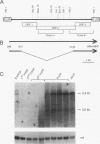
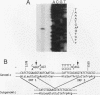
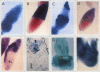
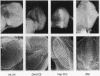
Abstract
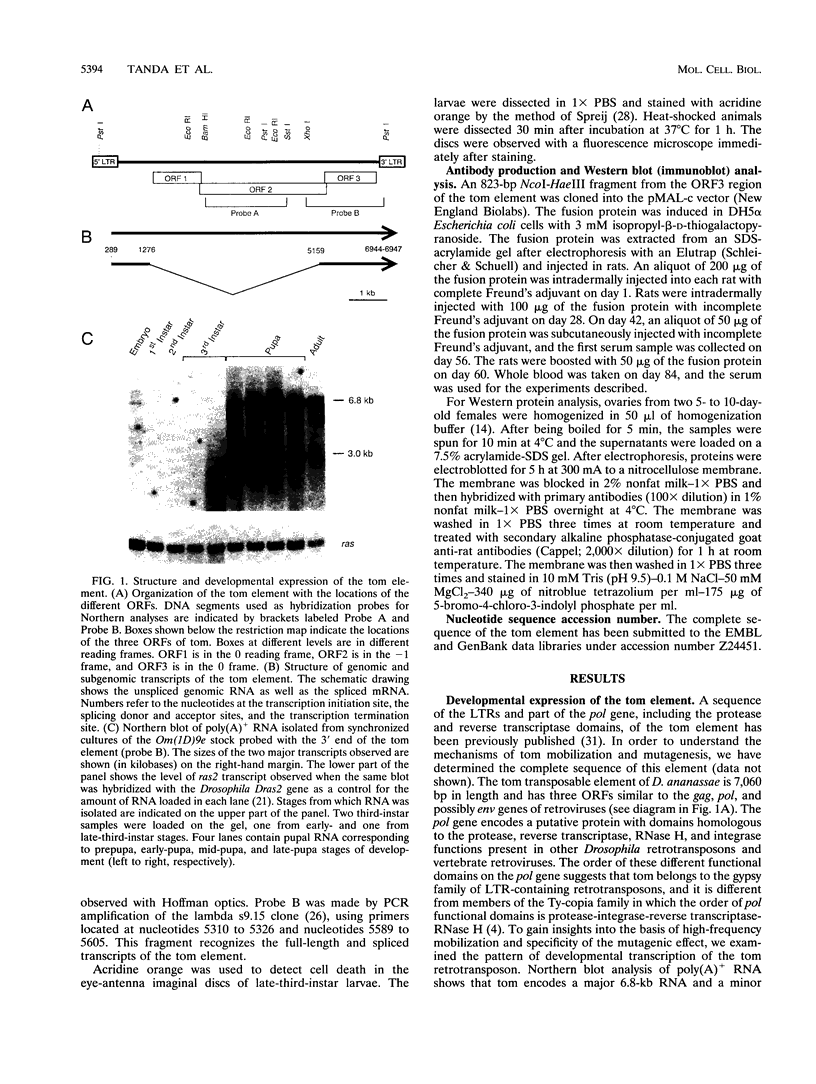
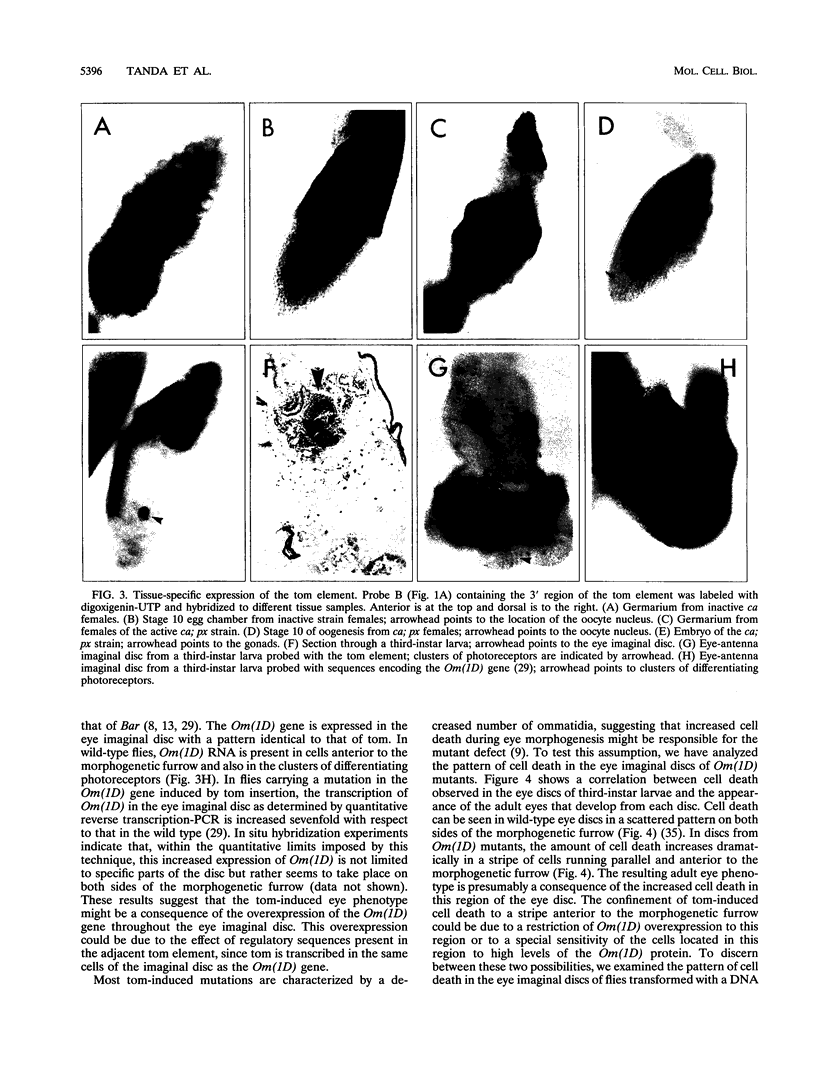
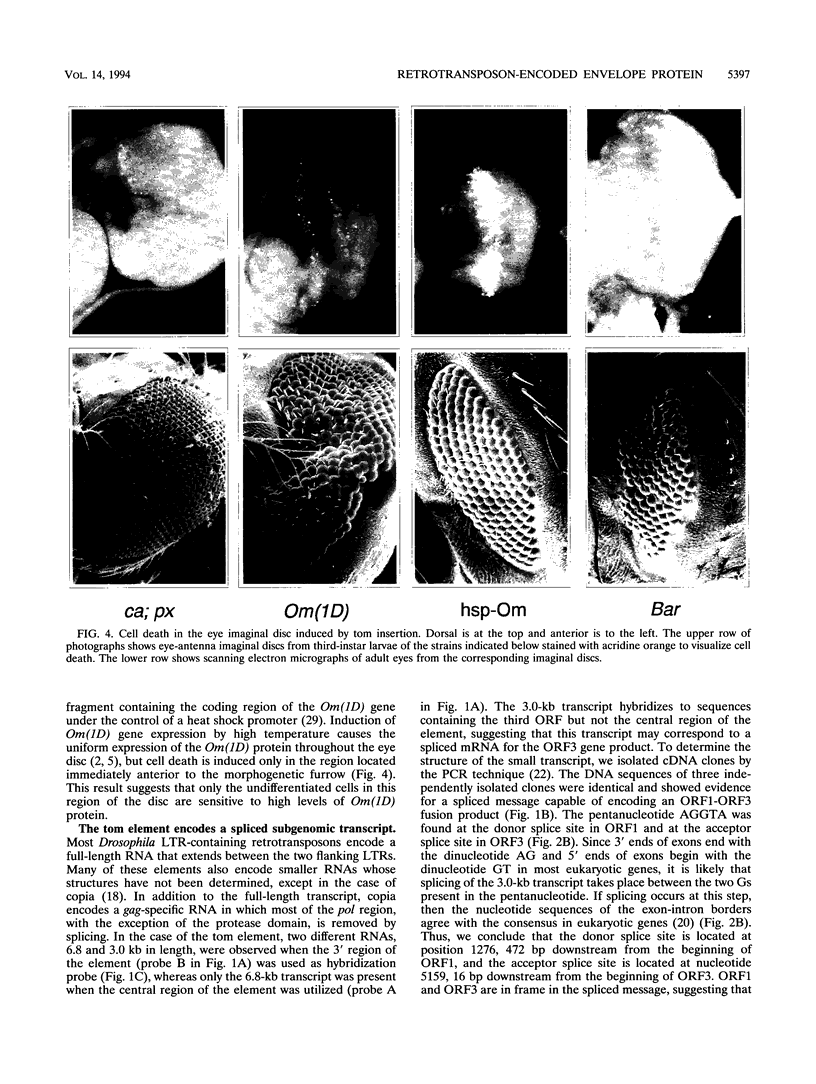
The tom transposable element of Drosophila ananassae is mobilized with high frequency in the germ line of females from the ca; px strain, and its insertion results in mutations that show almost exclusively dominant eye phenotypes. tom is a long terminal repeat-containing retrotransposon that encodes three different open reading frames (ORFs). It is expressed in the nurse cells during oogenesis, in the central and peripheral nervous systems during embryonic development, and in the imaginal discs of the larva. tom RNA accumulates in the germarium of ovaries from ca; px females but not in the parental inactive strain, suggesting that this altered pattern of tom expression might be the cause of the high rate of mobilization of this retrotransposon. The specificity of tom-induced eye phenotypes can be explained by the presence of regulatory sequences responsible for expression of tom in the eye imaginal discs of third-instar larvae. These sequences might cause overexpression of adjacent genes affected by tom-induced mutations, resulting in the death of undifferentiated cells located anterior to the morphogenetic furrow. In addition to the full-length RNA, tom is also transcribed into a spliced subgenomic transcript that encodes a protein resulting from the fusion between the amino-terminal region of the first (gag) and the third ORFs. The protein encoded by this RNA shows structural characteristics such as a signal peptide, glycosylation sites, endopeptidase cleavage site, and fusion peptide that are typical of the envelope proteins of retroviruses. Antibodies against tom ORF3 recognize two different proteins present in female ovaries, suggesting that tom might be able to form infective viral particles that could play a role in the horizontal transmission of this retrotransposon.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Awasaki T., Juni N., Hamabata T., Yoshida K., Matsuda M., Tobari Y. N., Hori S. H. Retrotransposon-induced ectopic expression of cut causes the Om(1A) mutant in Drosophila ananassae. Genetics. 1994 May;137(1):165–174. doi: 10.1093/genetics/137.1.165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basler K., Hafen E. Ubiquitous expression of sevenless: position-dependent specification of cell fate. Science. 1989 Feb 17;243(4893):931–934. doi: 10.1126/science.2493159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. G., 3rd, Corces V. G. Expression of an activated ras gene causes developmental abnormalities in transgenic Drosophila melanogaster. Genes Dev. 1988 May;2(5):567–577. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.5.567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeke J. D., Corces V. G. Transcription and reverse transcription of retrotransposons. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1989;43:403–434. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.43.100189.002155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowtell D. D., Simon M. A., Rubin G. M. Ommatidia in the developing Drosophila eye require and can respond to sevenless for only a restricted period. Cell. 1989 Mar 24;56(6):931–936. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90626-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finnegan D. J., Fawcett D. H. Transposable elements in Drosophila melanogaster. Oxf Surv Eukaryot Genes. 1986;3:1–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerasimova T. I., Matjunina L. V., Mizrokhi L. J., Georgiev G. P. Successive transposition explosions in Drosophila melanogaster and reverse transpositions of mobile dispersed genetic elements. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 30;4(13B):3773–3779. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04147.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashijima S., Kojima T., Michiue T., Ishimaru S., Emori Y., Saigo K. Dual Bar homeo box genes of Drosophila required in two photoreceptor cells, R1 and R6, and primary pigment cells for normal eye development. Genes Dev. 1992 Jan;6(1):50–60. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.1.50. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinton C. W. Formal relations between Om mutants and their suppressors in Drosophila ananassae. Genetics. 1988 Dec;120(4):1035–1042. doi: 10.1093/genetics/120.4.1035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinton C. W. Morphogenetically Specific Mutability in DROSOPHILA ANANASSAE. Genetics. 1984 Apr;106(4):631–653. doi: 10.1093/genetics/106.4.631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultmark D., Klemenz R., Gehring W. J. Translational and transcriptional control elements in the untranslated leader of the heat-shock gene hsp22. Cell. 1986 Feb 14;44(3):429–438. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90464-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter E., Hill E., Hardwick M., Bhown A., Schwartz D. E., Tizard R. Complete sequence of the Rous sarcoma virus env gene: identification of structural and functional regions of its product. J Virol. 1983 Jun;46(3):920–936. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.3.920-936.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laverty T. R., Lim J. K. Site-specific instability in Drosophila melanogaster: evidence for transposition of destabilizing element. Genetics. 1982 Jul-Aug;101(3-4):461–476. doi: 10.1093/genetics/101.3-4.461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKearin D. M., Spradling A. C. bag-of-marbles: a Drosophila gene required to initiate both male and female gametogenesis. Genes Dev. 1990 Dec;4(12B):2242–2251. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.12b.2242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller K., Rosenbaum J., Zbrzezna V., Pogo A. O. The nucleotide sequence of Drosophila melanogaster copia-specific 2.1-kb mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Mar 11;17(5):2134–2134. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.5.2134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyake T., Mae N., Shiba T., Kondo S. Production of virus-like particles by the transposable genetic element, copia, of Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Apr;207(1):29–37. doi: 10.1007/BF00331487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount S. M. A catalogue of splice junction sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 22;10(2):459–472. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.2.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mozer B., Marlor R., Parkhurst S., Corces V. Characterization and developmental expression of a Drosophila ras oncogene. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Apr;5(4):885–889. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.4.885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mével-Ninio M., Mariol M. C., Gans M. Mobilization of the gypsy and copia retrotransposons in Drosophila melanogaster induces reversion of the ovo dominant female-sterile mutations: molecular analysis of revertant alleles. EMBO J. 1989 May;8(5):1549–1558. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03539.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Scharf S., Faloona F., Mullis K. B., Horn G. T., Erlich H. A., Arnheim N. Enzymatic amplification of beta-globin genomic sequences and restriction site analysis for diagnosis of sickle cell anemia. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1350–1354. doi: 10.1126/science.2999980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiba T., Saigo K. Retrovirus-like particles containing RNA homologous to the transposable element copia in Drosophila melanogaster. Nature. 1983 Mar 10;302(5904):119–124. doi: 10.1038/302119a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shrimpton A. E., Montgomery E. A., Langley C. H. OM Mutations in DROSOPHILA ANANASSAE Are Linked to Insertions of a Transposable Element. Genetics. 1986 Sep;114(1):125–135. doi: 10.1093/genetics/114.1.125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spradling A. C., Mahowald A. P. Identification and genetic localization of mRNAs from ovarian follicle cells of Drosophila melanogaster. Cell. 1979 Mar;16(3):589–598. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90032-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanda S., Corces V. G. Retrotransposon-induced overexpression of a homeobox gene causes defects in eye morphogenesis in Drosophila. EMBO J. 1991 Feb;10(2):407–417. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07962.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanda S., Shrimpton A. E., Chueh L. L., Itayama H., Matsubayashi H., Saigo K., Tobari Y. N., Langley C. H. Retrovirus-like features and site specific insertions of a transposable element, tom, in Drosophila ananassae. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Nov;214(3):405–411. doi: 10.1007/BF00330473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanda S., Shrimpton A. E., Hinton C. W., Langley C. H. Analysis of the Om(1D) locus in Drosophila ananassae. Genetics. 1989 Nov;123(3):495–502. doi: 10.1093/genetics/123.3.495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tautz D., Pfeifle C. A non-radioactive in situ hybridization method for the localization of specific RNAs in Drosophila embryos reveals translational control of the segmentation gene hunchback. Chromosoma. 1989 Aug;98(2):81–85. doi: 10.1007/BF00291041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff T., Ready D. F. Cell death in normal and rough eye mutants of Drosophila. Development. 1991 Nov;113(3):825–839. doi: 10.1242/dev.113.3.825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. A new method for predicting signal sequence cleavage sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 11;14(11):4683–4690. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.11.4683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]