin Cancer Biol. 1990 Feb;1(1):89–95. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada H., Fujita T., Miyamoto M., Kimura Y., Maruyama M., Furia A., Miyata T., Taniguchi T. Structurally similar but functionally distinct factors, IRF-1 and IRF-2, bind to the same regulatory elements of IFN and IFN-inducible genes. Cell. 1989 Aug 25;58(4):729–739. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90107-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada H., Willison K., Sakakibara J., Miyamoto M., Fujita T., Taniguchi T. Absence of the type I IFN system in EC cells: transcriptional activator (IRF-1) and repressor (IRF-2) genes are developmentally regulated. Cell. 1990 Oct 19;63(2):303–312. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90163-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiscott J., Alper D., Cohen L., Leblanc J. F., Sportza L., Wong A., Xanthoudakis S. Induction of human interferon gene expression is associated with a nuclear factor that interacts with the NF-kappa B site of the human immunodeficiency virus enhancer. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2557–2566. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2557-2566.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imam A. M., Ackrill A. M., Dale T. C., Kerr I. M., Stark G. R. Transcription factors induced by interferons alpha and gamma. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Nov 25;18(22):6573–6580. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.22.6573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr I. M., Stark G. R. The control of interferon-inducible gene expression. FEBS Lett. 1991 Jul 22;285(2):194–198. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80802-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler D. S., Levy D. E., Darnell J. E., Jr Two interferon-induced nuclear factors bind a single promoter element in interferon-stimulated genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8521–8525. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraft R., Tardiff J., Krauter K. S., Leinwand L. A. Using mini-prep plasmid DNA for sequencing double stranded templates with Sequenase. Biotechniques. 1988 Jun;6(6):544-6, 549. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhl D., de la Fuente J., Chaturvedi M., Parimoo S., Ryals J., Meyer F., Weissmann C. Reversible silencing of enhancers by sequences derived from the human IFN-alpha promoter. Cell. 1987 Sep 25;50(7):1057–1069. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90172-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusari J., Sen G. C. Regulation of synthesis and turnover of an interferon-inducible mRNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2062–2067. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leblanc J. F., Cohen L., Rodrigues M., Hiscott J. Synergism between distinct enhanson domains in viral induction of the human beta interferon gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):3987–3993. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.3987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenardo M. J., Fan C. M., Maniatis T., Baltimore D. The involvement of NF-kappa B in beta-interferon gene regulation reveals its role as widely inducible mediator of signal transduction. Cell. 1989 Apr 21;57(2):287–294. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90966-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy D. E., Kessler D. S., Pine R., Darnell J. E., Jr Cytoplasmic activation of ISGF3, the positive regulator of interferon-alpha-stimulated transcription, reconstituted in vitro. Genes Dev. 1989 Sep;3(9):1362–1371. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.9.1362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy D. E., Kessler D. S., Pine R., Reich N., Darnell J. E., Jr Interferon-induced nuclear factors that bind a shared promoter element correlate with positive and negative transcriptional control. Genes Dev. 1988 Apr;2(4):383–393. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.4.383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald N. J., Kuhl D., Maguire D., Näf D., Gallant P., Goswamy A., Hug H., Büeler H., Chaturvedi M., de la Fuente J. Different pathways mediate virus inducibility of the human IFN-alpha 1 and IFN-beta genes. Cell. 1990 Mar 9;60(5):767–779. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90091-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGregor G. R., Caskey C. T. Construction of plasmids that express E. coli beta-galactosidase in mammalian cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Mar 25;17(6):2365–2365. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.6.2365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama M., Fujita T., Taniguchi T. Sequence of a cDNA coding for human IRF-1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Apr 25;17(8):3292–3292. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.8.3292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto M., Fujita T., Kimura Y., Maruyama M., Harada H., Sudo Y., Miyata T., Taniguchi T. Regulated expression of a gene encoding a nuclear factor, IRF-1, that specifically binds to IFN-beta gene regulatory elements. Cell. 1988 Sep 9;54(6):903–913. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)91307-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordeen S. K. Luciferase reporter gene vectors for analysis of promoters and enhancers. Biotechniques. 1988 May;6(5):454–458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Näf D., Hardin S. E., Weissmann C. Multimerization of AAGTGA and GAAAGT generates sequences that mediate virus inducibility by mimicking an interferon promoter element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1369–1373. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pine R., Decker T., Kessler D. S., Levy D. E., Darnell J. E., Jr Purification and cloning of interferon-stimulated gene factor 2 (ISGF2): ISGF2 (IRF-1) can bind to the promoters of both beta interferon- and interferon-stimulated genes but is not a primary transcriptional activator of either. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2448–2457. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid L. E., Brasnett A. H., Gilbert C. S., Porter A. C., Gewert D. R., Stark G. R., Kerr I. M. A single DNA response element can confer inducibility by both alpha- and gamma-interferons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(3):840–844. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.3.840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reis L. F., Harada H., Wolchok J. D., Taniguchi T., Vilcek J. Critical role of a common transcription factor, IRF-1, in the regulation of IFN-beta and IFN-inducible genes. EMBO J. 1992 Jan;11(1):185–193. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05041.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro D. J., Sharp P. A., Wahli W. W., Keller M. J. A high-efficiency HeLa cell nuclear transcription extract. DNA. 1988 Jan-Feb;7(1):47–55. doi: 10.1089/dna.1988.7.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G., Kamen R. A conserved AU sequence from the 3' untranslated region of GM-CSF mRNA mediates selective mRNA degradation. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):659–667. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90341-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsang S. Y., Nakanishi M., Peterlin B. M. B-cell-specific and interferon-gamma-inducible regulation of the HLA-DR alpha gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8598–8602. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Visvanathan K. V., Goodbourn S. Double-stranded RNA activates binding of NF-kappa B to an inducible element in the human beta-interferon promoter. EMBO J. 1989 Apr;8(4):1129–1138. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03483.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissmann C., Weber H. The interferon genes. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1986;33:251–300. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60026-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu-Lee L. Y., Hrachovy J. A., Stevens A. M., Schwarz L. A. Interferon-regulatory factor 1 is an immediate-early gene under transcriptional regulation by prolactin in Nb2 T cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):3087–3094. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.3087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zabel U., Schreck R., Baeuerle P. A. DNA binding of purified transcription factor NF-kappa B. Affinity, specificity, Zn2+ dependence, and differential half-site recognition. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 5;266(1):252–260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinn K., Maniatis T. Detection of factors that interact with the human beta-interferon regulatory region in vivo by DNAase I footprinting. Cell. 1986 May 23;45(4):611–618. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90293-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]