Abstract
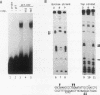
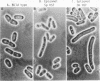
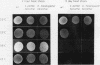
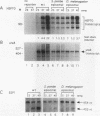
Schizosaccharomyces pombe is becoming an increasingly useful organism for the study of cellular processes, since in certain respects, such as the cell cycle and splicing, it is similar to metazoans. Previous biochemical studies have shown that the DNA binding ability of S. pombe heat shock factor (HSF) is fully induced only under stressed conditions, in a manner similar to that of Drosophila melanogaster and humans but differing from the constitutive binding by HSF in the budding yeasts. We report the isolation of the cDNA and gene for the HSF from S. pombe. S. pombe HSF has a domain structure that is more closely related to the structure of human and D. melanogaster HSFs than to the structure of the budding yeast HSFs, further arguing that regulation of HSF in S. pombe is likely to reflect regulation in metazoans. Surprisingly, the S. pombe HSF gene is required for growth at normal temperatures. We show that the S. pombe HSF gene can be replaced by the D. melanogaster HSF gene and that strains containing either of these genes behave similarly to transiently heat-shocked strains with respect to viability and the level of heat-induced transcripts from heat shock promoters. Strains containing the D. melanogaster HSF gene, however, have lower growth rates and show altered morphology at normal growth temperatures. These data demonstrate the functional conservation of domains of HSF that are required for response to heat shock. They further suggest a general role for HSF in growth of eukaryotic cells under normal (nonstressed) growth conditions.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abravaya K., Phillips B., Morimoto R. I. Attenuation of the heat shock response in HeLa cells is mediated by the release of bound heat shock transcription factor and is modulated by changes in growth and in heat shock temperatures. Genes Dev. 1991 Nov;5(11):2117–2127. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.11.2117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abravaya K., Phillips B., Morimoto R. I. Heat shock-induced interactions of heat shock transcription factor and the human hsp70 promoter examined by in vivo footprinting. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;11(1):586–592. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.1.586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amin J., Ananthan J., Voellmy R. Key features of heat shock regulatory elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;8(9):3761–3769. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.9.3761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeke J. D., Trueheart J., Natsoulis G., Fink G. R. 5-Fluoroorotic acid as a selective agent in yeast molecular genetics. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:164–175. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54076-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner J. J., Heyward S., Fackenthal D. L. Temperature-dependent regulation of a heterologous transcriptional activation domain fused to yeast heat shock transcription factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;12(3):1021–1030. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.3.1021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cai M., Davis R. W. Yeast centromere binding protein CBF1, of the helix-loop-helix protein family, is required for chromosome stability and methionine prototrophy. Cell. 1990 May 4;61(3):437–446. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90525-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clos J., Westwood J. T., Becker P. B., Wilson S., Lambert K., Wu C. Molecular cloning and expression of a hexameric Drosophila heat shock factor subject to negative regulation. Cell. 1990 Nov 30;63(5):1085–1097. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90511-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fikes J. D., Becker D. M., Winston F., Guarente L. Striking conservation of TFIID in Schizosaccharomyces pombe and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nature. 1990 Jul 19;346(6281):291–294. doi: 10.1038/346291a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallo G. J., Schuetz T. J., Kingston R. E. Regulation of heat shock factor in Schizosaccharomyces pombe more closely resembles regulation in mammals than in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;11(1):281–288. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.1.281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner M. M., Revzin A. A gel electrophoresis method for quantifying the binding of proteins to specific DNA regions: application to components of the Escherichia coli lactose operon regulatory system. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):3047–3060. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.3047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
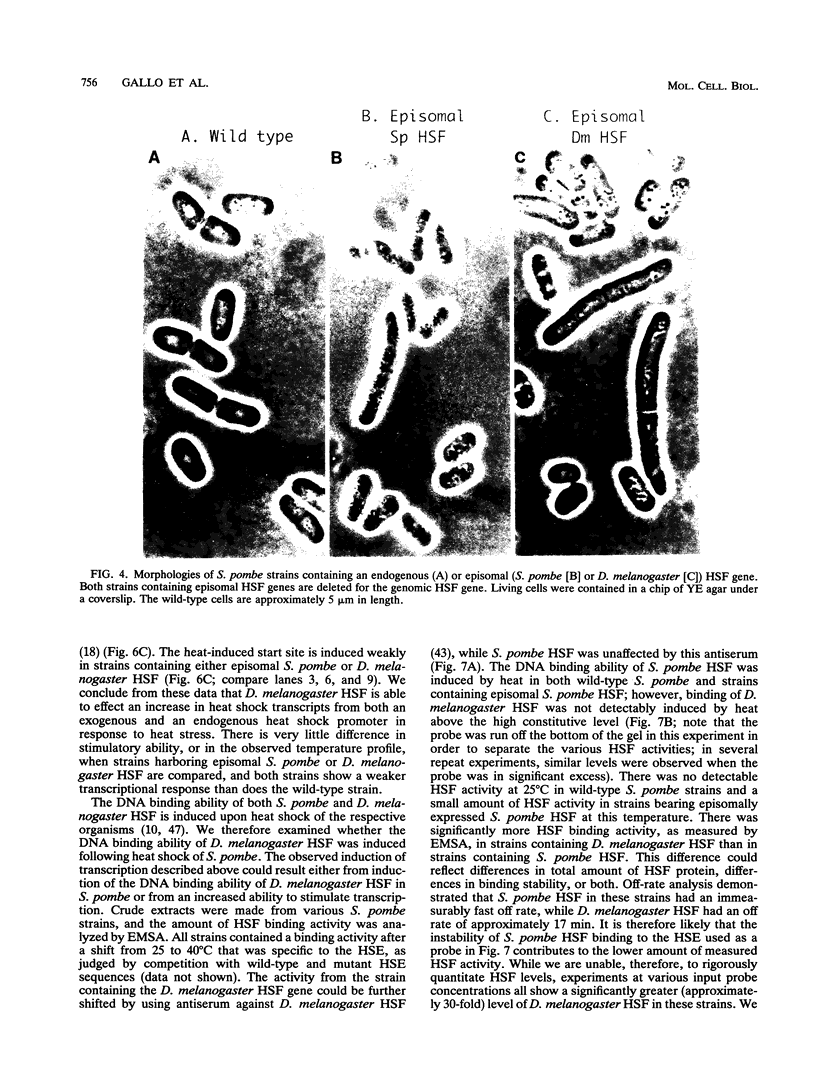
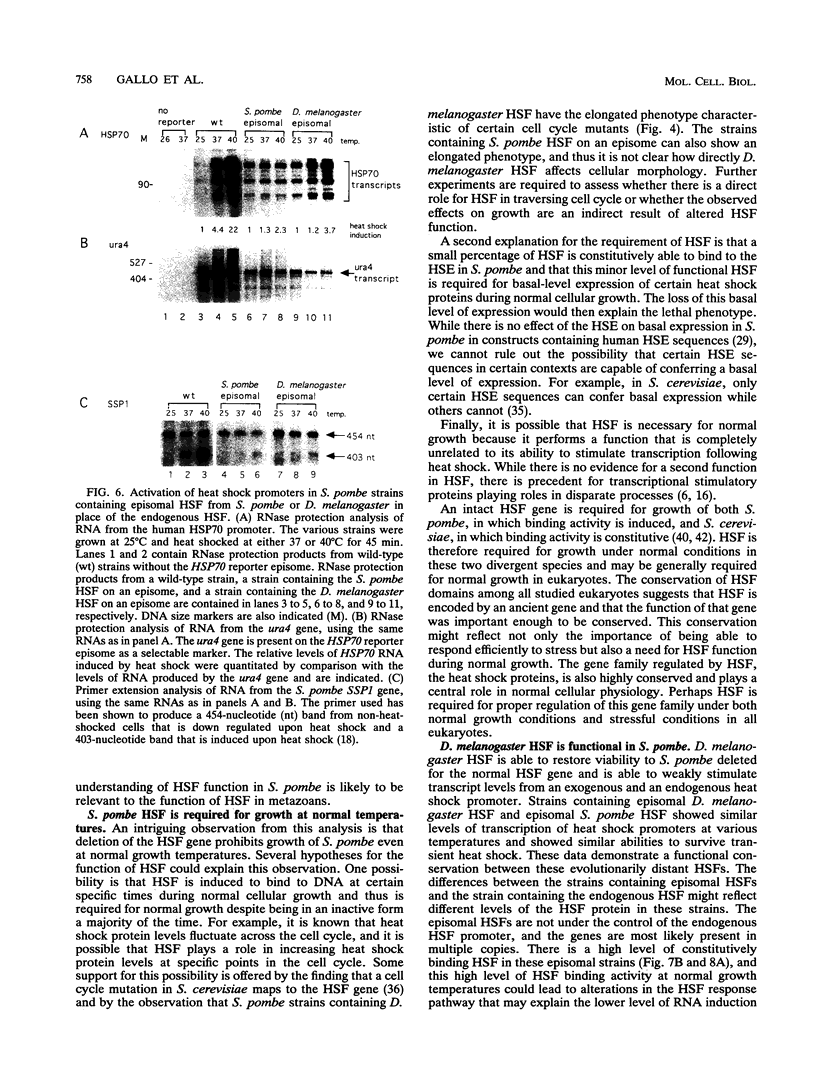
- Gilman M. Z., Wilson R. N., Weinberg R. A. Multiple protein-binding sites in the 5'-flanking region regulate c-fos expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4305–4316. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hensold J. O., Hunt C. R., Calderwood S. K., Housman D. E., Kingston R. E. DNA binding of heat shock factor to the heat shock element is insufficient for transcriptional activation in murine erythroleukemia cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1600–1608. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakobsen B. K., Pelham H. R. A conserved heptapeptide restrains the activity of the yeast heat shock transcription factor. EMBO J. 1991 Feb;10(2):369–375. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07958.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakobsen B. K., Pelham H. R. Constitutive binding of yeast heat shock factor to DNA in vivo. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;8(11):5040–5042. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.11.5040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Kadonaga J. T., Rosenfeld P. J., Kelly T. J., Tjian R. A cellular DNA-binding protein that activates eukaryotic transcription and DNA replication. Cell. 1987 Jan 16;48(1):79–89. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90358-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jurivich D. A., Sistonen L., Kroes R. A., Morimoto R. I. Effect of sodium salicylate on the human heat shock response. Science. 1992 Mar 6;255(5049):1243–1245. doi: 10.1126/science.1546322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasai H., Isono K. Dual modes of transcriptional and translational initiation of SSP1, the gene for a mitochondrial HSP70, responding to heat-shock in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Oct 11;19(19):5331–5337. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.19.5331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingston R. E., Schuetz T. J., Larin Z. Heat-inducible human factor that binds to a human hsp70 promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;7(4):1530–1534. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.4.1530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larson J. S., Schuetz T. J., Kingston R. E. Activation in vitro of sequence-specific DNA binding by a human regulatory factor. Nature. 1988 Sep 22;335(6188):372–375. doi: 10.1038/335372a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindquist S., Craig E. A. The heat-shock proteins. Annu Rev Genet. 1988;22:631–677. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.22.120188.003215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDaniel D., Caplan A. J., Lee M. S., Adams C. C., Fishel B. R., Gross D. S., Garrard W. T. Basal-level expression of the yeast HSP82 gene requires a heat shock regulatory element. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):4789–4798. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.4789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLeod M., Stein M., Beach D. The product of the mei3+ gene, expressed under control of the mating-type locus, induces meiosis and sporulation in fission yeast. EMBO J. 1987 Mar;6(3):729–736. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04814.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosser D. D., Kotzbauer P. T., Sarge K. D., Morimoto R. I. In vitro activation of heat shock transcription factor DNA-binding by calcium and biochemical conditions that affect protein conformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(10):3748–3752. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.10.3748. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosser D. D., Theodorakis N. G., Morimoto R. I. Coordinate changes in heat shock element-binding activity and HSP70 gene transcription rates in human cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;8(11):4736–4744. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.11.4736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R. A regulatory upstream promoter element in the Drosophila hsp 70 heat-shock gene. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):517–528. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90249-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prentice H. L. High efficiency transformation of Schizosaccharomyces pombe by electroporation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Feb 11;20(3):621–621. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.3.621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prentice H. L., Kingston R. E. Mammalian promoter element function in the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jul 11;20(13):3383–3390. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.13.3383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabindran S. K., Giorgi G., Clos J., Wu C. Molecular cloning and expression of a human heat shock factor, HSF1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):6906–6910. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.6906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarge K. D., Zimarino V., Holm K., Wu C., Morimoto R. I. Cloning and characterization of two mouse heat shock factors with distinct inducible and constitutive DNA-binding ability. Genes Dev. 1991 Oct;5(10):1902–1911. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.10.1902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scharf K. D., Rose S., Zott W., Schöffl F., Nover L., Schöff F. Three tomato genes code for heat stress transcription factors with a region of remarkable homology to the DNA-binding domain of the yeast HSF. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(13):4495–4501. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07900.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherer S., Davis R. W. Replacement of chromosome segments with altered DNA sequences constructed in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):4951–4955. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.4951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuetz T. J., Gallo G. J., Sheldon L., Tempst P., Kingston R. E. Isolation of a cDNA for HSF2: evidence for two heat shock factor genes in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):6911–6915. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.6911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slater M. R., Craig E. A. Transcriptional regulation of an hsp70 heat shock gene in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1906–1916. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith B. J., Yaffe M. P. A mutation in the yeast heat-shock factor gene causes temperature-sensitive defects in both mitochondrial protein import and the cell cycle. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2647–2655. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorger P. K., Lewis M. J., Pelham H. R. Heat shock factor is regulated differently in yeast and HeLa cells. Nature. 1987 Sep 3;329(6134):81–84. doi: 10.1038/329081a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorger P. K., Nelson H. C. Trimerization of a yeast transcriptional activator via a coiled-coil motif. Cell. 1989 Dec 1;59(5):807–813. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90604-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorger P. K., Pelham H. R. Purification and characterization of a heat-shock element binding protein from yeast. EMBO J. 1987 Oct;6(10):3035–3041. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02609.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorger P. K., Pelham H. R. Yeast heat shock factor is an essential DNA-binding protein that exhibits temperature-dependent phosphorylation. Cell. 1988 Sep 9;54(6):855–864. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)91219-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Dubendorff J. W. Use of T7 RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:60–89. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westwood J. T., Clos J., Wu C. Stress-induced oligomerization and chromosomal relocalization of heat-shock factor. Nature. 1991 Oct 31;353(6347):822–827. doi: 10.1038/353822a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiederrecht G., Seto D., Parker C. S. Isolation of the gene encoding the S. cerevisiae heat shock transcription factor. Cell. 1988 Sep 9;54(6):841–853. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)91197-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. Two protein-binding sites in chromatin implicated in the activation of heat-shock genes. Nature. 1984 May 17;309(5965):229–234. doi: 10.1038/309229a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiao H., Lis J. T. Germline transformation used to define key features of heat-shock response elements. Science. 1988 Mar 4;239(4844):1139–1142. doi: 10.1126/science.3125608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimarino V., Tsai C., Wu C. Complex modes of heat shock factor activation. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;10(2):752–759. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.2.752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimarino V., Wu C. Induction of sequence-specific binding of Drosophila heat shock activator protein without protein synthesis. 1987 Jun 25-Jul 1Nature. 327(6124):727–730. doi: 10.1038/327727a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]