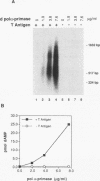
Abstract
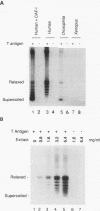
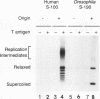
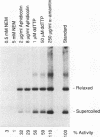
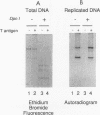
DNA replication of double-stranded simian virus 40 (SV40) origin-containing plasmids, which has been previously thought to be a species-specific process that occurs only with factors derived from primate cells, is catalyzed with an extract derived from embryos of the fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster. This reaction is dependent upon both large T antigen, the SV40-encoded replication initiator protein and DNA helicase, and a functional T-antigen binding site at the origin of DNA replication. The efficiency of replication with extracts derived from Drosophila embryos is approximately 10% of that observed with extracts prepared from human 293 cells. This activity is not a unique property of embryonic extracts, as cytoplasmic extracts from Drosophila tissue culture cells also support T-antigen-mediated replication of SV40 DNA. By using highly purified proteins, DNA synthesis is initiated by Drosophila polymerase alpha-primase in a T-antigen-dependent manner in the presence of Drosophila replication protein A (RP-A; also known as single-stranded DNA-binding protein), but neither human RP-A nor Escherichia coli single-stranded DNA-binding protein could substitute for Drosophila RP-A. In reciprocal experiments, however, Drosophila RP-A was able to substitute for human RP-A in reactions carried out with human polymerase alpha-primase. These results collectively indicate that many of the specific functional interactions among T antigen, polymerase alpha-primase, and RP-A are conserved from primates to Drosophila species. Moreover, the observation that SV40 DNA replication can be performed with Drosophila factors provides a useful assay for the study of bidirectional DNA replication in Drosophila species in the context of a complete replication reaction.
Full text
PDF


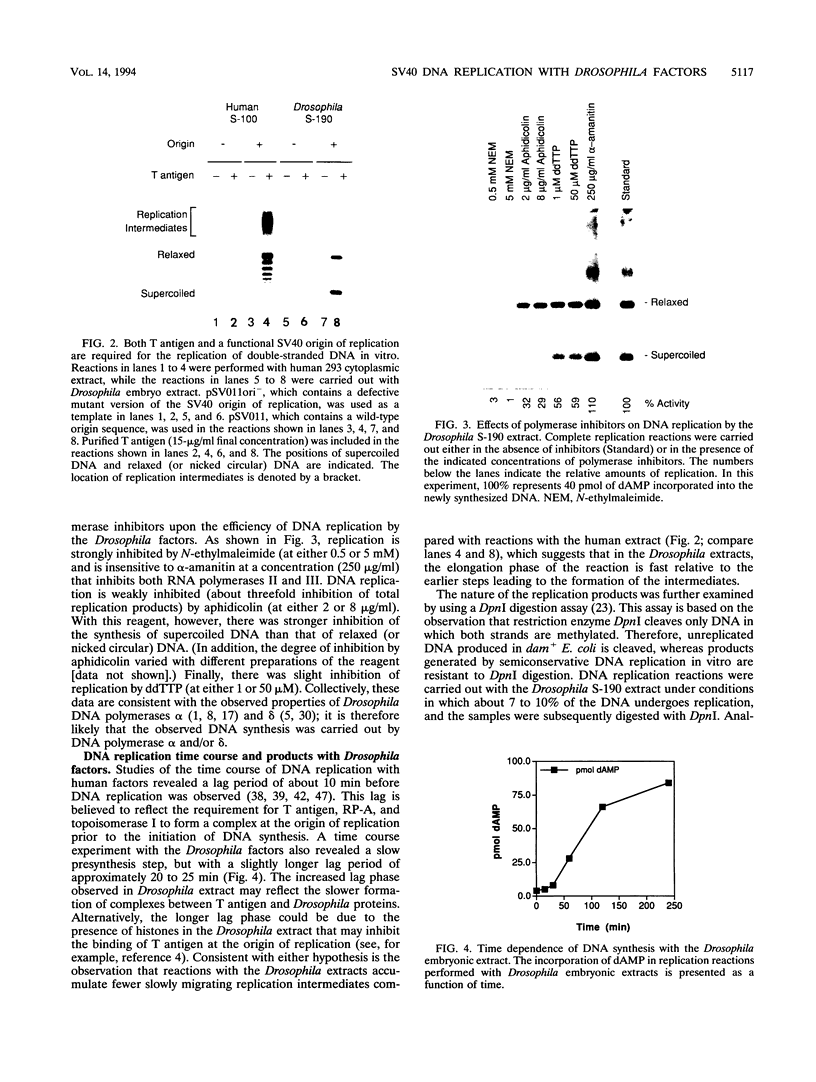



Images in this article
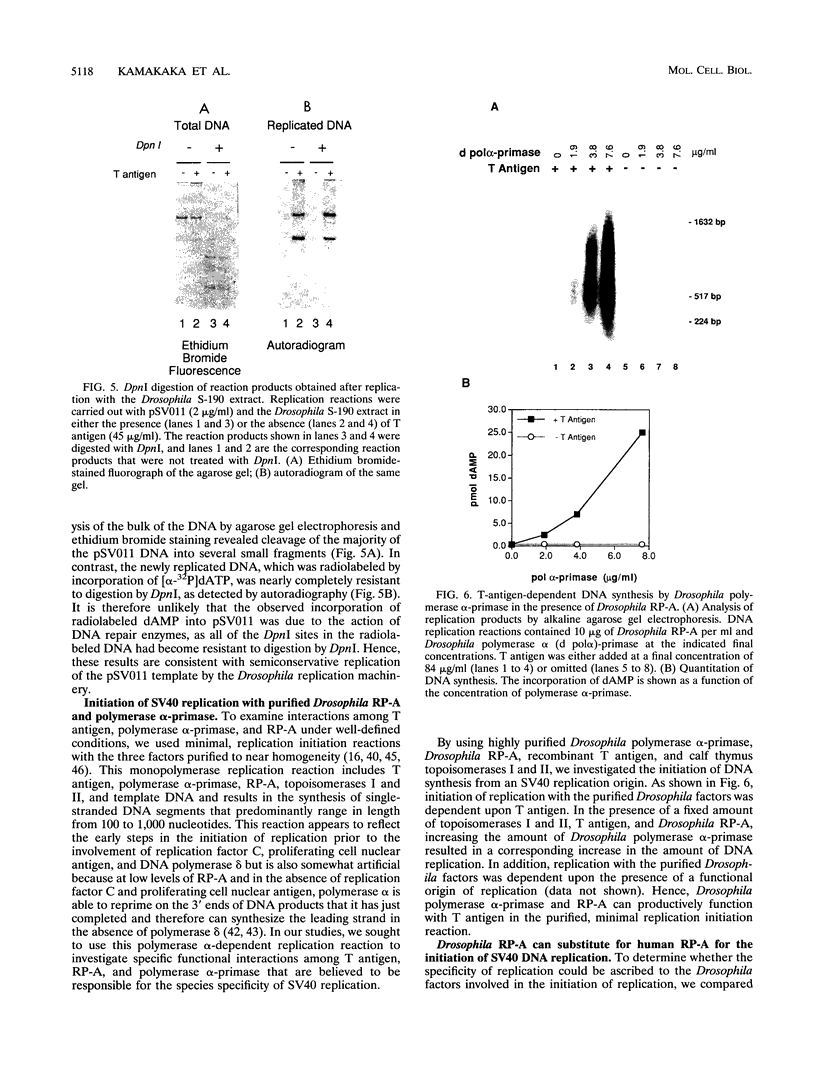
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banks G. R., Boezi J. A., Lehman I. R. A high molecular weight DNA polymerase from Drosophila melanogaster embryos. Purification, structure, and partial characterization. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 10;254(19):9886–9892. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker P. B., Wu C. Cell-free system for assembly of transcriptionally repressed chromatin from Drosophila embryos. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 May;12(5):2241–2249. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.5.2241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brill S. J., Stillman B. Yeast replication factor-A functions in the unwinding of the SV40 origin of DNA replication. Nature. 1989 Nov 2;342(6245):92–95. doi: 10.1038/342092a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng L., Kelly T. J. Transcriptional activator nuclear factor I stimulates the replication of SV40 minichromosomes in vivo and in vitro. Cell. 1989 Nov 3;59(3):541–551. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90037-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiang C. S., Mitsis P. G., Lehman I. R. DNA polymerase delta from embryos of Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Oct 1;90(19):9105–9109. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.19.9105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins K. L., Kelly T. J. Effects of T antigen and replication protein A on the initiation of DNA synthesis by DNA polymerase alpha-primase. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):2108–2115. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.2108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins K. L., Russo A. A., Tseng B. Y., Kelly T. J. The role of the 70 kDa subunit of human DNA polymerase alpha in DNA replication. EMBO J. 1993 Dec;12(12):4555–4566. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06144.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotterill S., Chui G., Lehman I. R. DNA polymerase-primase from embryos of Drosophila melanogaster. The DNA polymerase subunit. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 25;262(33):16100–16104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diffley J. F. Early events in eukaryotic DNA replication. Trends Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;2(10):298–303. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(92)90119-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dornreiter I., Copeland W. C., Wang T. S. Initiation of simian virus 40 DNA replication requires the interaction of a specific domain of human DNA polymerase alpha with large T antigen. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Feb;13(2):809–820. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.2.809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dornreiter I., Erdile L. F., Gilbert I. U., von Winkler D., Kelly T. J., Fanning E. Interaction of DNA polymerase alpha-primase with cellular replication protein A and SV40 T antigen. EMBO J. 1992 Feb;11(2):769–776. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05110.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dornreiter I., Höss A., Arthur A. K., Fanning E. SV40 T antigen binds directly to the large subunit of purified DNA polymerase alpha. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3329–3336. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07533.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echalier G., Ohanessian A. In vitro culture of Drosophila melanogaster embryonic cells. In Vitro. 1970 Nov-Dec;6(3):162–172. doi: 10.1007/BF02617759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erdile L. F., Heyer W. D., Kolodner R., Kelly T. J. Characterization of a cDNA encoding the 70-kDa single-stranded DNA-binding subunit of human replication protein A and the role of the protein in DNA replication. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 25;266(18):12090–12098. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluzman Y., Frisque R. J., Sambrook J. Origin-defective mutants of SV40. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1980;44(Pt 1):293–300. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1980.044.01.033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishimi Y., Claude A., Bullock P., Hurwitz J. Complete enzymatic synthesis of DNA containing the SV40 origin of replication. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 25;263(36):19723–19733. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaguni L. S., Rossignol J. M., Conaway R. C., Lehman I. R. Isolation of an intact DNA polymerase-primase from embryos of Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(8):2221–2225. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.8.2221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamakaka R. T., Bulger M., Kadonaga J. T. Potentiation of RNA polymerase II transcription by Gal4-VP16 during but not after DNA replication and chromatin assembly. Genes Dev. 1993 Sep;7(9):1779–1795. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.9.1779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly T. J. SV40 DNA replication. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 5;263(34):17889–17892. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny M. K., Lee S. H., Hurwitz J. Multiple functions of human single-stranded-DNA binding protein in simian virus 40 DNA replication: single-strand stabilization and stimulation of DNA polymerases alpha and delta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):9757–9761. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.9757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornbluth S., Smythe C., Newport J. W. In vitro cell cycle arrest induced by using artificial DNA templates. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jul;12(7):3216–3223. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.7.3216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanford R. E. Expression of simian virus 40 T antigen in insect cells using a baculovirus expression vector. Virology. 1988 Nov;167(1):72–81. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90055-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J. J., Kelly T. J. Simian virus 40 DNA replication in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):6973–6977. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.6973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J. J., Kelly T. J. Simian virus 40 DNA replication in vitro: specificity of initiation and evidence for bidirectional replication. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;5(6):1238–1246. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.6.1238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu L. F., Miller K. G. Eukaryotic DNA topoisomerases: two forms of type I DNA topoisomerases from HeLa cell nuclei. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3487–3491. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melendy T., Stillman B. An interaction between replication protein A and SV40 T antigen appears essential for primosome assembly during SV40 DNA replication. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 15;268(5):3389–3395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitsis P. G., Kowalczykowski S. C., Lehman I. R. A single-stranded DNA binding protein from Drosophila melanogaster: characterization of the heterotrimeric protein and its interaction with single-stranded DNA. Biochemistry. 1993 May 18;32(19):5257–5266. doi: 10.1021/bi00070a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami Y., Wobbe C. R., Weissbach L., Dean F. B., Hurwitz J. Role of DNA polymerase alpha and DNA primase in simian virus 40 DNA replication in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):2869–2873. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.2869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newport J. Nuclear reconstitution in vitro: stages of assembly around protein-free DNA. Cell. 1987 Jan 30;48(2):205–217. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90424-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peck V. M., Gerner E. W., Cress A. E. Delta-type DNA polymerase characterized from Drosophila melanogaster embryos. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Nov 11;20(21):5779–5784. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.21.5779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prelich G., Stillman B. Coordinated leading and lagging strand synthesis during SV40 DNA replication in vitro requires PCNA. Cell. 1988 Apr 8;53(1):117–126. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90493-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simanis V., Lane D. P. An immunoaffinity purification procedure for SV40 large T antigen. Virology. 1985 Jul 15;144(1):88–100. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90308-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smale S. T., Tjian R. T-antigen-DNA polymerase alpha complex implicated in simian virus 40 DNA replication. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):4077–4087. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.4077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S., Stillman B. Purification and characterization of CAF-I, a human cell factor required for chromatin assembly during DNA replication in vitro. Cell. 1989 Jul 14;58(1):15–25. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90398-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stillman B. W., Gluzman Y. Replication and supercoiling of simian virus 40 DNA in cell extracts from human cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):2051–2060. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.2051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stillman B. Chromatin assembly during SV40 DNA replication in vitro. Cell. 1986 May 23;45(4):555–565. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90287-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stillman B. Initiation of eukaryotic DNA replication in vitro. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1989;5:197–245. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.05.110189.001213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsurimoto T., Fairman M. P., Stillman B. Simian virus 40 DNA replication in vitro: identification of multiple stages of initiation. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;9(9):3839–3849. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.9.3839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsurimoto T., Melendy T., Stillman B. Sequential initiation of lagging and leading strand synthesis by two different polymerase complexes at the SV40 DNA replication origin. Nature. 1990 Aug 9;346(6284):534–539. doi: 10.1038/346534a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsurimoto T., Stillman B. Replication factors required for SV40 DNA replication in vitro. I. DNA structure-specific recognition of a primer-template junction by eukaryotic DNA polymerases and their accessory proteins. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 25;266(3):1950–1960. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsurimoto T., Stillman B. Replication factors required for SV40 DNA replication in vitro. II. Switching of DNA polymerase alpha and delta during initiation of leading and lagging strand synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 25;266(3):1961–1968. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wampler S. L., Tyree C. M., Kadonaga J. T. Fractionation of the general RNA polymerase II transcription factors from Drosophila embryos. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 5;265(34):21223–21231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg D. H., Collins K. L., Simancek P., Russo A., Wold M. S., Virshup D. M., Kelly T. J. Reconstitution of simian virus 40 DNA replication with purified proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(22):8692–8696. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.22.8692. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wobbe C. R., Weissbach L., Borowiec J. A., Dean F. B., Murakami Y., Bullock P., Hurwitz J. Replication of simian virus 40 origin-containing DNA in vitro with purified proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(7):1834–1838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.7.1834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wold M. S., Li J. J., Kelly T. J. Initiation of simian virus 40 DNA replication in vitro: large-tumor-antigen- and origin-dependent unwinding of the template. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3643–3647. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]