Abstract
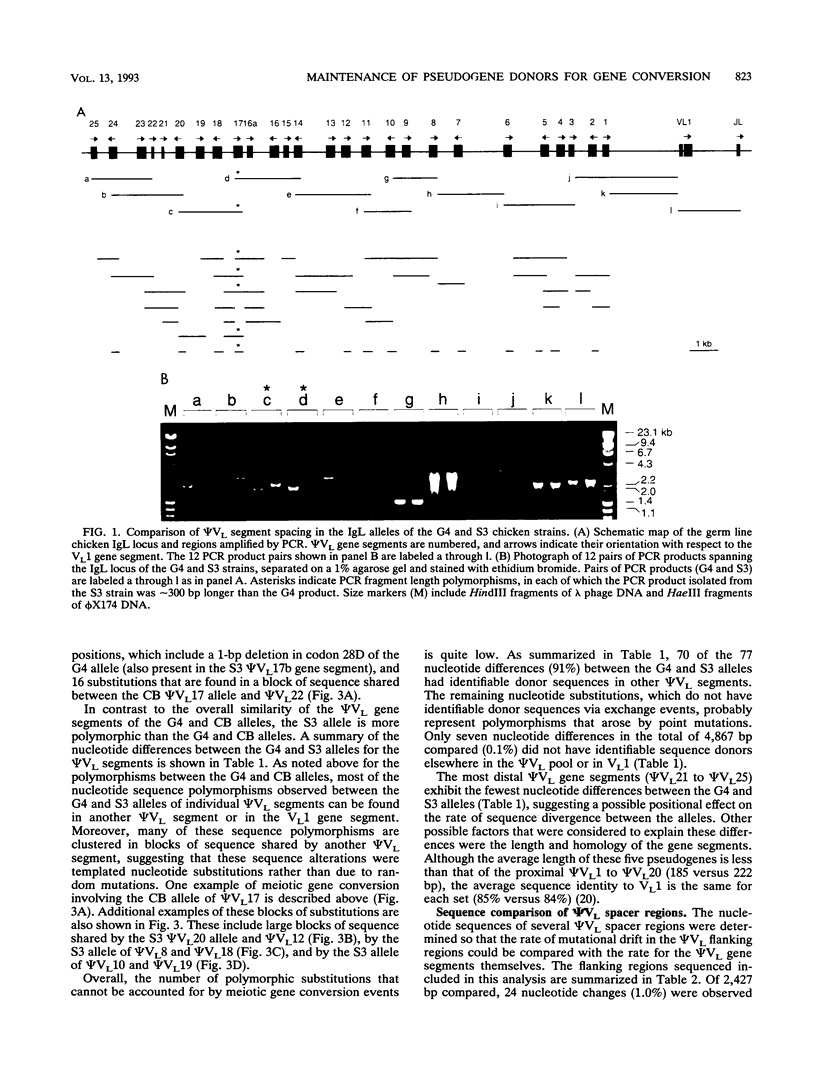
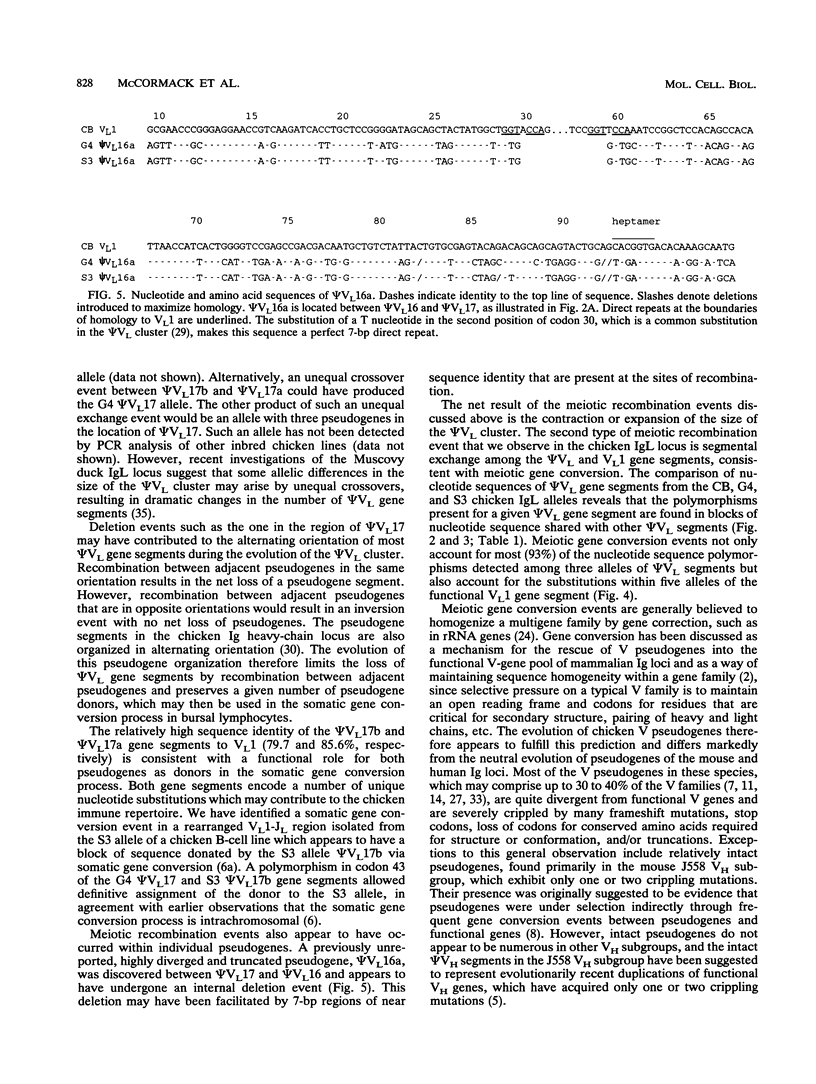
Somatic immunoglobulin diversity is generated in avian species by sequential gene conversion of variable (V) gene segments of the immunoglobulin heavy- and light-chain loci during B-cell development. The germ line pools of donor sequence information for somatic V-region gene conversion are found in families of V pseudogenes, located 5' of the single functional V gene of each locus. The sequence relationships among the pseudogenes (psi VL) and functional VL1 gene of the chicken light-chain alleles in three inbred strains were compared to determine the extent of diversity within the germ line pseudogene cluster. Numerous differences were observed. For example, compared with the previously reported CB allele and the G4 allele, the S3 allele contains two intact pseudogenes between psi VL16 and psi VL18. These two adjacent psi VL gene segments (psi VL17a and psi VL17b) could have given rise to the psi VL17 segment of the G4 and CB alleles by homologous recombination. The majority of other sequence polymorphisms among the psi VL alleles appear to be the result of meiotic gene conversion. The incidence of untemplated mutations within psi VL segments is significantly lower than the incidence of mutation within the pseudogene flanking regions. Together with the observations that most psi VL segments have open reading frames and lack stop codons, these data support the hypothesis that the psi VL cluster resembles a functional multigene family maintained by evolutionary selection for its functional role in generating somatic antibody diversity. Meiotic gene conversion events within the psi VL cluster serve both to introduce diversity by the exchange of short segments between family members and to prevent the accumulation of random mutations.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alt F. W., Blackwell T. K., DePinho R. A., Reth M. G., Yancopoulos G. D. Regulation of genome rearrangement events during lymphocyte differentiation. Immunol Rev. 1986 Feb;89:5–30. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1986.tb01470.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltimore D. Gene conversion: some implications for immunoglobulin genes. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):592–594. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90082-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker R. S., Knight K. L. Somatic diversification of immunoglobulin heavy chain VDJ genes: evidence for somatic gene conversion in rabbits. Cell. 1990 Nov 30;63(5):987–997. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90502-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker R. S., Suter M., Knight K. L. Restricted utilization of VH and DH genes in leukemic rabbit B cells. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Feb;20(2):397–402. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blankenstein T., Bonhomme F., Krawinkel U. Evolution of pseudogenes in the immunoglobulin VH-gene family of the mouse. Immunogenetics. 1987;26(4-5):237–248. doi: 10.1007/BF00346518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson L. M., McCormack W. T., Postema C. E., Humphries E. H., Thompson C. B. Templated insertions in the rearranged chicken IgL V gene segment arise by intrachromosomal gene conversion. Genes Dev. 1990 Apr;4(4):536–547. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.4.536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. B., Givol D. Allelic immunoglobulin VH genes in two mouse strains: possible germline gene recombination. EMBO J. 1983;2(11):2013–2018. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01693.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. B., Givol D. Conservation and divergence of immunoglobulin VH pseudogenes. EMBO J. 1983;2(10):1795–1800. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01660.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Currier S. J., Gallarda J. L., Knight K. L. Partial molecular genetic map of the rabbit VH chromosomal region. J Immunol. 1988 Mar 1;140(5):1651–1659. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson S. E., Cancro M. P., Osborne B. A. Analysis of a novel VHS107 haplotype in CLA-2 and WSA mice. Evidence for gene conversion among IgVH genes in outbred populations. J Exp Med. 1989 Dec 1;170(6):1811–1823. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.6.1811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honjo T. Immunoglobulin genes. Annu Rev Immunol. 1983;1:499–528. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.01.040183.002435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight K. L., Becker R. S. Molecular basis of the allelic inheritance of rabbit immunoglobulin VH allotypes: implications for the generation of antibody diversity. Cell. 1990 Mar 23;60(6):963–970. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90344-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight K. L. Restricted VH gene usage and generation of antibody diversity in rabbit. Annu Rev Immunol. 1992;10:593–616. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.10.040192.003113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kodaira M., Kinashi T., Umemura I., Matsuda F., Noma T., Ono Y., Honjo T. Organization and evolution of variable region genes of the human immunoglobulin heavy chain. J Mol Biol. 1986 Aug 20;190(4):529–541. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90239-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krawinkel U., Christoph T., Blankenstein T. Organization of the Ig VH locus in mice and humans. Immunol Today. 1989 Oct;10(10):339–344. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(89)90191-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linial M. Creation of a processed pseudogene by retroviral infection. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):93–102. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90759-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormack W. T., Dhanarajan P., Roux K. H. Comparison of latent and nominal rabbit Ig VHa1 allotype cDNA sequences. J Immunol. 1988 Sep 15;141(6):2063–2071. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormack W. T., Laster S. M., Marzluff W. F., Roux K. H. Dynamic gene interactions in the evolution of rabbit VH genes: a four codon duplication and block homologies provide evidence for intergenic exchange. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Oct 11;13(19):7041–7054. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.19.7041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormack W. T., Thompson C. B. Chicken IgL variable region gene conversions display pseudogene donor preference and 5' to 3' polarity. Genes Dev. 1990 Apr;4(4):548–558. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.4.548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormack W. T., Tjoelker L. W., Barth C. F., Carlson L. M., Petryniak B., Humphries E. H., Thompson C. B. Selection for B cells with productive IgL gene rearrangements occurs in the bursa of Fabricius during chicken embryonic development. Genes Dev. 1989 Jun;3(6):838–847. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.6.838. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormack W. T., Tjoelker L. W., Carlson L. M., Petryniak B., Barth C. F., Humphries E. H., Thompson C. B. Chicken IgL gene rearrangement involves deletion of a circular episome and addition of single nonrandom nucleotides to both coding segments. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):785–791. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90683-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormack W. T., Tjoelker L. W., Thompson C. B. Avian B-cell development: generation of an immunoglobulin repertoire by gene conversion. Annu Rev Immunol. 1991;9:219–241. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.09.040191.001251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagylaki T., Petes T. D. Intrachromosomal gene conversion and the maintenance of sequence homogeneity among repeated genes. Genetics. 1982 Feb;100(2):315–337. doi: 10.1093/genetics/100.2.315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohta T. The mutational load of a multigene family with uniform members. Genet Res. 1989 Apr;53(2):141–145. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300028020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlmutter R. M., Berson B., Griffin J. A., Hood L. Diversity in the germline antibody repertoire. Molecular evolution of the T15 VN gene family. J Exp Med. 1985 Dec 1;162(6):1998–2016. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.6.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rechavi G., Ram D., Glazer L., Zakut R., Givol D. Evolutionary aspects of immunoglobulin heavy chain variable region (VH) gene subgroups. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(3):855–859. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.3.855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynaud C. A., Anquez V., Dahan A., Weill J. C. A single rearrangement event generates most of the chicken immunoglobulin light chain diversity. Cell. 1985 Feb;40(2):283–291. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90142-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynaud C. A., Anquez V., Grimal H., Weill J. C. A hyperconversion mechanism generates the chicken light chain preimmune repertoire. Cell. 1987 Feb 13;48(3):379–388. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90189-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynaud C. A., Dahan A., Anquez V., Weill J. C. Somatic hyperconversion diversifies the single Vh gene of the chicken with a high incidence in the D region. Cell. 1989 Oct 6;59(1):171–183. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90879-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roux K. H., Dhanarajan P., Gottschalk V., McCormick W. T., Renshaw R. W. Latent a1 VH germline genes in an a2a2 rabbit. Evidence for gene conversion at both the germline and somatic levels. J Immunol. 1991 Mar 15;146(6):2027–2036. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiff C., Milili M., Fougereau M. Functional and pseudogenes are similarly organized and may equally contribute to the extensive antibody diversity of the IgVHII family. EMBO J. 1985 May;4(5):1225–1230. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03764.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson C. B., Neiman P. E. Somatic diversification of the chicken immunoglobulin light chain gene is limited to the rearranged variable gene segment. Cell. 1987 Feb 13;48(3):369–378. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90188-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh J. B. Sequence-dependent gene conversion: can duplicated genes diverge fast enough to escape conversion? Genetics. 1987 Nov;117(3):543–557. doi: 10.1093/genetics/117.3.543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




