Abstract
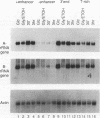
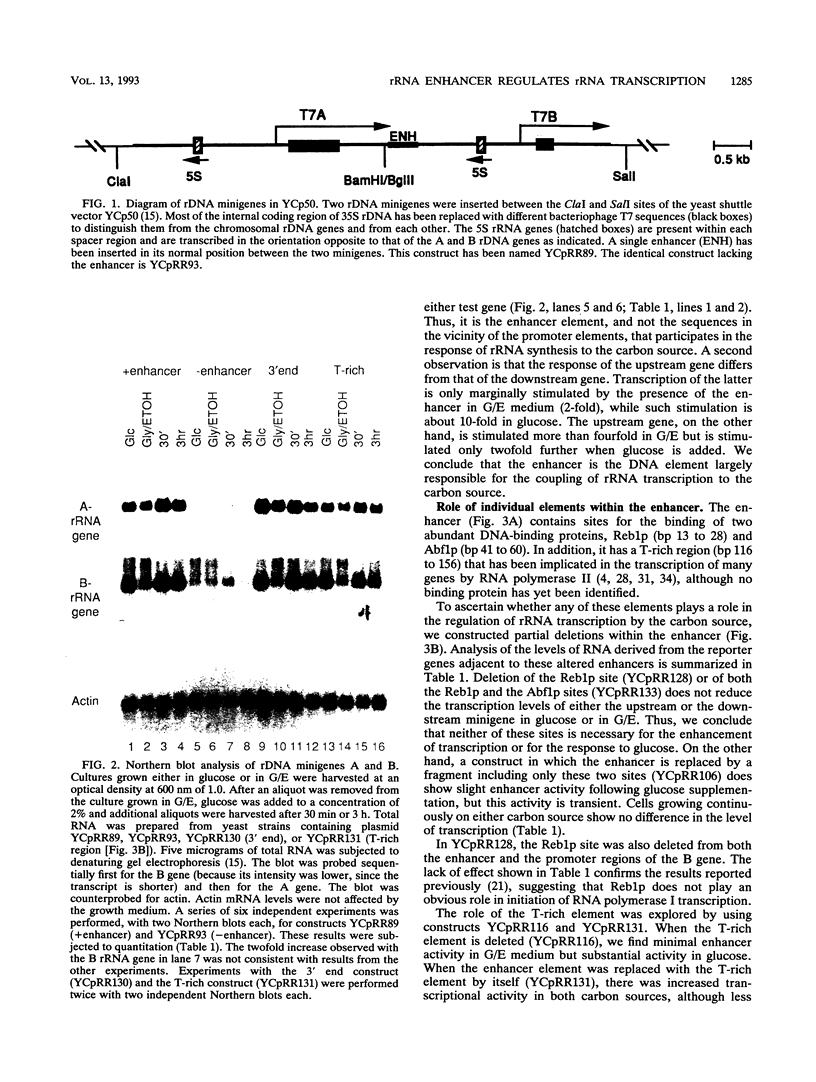
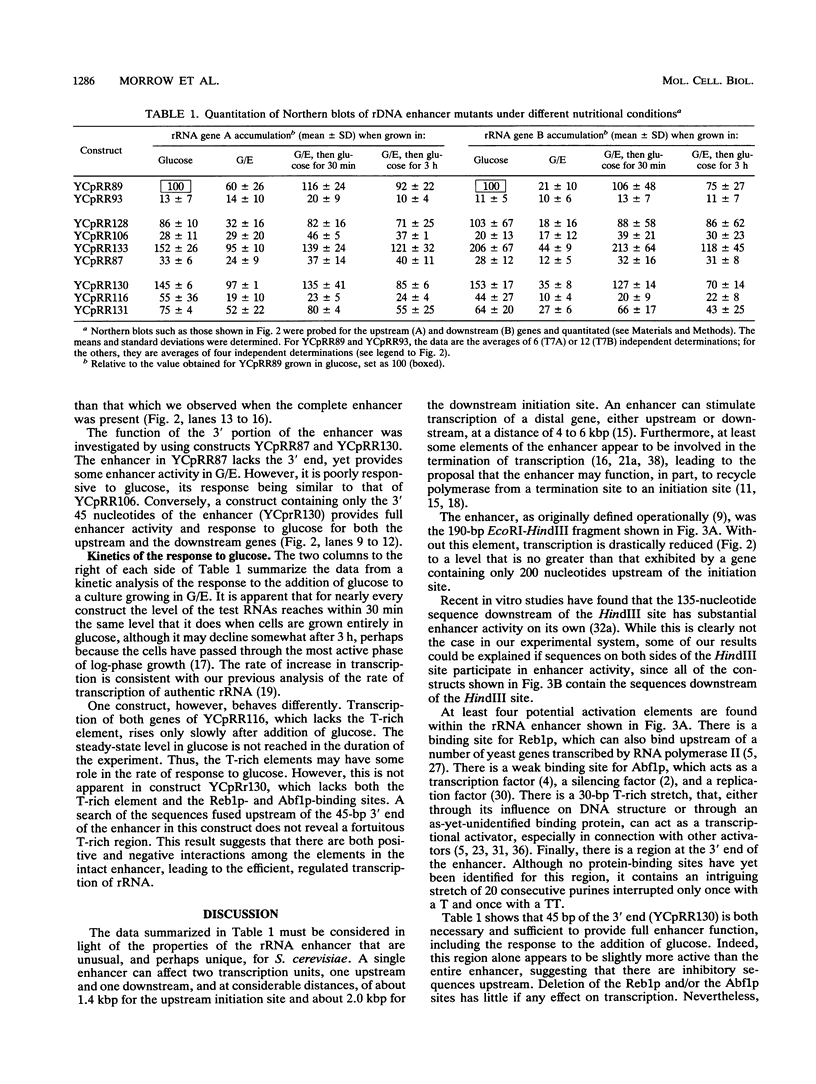
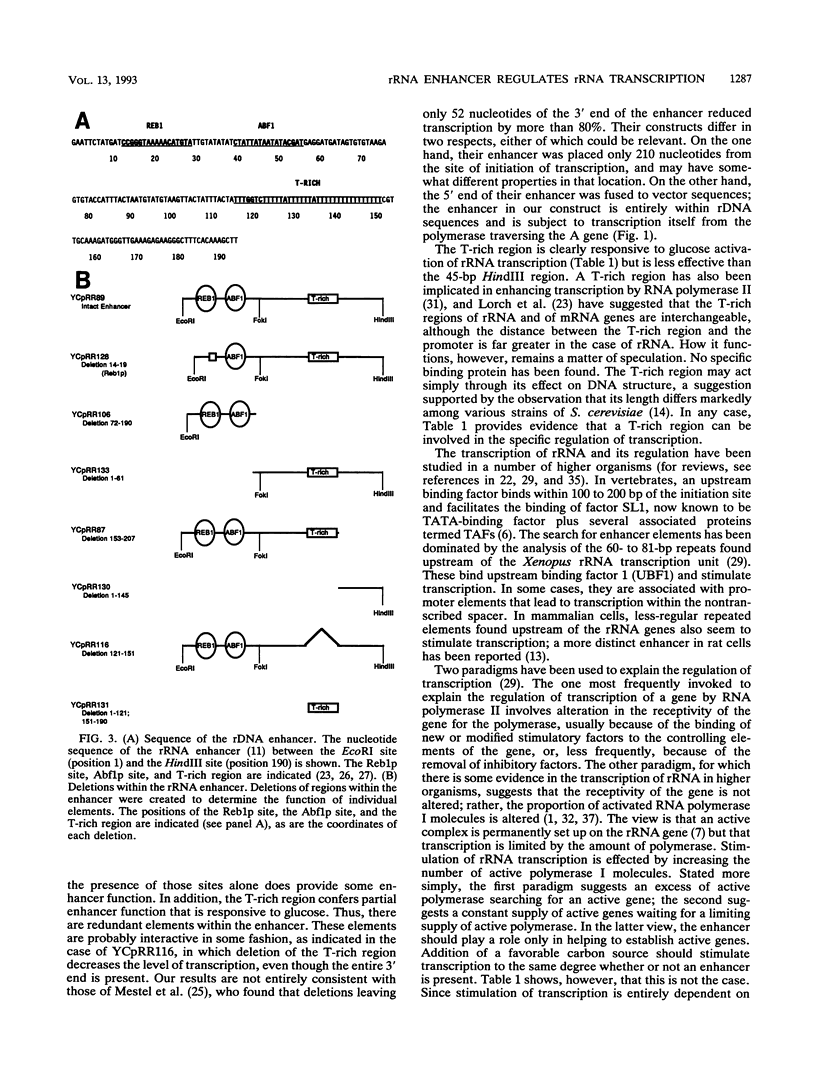
In Saccharomyces cerevisiae, the rRNA genes are organized as a tandem array of head-to-tail repeats. An enhancer of rRNA transcription is present just at the end of each transcription unit, 2 kb away from the next one. This enhancer is unusual for S. cerevisiae in that it acts both upstream and downstream of, and even across, genes. The role of the enhancer in the nutritional regulation of rRNA transcription was studied by introducing a centromere plasmid carrying two rRNA minigenes in tandem, flanking a single enhancer, into cells. Analysis of the transcripts from the two minigenes showed that the enhancer was absolutely required for the stimulation of transcription of rRNA that occurs when cells are shifted from a poor carbon source to a good carbon source. While full enhancer function is provided by a 45-bp region at the 3' end of the 190-bp enhancer, some activity was also conferred by other elements, including both a T-rich stretch and a region containing the binding sites for the proteins Reb1p and Abf1p. We conclude that the enhancer is composed of redundant elements and that it is a major element in the regulation of rRNA transcription.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bateman E., Paule M. R. Regulation of eukaryotic ribosomal RNA transcription by RNA polymerase modification. Cell. 1986 Nov 7;47(3):445–450. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90601-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brand A. H., Micklem G., Nasmyth K. A yeast silencer contains sequences that can promote autonomous plasmid replication and transcriptional activation. Cell. 1987 Dec 4;51(5):709–719. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90094-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandl C. J., Struhl K. A nucleosome-positioning sequence is required for GCN4 to activate transcription in the absence of a TATA element. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):4256–4265. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.4256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchman A. R., Kornberg R. D. A yeast ARS-binding protein activates transcription synergistically in combination with other weak activating factors. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;10(3):887–897. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.3.887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chasman D. I., Lue N. F., Buchman A. R., LaPointe J. W., Lorch Y., Kornberg R. D. A yeast protein that influences the chromatin structure of UASG and functions as a powerful auxiliary gene activator. Genes Dev. 1990 Apr;4(4):503–514. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.4.503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comai L., Tanese N., Tjian R. The TATA-binding protein and associated factors are integral components of the RNA polymerase I transcription factor, SL1. Cell. 1992 Mar 6;68(5):965–976. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90039-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conconi A., Widmer R. M., Koller T., Sogo J. M. Two different chromatin structures coexist in ribosomal RNA genes throughout the cell cycle. Cell. 1989 Jun 2;57(5):753–761. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90790-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cormack B. P., Struhl K. The TATA-binding protein is required for transcription by all three nuclear RNA polymerases in yeast cells. Cell. 1992 May 15;69(4):685–696. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90232-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elion E. A., Warner J. R. An RNA polymerase I enhancer in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2089–2097. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elion E. A., Warner J. R. The major promoter element of rRNA transcription in yeast lies 2 kb upstream. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):663–673. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90473-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob S. T., Zhang J., Garg L. C., Book C. B. Multiple functional enhancer motifs of rat ribosomal gene. 1991 May 29-Jun 12Mol Cell Biochem. 104(1-2):155–162. doi: 10.1007/BF00229815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jemtland R., Maehlum E., Gabrielsen O. S., Oyen T. B. Regular distribution of length heterogeneities within non-transcribed spacer regions of cloned and genomic rDNA of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jul 11;14(13):5145–5158. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.13.5145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson S. P., Warner J. R. Termination of transcription of ribosomal RNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. 1991 May 29-Jun 12Mol Cell Biochem. 104(1-2):163–168. doi: 10.1007/BF00229816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson S. P., Warner J. R. Unusual enhancer function in yeast rRNA transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):4986–4993. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.4986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kempers-Veenstra A. E., Oliemans J., Offenberg H., Dekker A. F., Piper P. W., Planta R. J., Klootwijk J. 3'-End formation of transcripts from the yeast rRNA operon. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2703–2710. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04554.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kief D. R., Warner J. R. Coordinate control of syntheses of ribosomal ribonucleic acid and ribosomal proteins during nutritional shift-up in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Nov;1(11):1007–1015. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.11.1007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruse C., Johnson S. P., Warner J. R. Phosphorylation of the yeast equivalent of ribosomal protein S6 is not essential for growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(22):7515–7519. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.22.7515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulkens T., van Heerikhuizen H., Klootwijk J., Oliemans J., Planta R. J. A yeast ribosomal DNA-binding protein that binds to the rDNA enhancer and also close to the site of Pol I transcription initiation is not important for enhancer functioning. Curr Genet. 1989 Dec;16(5-6):351–359. doi: 10.1007/BF00340714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larson D. E., Zahradka P., Sells B. H. Control points in eucaryotic ribosome biogenesis. Biochem Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;69(1):5–22. doi: 10.1139/o91-002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorch Y., Lue N. F., Kornberg R. D. Interchangeable RNA polymerase I and II enhancers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8202–8206. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahajan P. B., Thompson E. A. Hormonal regulation of transcription of rDNA. Purification and characterization of the hormone-regulated transcription factor IC. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 25;265(27):16225–16233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mestel R., Yip M., Holland J. P., Wang E., Kang J., Holland M. J. Sequences within the spacer region of yeast rRNA cistrons that stimulate 35S rRNA synthesis in vivo mediate RNA polymerase I-dependent promoter and terminator activities. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;9(3):1243–1254. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.3.1243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrow B. E., Johnson S. P., Warner J. R. Proteins that bind to the yeast rDNA enhancer. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):9061–9068. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrow B. E., Ju Q., Warner J. R. Purification and characterization of the yeast rDNA binding protein REB1. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 5;265(34):20778–20783. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Planta R. J., Raué H. A. Control of ribosome biogenesis in yeast. Trends Genet. 1988 Mar;4(3):64–68. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(88)90042-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeder R. H. Regulatory elements of the generic ribosomal gene. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;1(3):466–474. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(89)90007-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhode P. R., Sweder K. S., Oegema K. F., Campbell J. L. The gene encoding ARS-binding factor I is essential for the viability of yeast. Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12A):1926–1939. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12a.1926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotenberg M. O., Woolford J. L., Jr Tripartite upstream promoter element essential for expression of Saccharomyces cerevisiae ribosomal protein genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;6(2):674–687. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.2.674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnapp A., Grummt I. Transcription complex formation at the mouse rDNA promoter involves the stepwise association of four transcription factors and RNA polymerase I. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 25;266(36):24588–24595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz M. C., Reeder R. H., Hahn S. Variants of the TATA-binding protein can distinguish subsets of RNA polymerase I, II, and III promoters. Cell. 1992 May 15;69(4):697–702. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90233-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwindinger W. F., Warner J. R. Transcriptional elements of the yeast ribosomal protein gene CYH2. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 25;262(12):5690–5695. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollner-Webb B., Mougey E. B. News from the nucleolus: rRNA gene expression. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Feb;16(2):58–62. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90025-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K. Naturally occurring poly(dA-dT) sequences are upstream promoter elements for constitutive transcription in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8419–8423. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tower J., Sollner-Webb B. Transcription of mouse rDNA is regulated by an activated subform of RNA polymerase I. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):873–883. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90514-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldron C., Lacroute F. Effect of growth rate on the amounts of ribosomal and transfer ribonucleic acids in yeast. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jun;122(3):855–865. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.3.855-865.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Sande C. A., Kulkens T., Kramer A. B., de Wijs I. J., van Heerikhuizen H., Klootwijk J., Planta R. J. Termination of transcription by yeast RNA polymerase I. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Nov 25;17(22):9127–9146. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.22.9127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]