Abstract
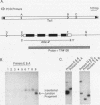
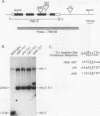
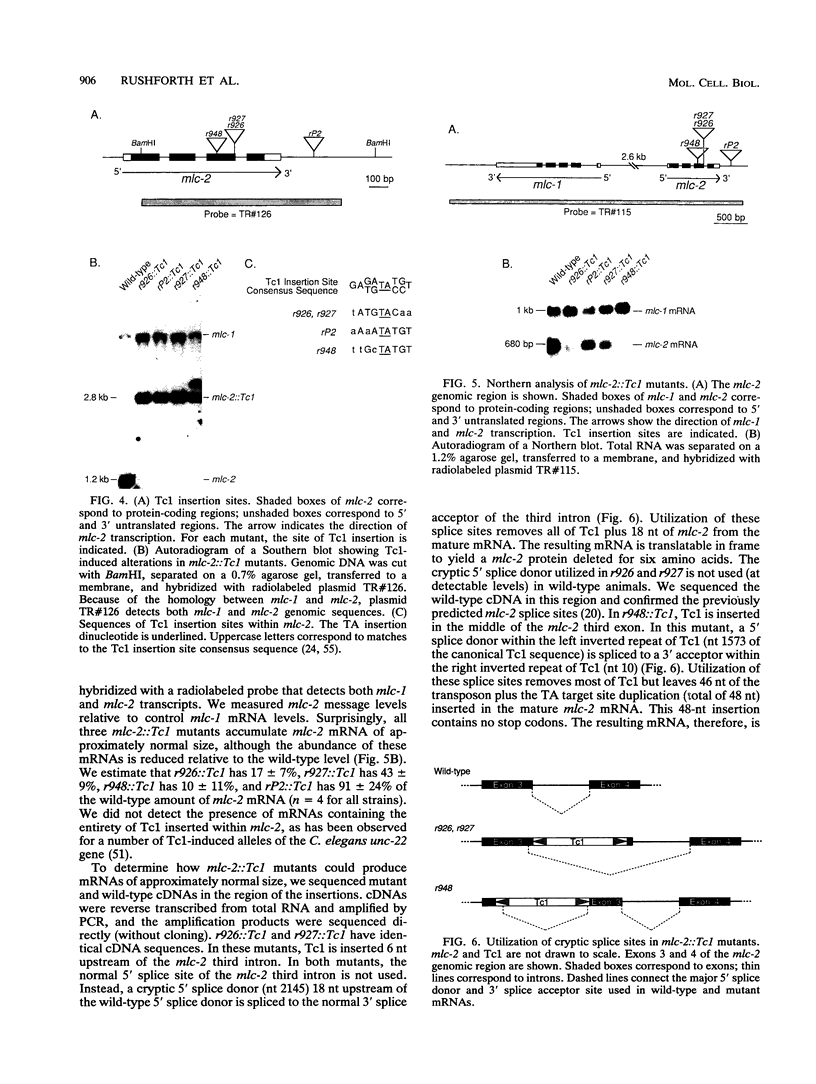
We used the polymerase chain reaction to detect insertions of the transposon Tc1 into mlc-2, one of two Caenorhabditis elegans regulatory myosin light chain genes. Our goals were to develop a general method to identify mutations in any sequenced gene and to establish the phenotype of mlc-2 loss-of-function mutants. The sensitivity of the polymerase chain reaction allowed us to identify nematode populations containing rare Tc1 insertions into mcl-2. mlc-2::Tc1 mutants were subsequently isolated from these populations by a sib selection procedure. We isolated three mutants with Tc1 insertions within the mlc-2 third exon and a fourth strain with Tc1 inserted in nearby noncoding DNA. To demonstrate the generality of our procedure, we isolated two additional mutants with Tc1 insertions within hlh-1, the C. elegans MyoD homolog. All of these mutants are essentially wild type when homozygous. Despite the fact that certain of these mutants have Tc1 inserted within exons of the target gene, these mutations may not be true null alleles. All three of the mlc-2 mutants contain mlc-2 mRNA in which all or part of Tc1 is spliced from the pre-mRNA, leaving small in-frame insertions or deletions in the mature message. There is a remarkable plasticity in the sites used to splice Tc1 from these mlc-2 pre-mRNAs; certain splice sites used in the mutants are very different from typical eukaryotic splice sites.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adelstein R. S., Eisenberg E. Regulation and kinetics of the actin-myosin-ATP interaction. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:921–956. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.004421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson P. Molecular genetics of nematode muscle. Annu Rev Genet. 1989;23:507–525. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.23.120189.002451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babity J. M., Starr T. V., Rose A. M. Tc1 transposition and mutator activity in a Bristol strain of Caenorhabditis elegans. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 Jun;222(1):65–70. doi: 10.1007/BF00283024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballinger D. G., Benzer S. Targeted gene mutations in Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9402–9406. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banga S. S., Boyd J. B. Oligonucleotide-directed site-specific mutagenesis in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 1;89(5):1735–1739. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.5.1735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baserga S. J., Benz E. J., Jr Nonsense mutations in the human beta-globin gene affect mRNA metabolism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(7):2056–2060. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.7.2056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bejsovec A., Anderson P. Functions of the myosin ATP and actin binding sites are required for C. elegans thick filament assembly. Cell. 1990 Jan 12;60(1):133–140. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90723-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumenthal T., Thomas J. Cis and trans mRNA splicing in C. elegans. Trends Genet. 1988 Nov;4(11):305–308. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(88)90107-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botstein D., Fink G. R. Yeast: an experimental organism for modern biology. Science. 1988 Jun 10;240(4858):1439–1443. doi: 10.1126/science.3287619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowerman B., Eaton B. A., Priess J. R. skn-1, a maternally expressed gene required to specify the fate of ventral blastomeres in the early C. elegans embryo. Cell. 1992 Mar 20;68(6):1061–1075. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90078-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner S. The genetics of Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics. 1974 May;77(1):71–94. doi: 10.1093/genetics/77.1.71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen L., Krause M., Draper B., Weintraub H., Fire A. Body-wall muscle formation in Caenorhabditis elegans embryos that lack the MyoD homolog hlh-1. Science. 1992 Apr 10;256(5054):240–243. doi: 10.1126/science.1314423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins J., Forbes E., Anderson P. The Tc3 family of transposable genetic elements in Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics. 1989 Jan;121(1):47–55. doi: 10.1093/genetics/121.1.47. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins J., Saari B., Anderson P. Activation of a transposable element in the germ line but not the soma of Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 1987 Aug 20;328(6132):726–728. doi: 10.1038/328726a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coney L. R., Roeder G. S. Control of yeast gene expression by transposable elements: maximum expression requires a functional Ty activator sequence and a defective Ty promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4009–4017. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulson A., Sulston J., Brenner S., Karn J. Toward a physical map of the genome of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7821–7825. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulson A., Waterston R., Kiff J., Sulston J., Kohara Y. Genome linking with yeast artificial chromosomes. Nature. 1988 Sep 8;335(6186):184–186. doi: 10.1038/335184a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R., Lomedico P. T., Ju G. Transcriptional interference in avian retroviruses--implications for the promoter insertion model of leukaemogenesis. Nature. 1984 Jan 19;307(5948):241–245. doi: 10.1038/307241a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cummins C., Anderson P. Regulatory myosin light-chain genes of Caenorhabditis elegans. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;8(12):5339–5349. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.12.5339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennis E. S., Sachs M. M., Gerlach W. L., Beach L., Peacock W. J. The Ds1 transposable element acts as an intron in the mutant allele Adh1-Fm335 and is spliced from the message. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 May 11;16(9):3815–3828. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.9.3815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eide D., Anderson P. Insertion and excision of Caenorhabditis elegans transposable element Tc1. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):737–746. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eide D., Anderson P. The gene structures of spontaneous mutations affecting a Caenorhabditis elegans myosin heavy chain gene. Genetics. 1985 Jan;109(1):67–79. doi: 10.1093/genetics/109.1.67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eide D., Anderson P. Transposition of Tc1 in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1756–1760. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emmons S. W., Roberts S., Ruan K. S. Evidence in a nematode for regulation of transposon excision by tissue-specific factors. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Mar;202(3):410–415. doi: 10.1007/BF00333270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emmons S. W., Yesner L. High-frequency excision of transposable element Tc 1 in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans is limited to somatic cells. Cell. 1984 Mar;36(3):599–605. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90339-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emmons S. W., Yesner L., Ruan K. S., Katzenberg D. Evidence for a transposon in Caenorhabditis elegans. Cell. 1983 Jan;32(1):55–65. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90496-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engels W. R., Johnson-Schlitz D. M., Eggleston W. B., Sved J. High-frequency P element loss in Drosophila is homolog dependent. Cell. 1990 Aug 10;62(3):515–525. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90016-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields C. Information content of Caenorhabditis elegans splice site sequences varies with intron length. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Mar 25;18(6):1509–1512. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.6.1509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fridell R. A., Pret A. M., Searles L. L. A retrotransposon 412 insertion within an exon of the Drosophila melanogaster vermilion gene is spliced from the precursor RNA. Genes Dev. 1990 Apr;4(4):559–566. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.4.559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwald I. lin-12, a nematode homeotic gene, is homologous to a set of mammalian proteins that includes epidermal growth factor. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):583–590. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90230-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser K., Goodwin S. F. "Site-selected" transposon mutagenesis of Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(5):1686–1690. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.5.1686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller S. A., Liptay S., Hajra A., Meisler M. H. Transgene-induced mutation of the murine steel locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):10019–10022. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.10019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim H. S., Smithies O. Recombinant fragment assay for gene targetting based on the polymerase chain reaction. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Sep 26;16(18):8887–8903. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.18.8887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim H. Y., Schiefelbein J. W., Raboy V., Furtek D. B., Nelson O. E., Jr RNA splicing permits expression of a maize gene with a defective Suppressor-mutator transposable element insertion in an exon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5863–5867. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinniburgh A. J., Maquat L. E., Schedl T., Rachmilewitz E., Ross J. mRNA-deficient beta o-thalassemia results from a single nucleotide deletion. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Sep 25;10(18):5421–5427. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.18.5421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleckner N. Transposable elements in prokaryotes. Annu Rev Genet. 1981;15:341–404. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.15.120181.002013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krause M., Fire A., Harrison S. W., Priess J., Weintraub H. CeMyoD accumulation defines the body wall muscle cell fate during C. elegans embryogenesis. Cell. 1990 Nov 30;63(5):907–919. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90494-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levis R., O'Hare K., Rubin G. M. Effects of transposable element insertions on RNA encoded by the white gene of Drosophila. Cell. 1984 Sep;38(2):471–481. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90502-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitt A., Emmons S. W. The Tc2 transposon in Caenorhabditis elegans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3232–3236. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liao L. W., Rosenzweig B., Hirsh D. Analysis of a transposable element in Caenorhabditis elegans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3585–3589. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim S. K., Sigmund C. D., Gross K. W., Maquat L. E. Nonsense codons in human beta-globin mRNA result in the production of mRNA degradation products. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;12(3):1149–1161. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.3.1149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Losson R., Lacroute F. Interference of nonsense mutations with eukaryotic messenger RNA stability. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5134–5137. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maquat L. E., Kinniburgh A. J., Rachmilewitz E. A., Ross J. Unstable beta-globin mRNA in mRNA-deficient beta o thalassemia. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(3 Pt 2):543–553. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90396-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moerman D. G., Benian G. M., Barstead R. J., Schriefer L. A., Waterston R. H. Identification and intracellular localization of the unc-22 gene product of Caenorhabditis elegans. Genes Dev. 1988 Jan;2(1):93–105. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.1.93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moerman D. G., Benian G. M., Waterston R. H. Molecular cloning of the muscle gene unc-22 in Caenorhabditis elegans by Tc1 transposon tagging. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2579–2583. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moerman D. G., Waterston R. H. Spontaneous unstable unc-22 IV mutations in C. elegans var. Bergerac. Genetics. 1984 Dec;108(4):859–877. doi: 10.1093/genetics/108.4.859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori I., Benian G. M., Moerman D. G., Waterston R. H. Transposable element Tc1 of Caenorhabditis elegans recognizes specific target sequences for integration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(3):861–864. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.3.861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori I., Moerman D. G., Waterston R. H. Analysis of a mutator activity necessary for germline transposition and excision of Tc1 transposable elements in Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics. 1988 Oct;120(2):397–407. doi: 10.1093/genetics/120.2.397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount S. M. A catalogue of splice junction sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 22;10(2):459–472. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.2.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padgett R. A., Grabowski P. J., Konarska M. M., Seiler S., Sharp P. A. Splicing of messenger RNA precursors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:1119–1150. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkhurst S. M., Corces V. G. Interactions among the gypsy transposable element and the yellow and the suppressor of hairy-wing loci in Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;6(1):47–53. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.1.47. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plasterk R. H., Groenen J. T. Targeted alterations of the Caenorhabditis elegans genome by transgene instructed DNA double strand break repair following Tc1 excision. EMBO J. 1992 Jan;11(1):287–290. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05051.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pret A. M., Searles L. L. Splicing of retrotransposon insertions from transcripts of the Drosophila melanogaster vermilion gene in a revertant. Genetics. 1991 Dec;129(4):1137–1145. doi: 10.1093/genetics/129.4.1137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raboy V., Kim H. Y., Schiefelbein J. W., Nelson-Jr O. E. Deletions in a dspm insert in a maize bronze-1 allele alter RNA processing and gene expression. Genetics. 1989 Jul;122(3):695–703. doi: 10.1093/genetics/122.3.695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose A. M., Snutch T. P. Isolation of the closed circular form of the transposable element Tc1 in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 1984 Oct 4;311(5985):485–486. doi: 10.1038/311485a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenzweig B., Liao L. W., Hirsh D. Target sequences for the C. elegans transposable element Tc1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Oct 25;11(20):7137–7140. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.20.7137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross J. A precursor of globin messenger RNA. J Mol Biol. 1976 Sep 15;106(2):403–420. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90093-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowland L. J., Strommer J. N. Insertion of an unstable element in an intervening sequence of maize Adh1 affects transcription but not processing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2875–2879. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruan K., Emmons S. W. Extrachromosomal copies of transposon Tc1 in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):4018–4022. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.4018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruvkun G., Ambros V., Coulson A., Waterston R., Sulston J., Horvitz H. R. Molecular genetics of the Caenorhabditis elegans heterochronic gene lin-14. Genetics. 1989 Mar;121(3):501–516. doi: 10.1093/genetics/121.3.501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon R, Starlinger P. Transposable element Ds2 of Zea mays influences polyadenylation and splice site selection. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Aug;209(1):198–199. doi: 10.1007/BF00329859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smithies O., Gregg R. G., Boggs S. S., Koralewski M. A., Kucherlapati R. S. Insertion of DNA sequences into the human chromosomal beta-globin locus by homologous recombination. Nature. 1985 Sep 19;317(6034):230–234. doi: 10.1038/317230a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sulston J. E., Brenner S. The DNA of Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics. 1974 May;77(1):95–104. doi: 10.1093/genetics/77.1.95. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas K. R., Capecchi M. R. Introduction of homologous DNA sequences into mammalian cells induces mutations in the cognate gene. Nature. 1986 Nov 6;324(6092):34–38. doi: 10.1038/324034a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas K. R., Capecchi M. R. Site-directed mutagenesis by gene targeting in mouse embryo-derived stem cells. Cell. 1987 Nov 6;51(3):503–512. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90646-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas K. R., Folger K. R., Capecchi M. R. High frequency targeting of genes to specific sites in the mammalian genome. Cell. 1986 Feb 14;44(3):419–428. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90463-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urlaub G., Mitchell P. J., Ciudad C. J., Chasin L. A. Nonsense mutations in the dihydrofolate reductase gene affect RNA processing. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;9(7):2868–2880. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.7.2868. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessler S. R., Baran G., Varagona M. The maize transposable element Ds is spliced from RNA. Science. 1987 Aug 21;237(4817):916–918. doi: 10.1126/science.3039661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. A., Pappu S. S., Bell J. B. Molecular analysis of hybrid dysgenesis-induced derivatives of a P-element allele at the vg locus. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1489–1497. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan J. Y., Finney M., Tsung N., Horvitz H. R. Tc4, a Caenorhabditis elegans transposable element with an unusual fold-back structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):3334–3338. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]