Abstract
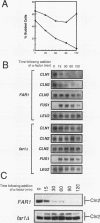
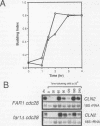
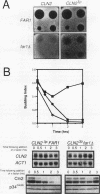
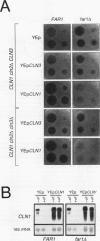
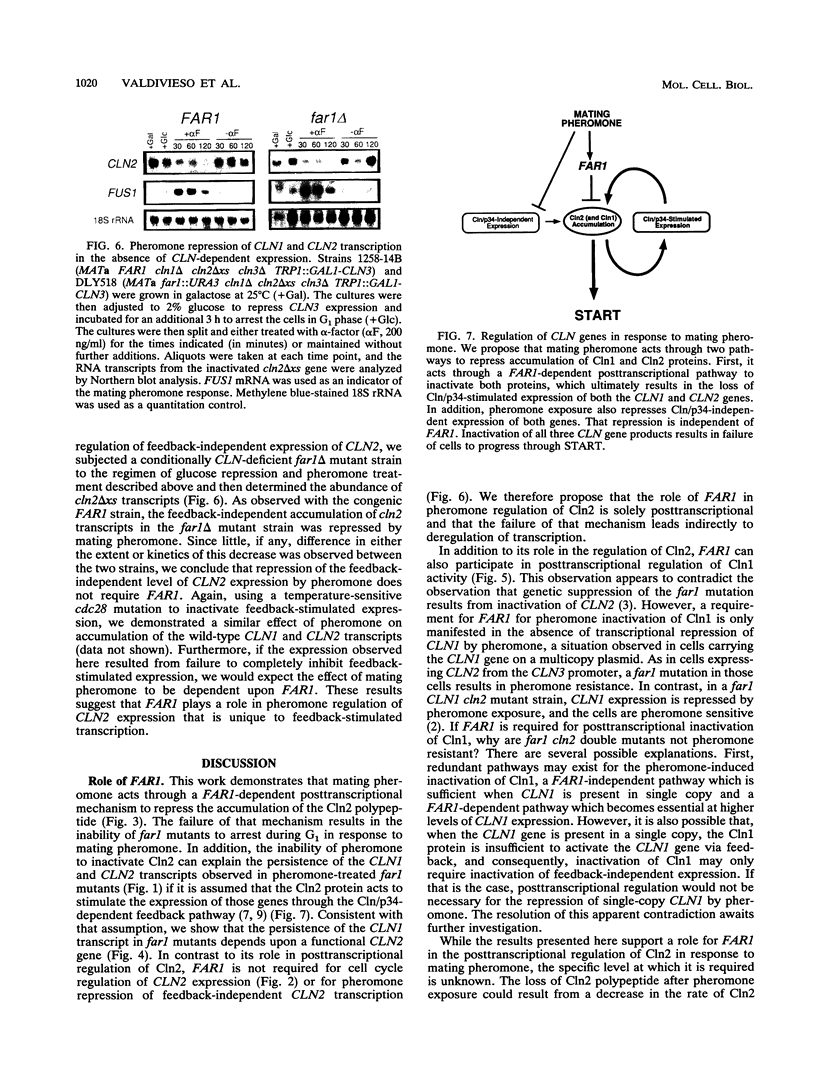
Yeast cells arrest during the G1 interval of the cell cycle in response to peptide mating pheromones. The FAR1 gene is required for cell cycle arrest but not for a number of other aspects of the pheromone response. Genetic evidence suggests that FAR1 is required specifically for inactivation of the G1 cyclin CLN2. From these observations, the FAR1 gene has been proposed to encode an element of the interface between the mating pheromone signal transduction pathway and the cell cycle regulatory apparatus. We show here that FAR1 is necessary for the decrease in CLN1 and CLN2 transcript accumulation observed in response to mating pheromone but is unnecessary for regulation of the same transcripts during vegetative growth. However, the defect in regulation of CLN1 expression is dependent upon CLN2. We show that pheromone regulates the abundance of Cln2 at a posttranscriptional level and that FAR1 is required for that regulation. From these observations, we suggest that FAR1 function is limited to posttranscriptional regulation of CLN2 expression by mating pheromone. The failure of mating pheromone to repress CLN2 transcript levels in far1 mutants can be explained by the stimulatory effect of the persistent Cln2 protein on CLN2 transcription via the CLN/CDC28-dependent feedback pathway.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Breeden L., Nasmyth K. Cell cycle control of the yeast HO gene: cis- and trans-acting regulators. Cell. 1987 Feb 13;48(3):389–397. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90190-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang F., Herskowitz I. Identification of a gene necessary for cell cycle arrest by a negative growth factor of yeast: FAR1 is an inhibitor of a G1 cyclin, CLN2. Cell. 1990 Nov 30;63(5):999–1011. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90503-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang F., Herskowitz I. Phosphorylation of FAR1 in response to alpha-factor: a possible requirement for cell-cycle arrest. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Apr;3(4):445–450. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.4.445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole G. M., Stone D. E., Reed S. I. Stoichiometry of G protein subunits affects the Saccharomyces cerevisiae mating pheromone signal transduction pathway. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;10(2):510–517. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.2.510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross F. R. Cell cycle arrest caused by CLN gene deficiency in Saccharomyces cerevisiae resembles START-I arrest and is independent of the mating-pheromone signalling pathway. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6482–6490. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross F. R. DAF1, a mutant gene affecting size control, pheromone arrest, and cell cycle kinetics of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;8(11):4675–4684. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.11.4675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross F. R., Tinkelenberg A. H. A potential positive feedback loop controlling CLN1 and CLN2 gene expression at the start of the yeast cell cycle. Cell. 1991 May 31;65(5):875–883. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90394-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross S. L., Smith M. M. Comparison of the structure and cell cycle expression of mRNAs encoded by two histone H3-H4 loci in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):945–954. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dirick L., Nasmyth K. Positive feedback in the activation of G1 cyclins in yeast. Nature. 1991 Jun 27;351(6329):754–757. doi: 10.1038/351754a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolan J. W., Fields S. Overproduction of the yeast STE12 protein leads to constitutive transcriptional induction. Genes Dev. 1990 Apr;4(4):492–502. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.4.492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolan J. W., Kirkman C., Fields S. The yeast STE12 protein binds to the DNA sequence mediating pheromone induction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5703–5707. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elder R. T., Loh E. Y., Davis R. W. RNA from the yeast transposable element Ty1 has both ends in the direct repeats, a structure similar to retrovirus RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2432–2436. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elion E. A., Brill J. A., Fink G. R. FUS3 represses CLN1 and CLN2 and in concert with KSS1 promotes signal transduction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9392–9396. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elion E. A., Grisafi P. L., Fink G. R. FUS3 encodes a cdc2+/CDC28-related kinase required for the transition from mitosis into conjugation. Cell. 1990 Feb 23;60(4):649–664. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90668-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Errede B., Ammerer G. STE12, a protein involved in cell-type-specific transcription and signal transduction in yeast, is part of protein-DNA complexes. Genes Dev. 1989 Sep;3(9):1349–1361. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.9.1349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghiara J. B., Richardson H. E., Sugimoto K., Henze M., Lew D. J., Wittenberg C., Reed S. I. A cyclin B homolog in S. cerevisiae: chronic activation of the Cdc28 protein kinase by cyclin prevents exit from mitosis. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):163–174. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90417-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gietz R. D., Sugino A. New yeast-Escherichia coli shuttle vectors constructed with in vitro mutagenized yeast genes lacking six-base pair restriction sites. Gene. 1988 Dec 30;74(2):527–534. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90185-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadwiger J. A., Reed S. I. Nucleotide sequence of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae CLN1 and CLN2 genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jul 11;18(13):4025–4025. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.13.4025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadwiger J. A., Wittenberg C., Richardson H. E., de Barros Lopes M., Reed S. I. A family of cyclin homologs that control the G1 phase in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(16):6255–6259. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.16.6255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwell L. H., Culotti J., Pringle J. R., Reid B. J. Genetic control of the cell division cycle in yeast. Science. 1974 Jan 11;183(4120):46–51. doi: 10.1126/science.183.4120.46. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius D., Blair L., Brake A., Sprague G., Thorner J. Yeast alpha factor is processed from a larger precursor polypeptide: the essential role of a membrane-bound dipeptidyl aminopeptidase. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):839–852. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90070-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lew D. J., Marini N. J., Reed S. I. Different G1 cyclins control the timing of cell cycle commitment in mother and daughter cells of the budding yeast S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1992 Apr 17;69(2):317–327. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90412-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marini N. J., Reed S. I. Direct induction of G1-specific transcripts following reactivation of the Cdc28 kinase in the absence of de novo protein synthesis. Genes Dev. 1992 Apr;6(4):557–567. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.4.557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh L., Neiman A. M., Herskowitz I. Signal transduction during pheromone response in yeast. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1991;7:699–728. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.07.110191.003411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash R., Tokiwa G., Anand S., Erickson K., Futcher A. B. The WHI1+ gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae tethers cell division to cell size and is a cyclin homolog. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4335–4346. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03332.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasmyth K. A repetitive DNA sequence that confers cell-cycle START (CDC28)-dependent transcription of the HO gene in yeast. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):225–235. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80118-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasmyth K., Dirick L. The role of SWI4 and SWI6 in the activity of G1 cyclins in yeast. Cell. 1991 Sep 6;66(5):995–1013. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90444-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng R., Abelson J. Isolation and sequence of the gene for actin in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3912–3916. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogas J., Andrews B. J., Herskowitz I. Transcriptional activation of CLN1, CLN2, and a putative new G1 cyclin (HCS26) by SWI4, a positive regulator of G1-specific transcription. Cell. 1991 Sep 6;66(5):1015–1026. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90445-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pines J., Hunter T. Cyclin-dependent kinases: a new cell cycle motif? Trends Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;1(5):117–121. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(91)90116-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed S. I. The selection of S. cerevisiae mutants defective in the start event of cell division. Genetics. 1980 Jul;95(3):561–577. doi: 10.1093/genetics/95.3.561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed S. I., Wittenberg C. Mitotic role for the Cdc28 protein kinase of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):5697–5701. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.15.5697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson H. E., Wittenberg C., Cross F., Reed S. I. An essential G1 function for cyclin-like proteins in yeast. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):1127–1133. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90768-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein R. J. One-step gene disruption in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:202–211. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01015-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein R. Targeting, disruption, replacement, and allele rescue: integrative DNA transformation in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:281–301. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94022-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern M., Jensen R., Herskowitz I. Five SWI genes are required for expression of the HO gene in yeast. J Mol Biol. 1984 Oct 5;178(4):853–868. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90315-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surana U., Robitsch H., Price C., Schuster T., Fitch I., Futcher A. B., Nasmyth K. The role of CDC28 and cyclins during mitosis in the budding yeast S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):145–161. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90416-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trueheart J., Boeke J. D., Fink G. R. Two genes required for cell fusion during yeast conjugation: evidence for a pheromone-induced surface protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;7(7):2316–2328. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.7.2316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittenberg C., Sugimoto K., Reed S. I. G1-specific cyclins of S. cerevisiae: cell cycle periodicity, regulation by mating pheromone, and association with the p34CDC28 protein kinase. Cell. 1990 Jul 27;62(2):225–237. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90361-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]